Reduced Graphene Oxide-Coated CuFeO2 with Fenton-like Catalytic Degradation Performance for Terramycin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
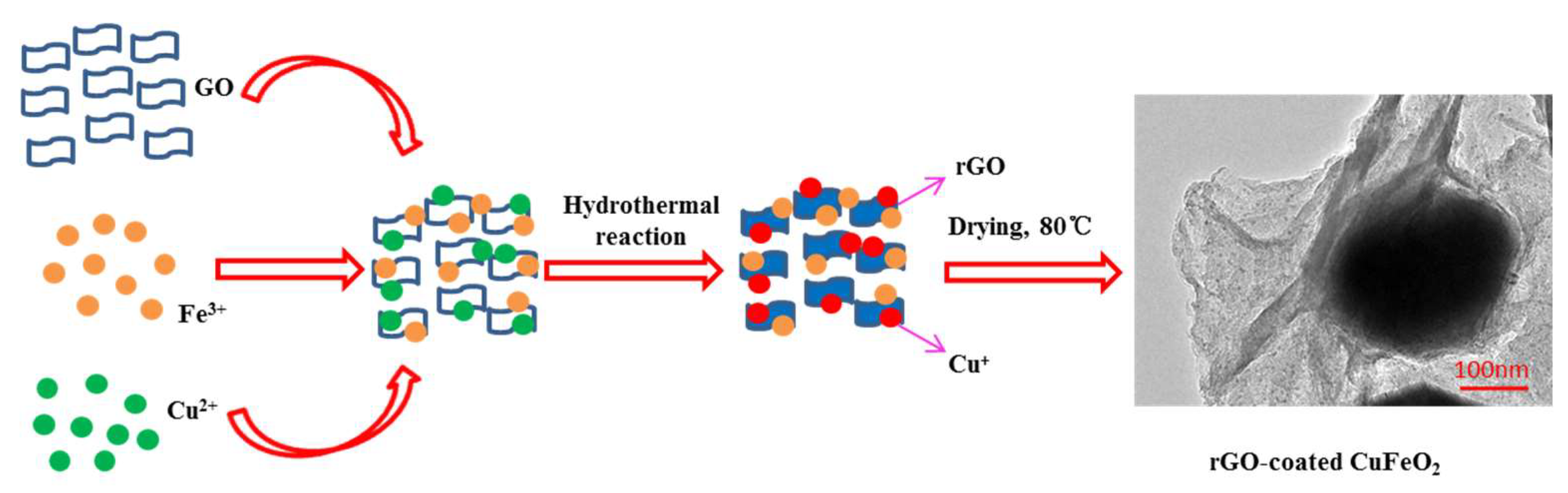
2.2. Catalyst Preparation
2.3. Characterizations
2.4. Batch Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
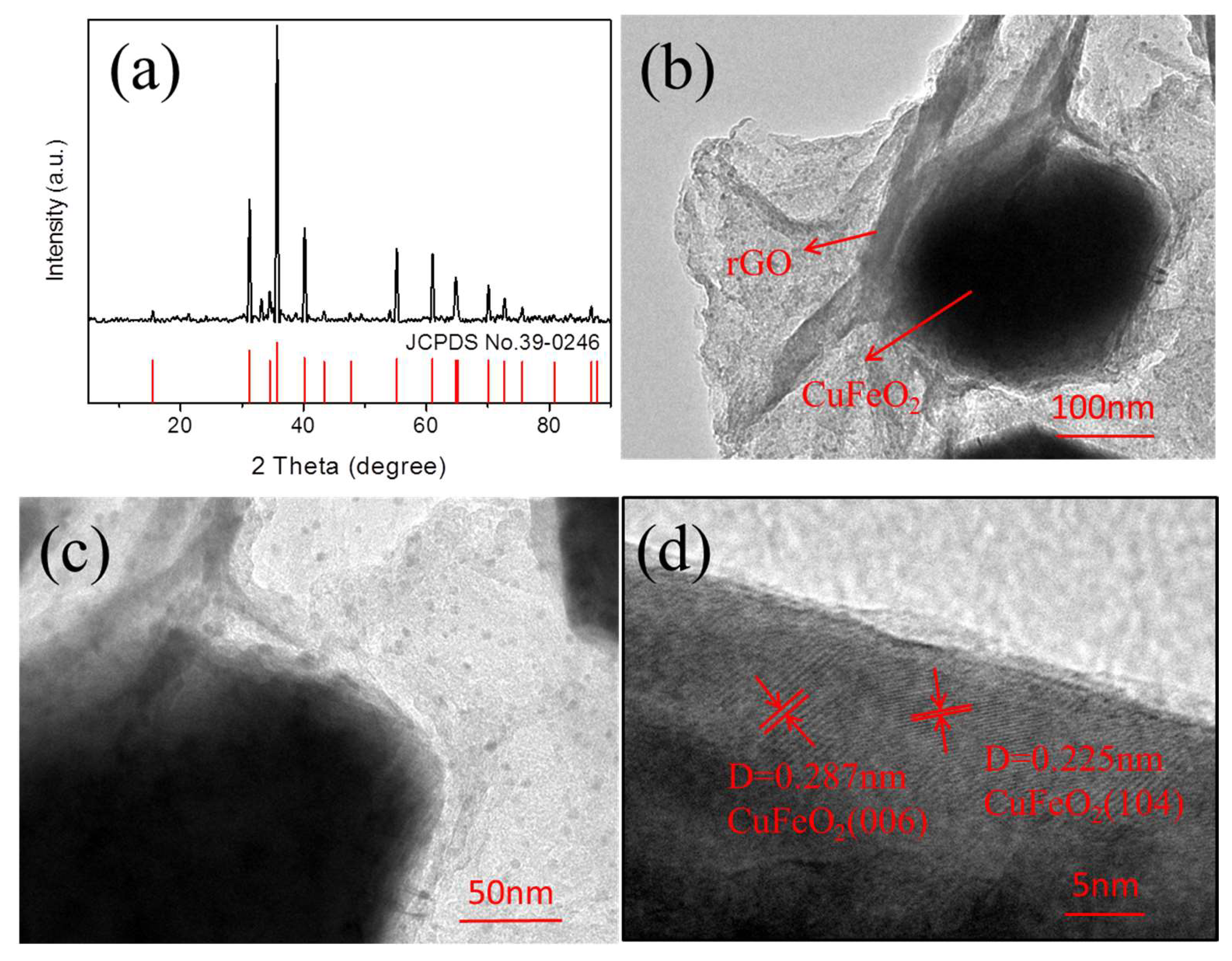
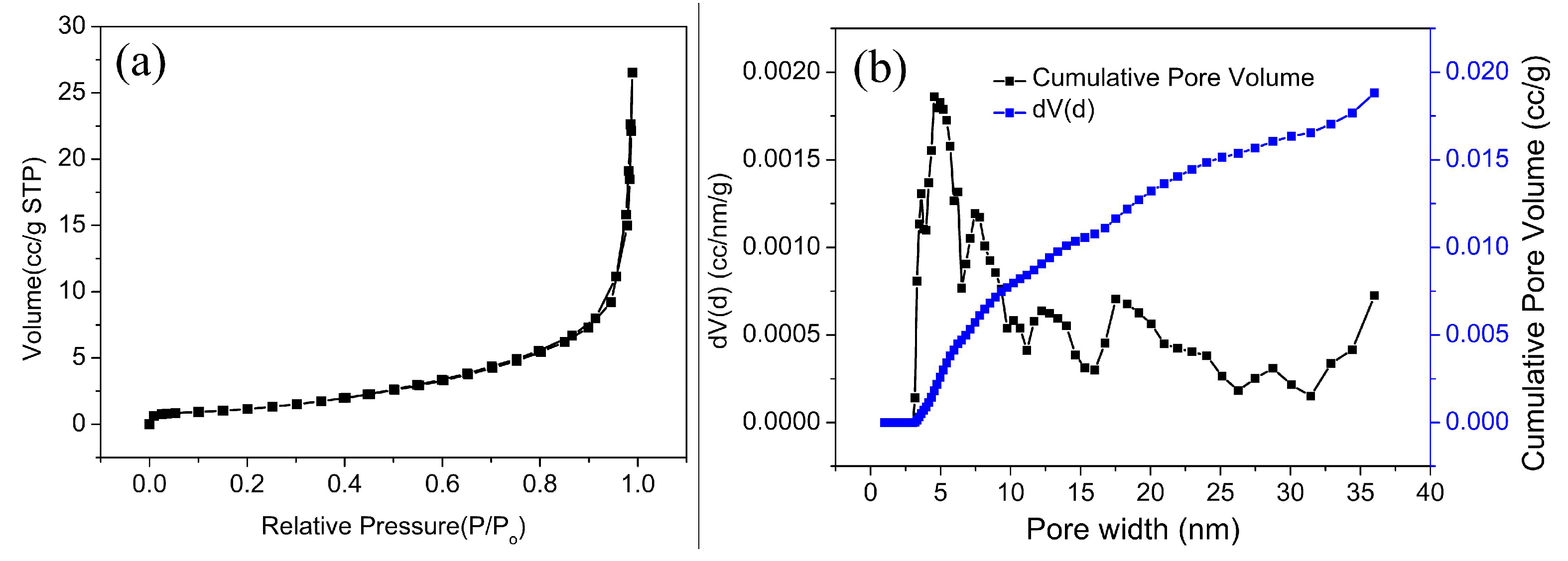
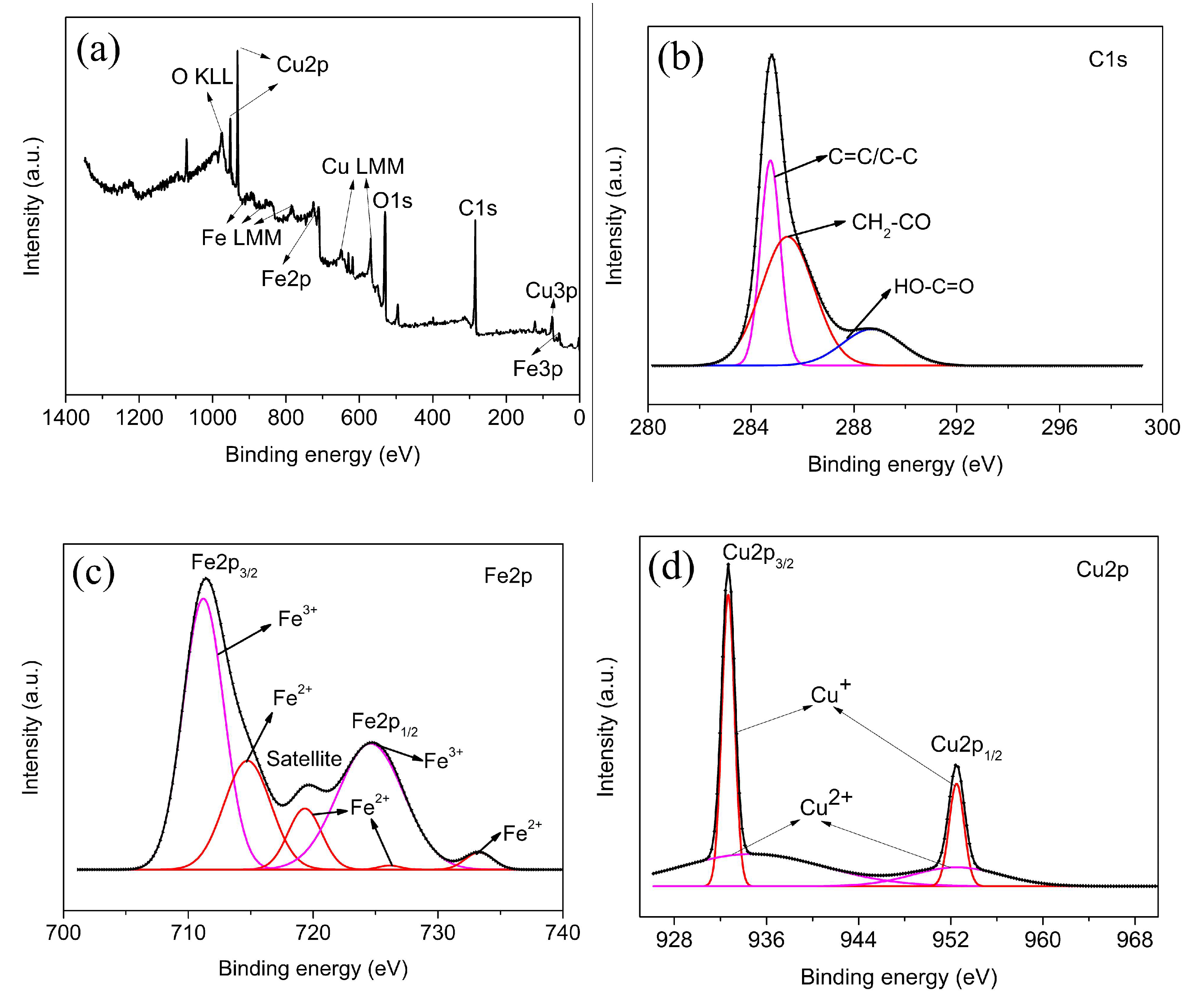
3.1. Structure and Characterization
3.1.1. Morphology and the Content Distribution of Elements
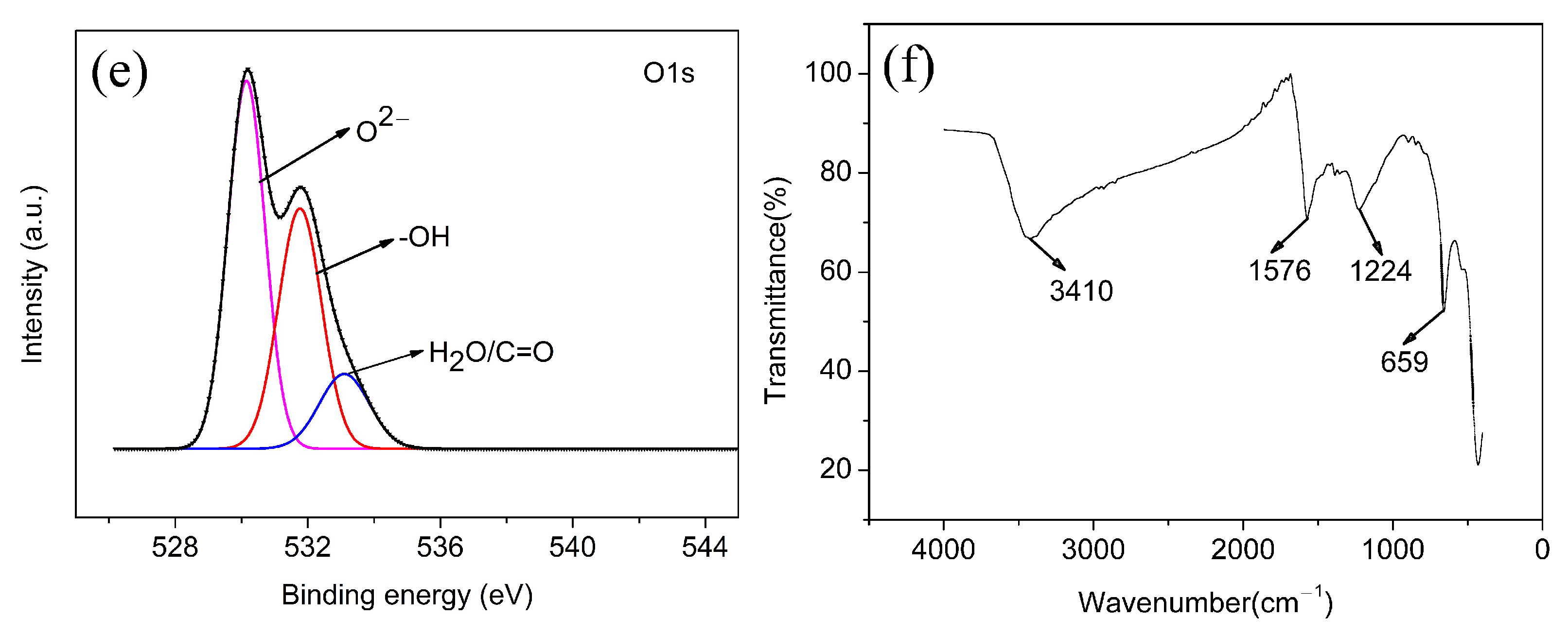
3.1.2. Surface Structure and Properties
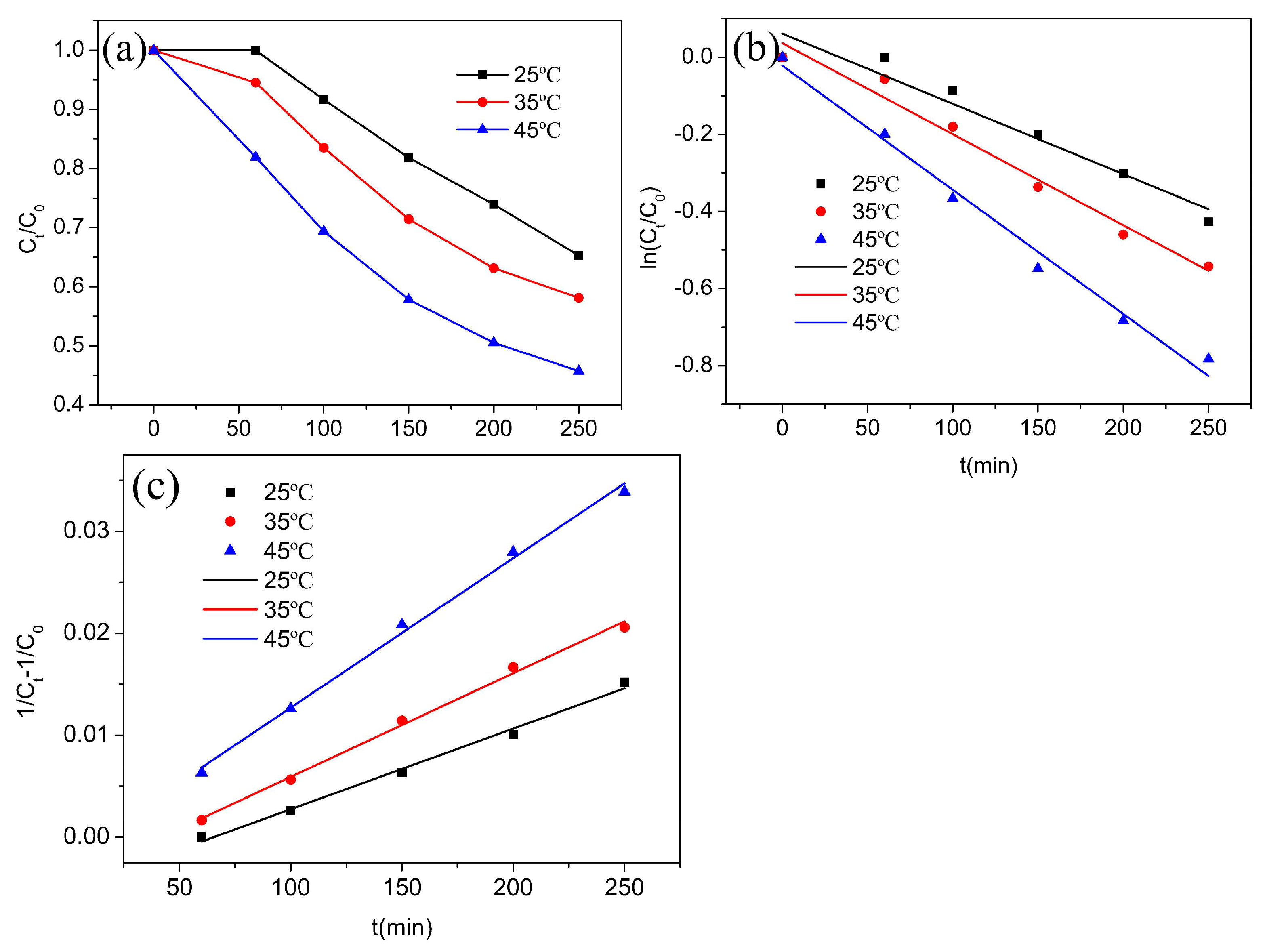
3.2. Catalytic Performance of rGO-Coated CuFeO2 in a Fenton-like Process
3.3. The Possible Mechanism of Terramycin Degradation
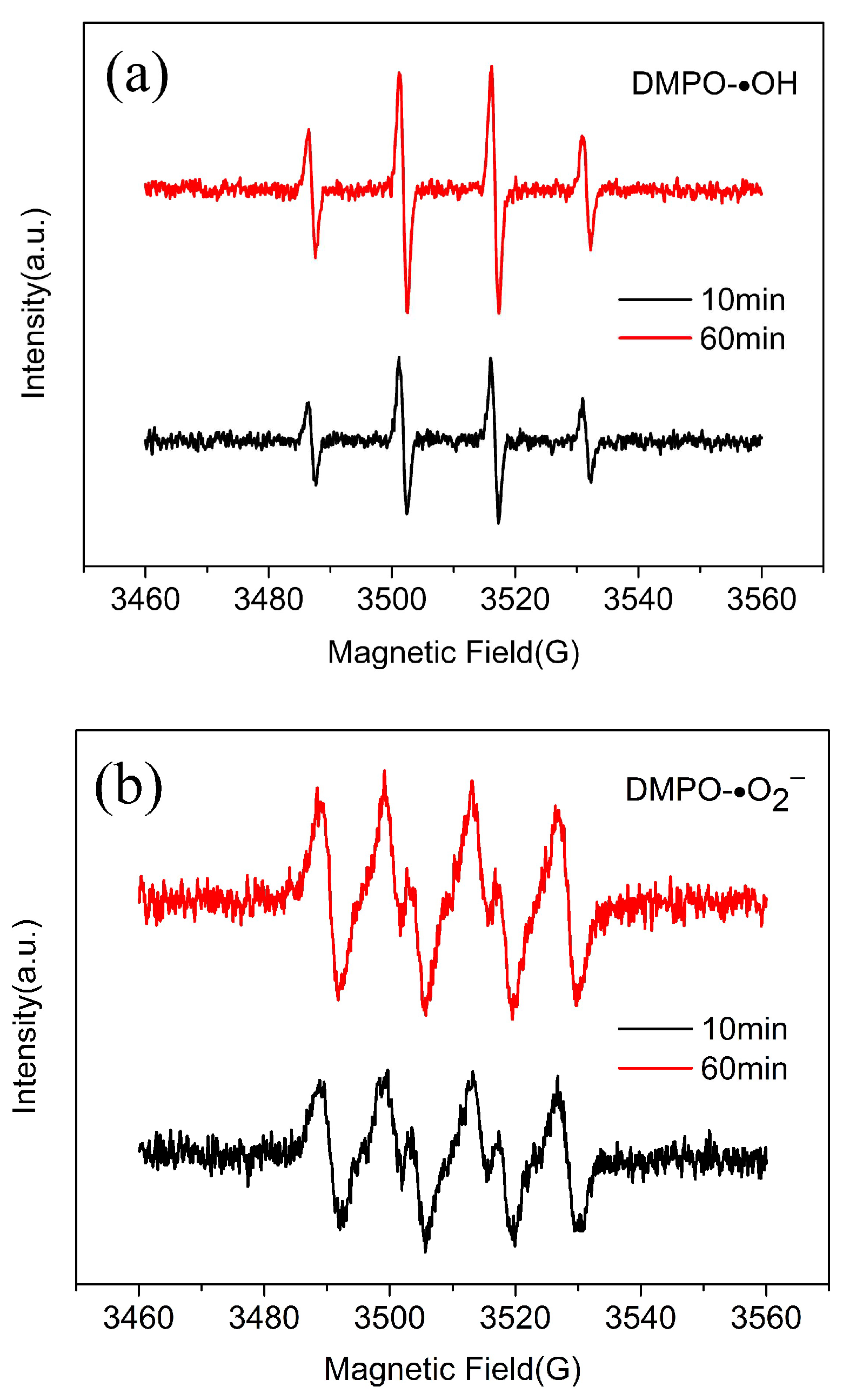
3.3.1. Identification of Mainly Free Radical Species
3.3.2. Catalytic Degradation Pathway
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jovanovic, O.; Amábile-Cuevas, C.F.; Shang, C.; Wang, C.; Ngai, K.W. What Water Professionals Should Know about Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance: An Overview. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 1334–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K.S.; Wilson, J.D.; Marschall, J.; Mucha, P.J.; Henderson, J.P. Network Analysis Reveals Sex- and Antibiotic Resistance-Associated Antivirulence Targets in Clinical Uropathogens. ACS Infect. Dis. 2015, 1, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.D. Antibiotic resistance in the environment: A link to the clinic? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, F.C.T.; Feil, E.J.; Snape, J.; Gaze, W.H.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. The role of stereochemistry of antibiotic agents in the development of antibiotic resistance in the environment. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmolla, E.; Chaudhuri, M. Optimization of Fenton process for treatment of amoxicillin, ampicillin and cloxacillin antibiotics in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmolla, E.S.; Chaudhuri, M.; Eltoukhy, M.M. The use of artificial neural network (ANN) for modeling of COD removal from antibiotic aqueous solution by the Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titouhi, H.; Belgaied, J.E. Removal of ofloxacin antibiotic using heterogeneous Fenton process over modified alginate beads. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 45, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.P.; Sun, D.Z. Treatment of antibiotic fermentation wastewater by combined polyferric sulfate coagulation, Fenton and sedimentation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1264–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Pan, X.; Zhai, X.; Jiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, W.; Qi, X. Highly efficient removal of antibiotic from biomedical wastewater using Fenton-like catalyst magnetic pullulan hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 262, 117951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Synergetic adsorption and Fenton-like oxidation for simultaneous removal of ofloxacin and enrofloxacin using green synthesized Fe NPs. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Hong, P.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xie, C.; He, J.; Zhang, K.; Kong, L.; Liu, J. Enhanced Fenton-like degradation of sulfadiazine by single atom iron materials fixed on nitrogen-doped porous carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 597, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Lim, T.-T. Synergistic catalytic degradation of antibiotic sulfamethazine in a heterogeneous sonophotolytic goethite/oxalate Fenton-like system. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 136–137, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, I.; Samapti, K.; Neriya, P.L.; Adi, R. Heterogeneous Fenton catalyst based on clay decorated with nano-sized amorphous iron oxides prevents oxidant scavenging through surface complexation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134609. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Lai, Y.; Wang, F. Heterogeneous Fenton degradation of bisphenol A using Fe3O4@β-CD/rGO composite: Synergistic effect, principle and way of degradation. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furia, F.; Minella, M.; Gosetti, F.; Turci, F.; Sabatino, R.; Di Cesare, A.; Corno, G.; Vione, D. Elimination from wastewater of antibiotics reserved for hospital settings, with a Fenton process based on zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; An, Y.; Sun, W.; Peng, A.; Zhou, H. Aerosol-assisted submicron γ-Fe2O3/C spheres as a promising heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst for soil and groundwater remediation: Transport, adsorption and catalytic ability. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Degradation of chloramphenicol by pulsed discharge plasma with heterogeneous Fenton process using Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 253, 117540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, P.; Ma, S.; Xie, B.; Yang, K.; Zhao, Y. Novel up-conversion carbon quantum dots/α-FeOOH nanohybrids eliminate tetracycline and its related drug resistance in visible-light responsive Fenton system. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 263, 118336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, N.; Guo, J.; Wang, J. Catalytic activation of O2 by Al0-CNTs-Cu2O composite for Fenton-like degradation of sulfamerazine antibiotic at wide pH range. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Cheng, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Degradation of ofloxacin, amoxicillin and tetracycline antibiotics using magnetic core-shell MnFe2O4@C-NH2 as a heterogeneous Fenton catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Shi, M.; Zhang, W.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Lu, J.; Shan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, L.; Pan, B. Enhancing the Fenton-like Catalytic Activity of nFe2O3 by MIL-53(Cu) Support: A Mechanistic Investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5258–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, S.; Liu, G.; Ma, X.; Gong, J.; Ma, B.; Yan, Q.; Chen, Q.; Ma, D.; Zhang, G.; Gao, M.; et al. High efficiency heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst biochar modified CuFeO2 for the degradation of tetracycline: Economical synthesis, catalytic performance and mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 280, 119386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.P.; He, Y.Y.; Xu, K.J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.B.; Xu, Z.J.; Chen, X. Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride by Cu-Doped MIL-101(Fe) Loaded Diatomite Heterogeneous Fenton Catalyst. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, X.; Feng, X.; Yu, A. Adsorption and Fenton-like Degradation of Ciprofloxacin Using Corncob Biochar-Based Magnetic Iron–Copper Bimetallic Nanomaterial in Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.; Iqbal, J.; Mansoor, Q. Graphene/Fe3O4 nanocomposite: Solar light driven Fenton like reaction for decontamination of water and inhibition of bacterial growth. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 474, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Shi, B. Tetracycline removal by double-metal-crosslinked alginate/graphene hydrogels through an enhanced Fenton reaction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, J. Removal of sulfamethazine antibiotics using CeFe-graphene nanocomposite as catalyst by Fenton-like process. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Fan, W.; Song, S.; Yang, J. Adsorption and degradation of sulfadiazine over nanoscale zero-valent iron encapsulated in three-dimensional graphene network through oxygen-driven heterogeneous Fenton-like reactions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 259, 118057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, J. An enhancement of singlet oxygen generation from dissolved oxygen activated by three-dimensional graphene wrapped nZVI-doped amorphous Al species for chloramphenicol removal in the Fenton-like system. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, G.; Dong, B.; Jin, R.; Zhou, J. Synergistic catalytic Fenton-like degradation of sulfanilamide by biosynthesized goethite-reduced graphene oxide composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; An, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Feng, J.; Wei, T.; Ren, Y. High active radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by mixed crystal types of CuFeO2 as catalysts in the water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 484, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Ma, B.; Zhang, C.; Ma, X.; Xu, P.; Zhang, G.; Gao, M.; Xin, Y. Catalytic activation of peroxydisulfate by alfalfa-derived nitrogen self-doped porous carbon supported CuFeO2 for nimesulide degradation: Performance, mechanism and DFT calculation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 294, 120247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Xie, J. Self-Assembled Nano-Fe3C Embedded in Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel with Efficient Fenton-Like Catalysis. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Crittenden, J.C.; Shen, C. Novel RGO/α-FeOOH supported catalyst for Fenton oxidation of phenol at a wide pH range using solar-light-driven irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 329, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, I.S.X.; Pacheco, P.H.V.V.; Coelho, J.V.; Lorençon, E.; Ardisson, J.D.; Fabris, J.D.; de Souza, P.P.; Krambrock, K.W.H.; Oliveira, L.C.A.; Pereira, M.C. Nanostructured δ-FeOOH: An efficient Fenton-like catalyst for the oxidation of organics in water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 119–120, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element | Weight% | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|
| C K | 55.41 | 73.14 |
| O K | 20.68 | 20.49 |
| Fe K | 11.71 | 3.32 |
| Cu K | 12.21 | 3.05 |
| Kinetics Models | Parameters | 25 °C | 35 °C | 45 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order kinetics | k1 (min−1) | 0.00182 | 0.00236 | 0.00322 |
| r2 | 0.9296 | 0.9733 | 0.9851 | |
| Pseudo-second-order kinetics | k2 (L·mg−1·min−1) | 7.907 × 10−5 | 1.018 × 10−4 | 1.467 × 10−4 |
| r2 | 0.9907 | 0.9945 | 0.9948 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Zhang, M.; Luo, K.; Pang, Y. Reduced Graphene Oxide-Coated CuFeO2 with Fenton-like Catalytic Degradation Performance for Terramycin. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4391. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12244391
Wang L, Liu G, Zhang M, Luo K, Pang Y. Reduced Graphene Oxide-Coated CuFeO2 with Fenton-like Catalytic Degradation Performance for Terramycin. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(24):4391. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12244391
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liping, Gonghao Liu, Mingyu Zhang, Kun Luo, and Ya Pang. 2022. "Reduced Graphene Oxide-Coated CuFeO2 with Fenton-like Catalytic Degradation Performance for Terramycin" Nanomaterials 12, no. 24: 4391. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12244391
APA StyleWang, L., Liu, G., Zhang, M., Luo, K., & Pang, Y. (2022). Reduced Graphene Oxide-Coated CuFeO2 with Fenton-like Catalytic Degradation Performance for Terramycin. Nanomaterials, 12(24), 4391. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12244391






