Preparation of Bimodal Silver Nanoparticle Ink Based on Liquid Phase Reduction Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Equipment
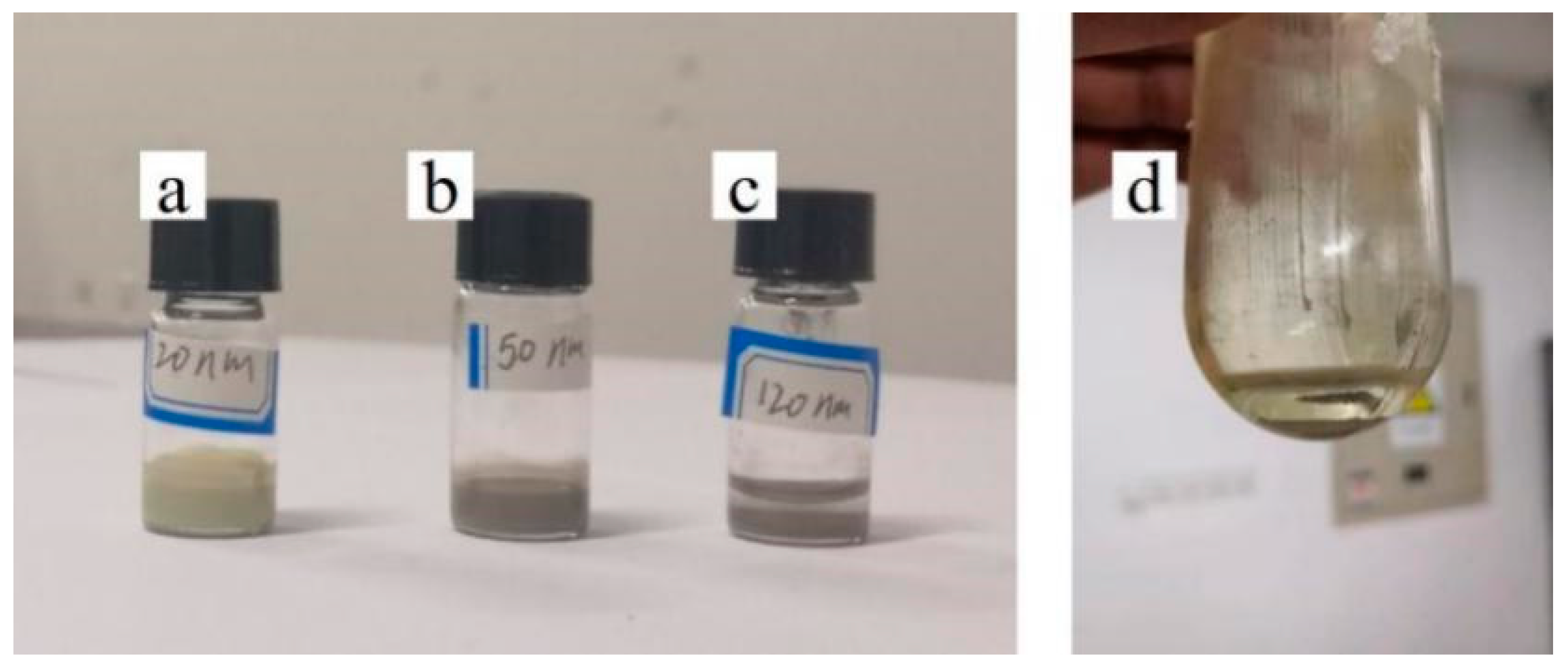
2.2. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticle Ink
2.3. Preparation of Silver-Filling Nanoparticles
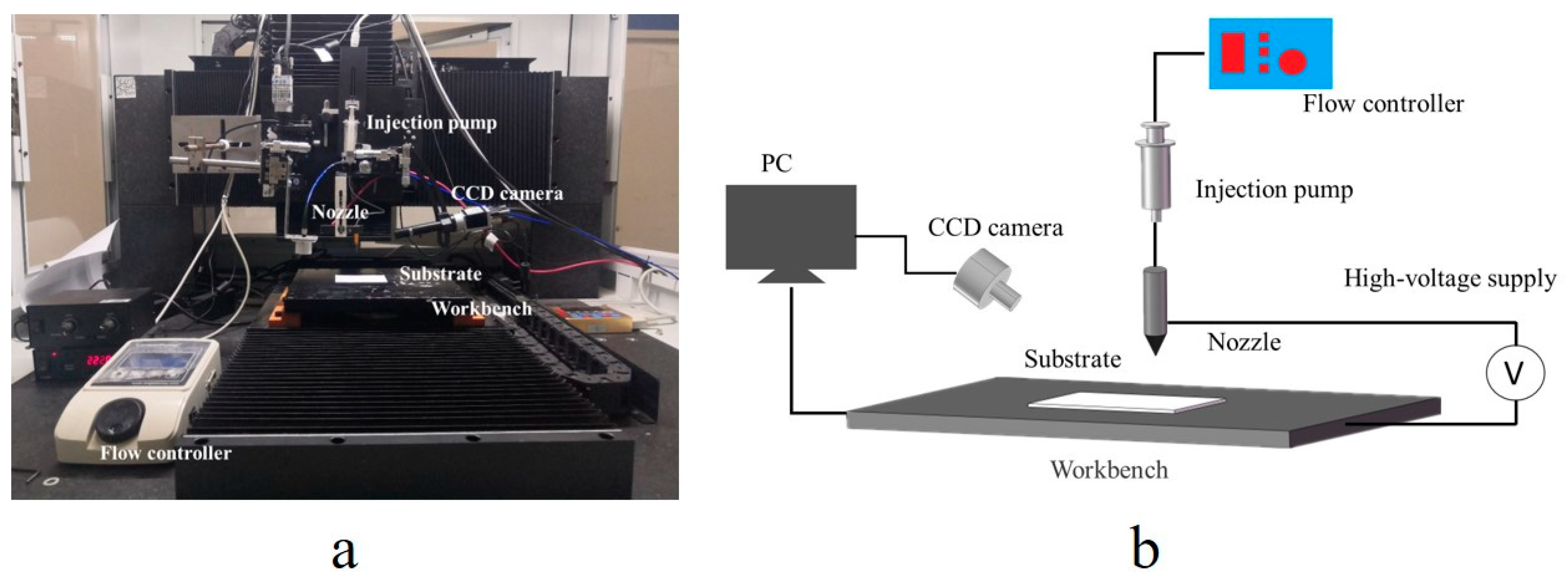
2.4. Printing and Sintering
2.5. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Silver Particle Concentration on Dispersion
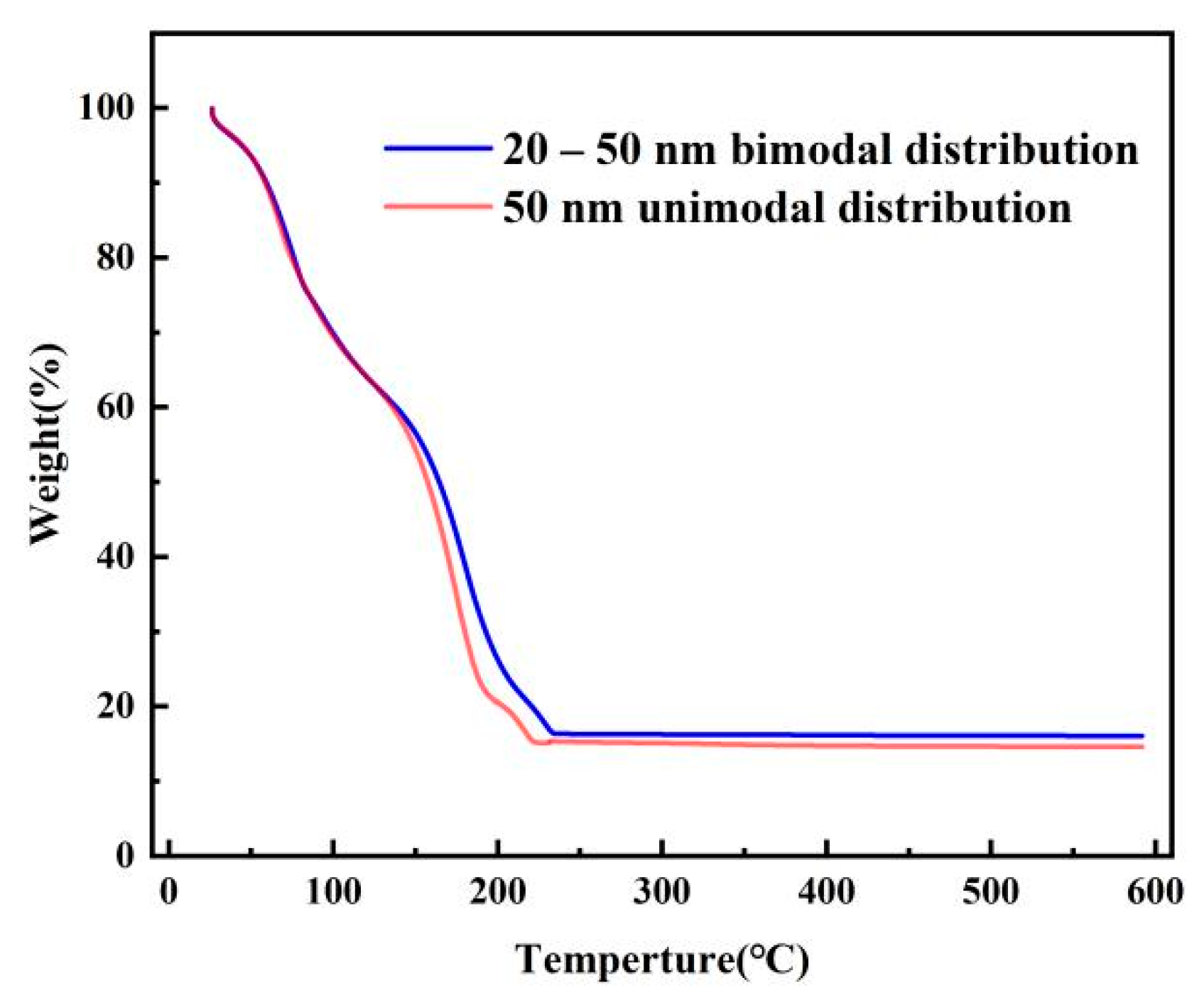
3.2. Effect of Silver Particle Size on Dispersion
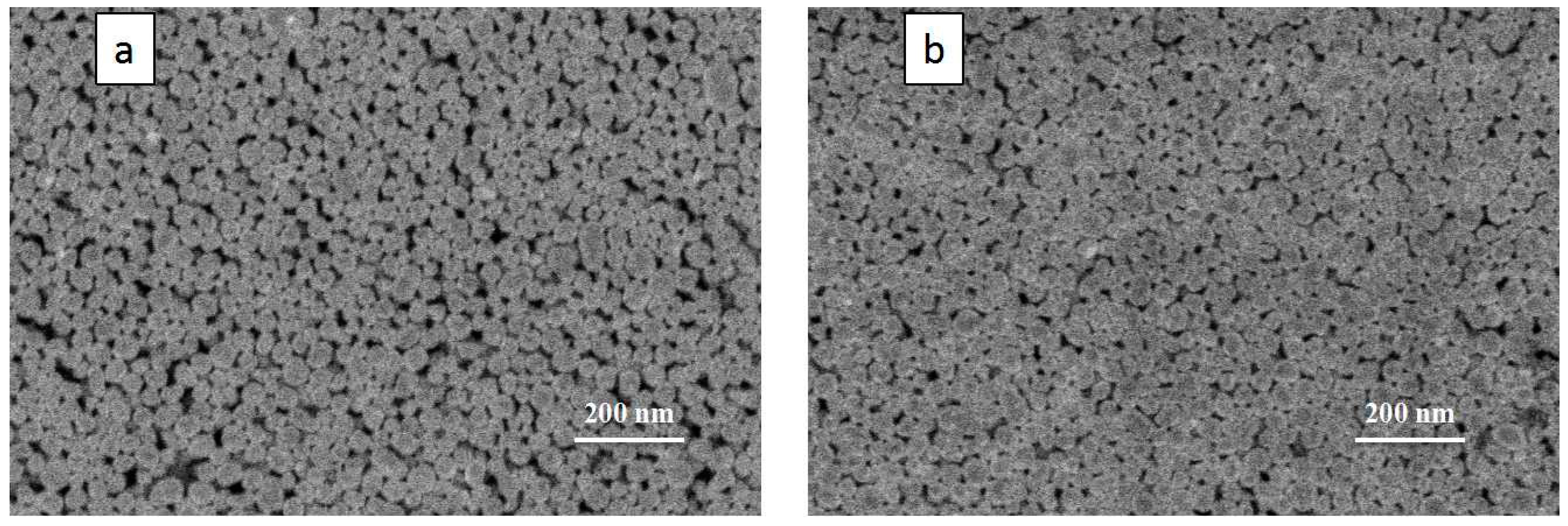
3.3. Effect of Filling Particles on the Conductivity of Printed Patterns
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Sutton, D.; Burgess, A.; Graham, D.; Calvert, P.D. Conductive copper and nickel lines via reactive inkjet printing. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 22, 3719–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Seo, Y.; Choi, J.; Kim, T.; Cho, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, D. Sintering of inkjet printed copper nanoparticles for flexible electronics. Scr. Mater. 2010, 5, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, D.; Lee, W.Y.; Fong, H.H. Highly smooth and conductive silver film with metallo-organic decomposition ink for all-solution-processed flexible organic thin-film transistors. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 33, 15908–15918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K.; Ahn, J.H. Graphene based field effect transistors: Efforts made towards flexible electronics. Solid State Electron. 2013, 89, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeka, D.O.; Batchelor, J.C. Robustness evaluation of an inkjet-printed epidermal ultra-high-frequency radio frequency identification tag. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2021, 1, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Qian, B.; Uto, K.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Minari, T. Functional biomaterials towards flexible electronics and sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 119, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chi, X.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F. An electrohydrodynamic (EHD) printing method with nanosilver ink for flexible electronics. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2020, 17, 2050154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niittynen, J.; Abbel, R.; Mäntysalo, M.; Perelaer, J.; Schubert, U.S.; Lupo, D. Alternative sintering methods compared to conventional thermal sintering for inkjet printed silver nanoparticle ink. Thin Solid Film. 2014, 556, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Ryu, K.; Park, K.H.; Moon, Y.J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Moon, S.J. Temperature effect on physical properties and surface morphology of printed silver ink during continuous laser scanning sintering. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 108, 1960–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, H.; Inui, T.; Miyamoto, I.; Sekiguchi, T.; Nogi, M.; Suganuma, K. A high-sensitivity printed antenna prepared by rapid low-temperature sintering of silver ink. RSC Adv. 2016, 87, 84363–84368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.W.; Zhou, T.; Singh, M.; Jabbour, G.E. Recent developments and directions in printed nanomaterials. Nanoscale 2015, 8, 3338–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yu, Z.; Huang, F.; Tang, C.; Yang, C. Method of multi-layer near-field electrohydraulic printing and sintering of nano-silver ink prepared by liquid phase reduction. AIP Adv. 2021, 8, 085220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Liu, Q.; Wen, G.; Jiang, Z. The surface-plasmon-resonance effect of nanogold/silver and its analytical applications. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffo, M.S.; Carter, S.A.; Holt, A.L. Enhanced photoluminescence of conjugated polymer thin films on nanostructured silver. J. Lumin. 2011, 8, 1594–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; He, X.F.; Yang, X.; Li, Q. Visible Light-Assisted Soft-Chemistry Route to Silver Nanomaterials at Room Temperature. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 807, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.O.; Elias, W.C.; Signori, A.M.; Giacomelli, F.C.; Yang, H.; Domingos, J.B. Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of Silver Nanoparticle–Linear Polyethylene Imine Colloidal Systems. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 7, 4594–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atar, N.; Eren, T.; Demirdögen, B.; Yola, M.L.; Çağlayan, M.O. Silver, gold, and silver@gold nanoparticle-anchored l-cysteine-functionalized reduced graphene oxide as electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation. Ionics 2015, 8, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; He, T.; Lee, C. More than energy harvesting—Combining triboelectric nanogenerator and flexible electronics technology for enabling novel micro-/nano-systems. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 851–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Sun, J.X.; Cheng, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Compagnini, G.; Yin, P.; Wei, S.R.; Li, S.J.; Li, D.B.; Scardaci, V.; et al. Recent progress on metal-based nanomaterials: Fabrications, optical properties, and applications in ultrafast photonics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2107363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglini, M.; Marino, A.; Carmignani, A.; Tapeinos, C.; Cauda, V.; Ancona, A.; Garino, N.; Vighetto, V.; Rosa, G.L.; Sinibaldi, E.; et al. Polydopamine nanoparticles as an organic and biodegradable multitasking tool for neuroprotection and remote neuronal stimulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35782–35798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.H.; Xu, Y.; Tian, X. Silver-modified graphene oxide nanosheets for antibacterial performance of bone scaffold. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 015024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Liu, Q.X.; Jin, J.B.; Ye, W.; Hu, C.Y.; Hu, S.W.; Qi, Z.M.; Long, R.; Song, L.; Zhu, J.F.; et al. Controlling Au–Pd surface on Au nanocubes for selective catalytic alkyne semihydrogenation. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1700377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, L.E. Organic reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Tang, Z.Y. Nanoparticle assemblies for biological and chemical sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmala, A.; Wright, R.; Zhang, Q.; Kirby, P. Synthesis of silver nano particles and fabrication of aqueous Ag inks for inkjet printing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 3, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajan, K.; Roppolo, I.; Chiappone, A.; Bocchini, S.; Perrone, D.; Chiolerio, A. Silver nanoparticle ink technology: State of the art. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2016, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, D.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, P.; Tong, Y. Simple and green fabrication process of nano silver conductive ink and the application in frequency selective surface. Nanotechnology 2020, 10, 105705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.L.; Cheng, C.; Ma, Y.L.; Zhao, C.S. Preparation of silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial activities and the researches of their biocompatibilities. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 10, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.H.; Deng, D.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.Y. Preparation of ultrafine silver powders with controllable size and morphology. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2018, 3, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, S.H.; Jung, S.C.; Yun, J.J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, D.H. Preparation of nonaggregated silver nanoparticles by the liquid phase plasma reduction method. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 8, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Barrasa, J.; López-de-Luzuriaga, J.; Monge, M. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis through chemical methods in solution and biomedical applications. Open Chem. 2011, 1, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khondoker, M.A.H.; Mun, S.C.; Kim, J. Synthesis and characterization of conductive silver ink for electrode printing on cellulose film. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 2, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Mao, P.; He, H. Dispensing of high concentration Ag nano-particles ink for ultra-low resistivity paper-based writing electronics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.C.; Chang, S.J.; Su, F.J.; Lin, S.W.; Chou, Y.C. Effects of capping agents on the dispersion of silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A 2013, 419, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumirat, I.; Ando, Y.; Shimamura, S. Theoretical consideration of the effect of porosity on thermal conductivity of porous materials. J. Porous Mater. 2006, 13, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, Q.; Wu, Z.; Yao, W.; Dai, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, W. Preparing of Highly Conductive Patterns on Flexible Substrates by Screen Printing of Silver Nanoparticles with Different Size Distribution. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 1, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, T.; Tang, C.; Xing, B.; Lu, Y.; Huang, F.; Zuo, C. Conductive Ink Prepared by Microwave Method: Effect of Silver Content on the Pattern Conductivity. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 1, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia, D.; Chirone, R.; Lettieri, P.; Barletta, D.; Poletto, M. Selective laser sintering of ceramic powders with bimodal particle size distribution. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 136, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Guo, Y.; Hu, S.; Dong, D.; Poprawe, R.; Schleifenbaum, J.H.; Ziegler, S. Numerical simulation in the absorption behavior of Ti6Al4V powder materials to laser energy during SLM. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2019, 268, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.S.; Amert, A.K.; Woessner, S.M.; Decker, S.; Kang, S.M.; Han, K.N. Effect of metal powder packing on the conductivity of nanometal ink. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 11, 3902–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.C.; Feng, X.L.; Huang, J.H.; Jiao, D.L.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, W.Q.; Liu, Z.W.; Ramanujan, R.V. A bimodal particle size distribution enhances mechanical and magnetocaloric properties of low-temperature hot pressed Sn-bonded La0.8Ce0.2(Fe0.95Co0.05)11.8Si1.2 bulk composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 469, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simchi, A.; Ahmadi, R.; Reihani, S.M.S.; Mahdavi, A. Kinetics and mechanisms of nanoparticle formation and growth in vapor phase condensation process. Mater. Des. 2007, 3, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, F.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J. Structure Tuning of Bi2MoO6 and Their Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalytic Performances. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 5, 347–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonouz, A.F.; Ashrafi, M.; Ghiyasiyan-Arani, M.; Hamadanian, M. Effect of sol–gel synthesized Al0.1Zr0.9O1.95 nanoparticles and PVP on PVDF-based separators in lithium-ion battery performance: The RSM study. J. Elastomers Plast. 2020, 53, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, K.; Huang, F.; Tang, C. Preparation of Bimodal Silver Nanoparticle Ink Based on Liquid Phase Reduction Method. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030560
Yu Z, Zhang T, Li K, Huang F, Tang C. Preparation of Bimodal Silver Nanoparticle Ink Based on Liquid Phase Reduction Method. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(3):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030560
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhiheng, Tiancheng Zhang, Kaifeng Li, Fengli Huang, and Chengli Tang. 2022. "Preparation of Bimodal Silver Nanoparticle Ink Based on Liquid Phase Reduction Method" Nanomaterials 12, no. 3: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030560
APA StyleYu, Z., Zhang, T., Li, K., Huang, F., & Tang, C. (2022). Preparation of Bimodal Silver Nanoparticle Ink Based on Liquid Phase Reduction Method. Nanomaterials, 12(3), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030560





