Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods for Producing PNPs
2.1. Formation of NPs from Preformed Polymers
2.1.1. Nanoprecipitation
2.1.2. Emulsification-Solvent Evaporation
2.1.3. Emulsification Solvent Diffusion
2.1.4. Salting-Out Technique
2.2. Formation of Nanoparticles by Polymerization of Monomers
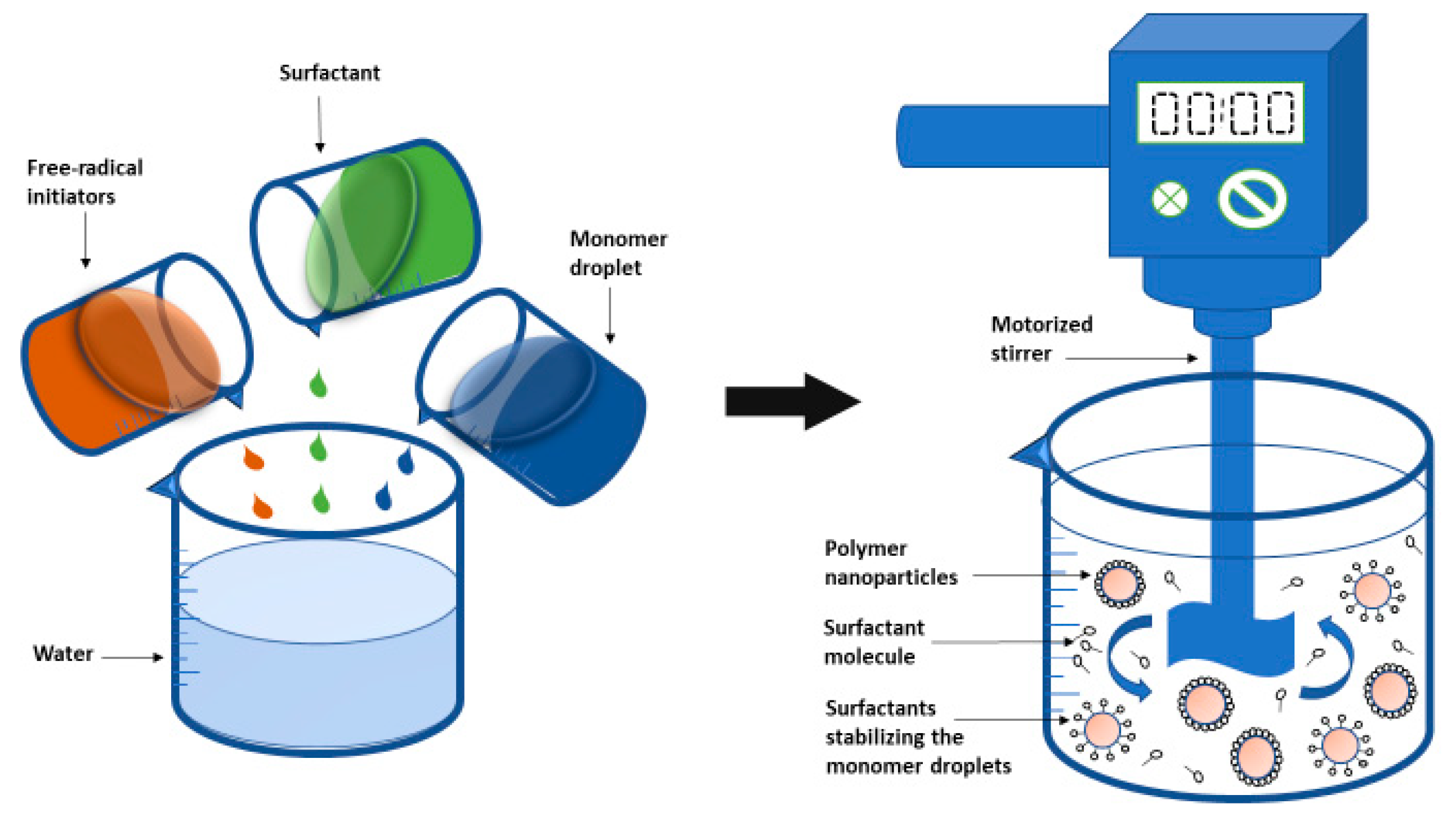
2.2.1. Emulsion Polymerization
2.2.2. Surfactant-Free Emulsion Polymerization
2.2.3. Mini-Emulsion Polymerization
2.2.4. Micro-Emulsion Polymerization
3. Biologically Synthesized Biodegradable Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Based Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatia, S. Nanoparticles Types, Classification, Characterization, Fabrication Methods and Drug Delivery Applications. In Natural Polymer Drug Delivery Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 33–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Tang, P.S.; Chan, W.C. The Effect of Nanoparticle Size, Shape, and Surface Chemistry on Biological Systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Docter, D.; Strieth, S.; Westmeier, D.; Hayden, O.; Gao, M.; Knauer, S.K.; Stauber, R.H. No king without a crown—impact of the nanomaterial-protein corona on nanobiomedicine. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joye, I.J.; McClements, D.J. Production of Nanoparticles by Anti-Solvent Precipitation for Use in Food Systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Laurent, S.; Tawil, N.; Yahia, L.H.; Mahmoudi, M. Nanoparticle and Protein Corona. In Protein-nanoparticle interactions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Lynch, I.; Ejtehadi, M.R.; Monopoli, M.P.; Bombelli, F.B.; Laurent, S. Protein−Nanoparticle Interactions: Opportunities and Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5610–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhilarasi, P.N.; Karthik, P.; Chhanwal, N.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Nanoencapsulation Techniques for Food Bioactive Components: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 628–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripriyalakshmi, S.; Jose, P.; Ravindran, A.; Anjali, C.H. Recent Trends in Drug Delivery System Using Protein Nanoparticles. Cell Biophys. 2014, 70, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifácio, B.V.; Silva, P.B.; Ramos, M.A.; Negri, K.M.; Bauab, T.M.; Chorilli, M. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems and herbal medicines: A review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, J.; Takhistov, P.; McClements, D.J. Functional Materials in Food Nanotechnology. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, R107–R116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhlbusch, T.A.; Asbach, C.; Fissan, H.; Göhler, D.; Stintz, M. Nanoparticle exposure at nanotechnology workplaces: A review. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanguansri, P.; Augustin, M.A. Nanoscale Materials Development–A Food Industry Perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A. Role of nanotechnology in agriculture with special reference to management of insect pests. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin, C.; Philip, S.A.; Samrot, A.V. Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) and utilization of SPIONs in X-ray imaging. Appl. Nanosci. 2017, 7, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Hall, J.B.; McLeland, C.B.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Nanoparticle interaction with plasma proteins as it relates to particle biodistribution, biocompatibility and therapeutic efficacy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kharazian, B.; Hadipour, N.; Ejtehadi, M. Understanding the nanoparticle–protein corona complexes using computational and experimental methods. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 75, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöttler, S.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V. Controlling the Stealth Effect of Nanocarriers through Understanding the Protein Corona. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8806–8815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshafiee, V.; Mahmoudi, M.; Lou, K.; Cheng, J.; Kraft, M.L. Protein corona significantly reduces active targeting yield. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2557–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Choi, E.-J.; Webster, T.J.; Kim, S.-H.; Khang, D. Effect of the protein corona on nanoparticles for modulating cytotoxicity and immunotoxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 10, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rak, J. Microparticles in Cancer. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2010, 36, 888–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mause, S.F.; Weber, C. Microparticles. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.A.; Saleh, A.M. Applications of nanoparticle systems in drug delivery technology. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 26, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenthamara, D.; Subramaniam, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.G.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Essa, M.M.; Lin, F.H.; Qoronfleh, M.W. Therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles and routes of administration. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, Z.; Seven, E.S.; Leblanc, R.M. Crossing the blood-brain barrier with nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2017, 270, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ahmad, E.; Zaman, M.; Qadeer, A.; Rabbani, G. Nanoparticles in relation to peptide and protein aggregation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magazù, S.; Migliardo, F.; Telling, M. Structural and dynamical properties of water in sugar mixtures. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrot, A.; Burman, U.; Philip, S.A.; Shobana, N.; Chandrasekaran, K. Synthesis of curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticles from crab shell derived chitosan for drug delivery. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2018, 10, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panhwar, A.H.; Tuzen, M.; Hazer, B.; Kazi, T.G. Solid phase microextraction method using a novel polystyrene oleic acid imidazole polymer in micropipette tip of syringe system for speciation and determination of antimony in environmental and food samples. Talanta 2018, 184, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarkar, H.; Barikani, M. Applications of Biopolymers I: Chitosan. Monatsh. Chem. 2009, 140, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Tuzen, M.; Sarı, A. Polyamide magnetic palygorskite for the simultaneous removal of Hg(II) and methyl mercury; with factorial design analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 211, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A.; Kausar, A.; Younus, A. A Review on Preparation, Properties and Applications of Polymeric Nanoparticle-Based Materials. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2014, 54, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geckeler, K.E.; Nishide, H. Advanced Nanomaterials; Wiley Online Library: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derman, S.; Kizilbey, K.; Akdeste, Z.M. Polymeric Nanoparticles. Sigma J. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2013, 31, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, K. Serbest Radikal Temizleyici Madde İçeren Nanopartiküler Taşıyıcı Sistemlerin Tasarımı Ve Değerlendirilmesi. Master’s Thesis, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey, 2010. Available online: http://nek.istanbul.edu.tr:4444/ekos/TEZ/47041.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Wang, Y.-J.; Larsson, M.; Huang, W.-T.; Chiou, S.-H.; Nicholls, S.J.; Chao, J.-I.; Liu, D.-M. The use of polymer-based nanoparticles and nanostructured materials in treatment and diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases: Recent advances and emerging designs. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 57, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-W.; Edirisinghe, M.; Stride, E. Ultrasound mediated release from stimuli-responsive core–shell capsules. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3962–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, R.H.; Keck, C.M. Challenges and Solutions for the Delivery of Biotech Drugs–A Review of Drug Nanocrystal Technology and Lipid Nanoparticles. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 113, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.; Neufeld, R.J.; Ribeiro, A.; Veiga, F. Nanoencapsulation, I. Methods for preparation of drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2006, 2, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, D.G.; Burdick, J.A.; Langer, R. Smart Biomaterials. Science 2004, 305, 1923–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klodzinska, S.N.; Wan, F.; Jumaa, H.; Sternberg, C.; Rades, T.; Nielsen, H.M. Improved drug loading and antibacterial activity of minocycline-loaded PLGA nanoparticles prepared by solid/oil/water ion pairing method. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hornig, S.; Heinze, T.; Becer, C.R.; Schubert, U.S. Synthetic polymeric nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3838–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarwal, R.C.; Kant, S.; Singh, P.N.; Maiti, P.; Pandit, J.K. Polymeric nanoparticulate system: A potential approach for ocular drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2009, 136, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Vega, A.-I.; Gómez-Quintero, T.; Nuñez-Anita, R.E.; Acosta-Torres, L.-S.; Castaño, V. Polymeric and Ceramic Nanoparticles in Biomedical Applications. J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, H.K.; Almokdad, A.A.; Shaluf, S.I.; Debe, M.S. Polymer-Based Nanomaterials for Drug-Delivery Carriers. In Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 531–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailaja, A.K. A Review on Biomedical Applications of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Drug Des. Intellect. Prop. Int. J. 2018, 2, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Misra, R.; Sahoo, S.K. Nanoparticles: A Boon to Drug Delivery, Therapeutics, Diagnostics and Imaging. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.; Borm, P.J.A. Drug delivery and Nanoparticles: Applications and Hazards. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pignatello, R.; Impallomeni, G.; Cupri, S.; Puzzo, G.; Curcio, C.; Rizzo, M.G.; Guglielmino, S.; Ballistreri, A. Unsaturated Poly(Hydroxyalkanoates) for the Production of Nanoparticles and the Effect of Cross-Linking on Nanoparticle Features. Materials 2019, 12, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umesh, M.; Priyanka, K.; Thazeem, B.; Preethi, K. Biogenic PHA nanoparticle synthesis and characterization from Bacillus subtilis NCDC0671 using orange peel medium. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2017, 67, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koosha, F.; Muller, R.; Washington, C. Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Nanoparticles for Drug Targeting. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1987, 39, 136P. [Google Scholar]
- Koosha, F.; Muller, R.; Davis, S.S.; Davies, M.C. The surface chemical structure of poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) microparticles produced by solvent evaporation process. J. Control. Release 1989, 9, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyler, I.; Appel, M.; Devissaguet, J.-P.; Legrand, P.; Barratt, G. Macrophage Activation by a Lipophilic Derivative of Muramyldipeptide within Nanocapsules: Investigation of the Mechanism of Drug Delivery. J. Nanopart. Res. 1999, 1, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, P.; Lesieur, S.; Bochot, A.; Gref, R.; Raatjes, W.; Barratt, G.; Vauthier, C. Influence of polymer behaviour in organic solution on the production of polylactide nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 344, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M.; Kreuter, J. Optimization of the preparation of loperamide-loaded poly (L-lactide) nanoparticles by high pressure emulsification-solvent evaporation. J. Microencapsul. 1997, 14, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehilla, B.J.; Bergkvist, M.; Popat, K.C.; Desai, T.A. Purified and surfactant-free coenzyme Q10-loaded biodegradable nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 348, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Gupta, B.K.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C. Fabrication of curcumin encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles for improved therapeutic effects in metastatic cancer cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, L.B.; Huber, S.C.; Barnabé, A.; Bassora, F.D.S.; Paixão, D.S.; Durán, N.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M. Characterization of PCL and Chitosan Nanoparticles as Carriers of Enoxaparin and Its Antithrombotic Effect in Animal Models of Venous Thrombosis. J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajiboye, A.L.; Trivedi, V.; Mitchell, J. Preparation of polycaprolactone nanoparticles via supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of emulsions. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 8, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shokri, N.; Javar, H.A.; Fouladdel, S.; Khalaj, A.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Dinarvand, R.; Atyabi, F.; Nomani, A.; Azizi, E. Preparation and Evaluation of Poly (Caprolactone Fumarate) Nanoparticles Containing Doxorubicin HCl. Daru J. Fac. Pharm. Tehran Univ. Med. Sci. 2011, 19, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kateb, B.; Chiu, K.; Black, K.L.; Yamamoto, V.; Khalsa, B.; Ljubimova, J.Y.; Ding, H.; Patil, R.; Portilla-Arias, J.A.; Modo, M.; et al. Nanoplatforms for constructing new approaches to cancer treatment, imaging, and drug delivery: What should be the policy? NeuroImage 2011, 54, S106–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansour, H.M.; Sohn, M.; Al-Ghananeem, A.; DeLuca, P.P. Materials for Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Molecular Pharmaceutics and Controlled Release Drug Delivery Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 3298–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundar, S.; Kundu, J.; Kundu, S.C. Biopolymeric Nanoparticles. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2010, 11, 014104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A. The use of mucoadhesive polymers in ocular drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1595–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz-Landázuri, A.; Portilla-Arias, J.; De Ilarduya, A.M.; Álvarez, M.G.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Nanoparticles of Esterified Polymalic Acid for Controlled Anticancer Drug Release. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loyer, P.; Cammas-Marion, S. Natural and synthetic poly(malic acid)-based derivates: A family of versatile biopolymers for the design of drug nanocarriers. J. Drug Target. 2014, 22, 556–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutul, T.; Rusu, E.; Condur, N.; Ursaki, V.; Goncearenco, E.; Vlazan, P. Preparation of poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone)-stabilized ZnO colloid nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahu, A.; Solanki, P.; Mitra, S. Curcuminoid-loaded poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendes, A.N.; Hubber, I.; Siqueira, M.; Barbosa, G.M.; Moreira, D.D.L.; Holandino, C.; Pinto, J.C.; Nele, M. Preparation and Cytotoxicity of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Nanoparticles for Drug Encapsulation. Macromol. Symp. 2012, 319, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, S.; Chong, S.-F.; Wohl, B.M.; Goldie, K.N.; Zelikin, A.N. Poly(vinyl alcohol) Physical Hydrogel Nanoparticles, Not Polymer Solutions, Exert Inhibition of Nitric Oxide Synthesis in Cultured Macrophages. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madlova, M.; Jones, S.; Zwerschke, I.; Ma, Y.; Hider, R.; Forbes, B. Poly(vinyl alcohol) nanoparticle stability in biological media and uptake in respiratory epithelial cell layers in vitro. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ding, Y.; Ge, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, C. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan–poly(acrylic acid) nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3193–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, R.M.; Bodnar, M.; Hartmann, J.F.; Borbely, J. Preparation and characterization of poly(acrylic acid)-based nanoparticles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualdesi, M.; Igarzabal, C.A.; Vara, J.; Ortiz, C. Synthesis and physicochemical properties of polyacrylamide nanoparticles as photosensitizer carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 512, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuntini, F.; Dumoulin, F.; Daly, R.; Ahsen, V.; Scanlan, E.M.; Lavado, A.S.P.; Aylott, J.W.; Rosser, G.A.; Beeby, A.; Boyle, R.W. Orthogonally bifunctionalised polyacrylamide nanoparticles: A support for the assembly of multifunctional nanodevices. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2034–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Muñoz, R.; Treviño, M.E.; Morales, G.; Valdez-Garza, J.A.; de León, R.D.; Saade, H.; Enríquez-Medrano, F.J.; López, R.G. Ultrafine Nanoparticles of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate-co-Methacrylic Acid) Loaded with Aspirin. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, J.X.; Clegg, J.R.; Ander, E.W.; Peppas, N.A. Tunable poly(methacrylic acid-co-acrylamide) nanoparticles through inverse emulsion polymerization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Tran, T.T.-D.; Zhang, J.; Kong, L. Manufacturing Techniques and Surface Engineering of Polymer Based Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery to Cancer. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zielińska, A.; Carreiró, F.; Oliveira, A.; Neves, A.; Pires, B.; Venkatesh, D.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Eder, P.; Silva, A.; et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles: Production, Characterization, Toxicology and Ecotoxicology. Molecules 2020, 25, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucho, C.I.C.; Barros, M.T. Polymeric nanoparticles: A study on the preparation variables and characterization methods. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 80, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, D.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. DNA Encapsulation via Double Emulsion Like Process. J. Colloid Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 2, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, B.; Guo, T. Preparation of Eudragit L 100-55 enteric nanoparticles by a novel emulsion diffusion method. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 108, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, S.; Radha, K.V. Review of Nanobiopolymers for Controlled Drug Delivery. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2014, 53, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, I.M.; Moreira, M.M.; Neves, P.; Da Fé, T.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Almeida, P.J.; Rodrigues, J.A. An Insight on Salting-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction for Phytoanalysis. Phytochem. Anal. 2017, 28, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, A.M.; Zultanski, S.L.; Waldman, J.H.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Shevlin, M.; Peng, F. General Principles and Strategies for Salting-Out Informed by the Hofmeister Series. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Distler, D.; Neto, W.S.; Machado, F. Emulsion Polymerization. Ref. Modul. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamak, H.B. Emulsion Polymerization: Effects of Polymerization Variables on The Properties of Vinyl Acetate Based Emulsion Polymers. In Polymer Science; Yilmaz, F., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; pp. 35–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Yao, H.; Ma, J. Recent advances in RAFT-mediated surfactant-free emulsion polymerization. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2532–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, S.; Tomovska, R.; Asua, J.M. Surfactant-free high solids content polymer dispersions. Polymer 2017, 117, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucheu, J.; Gauthier, C.; Chazeau, L.; Cavaillé, J.-Y.; Mellon, V.; Lami, E.B. Miniemulsion polymerization for synthesis of structured clay/polymer nanocomposites: Short review and recent advances. Polymer 2010, 51, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespy, D.; Landfester, K. Miniemulsion polymerization as a versatile tool for the synthesis of functionalized polymers. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2010, 6, 1132–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Zafar, N.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Double emulsion solvent evaporation techniques used for drug encapsulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, N.; Peralta, R.; López, R.; Ramos, L.; Katime, I.; Cesteros, C.; Mendizábal, E.; Puig, J. A comparison of the characteristics of poly(vinyl acetate) latex with high solid content made by emulsion and semi-continuous microemulsion polymerization. Polymer 2001, 42, 6923–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, B.H.A. Bacterial polymers: Biosynthesis, modifications and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradali, M.F.; Rehm, B.H.A. Bacterial biopolymers: From pathogenesis to advanced materials. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Niu, A.; Peng, S.; Jiang, M.; Tu, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, C. Formation of Novel Polymeric Nanoparticles. Accounts Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Allémann, E.; Fessi, H.; Doelker, E. Preparation Techniques and Mechanisms of Formation of Biodegradable Nanoparticles from Preformed Polymers. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1998, 24, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvreur, P.; Dubernet, C.; Puisieux, F. Controlled Drug Delivery with Nanoparticles: Current Possibilities and Future Trends. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1995, 41, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, P.; Ren, W.; Xin, K.; Yang, Y.; Xie, C.; Yang, C.; Liu, Q.; Yu, L.; Jiang, X.; et al. Comparative studies of salinomycin-loaded nanoparticles prepared by nanoprecipitation and single emulsion method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Sawant, K. Encapsulation of exemestane in polycaprolactone nanoparticles: Optimization, characterization, and release kinetics. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthi, C.; Kathiresan, K. Fabrication of Dual Drug Loaded Polymeric Nanosuspension: Incorporating Analytical Hierarchy Process and Data Envelopment Analysis in the Selection of A Suitable Method. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Mora-Huertas, C.E.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Polymer-based nanocapsules for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega-Peláez, E.K.; Mendoza-Muñoz, N.; Ganem-Quintanar, A.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. Optimization of the emulsification and solvent displacement method for the preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 37, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Bugnicourt, E.; Latorre, M.; Jorda, M.; Echegoyen Sanz, Y.E.; Lagaron, J.M.; Miesbauer, O.; Bianchin, A.; Hankin, S.; Bölz, U.; et al. Review on the Processing and Properties of Polymer Nanocomposites and Nanocoatings and Their Applications in the Packaging, Automotive and Solar Energy Fields. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, A.D.; Beatrice, C.A.G. Polymer Nanocomposites with Different Types of Nanofiller. In Nanocomposites-Recent Evolutions; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parambath, A. Engineering of Biomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems: Beyond Polyethylene Glycol; Woodhead Publishing: Kidlington, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sailaja, A.K.; Shreya, M. Preparation and Characterization of Naproxen Loaded Niosomes by Ether Injection Method. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2018, 10, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, J.-A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Numata, K. Engineering Peptide-based Carriers for Drug and Gene Delivery. In Engineering in Translational Medicine; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 667–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mascolo, D.; Basnett, P.; Palange, A.L.; Francardi, M.; Roy, I.; Decuzzi, P. Tuning core hydrophobicity of spherical polymeric nanoconstructs for docetaxel delivery. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshyar, N.; Gray, S.; Han, H.; Bao, G. The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 673–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Trase, I.; Ren, M.; Duval, K.; Guo, X.; Chen, Z. Design of Nanoparticle-Based Carriers for Targeted Drug Delivery. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jnm/2016/1087250/ (accessed on 14 February 2021).
- Ageitos, J.M.; Chuah, J.-A.; Numata, K. Chapter Design Considerations for Properties of Nanocarriers on Disposition and Efficiency of Drug and Gene Delivery. In Nanomedicines: Design, Delivery and Detection; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, M.; Krishnasamy, K. Application of Plackett-Burman Factorial Design in The Development of Curcumin Loaded Eudragit E 100 Nanoparticles. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2013, 5, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hickey, J.; Santos, J.L.; Williford, J.-M.; Mao, H.-Q. Control of polymeric nanoparticle size to improve therapeutic delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, Applications and Toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Serra, C.A.; Vandamme, T.F.; Yu, W.; Anton, N. Double Emulsions Prepared by Two–Step Emulsification: History, State-Of-The-Art and Perspective. J. Control. Release 2019, 295, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, F.; Zendehboudi, S. A Comprehensive Review on Emulsions and Emulsion Stability in Chemical and Energy Industries. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 97, 281–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aubry, J.; Ganachaud, F.; Addad, J.-P.C.; Cabane, B. Nanoprecipitation of Polymethylmethacrylate by Solvent Shifting:Boundaries. Langmuir 2009, 25, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Huertas, C.E.; Garrigues, O.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Nanocapsules prepared via nanoprecipitation and emulsification–diffusion methods: Comparative study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepeltier, E.; Bourgaux, C.; Couvreur, P. Nanoprecipitation and the “Ouzo effect”: Application to Drug Delivery Devices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 71, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoyav, B.; Benny, O. Controlled and tunable polymer particles’ production using a single microfluidic device. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vauthier, C.; Dubernet, C.; Fattal, E.; Pinto-Alphandary, H.; Couvreur, P. Poly(alkylcyanoacrylates) as biodegradable materials for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 519–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Patel, B.B.; Tiwari, S. Colloidal nanocarriers: A review on formulation technology, types and applications toward targeted drug delivery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshfeghi, A.A.; Peyman, G.A. Micro-and Nanoparticulates. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Román, R.; Cavazos-Rodríguez, M.; Chávez-Montes, A.; Castro-Ríos, R.; Waksman de Torres, N.; Salazar-Cavazos, M.; Galindo Rodríguez, S. Formulación y caracterización de nanocápsulas con un antioxidante natural para su aplicación cutánea (Formulation and Characterization of Nanocapsules as a Natural Antioxidant for Cutaneous Application). Química Hoy (Chem. Sci.) 2011, 1, 29–35. Available online: http://eprints.uanl.mx/13446/1/Art6.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Yuan, Y.; Xing, E.-M.; Qin, Y.; Peng, Z.-J.; Zhang, Z.-P.; Yang, K.-Y. Optimization of parameters for preparation of docetaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation method. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Q. Development and Application of Nanoparticles Synthesized with Folic Acid Conjugated Soy Protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, Y.S. Production of gliadin-poly(ethyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles for hydrophilic coating. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebouille, J.G.J.L.; Stepanyan, R.; Slot, J.J.M.; Stuart Cohen, M.A.; Tuinier, R. Nanoprecipitation of Polymers in a Bad Solvent. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 460, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthi, C.; Kathiresan, K. Fabrication of highly stable sonication assisted curcumin nanocrystals by nanoprecipitation method. Drug Inven. Today 2013, 5, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Structure Evolution of Curcumin Nanoprecipitation from a Micromixer. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, L.; Aitta, J.; Hyvönen, S.; Karjalainen, M.; Hirvonen, J. Improved Entrapment Efficiency of Hydrophilic Drug Substance During Nanoprecipitation of Poly(I)Lactide Nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Chen, L.; Hu, F.; Wu, W. Food proteins as novel nanosuspension stabilizers for poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Delgado, M.; Fu, A.; Alcouffe, P.; Gouin, S.G.; Fleury, E.; Katz, J.L.; Ganachaud, F.; Bernard, J. Simple but Precise Engineering of Functional Nanocapsules through Nanoprecipitation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6910–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, E.; Sah, H. Recent Trends in Preparation of Poly(lactide- co -glycolide) Nanoparticles by Mixing Polymeric Organic Solution with Antisolvent. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barreras-Urbina, C.G.; Ramírez-Wong, B.; López-Ahumada, G.A.; Ibarra, S.E.B.; Martínez-Cruz, O.; Tapia-Hernández, J.A.; Félix, F.R. Nano- and Micro-Particles by Nanoprecipitation: Possible Application in the Food and Agricultural Industries. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.J.; Alshahrani, S. Nano-encapsulation and characterization of baricitinib using poly-lactic-glycolic acid co-polymer. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Madan, P.; Lin, S. Effect of process and formulation variables on the preparation of parenteral paclitaxel-loaded biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles: A co-surfactant study. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calzoni, E.; Cesaretti, A.; Polchi, A.; Di Michele, A.; Tancini, B.; Emiliani, C. Biocompatible Polymer Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Applications in Cancer and Neurodegenerative Disorder Therapies. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.; Jallouli, Y.; Kroubi, M.; Yuan, X.-B.; Feng, W.; Kang, C.-S.; Pu, P.-Y.; Betbeder, D. Characterization of endocytosis of transferrin-coated PLGA nanoparticles by the blood–brain barrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, T.; Rom, A.; Nyska, A.; Benita, S. Novel double coated nanocapsules for intestinal delivery and enhanced oral bioavailability of tacrolimus, a P-gp substrate drug. J. Control. Release 2009, 133, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Assis, D.N.; Mosqueira, V.C.F.; Vilela, J.M.C.; Andrade, M.S.; Cardoso, V.N. Release Profiles and Morphological Characterization by Atomic Force Microscopy and Photon Correlation Spectroscopy of 99mTechnetium-Fluconazole Nanocapsules. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 349, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugheirbi, N.A.; Paluch, K.J.; Tajber, L. Heat induced evaporative antisolvent nanoprecipitation (HIEAN) of itraconazole. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salatin, S.; Barar, J.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Adibkia, K.; Kiafar, F.; Jelvehgari, M. Development of a nanoprecipitation method for the entrapment of a very water soluble drug into Eudragit RL nanoparticles. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, C. Tuning the Size of Poly(lactic-co-glycolic Acid) (PLGA) Nanoparticles Fabricated by Nanoprecipitation. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 13, 1700203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, F.; Esnaashari, S.S.; Mujokoro, B.; Dorkoosh, F.; Khosravani, M.; Adabi, M. Investigation of Effective Parameters on Size of Paclitaxel Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, S.K.; Patel, D.K.; Thakur, R.; Mishra, D.P.; Maiti, P.; Haldar, C. Anti-cancer evaluation of quercetin embedded PLA nanoparticles synthesized by emulsified nanoprecipitation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuddanda, P.R.; Mishra, A.; Singh, S.K. Development of polymeric nanoparticles with highly entrapped herbal hydrophilic drug using nanoprecipitation technique: An approach of quality by design. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 20, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, A.; Ozturk, N.; Sarisozen, C.; Vural, I. Investigation of Formulation Parameters of PLGA Nanoparticles Prepared by Nanoprecipitation Technique. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Nanotechnology: Fundamentals and Application, Prague, Czech Republic, 11–13 August 2014; p. 94. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, P.; Vaysse, M.; Aubry, J.; Mariot, D.; Sonnier, R.; Ganachaud, F. Finest nanocomposite films from carbon nanotube-loaded poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles obtained by the Ouzo effect. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 5528–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.S.; Sawant, K.K. Modified Nanoprecipitation Method for Preparation of Cytarabine-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.A.; Schneider, M. Improvement of Nanoprecipitation Technique for Preparation of Gelatin Nanoparticles and Potential Macromolecular Drug Loading. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Shen, Z.-G.; Zhong, J.; Hu, T.-T.; Chen, J.-F.; Ma, Z.-Q.; Yun, J. Preparation of amorphous cefuroxime axetil nanoparticles by controlled nanoprecipitation method without surfactants. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 323, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M. Factors Affecting Preparation and Properties of Nanoparticles by Nanoprecipitation Method. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 4, 4854–4858. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Preparation of Particulate Polymeric Therapeutics for Medical Applications. Small Methods 2017, 1, 1700147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilati, U.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E. Development of a nanoprecipitation method intended for the entrapment of hydrophilic drugs into nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 24, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lince, F.; Marchisio, D.; Barresi, A. Strategies to control the particle size distribution of poly-ε-caprolactone nanoparticles for pharmaceutical applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.C.; Luo, G.S. Modified nanoprecipitation method for polysulfone nanoparticles preparation. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3414–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.M.; Jäger, E.; Jäger, A.; Stepánek, P.; Giacomelli, F.C. Physicochemical aspects behind the size of biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles: A step forward. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 436, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olenius, T.; Yli-Juuti, T.; Elm, J.; Kontkanen, J.; Riipinen, I. New Particle Formation and Growth: Creating a New Atmospheric Phase Interface. In Physical Chemistry of Gas-Liquid Interface; Faust, J.A., House, J.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 11; pp. 315–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.; Vigil, R.; Fox, R. A competitive aggregation model for Flash NanoPrecipitation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.P.; Geckeler, K.E. Polymer nanoparticles: Preparation techniques and size-control parameters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 887–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorny, M.; Fishbein, I.; Danenberg, H.D.; Golomb, G. Lipophilic drug loaded nanospheres prepared by nanoprecipitation: Effect of formulation variables on size, drug recovery and release kinetics. J. Control. Release 2002, 83, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Salari, D.; Hamidi, M. Preparation of biodegradable nanoparticles of tri-block PLA–PEG–PLA copolymer and determination of factors controlling the particle size using artificial neural network. J. Microencapsul. 2011, 28, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamsan, A. Nanoprecipitation is more efficient than emulsion solvent evaporation method to encapsulate cucurbitacin I in PLGA nanoparticles. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 22, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.C.; Pramanik, S. Formulation and Characterization of Mefenamic Acid Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Lancheros, R.; Guerrero, C.A.; Godoy-Silva, R.D. Improvement of N-Acetylcysteine Loaded in PLGA Nanoparticles by Nanoprecipitation Method. J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chidambaram, M.; Krishnasamy, K. Modifications to the Conventional Nanoprecipitation Technique: An Approach to Fabricate Narrow Sized Polymeric Nanoparticles. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 4, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilati, U.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E. Nanoprecipitation versus emulsion-based techniques for the encapsulation of proteins into biodegradable nanoparticles and process-related stability issues. AAPS PharmSciTech 2005, 6, E594–E604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, C.; Okubo, T.; Nangrejo, M.; Edirisinghe, M. Preparation of polymeric nanoparticles by novel electrospray nanoprecipitation. Polym. Int. 2014, 64, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-X.; He, L.; Qiao, S.Z.; Middelberg, A.P. Nanoparticle synthesis in microreactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 1463–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmatnezhad, F.; Nazar, A.R.S. On-chip controlled synthesis of polycaprolactone nanoparticles using continuous-flow microfluidic devices. J. Flow Chem. 2020, 10, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J. Microfluidic Methods for Fabrication and Engineering of Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2019, 3, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, P.; Dawn, S.S.; Saipriya, C.; Samrot, A.V. Synthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate nanoparticles using surfactant (SPAN20) for hydrophobic drug delivery. Rasayan J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, F.; Shakeri, S.; Hojjatoleslami, M. Preparation and Characterization of Carvacrol Loaded Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanoparticles by Nanoprecipitation and Dialysis Methods. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, N697–N705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, N.; Benoit, J.-P.; Saulnier, P. Design and production of nanoparticles formulated from nano-emulsion templates—A review. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.L.; Jana, U.; Manna, P.K.; Mohanta, G.P.; Manavalan, R. Nanoparticle: An Overview of Preparation and Characterization. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson, A.; Rayner, M. General Principles of Nanoemulsion Formation by High-Energy Mechanical Methods. Nanoemulsions 2018, 103–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.K.; Garg, T.; Bhandari, S.; Rath, G. Advancement in pulmonary drug delivery systems for treatment of tuberculosis. In Nanostructures for Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 669–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, A.; Agyei, D.; Wang, Q. Formulation of water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsions containing trans-resveratrol. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35917–35927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stauffer, F.; Peter, B.; Alem, H.; Funfschilling, D.; Dumas, N.; Serra, C.; Roques-Carmes, T. Polyelectrolytes layer-by-layer surface modification of PDMS microchips for the production of simple O/W and double W/O/W emulsions: From global to localized treatment. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2019, 146, 107685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khadem, B.; Sheibat-Othman, N. Modeling droplets swelling and escape in double emulsions using population balance equations. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 382, 122824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, B.; Khellaf, M.; Sheibat-Othman, N. Investigating Swelling-Breakdown in Double Emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 585, 124181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Muñoz, N.; Alcalá-Alcalá, S.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. Preparation of Polymer Nanoparticles by the Emulsification-Solvent Evaporation Method: From Vanderhoff’s Pioneer Approach to Recent Adaptations. In Polymer Nanoparticles for Nanomedicines; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 87–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Peng, Z.; She, F.H.; Kong, L.X. Microencapsulation of Nanoparticles with Enhanced Drug Loading for pH-Sensitive Oral Drug Delivery for the Treatment of Colon Cancer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosca, I.D.; Watari, F.; Uo, M. Microparticle formation and its mechanism in single and double emulsion solvent evaporation. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppimath, K.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Rudzinski, W.E. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J. Control. Release 2001, 70, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, E.; Fattal, E.; Paris, J.; Ringard, C.; Rosilio, V.; Tsapis, N. Surfactant dependent morphology of polymeric capsules of perfluorooctyl bromide: Influence of polymer adsorption at the dichloromethane–water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 326, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.-I.; Cho, C.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Ko, K.-S.; Kim, S.-I.; Shim, Y.-H.; Nah, J.-W. Preparation of poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles without surfactant. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 2228–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, R.H.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D. Recent Advances in the Emulsion Solvent Evaporation Technique for the Preparation of Nanoparticles and Nanocapsules. In Hierarchical Macromolecular Structures: 60 Years after the Staudinger Nobel Prize II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, R.; Wagh, P.; Naik, J. Solvent evaporation and spray drying technique for micro- and nanospheres/particles preparation: A review. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 1758–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musyanovych, A.; Schmitz-Wienke, J.; Mailänder, V.; Walther, P.; Landfester, K. Preparation of Biodegradable Polymer Nanoparticles by Miniemulsion Technique and Their Cell Interactions. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhian, A.; Siegel, S.J.; Winey, K.I. Haloperidol-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: Systematic study of particle size and drug content. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 336, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilati, U.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E. Sonication Parameters for the Preparation of Biodegradable Nanocapsules of Controlled Size by the Double Emulsion Method. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2003, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardes, R.M.; Evangelista, R.C. Praziquantel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: Preparation and characterization. J. Microencapsul. 2005, 22, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potineni, A.; Lynn, D.M.; Langer, R.; Amiji, M.M. Poly (Ethylene Oxide)-Modified Poly (β-amino ester) Nanoparticles as A pH-Sensitive Biodegradable System for Paclitaxel Delivery. J. Control. Release 2003, 86, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıçay, E.; Demirbilek, M.; Türk, M.; Güven, E.; Hazer, B.; Denkbas, E.B. Preparation and characterization of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) (PHBHHX) based nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Valour, J.-P.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Preparation of biodegradable PCL particles via double emulsion evaporation method using ultrasound technique. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 293, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L. Folate-decorated Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyoctanoate) Nanoparticles for Targeting Delivery: Optimization and In Vivo Antitumor Activity. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.-Y.; Li, M.; Zhu, X.-L.; Fan, F.; Wang, L.-L.; Ma, J.-G. Microbial synthesized biodegradable PHBHHxPEG hybrid copolymer as an efficient intracellular delivery nanocarrier for kinase inhibitor. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, M.; Ullah, N.; Choi, M.H.; Kim, M.O.; Yoon, S.C. Amorphous Amphiphilic P(3HV-co-4HB)-b-mPEG Block Copolymer Synthesized from Bacterial Copolyester Via Melt Transesterification: Nanoparticle Preparation, Cisplatin-Loading for Cancer Therapy and In Vitro Evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilicay, E.; Karahaliloglu, Z.; Hazer, B.; Tekin, I.; Denkbas, E.B. Concanavaline A conjugated bacterial polyester-based PHBHHx nanoparticles loaded with curcumin for breast cancer therapy. J. Microencapsul. 2016, 33, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, F.; Chen, P.; Yasin, T.; Fatima, N.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A. Encapsulation of Ellipticine in poly-(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) based nanoparticles and its in vitro application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Ullah, N.; Choi, M.H.; Yoon, S.C. Nanoscale Poly(4-Hydroxybutyrate)-mPEG Carriers for Anticancer Drugs Delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 8416–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben David-Naim, M.; Grad, E.; Aizik, G.; Nordling-David, M.M.; Moshel, O.; Granot, Z.; Golomb, G. Polymeric nanoparticles of siRNA prepared by a double-emulsion solvent-diffusion technique: Physicochemical properties, toxicity, biodistribution and efficacy in a mammary carcinoma mice model. Biomaterials 2017, 145, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, S.; Boyd, B.J.; McIntosh, M.P.; Pouton, C.W.; Kaminskas, L.M.; Whittaker, M. Suggested Procedures for The Reproducible Synthesis of Poly(d,l-Lactide-co-Glycolide) Nanoparticles using The Emulsification Solvent Diffusion Platform. Curr. Nanosci. 2018, 14, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baena-Aristizábal, C.M.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A.; Mora-Huertas, C.E. Biodegradable microparticles preparation by double emulsification—Solvent extraction method: A Systematic study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 492, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Sugihara, H.; Nishiura, A.; Kadota, K.; Tozuka, Y.; Takeuchi, H. Appropriate Selection of An Aggregation Inhibitor of Fine Particles Used for Inhalation Prepared by Emulsion Solvent Diffusion. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Allémann, E.; Doelker, E.; Fessi, H. A mechanistic study of the formation of polymer nanoparticles by the emulsification-diffusion technique. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1997, 275, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohanraj, V.; Chen, Y. Nanoparticles-A Review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2006, 5, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagavarma, B.; Yadav, H.K.; Ayaz, A.; Vasudha, L.; Shivakumar, H. Different Techniques for Preparation of Polymeric Nanoparticles-A Review. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2012, 5, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, C.; Sanchez, A.; Putnam, D.; Ting, D.; Langer, R.; Alonso, M. Poly(lactic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol) nanoparticles as new carriers for the delivery of plasmid DNA. J. Control. Release 2001, 75, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Feng, P.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y. An improved interfacial coacervation technique to fabricate biodegradable nanocapsules of an aqueous peptide solution from polylactide and its block copolymers with poly(ethylene glycol). Colloid Polym. Sci. 2001, 279, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassou, M. Modélisation et Simulation de la Formation des Nanocapsules Polymériques Par la Méthode D’émulsion-Diffusion. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Claude Bernard-Lyon I, Villeurbanne, France, 2007. Available online: https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00264755v2/document (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Moinard-Chécot, D.; Chevalier, Y.; Briancon, S.; Beney, L.; Fessi, H. Mechanism of nanocapsules formation by the emulsion–diffusion process. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 317, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramual, S.; Assavanig, A.; Bergkvist, M.; Batt, C.A.; Sunintaboon, P.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Svasti, J.; Niamsiri, N. Development and characterization of bio-derived polyhydroxyalkanoate nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic photodynamic therapy agents. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-Y.; Ciraolo, E.; Stefenia, R.; Chen, G.-Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hirsch, E. Sustained release of PI3K inhibitor from PHA nanoparticles and in vitro growth inhibition of cancer cell lines. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, W.; Wang, D.-T.; Chen, C.-L.; Zhuang, Q.-Y.; Kong, X.-D. A modified spontaneous emulsification solvent diffusion method for the preparation of curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles with enhanced in vitro anti-tumor activity. Front. Mater. Sci. 2014, 8, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinebretière, S.; Briancon, S.; Lieto, J.; Mayer, C.; Fessi, H. Study of the emulsion-diffusion of solvent: Preparation and characterization of nanocapsules. Drug Dev. Res. 2002, 57, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimaille, T.; Pichot, C.; Fessi, H.; Delair, T. Poly(d,l-lactic acid) nanoparticle preparation and colloidal characterization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2003, 281, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surassmo, S.; Min, S.-G.; Bejrapha, P.; Choi, M.-J. Effects of surfactants on the physical properties of capsicum oleoresin-loaded nanocapsules formulated through the emulsion–diffusion method. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahana, D.; Mittal, G.; Bhardwaj, V.; Kumar, M. PLGA Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery of Hydrophobic Drugs: Influence of Organic Solvent on Nanoparticle Formation and Release Behavior In Vitro and In Vivo Using Estradiol as a Model Drug. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 1530–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Swarnakar, N.K.; Godugu, C.; Singh, R.; Jain, S. The effect of the oral administration of polymeric nanoparticles on the efficacy and toxicity of tamoxifen. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.C.; Ferreira, P.; Cordeiro, R.A.; Mendonça, P.V.; Góis, J.R.; Gil, M.H.; Coelho, J.F.J. Drug Delivery Systems for Predictive Medicine: Polymers as Tools for Advanced Applications. In New Strategies to Advance Pre/Diabetes Care: Integrative Approach by PPPM; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 399–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiong, X. Salting-Out Assisted Liquid–Liquid Extraction (SALLE) in LC-MS Bioanalysis. In Sample Preparation in LC-MS Bioanalysis; Li, W., Jian, W., Fu, Y., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Chapter 5; pp. 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Bose, R.; Kumar, A.; Mozumdar, S. Targeted Delivery of Pesticides Using Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Ma, L.; Sun, D.; Liu, L.; Qayum, A.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Purification of lactoperoxidase from bovine milk by integrating the technique of salting-out extraction with cation exchange chromatographic separation. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eley, J.G.; Pujari, V.D.; McLane, J. Poly (Lactide-co-Glycolide) Nanoparticles Containing Coumarin-6 for Suppository Delivery: In Vitro Release Profile and In Vivo Tissue Distribution. Drug Deliv. 2004, 11, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumezescu, A.M. Drug Targeting and Stimuli Sensitive Drug Delivery Systems; William Andrew: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Niknafs, M.; Kaviani, R.; Gharekhani, A.; Jouyban, A.; Shayanfar, A. Salting-out liquid–liquid microextraction to the determination of mycophenolic acid in plasma samples. Chem. Pap. 2019, 74, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, M.; Shivanna, D.K.; Kamate, M.; AB, V.; Tp, K.-V. Single Lysis-Salting Out Method of Genomic DNA Extraction From Dried Blood Spots. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2016, 30, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujii, T.; Kawasaki, S.-I. Salting-out effects on vanillin extraction by supercritical carbon dioxide from aqueous vanillin solution containing salts. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 152, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.F.; Wang, Y.N.; Ma, J.B. Preparation of insulin nanoparticles and their encapsulation with biodegradable polyelectrolytes via the layer-by-layer adsorption. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 324, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeghere, F.; Allémann, E.; Feijen, J.; Kissel, T.; Doelker, E.; Gurny, R. Cellular Uptake of PEO Surface-Modified Nanoparticles: Evaluation of Nanoparticles Made of PLA: PEO Diblock and Triblock Copolymers. J. Drug Target. 2000, 8, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.; Hamid, Z.A. Polymer Nanoparticle Carriers in Drug Delivery Systems: Research Trend. In Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 10; pp. 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Mody, N.; Sharma, R.; Agrawal, U.; Vyas, S.P. Nanobiomaterials: Novel Nanoplatforms for Protein and Peptide Delivery. In Nanobiomaterials in Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Chapter 4; pp. 111–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Grijpma, D.W.; Feijen, J. Poly(trimethylene carbonate) and monomethoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(trimethylene carbonate) nanoparticles for the controlled release of dexamethasone. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Rodriguez, S.; Allémann, E.; Fessi, H.; Doelker, E. Physicochemical Parameters Associated with Nanoparticle Formation in the Salting-Out, Emulsification-Diffusion, and Nanoprecipitation Methods. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnasailaja, A.; Sarithareddy, A.; Abbaraju, K.; Aenugu, S. Preparation and Characterisation of Sulfasalazine Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles by Salting Out Technique. J. Bionanosci. 2017, 11, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Bi, Y.; Cai, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Hou, S. PLGA nanoparticles simultaneously loaded with vincristine sulfate and verapamil hydrochloride: Systematic study of particle size and drug entrapment efficiency. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 350, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konan, Y.N.; Gurny, R.; Allémann, E. Preparation and characterization of sterile and freeze-dried sub-200 nm nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 233, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, A.S.; Sailaja, A.K. Preparation and Characterization of Paracetamol Loaded Eudragit S100 Nanoparticles by Salting Out Technique. J. Dev. Drugs 2018, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweers, M.L.; Engbers, G.H.; Grijpma, D.W.; Feijen, J. Release of anti-restenosis drugs from poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(dl-lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweers, M.L.; Engbers, G.H.; Grijpma, D.W.; Feijen, J. In vitro degradation of nanoparticles prepared from polymers based on dl-lactide, glycolide and poly(ethylene oxide). J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.A.; Allémann, E.; Schwach, G.; Doelker, E.; Gurny, R. Synthesis of A Novel Fluorescent Poly (D, L-Lactide) End-Capped with 1-Pyrenebutanol Used for The Preparation of Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 20, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, C. Emulsion polymerization mechanisms and kinetics. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 443–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, G.; Rajagopalan, M.D.; Valluru, R.; Sridhar, K.A. Nanoparticles: A Novel Approach to Target Tumors. In Nano-and Microscale Drug Delivery Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Chapter 7; pp. 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. An Overview of Pickering Emulsions: Solid-Particle Materials, Classification, Morphology, and Applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerra, F.E.B. Emulsion Polymerization of Superhydrophobic Monomers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Basque Country, Donostia-San Sebastian, Spain, 2017. Available online: https://addi.ehu.es/bitstream/handle/10810/24229/TESIS_BOSCAN_GUERRA_FREDDY%20ENRIQUE.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Khan, M.U.; Reddy, K.R.; Snguanwongchai, T.; Haque, E.; Gomes, V.G. Polymer brush synthesis on surface modified carbon nanotubes via in situ emulsion polymerization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharieh, A.; Khoee, S.; Mahdavian, A.R. Emulsion and miniemulsion techniques in preparation of polymer nanoparticles with versatile characteristics. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 269, 152–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Bonilla, A.; van Herk, A.M.; Heuts, J.P. Preparation of Hairy Particles and Antifouling Films using Brush-Type Amphiphilic Block Copolymer Surfactants in Emulsion Polymerization. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2721–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay-Jimenez, J.C.; Gergeres, D.; Young, A.; Lim, D.V.; Turos, E. Physical properties and biological activity of poly(butyl acrylate–styrene) nanoparticle emulsions prepared with conventional and polymerizable surfactants. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009, 5, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.; Qu, R.; Forcada, J. Preparation of magnetic polymeric composite nanoparticles by seeded emulsion polymerization. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 770–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, C. Modified Structural Model for Predicting Particle Size in the Microemulsion and Emulsion Polymerization of Styrene under Microwave Irradiation. Langmuir 2004, 21, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Santos, A.; Fortuny, M.; Araújo, P.; Sayer, C. Kinetic advantages of using microwaves in the emulsion polymerization of MMA. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; He, Y. Ultrasonically irradiated emulsion polymerization of styrene in the presence of a polymeric surfactant. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-J.; Chun, H.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, N. Preparation of poly(N-vinylcarbazole) (PVK) nanoparticles by emulsion polymerization and PVK hollow particles. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeat-Lami, E.; França, A.J.P.G.; Chaparro, T.C.; Silva, R.D.; Dugas, P.-Y.; Alves, G.M.; Santos, A.M. Synthesis of Polymer/Silica Hybrid Latexes by Surfactant-Free RAFT-Mediated Emulsion Polymerization. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4431–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errezma, M.; Ben Mabrouk, A.; Magnin, A.; Dufresne, A.; Boufi, S. Surfactant-free emulsion Pickering polymerization stabilized by aldehyde-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias-Cepeda, L.; Herrera-Ordonez, J.; Estevez, M.; Luna-Barcenas, G.; Rosales-Marines, L. New Insights on surfactant-free styrene emulsion polymerization in The presence of sodium styrene sulfonate. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N.; Sengel, S.B. Surfactant Free Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(Vinyl Carbazole) Microgel and its Chemical Modifications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 514, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.J.; Park, I.J.; Lee, S.G.; Ha, J.-W.; Lee, S.-B.; Sohn, E.-H. Surfactant-free preparation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanoparticle dispersions and their use as surface coating agents. Green Chem. 2017, 20, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, S.; Zahari, S.B.; Tahrin, R.A.A.; Harun, N.A. Co-polymerization of methyl methacrylate and styrene via surfactant-free emulsion polymerization, as a potential material for photonic crystal application. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1885, 20018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Thomas, H.; Zhu, X.; Möller, M. Inclusion of Phase-Change Materials in Submicron Silica Capsules Using a Surfactant-Free Emulsion Approach. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10397–10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Tang, W.; Hawker, C.J.; Stucky, G.D. One-Step Microwave Preparation of Well-Defined and Functionalized Polymeric Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15054–15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, T.; Don, T. Synthesis and characterization of poly(methyl methacrylate) nanoparticles by emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization with a redox-initiated system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 3622–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.F.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, C.A. Synthesis and electrorheological response of nano-sized laponite stabilized poly(methyl methacrylate) spheres. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camli, S.T.; Buyukserin, F.; Balci, O.; Budak, G.G. Size controlled synthesis of sub-100nm monodisperse poly(methylmethacrylate) nanoparticles using surfactant-free emulsion polymerization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 344, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhong, S.; Wang, H. Emulsifier-free core–shell polyacrylate latex nanoparticles containing fluorine and silicon in shell. Polymer 2007, 48, 7241–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridi-Majidi, R.; Sharifi-Sanjani, N. Emulsifier-free miniemulsion polymerization of styrene and the investigation of encapsulation of nanoparticles with polystyrene via this procedure using an anionic initiator. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, N.; Bereli, N.; Akgöl, S.; Denizli, A. High capacity binding of antibodies by poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 67, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, S.J.; Jung, Y.J.; Kim, J.H. Fabrication of nano-structured polythiophene nanoparticles in aqueous dispersion. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2008, 8, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, H.; Ziener, U.; Landfester, K. Formation of Polyimide Nanoparticles in Heterophase with an Ionic Liquid as Continuous Phase. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 7846–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Cho, H.G.; Park, C.R. Fabrication of Unagglomerated Polypyrrole Nanospheres with Controlled Sizes From a Surfactant-Free Emulsion System. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9030–9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, J.; Brett, C.J.; Körstgens, V.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Ohm, W.; Malmström, E.; Roth, S.V. Core–Shell Nanoparticle Interface and Wetting Properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzior, S.A.; Marway, H.S.; Cranston, E.D. Tailoring Cellulose Nanocrystal and Surfactant Behavior in Miniemulsion Polymerization. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 2645–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauman, N.; Zaquen, N.; Junkers, T.; Boyer, C.; Zetterlund, P.B. Particle Size Control in Miniemulsion Polymerization via Membrane Emulsification. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 4492–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.S.J.; Negrell, C.; Ladmiral, V.; Lai-Kee-Him, J.; Bron, P.; Lacroix-Desmazes, P.; Joly-Duhamel, C.; Caillol, S. Cardanol-based polymer latex by radical aqueous miniemulsion polymerization. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2468–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Smith, K.W. Miniemulsion Polymerization to Prepare Drag Reducers. US20110184121A1, 24 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Landfester, K.; Antonietti, M. The polymerization of acrylonitrile in miniemulsions: “Crumpled latex particles” or polymer nanocrystals. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landfester, K.; Willert, M.; Antonietti, M. Preparation of Polymer Particles in Nonaqueous Direct and Inverse Miniemulsions. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 2370–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, C.-S.; Sheu, J.-C. Effects of carboxylic monomers on the styrene miniemulsion polymerizations stabilized by SDS/alkyl methacrylates. Polymer 2001, 42, 2349–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.L.; Gallardo, V.; Gómez-Lopera, S.A.; Plaza, R.; Delgado, A. Synthesis and characterization of poly(ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles with a magnetic core. J. Control. Release 2001, 77, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, H.T.; Choi, Y.S.; Chee, M.G.; Chung, I.J. Singlewall carbon nanotubes covered with polystyrene nanoparticles byin-situ miniemulsion polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 44, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.; Landfester, K.; Musyanovych, A. Synthesis of phosphonate-functionalized polystyrene and poly(methyl methacrylate) particles and their kinetic behavior in miniemulsion polymerization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Herk, A.; Forcada, J.; Pastorin, G. Synthetic Strategies for Synthesis of Polymer Nanoparticles. In Controlled Release Systems; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Chapter 5; pp. 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzio, R.A.; Marcato, Y.L.; Gomez, M.L.; Waiman, C.V.; Chesta, C.A.; Palacios, R.E. Crosslinked polymer nanoparticles containing single conjugated polymer chains. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2017, 5, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayempour, S.; Montazer, M. A modified microemulsion method for fabrication of hydrogel Tragacanth nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cankaya, N. Recent Research in Polymerization; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, J.E.; Rabelero, M. Semicontinuous Microemulsion Polymerization. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 25, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candau, F.; Anquetil, J.-Y. New Developments in Polymerization in Bicontinuous Microemulsions. In Micelles, Microemulsions, and Monolayers; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2018; pp. 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarov, Y.; Capek, I. Kinetic events of (micro)emulsion polymerization of styrene. Polym. Bull. 2019, 77, 4851–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Ramírez, L.G.; Nuño-Donlucas, S.M.; Cesteros, L.C.; Katime, I. Novel Functionalized Nanohydrogels, Synthesis and Some Applications. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. IOP Publ. 2008, 127, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, N.; Zaragoza, E.A.; Lopez, R.G.; Peralta, R.D.; Katime, I.; Becerra, F.; Mendizabal, E.; Puig, J.E. Unusual Free Radical Polymerization of Vinyl Acetate in Anionic Microemulsion Media. Langmuir 2000, 16, 3612–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrère, M.; da Silva, S.C.; Balic, R.; Ganachaud, F. Synthesis of Monodisperse Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Micro- and Macroemulsions. Langmuir 2001, 18, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, K.D.; Kaler, E.W. Kinetics and Mechanism of the Multiple Addition Microemulsion Polymerization of Hexyl Methacrylate. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-J.; Chen, F. Semi-Continuous Emulsion Copolymerization of Butyl Methacrylate with Polymerizable Anionic Surfactants. Polymer 2004, 45, 4801–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Oh, J.H.; Stucky, G.D. Fabrication of Ultrafine Conducting Polymer and Graphite Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 4016–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.G.; López, R.G.; Tauer, K. Studies on Semibatch Microemulsion Polymerization of Butyl Acrylate: Influence of the Potassium Peroxodisulfate Concentration. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2738–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Murphy, M.; Li, C.; Ting, K.; Soo, C.; Zheng, Z. Current development of biodegradable polymeric materials for biomedical applications. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 3117–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, P.Q.; Courchesne, N.M.D.; Duraj-Thatte, A.; Praveschotinunt, P.; Joshi, N.S. Engineered Living Materials: Prospects and Challenges for Using Biological Systems to Direct the Assembly of Smart Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, S. Biological nanoparticles and their influence on organisms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 28, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertici, G. Introduction to Bioresorbable Polymers for Biomedical Applications. In Bioresorbable polymers for Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Chapter 1; pp. 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroe, A.; Chek, M.F.; Hakoshima, T.; Sudesh, K.; Taguchi, S. Synthesis of Polyesters III: Acyltransferase as Catalyst. In Enzymatic Polymerization towards Green Polymer Chemistry; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 199–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, N.-A.A.; Ng, L.-M.; Foong, C.P.; Tai, Y.T.; Nanthini, J.; Sudesh, K. Complete Genome Sequence of a Novel Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Producer, Jeongeupia sp. USM3 (JCM 19920) and Characterization of Its PHA Synthases. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourmentza, C.; Plácido, J.; Venetsaneas, N.; Burniol-Figols, A.; Varrone, C.; Gavala, H.N.; Reis, M.A.M. Recent Advances and Challenges towards Sustainable Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Production. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mukheem, A.; Hossain, M.; Shahabuddin, S.; Muthoosamy, K.; Manickam, S.; Sudesh, K.; Saidur, R.; Sridewi, N.; Campus, N.M. Bioplastic Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Recent Advances in Modification and Medical Applications. arXiv 2018, arXiv:10.20944/preprints201808.0271.v1. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/ppr/ppr48118 (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Chek, M.F.; Hiroe, A.; Hakoshima, T.; Sudesh, K.; Taguchi, S. PHA synthase (PhaC): Interpreting the functions of bioplastic-producing enzyme from a structural perspective. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 103, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro, B.; Sanz, J.M. Polyhydroxyalkanoate-Associated Phasins as Phylogenetically Heterogeneous, Multipurpose Proteins. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokamura, A.; Fujino, K.; Isoda, Y.; Arizono, K.; Shiratsuchi, H.; Matsusaki, H. Characterization and identification of the proteins bound to two types of polyhydroxyalkanoate granules in Pseudomonas sp. 61-3. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinjaski, N.; Prieto, M.A. Smart polyhydroxyalkanoate nanobeads by protein based functionalization. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Carmona, E.; Villaverde, A. Nanostructured bacterial materials for innovative medicines. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M.J.M. Biodegradable and Biocompatible Polyhydroxy-alkanoates (PHA): Auspicious Microbial Macromolecules for Pharmaceutical and Therapeutic Applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prakash, P.; Lee, W.-H.; Loo, C.-Y.; Wong, H.S.J.; Parumasivam, T. Advances in Polyhydroxyalkanoate Nanocarriers for Effective Drug Delivery: An Overview and Challenges. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.F.; Martin, D.P. Applications of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) in Medicine and Pharmacy. Biopolym 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-C.; Zhan, X.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Zou, X.-H.; Wang, Z.-H.; Xiong, Y.-C.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.-Q. A specific drug targeting system based on polyhydroxyalkanoate granule binding protein PhaP fused with targeted cell ligands. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4823–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errico, C.; Bartoli, C.; Chiellini, F.; Chiellini, E. Poly(hydroxyalkanoates)-Based Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishatskaya, E.I.; Goreva, A.V.; Voinova, O.N.; Inzhevatkin, E.V.; Khlebopros, R.G.; Volova, T.G. Evaluation of antitumor activity of rubomycin deposited in absorbable polymeric microparticles. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 145, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z. Folate-mediated poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyoctanoate) nanoparticles for targeting drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 76, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursel, I.; Yagmurlu, F.; Korkusuz, F.; Hasirci, V. In vitro antibiotic release from poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) rods. J. Microencapsul. 2002, 19, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Azghani, A.O.; Omri, A. Antimicrobial efficacy of a new antibiotic-loaded poly(hydroxybutyric-co-hydroxyvaleric acid) controlled release system. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Itoh, Y.; Hosaka, Y.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakano, Y.; Maeda, I.; Umeda, F.; Yamakawa, J.; Nishimine, M.; Suenobu, T. Mechanism of Enhancement Effect of Dendrimer on Transdermal Drug Permeation Through Polyhydroxyalkanoate Matrix. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 96, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Method | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dispersion of preformed polymers | |||
| nanoprecipitation | Requires low energy Reproducible Single step Scalability | Size of NPs can be affected by stirring rate Low efficiency of drug encapsulation | [78,79] |
| emulsification solvent evaporation | Scalability Single step emulsion for hydrophobic agents Double or multiple step emulsion for hydrophilic agents | Requires heating or vacuum for evaporation Residual solvent or stabilizer Not stable | [80,81] |
| emulsification solvent diffusion | Does not require homogenizer High reproducibility Easy to scale up | Uses high volumes of water Probable leakage of water-soluble drugs into external phase Lower efficiency in lipophilic drug encapsulation | [82,83] |
| salting out | Does not require heating Avoids chlorinated solvents Suitable for DNA, RNA, and proteins | Requires high speed homogenization Exclusive for the encapsulation of lipophilic drugs Time-consuming Limited scalability | [84,85] |
| Direct polymerization | |||
| emulsion | Produce polymers with high molar mass Uses water as dispersion medium Excellent heat dissipation | Requires removal of surfactant Time consuming High cost | [86,87] |
| surfactant-free emulsion | Does not require surfactant Simple and green process Uses water-soluble initiators | Requires the preparation of monodisperse and uniformly distributed particle sizes | [88,89] |
| mini emulsion | Uses a low molecular mass co-stabilizer Small particle size Low volume of surfactant | Uses a high-shear device Surfactant is retained in the polymer | [90,91] |
| micro-emulsion | Uses water-soluble initiators Thermodynamically stable | Formation of empty micelles Destabilized microdroplets Increased particle size Requires a high ratio of surfactant | [92,93] |
| microbial | Non-toxic Eco-friendly Biocompatible | High production cost | [94,95] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pulingam, T.; Foroozandeh, P.; Chuah, J.-A.; Sudesh, K. Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030576
Pulingam T, Foroozandeh P, Chuah J-A, Sudesh K. Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(3):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030576
Chicago/Turabian StylePulingam, Thiruchelvi, Parisa Foroozandeh, Jo-Ann Chuah, and Kumar Sudesh. 2022. "Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 12, no. 3: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030576
APA StylePulingam, T., Foroozandeh, P., Chuah, J.-A., & Sudesh, K. (2022). Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 12(3), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030576






