Dependence of Electrical Conductivity on Phase Morphology for Graphene Selectively Located at the Interface of Polypropylene/Polyethylene Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
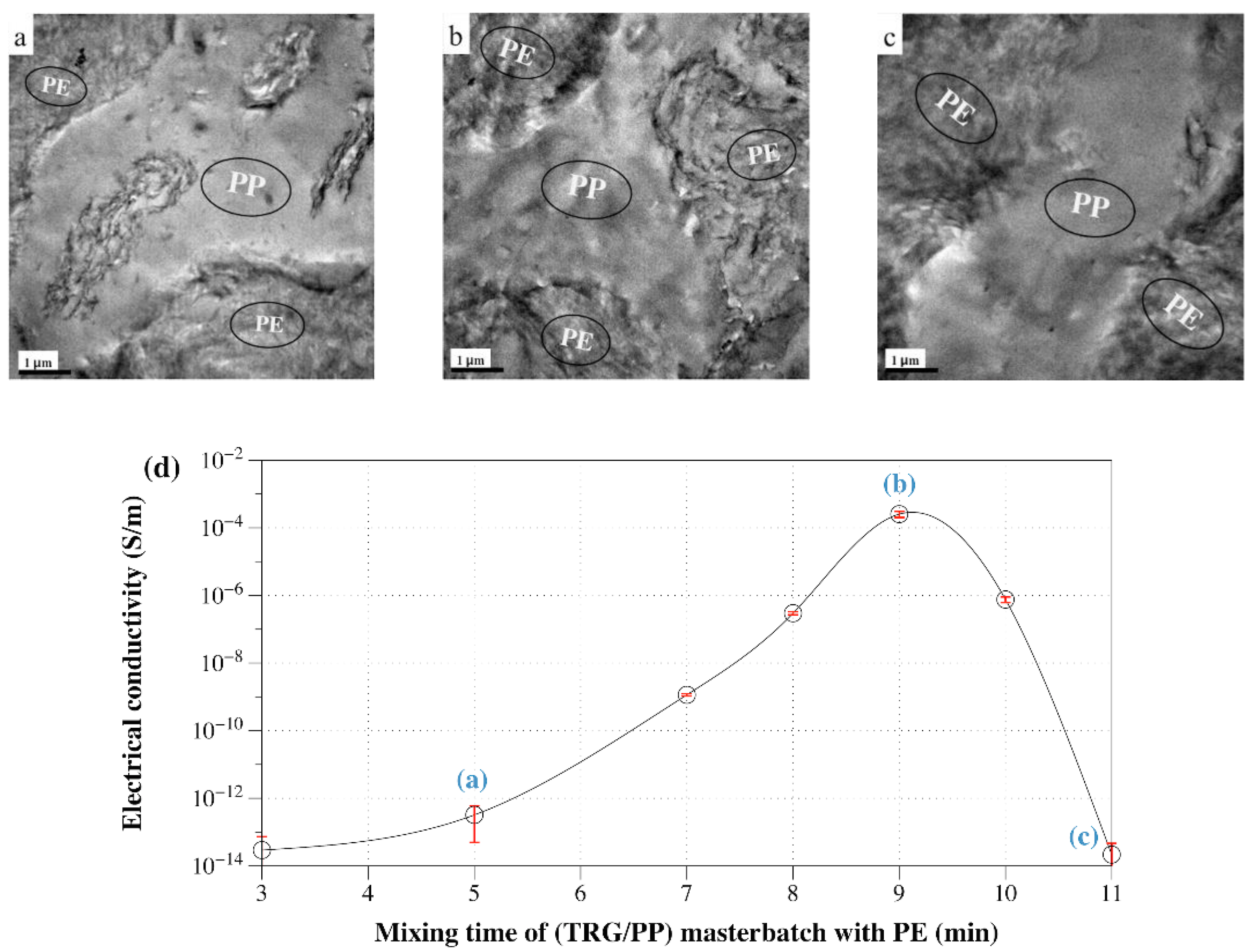
2.2. Composite Preparation
- TRG/PP/PE: The PP, PE, and TRG were melt-blended simultaneously for 7 min;
- (TRG/PP)/PE: The PP was first mixed with TRG for 2 min, and the resulting TRG/PP masterbatch was blended with PE for 5 min.
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.3. Electrical Properties
2.3.4. Rheological Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
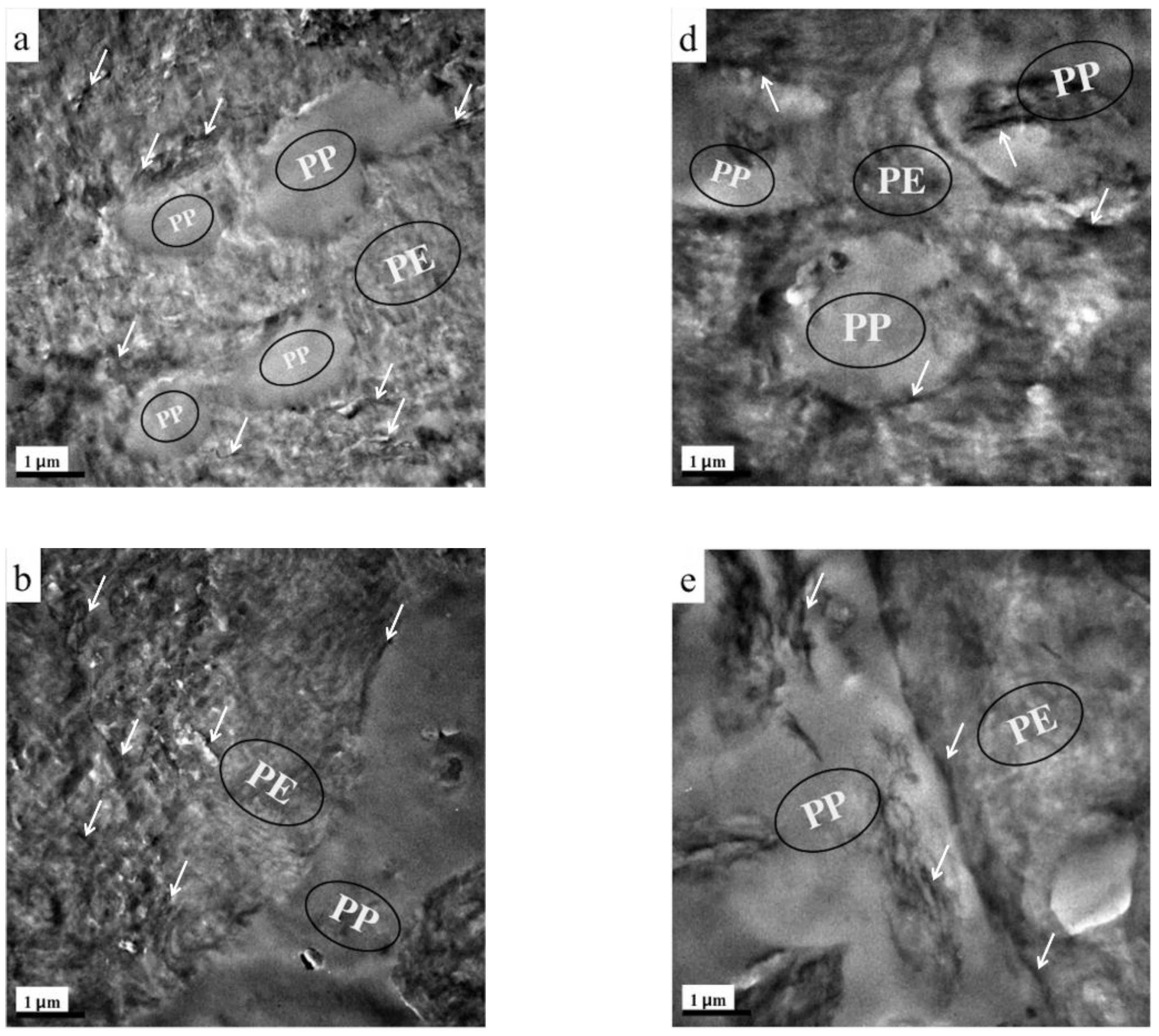
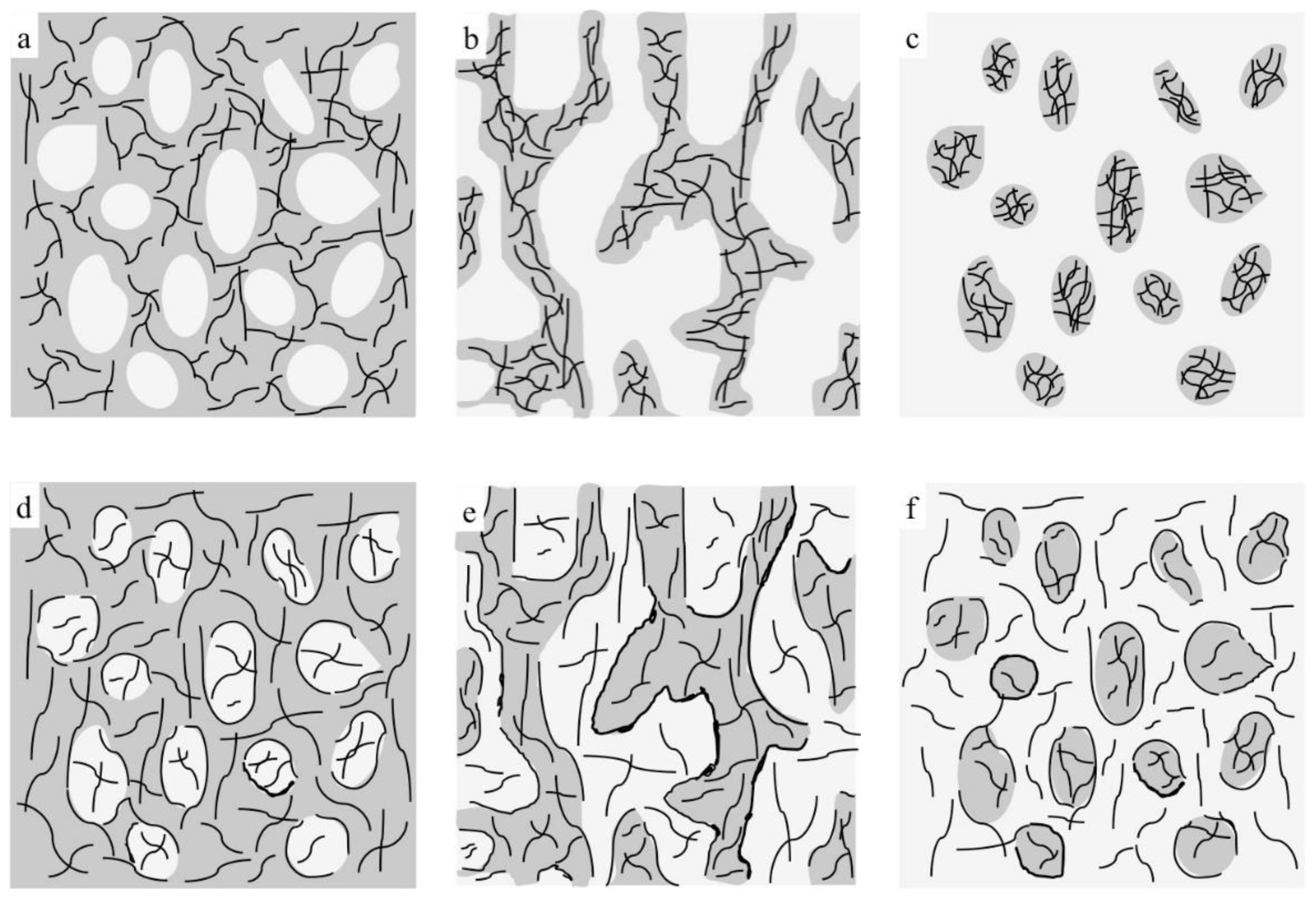
3.1. Composites Morphology
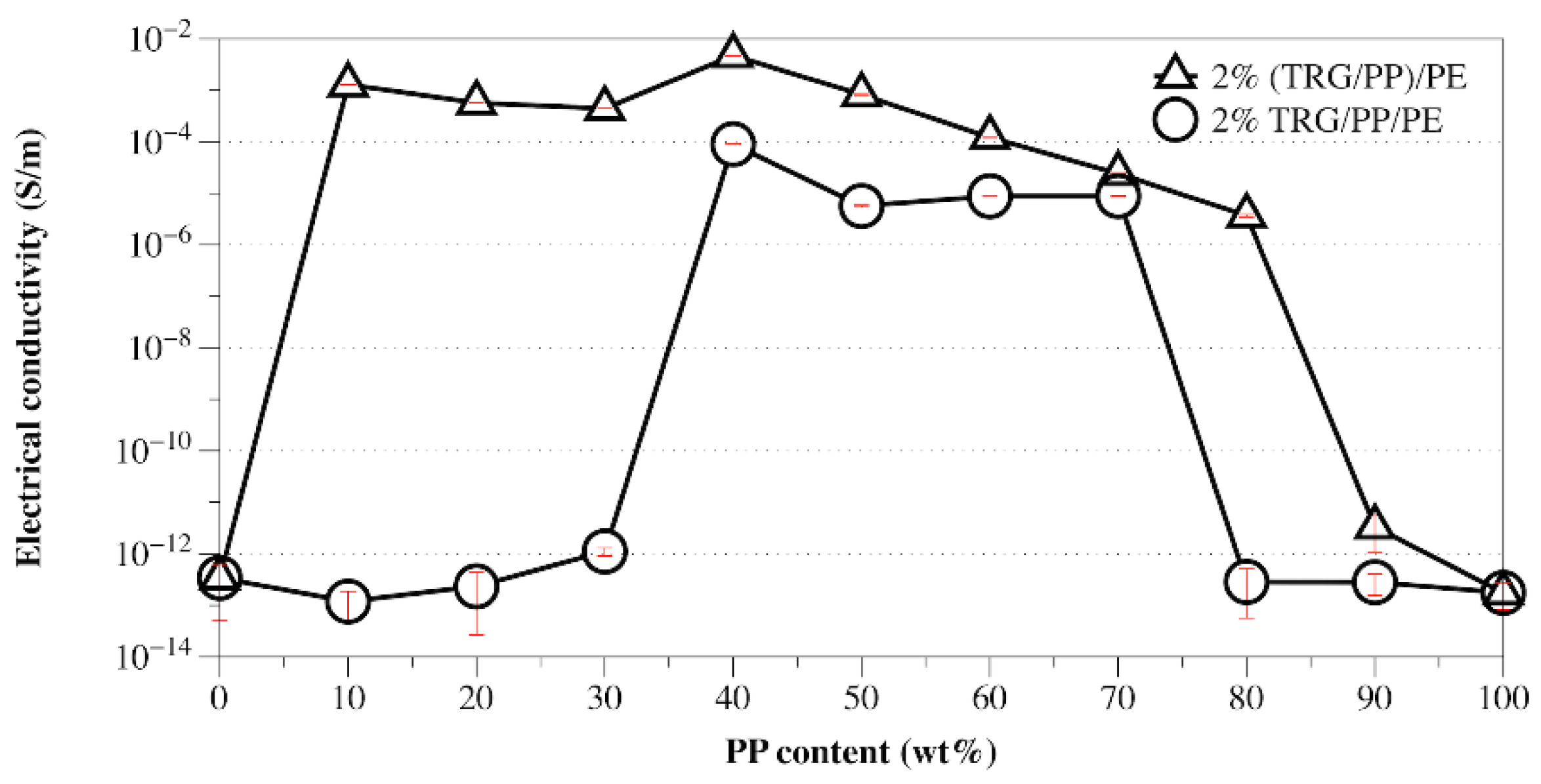
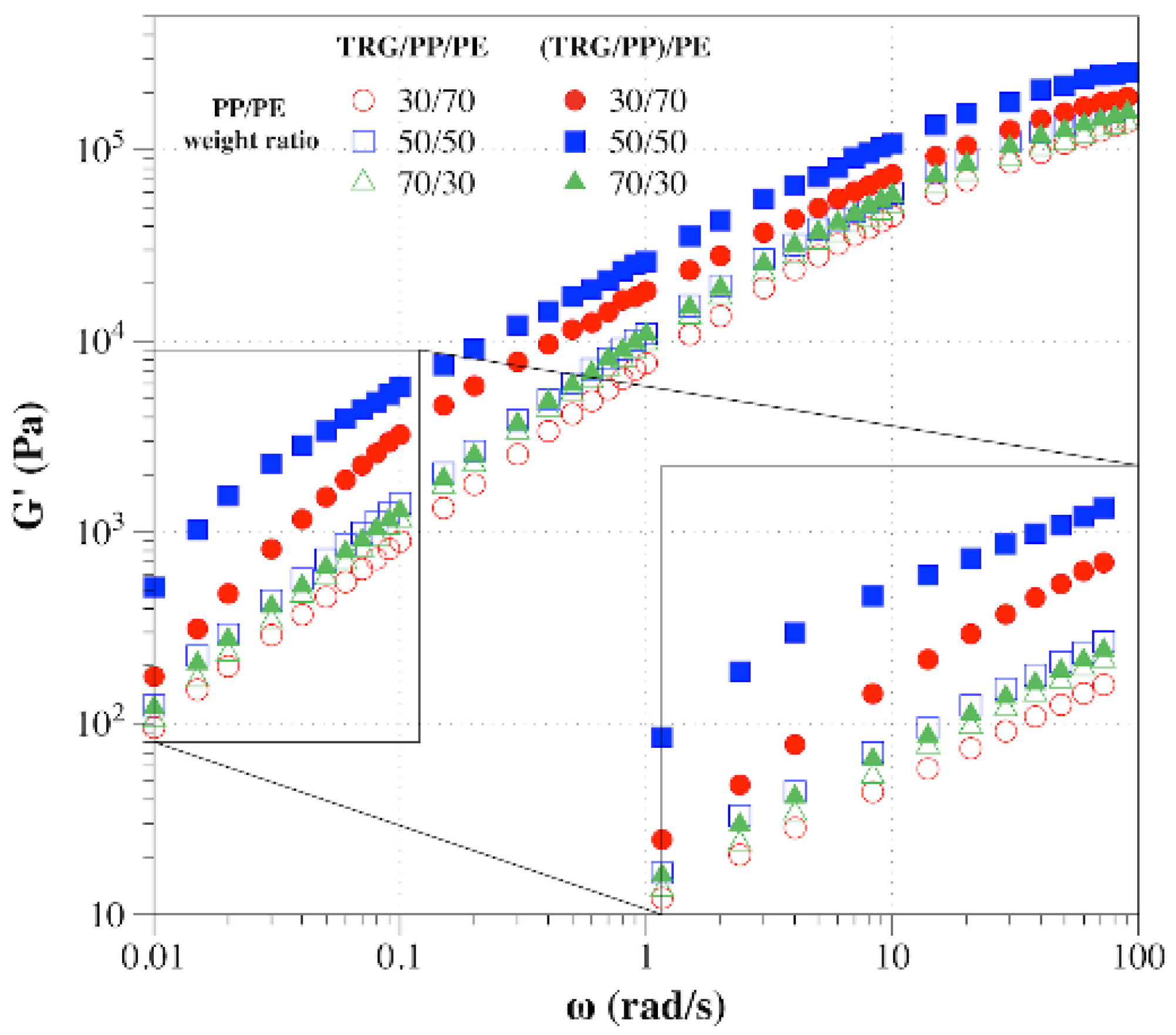
3.2. Effects of Phase Morphology and Localization of TRG on Electrical and Rheological Properties
3.3. Migration of TRG in the (TRG/PP)/PE Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geim, A.K. Graphene: Status and prospects. Science 2009, 324, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Sood, A.K.; Subrahmanyam, K.S.; Govindaraj, A. Graphene: The new two-dimensional nanomaterial. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7752–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Wang, X.D.; Wu, D.Z. Fabrication of spirocyclic phosphazene epoxy-based nanocomposites with graphene via exfoliation of graphite platelets and thermal curing for enhancement of mechanical and conductive properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10160–10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kobayashi, S.; AbdurRahim, M.A.; Zhang, M.J.; Khusainova, A.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Abdala, A.A.; Macosko, C.W. Graphene/polyethylene nanocomposites: Effect of polyethylene functionalization and blending methods. Polymer 2011, 52, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoonessi, M.; Gaier, J.R. Highly conductive multifunctional graphene polycarbonate nanocomposites. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 7211–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.B.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, W.G.; He, Z.; Yu, Z.Z. Tough graphene–polymer microcellular foams for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potschke, P.; Bhattacharyya, A.R.; Janke, A. Morphology and electrical resistivity of melt mixed blends of polyethylene and carbon nanotube filled polycarbonate. Polymer 2003, 44, 8061–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Abdala, A.A.; Macosko, C.W. Graphene/Polymer nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6515–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavagione, H.J.; Martinez, G.; Gomez, M.A. Synthesis of poly (vinyl alcohol)/reduced graphite oxide nanocomposites with improved thermal and electrical properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 5027–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Kohlhaas, K.M.; Zimney, E.J.; Stach, E.A.; Piner, R.D.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 2006, 442, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Y.; Yan, D.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, Y.K.; Yu, Z.Z.; Yavari, F.; Koratkar, N. Enhanced electrical conductivity in polystyrene nanocomposites at ultra-low graphene content. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3130–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumita, M.; Sakata, K.; Asai, S.; Miyasaka, K.; Nakagawa, H. Dispersion of fillers and the electrical conductivity of polymer blends filled with carbon black. Polym. Bull. 1991, 25, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Nagata, K.; Yan, S.K. Influence of melt-mixing processing sequence on electrical conductivity of polyethylene/polypropylene blends filled with graphene. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 1237–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbels, F.; Blacher, S.; Vanlathem, E.; Jerome, R.; Deltour, R.; Brouers, F.; Teyssie, P. Design of electrical composites: Determining the role of the morphology on the electrical properties of carbon black filled polymer blends. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.G.; Sun, N.; Li, H. Enhancement of electrical conductivity by changing phase morphology for composites consisting of polylactide and poly(ε-caprolactone) filled with acid-oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4858–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, W. Design of electrical conductive composites: Tuning the morphology to improve the electrical properties of graphene filled immiscible polymer blends. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5281–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, J.R.; Dreyer, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 2011, 52, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Yang, J.H.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y. Selective localization of reduced graphene oxides at the interface of PLA/EVA blend and its resultant electrical resistivity. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 1982–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schniepp, H.C.; Li, J.L.; McAllister, M.J.; Sai, H.; Herrera-Alonso, M.; Adamson, D.H.; Prud’homme, R.K.; Car, R.; Saville, D.A.; Aksay, I.A. Functionalized single graphene sheets derived from splitting graphite oxide. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 8535–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAllister, M.J.; Li, J.L.; Adamson, D.H.; Schniepp, H.C.; Abdala, A.A.; Liu, J.; Herrera-Alonso, M.; Milius, D.L.; Car, R.; Prud’homme, R.K.; et al. Single sheet functionalized graphene by oxidation and thermal expansion of graphite. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4396–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Nagata, K.; Yan, S.K. Morphology and electrical conductivity of polyethylene/polypropylene blend filled with thermally reduced graphene oxide and surfactant exfoliated graphene. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 2098–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yui, H.; Wu, G.; Sano, H.; Sumita, M.; Kino, K. Morphology and electrical conductivity of injection-molded polypropylene/carbon black composites with addition of high-density polyethylene. Polymer 2006, 47, 3599–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Ma, P.L.; Favis, B.D. The role of the blend interface type on morphology in cocontinuous polymer blends. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 2005–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.F.; Lin, D.P.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, D.M.; Lin, B.L. Selective localization of nanofillers: Effect on morphology and crystallization of PLA/PCL blends. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Xu, L.; Yan, D.X.; Li, Z.M. Conductive polymer composites with segregated structures. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1908–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, H.; Edathil, A.; Ncube, T.; Pokhrel, J.; Khoori, S.; Abraham, A.; Mittal, V. Mechanical and thermal properties of thermoset–graphene nanocomposites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guin, J.P.; Chaudhari, C.V.; Dubey, K.A.; Bhardwaj, Y.K.; Varshney, L. Graphene reinforced radiation crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyl cellulose nanocomposites for controlled drug release. Polym. Compos. 2015, 2017, E74–E80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.F.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhang, M.; Yu, W. Selective localization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in poly(ε-caprolactone)/polylactide blend. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laredo, E.; Grimau, M.; Bello, A.; Wu, D.F.; Zhang, Y.S.; Lin, D.P. AC conductivity of selectively located carbon nanotubes in poly(ε-caprolactone)/polylactide blend nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Fang, F.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhu, M.F.; Chen, D.J. Use of dynamic rheological behavior to estimate the dispersion of carbon nanotubes in carbon nanotube/polymer composites. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 12606–12611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, Y.H.; Lim, S.T.; Choi, H.J.; Jhon, M.S. Rheology of poly(ethylene oxide)/organoclay nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 8084–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Wu, S.Z.; Zhang, L.Q.; Wu, Y.P. High performance natural rubber composites with well-organized interconnected graphene networks for strain-sensing application. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4919–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.R.; Mao, C.; Zhu, Y.T.; Jiang, W.; Yang, X.D. Control of carbon nanotubes at the interface of a co-continuous immiscible polymer blend to fabricate conductive composites with ultralow percolation thresholds. Carbon 2014, 73, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, C.; Nagata, K.; Yan, S. Dependence of Electrical Conductivity on Phase Morphology for Graphene Selectively Located at the Interface of Polypropylene/Polyethylene Composites. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030509
Tu C, Nagata K, Yan S. Dependence of Electrical Conductivity on Phase Morphology for Graphene Selectively Located at the Interface of Polypropylene/Polyethylene Composites. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(3):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030509
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Ce, Kenji Nagata, and Shouke Yan. 2022. "Dependence of Electrical Conductivity on Phase Morphology for Graphene Selectively Located at the Interface of Polypropylene/Polyethylene Composites" Nanomaterials 12, no. 3: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030509






