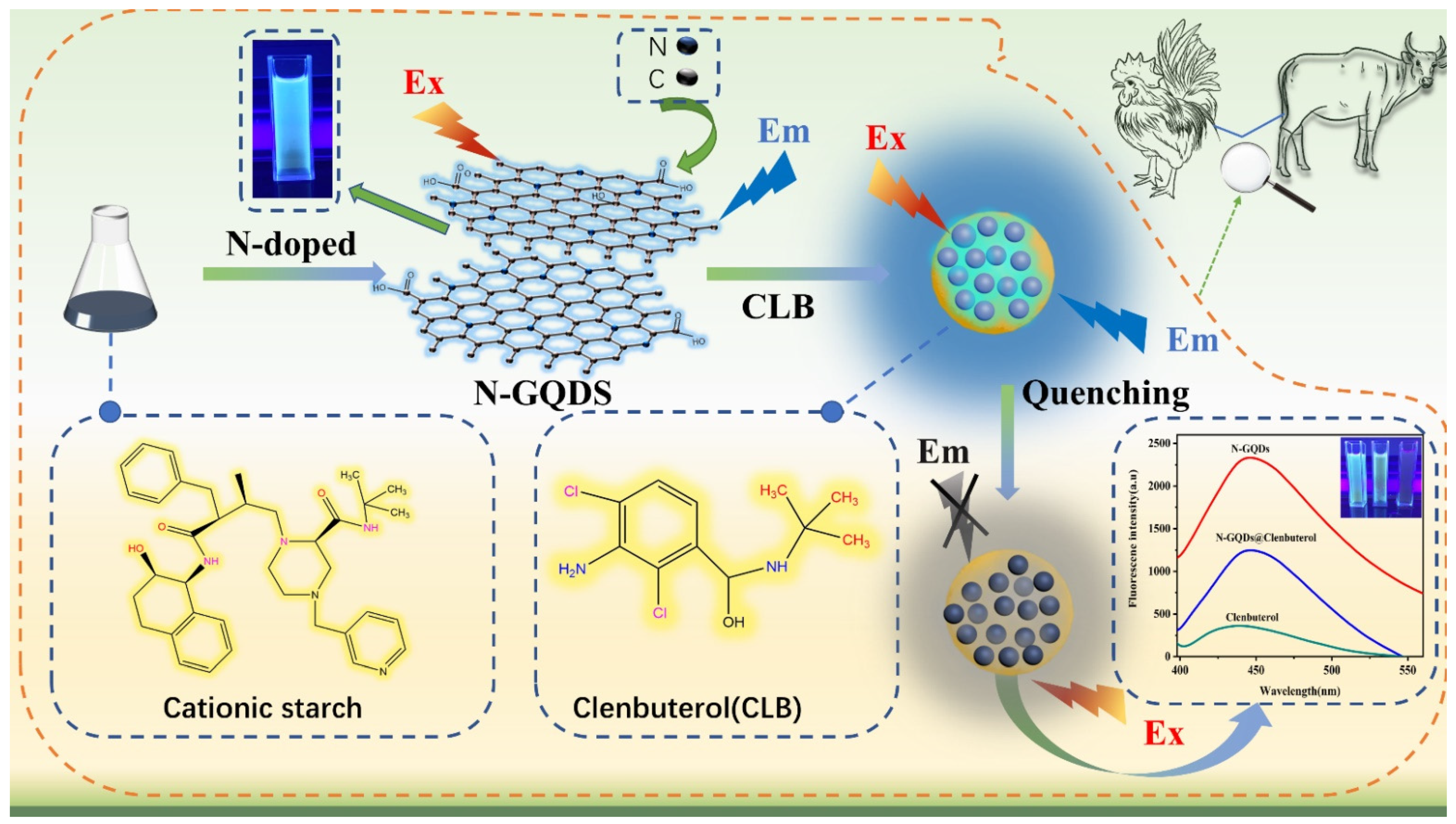
Sensitive and Selective Detection of Clenbuterol in Meat Samples by a Graphene Quantum Dot Fluorescent Probe Based on Cationic-Etherified Starch
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Preparation of N-GQDs and GQDs
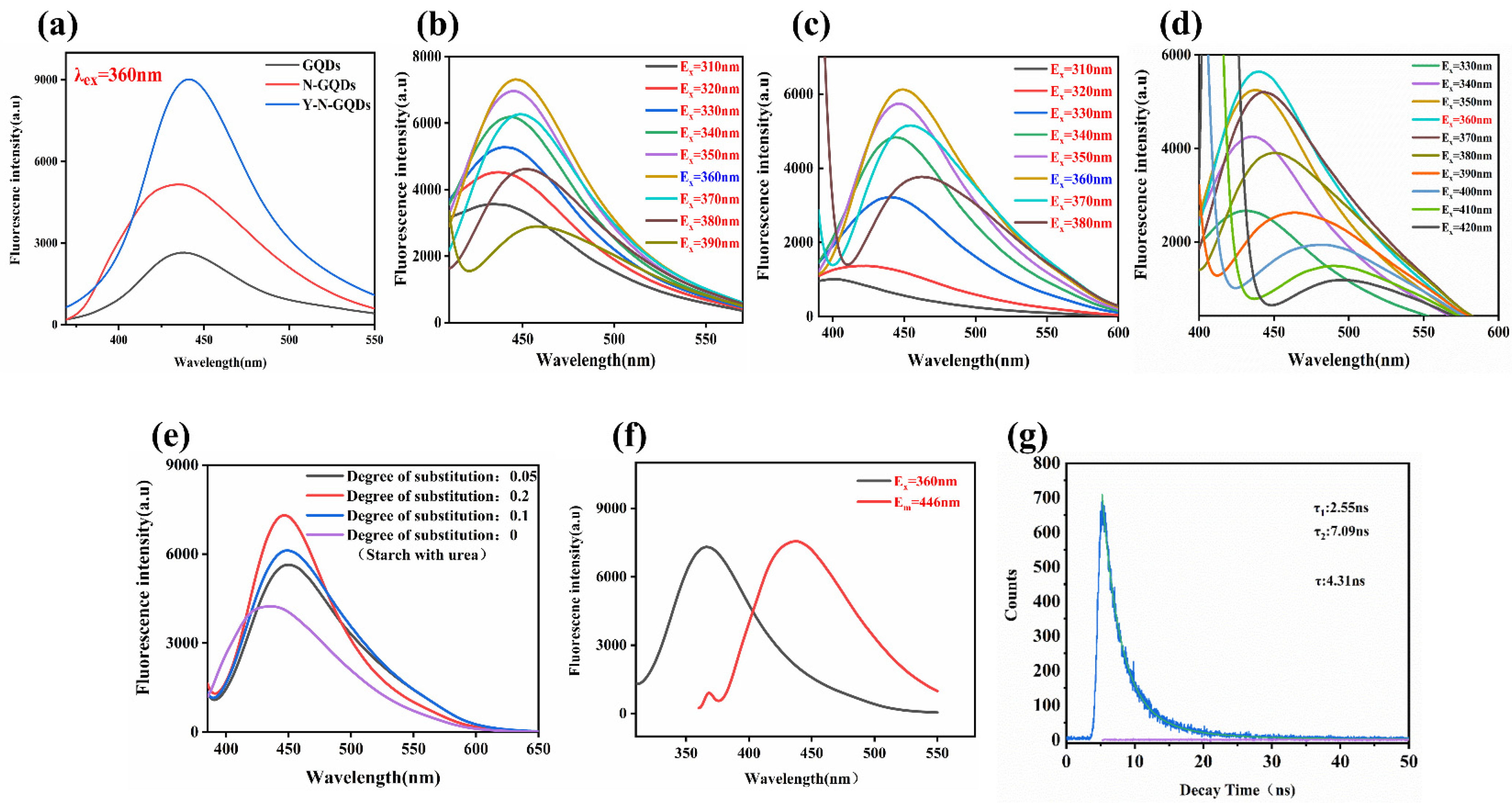
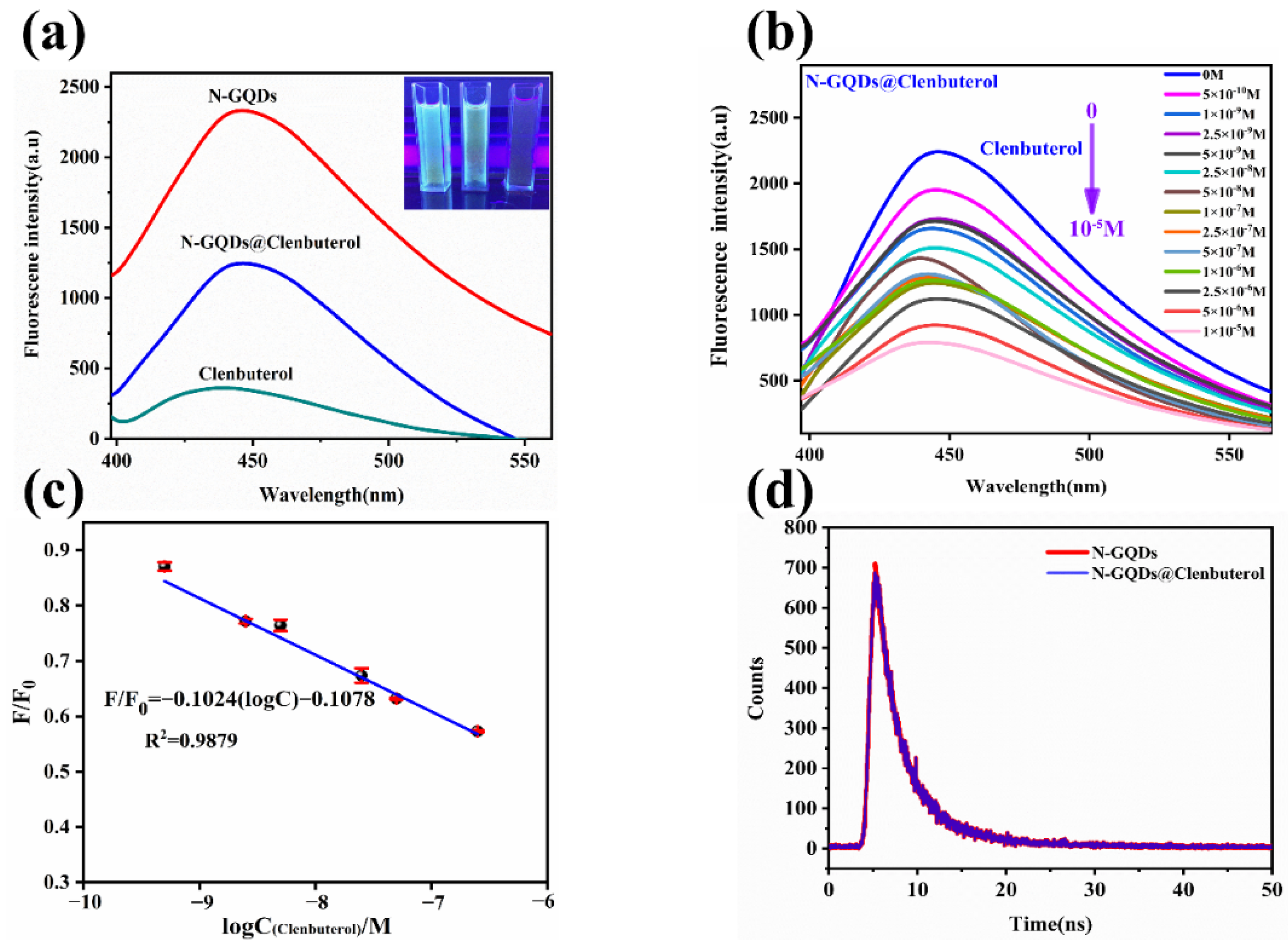
2.4. Calculation of Fluorescence Lifetime
2.5. Detection of CLB
2.6. Selective Assessment of CLB by Fluorescent Probes of N-GQDs
2.7. Determination of CLB in Real Samples
3. Results and Discussion
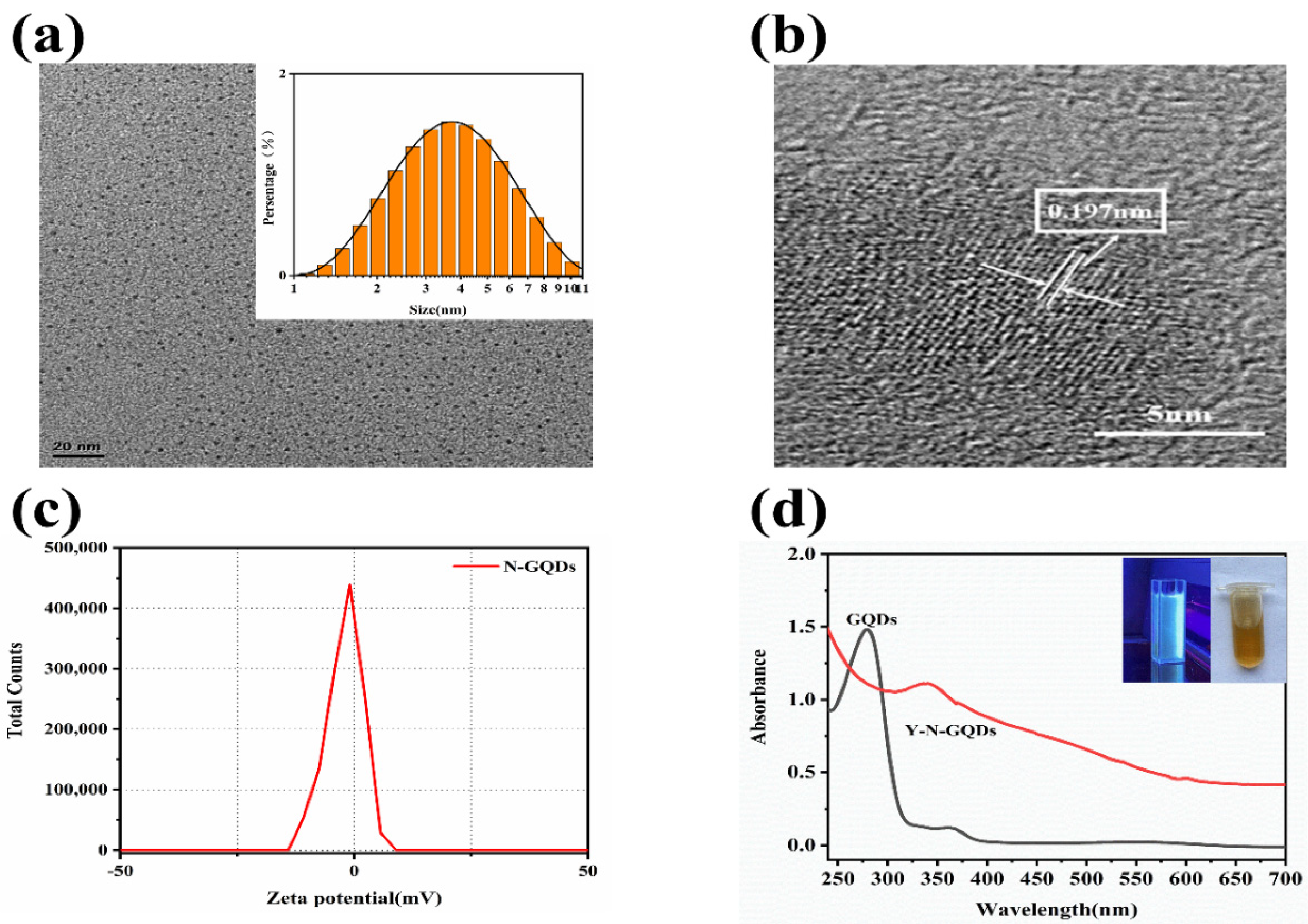
3.1. Characterization of N-GQDs
3.2. Fluorescence Spectroscopy of N-GQDs
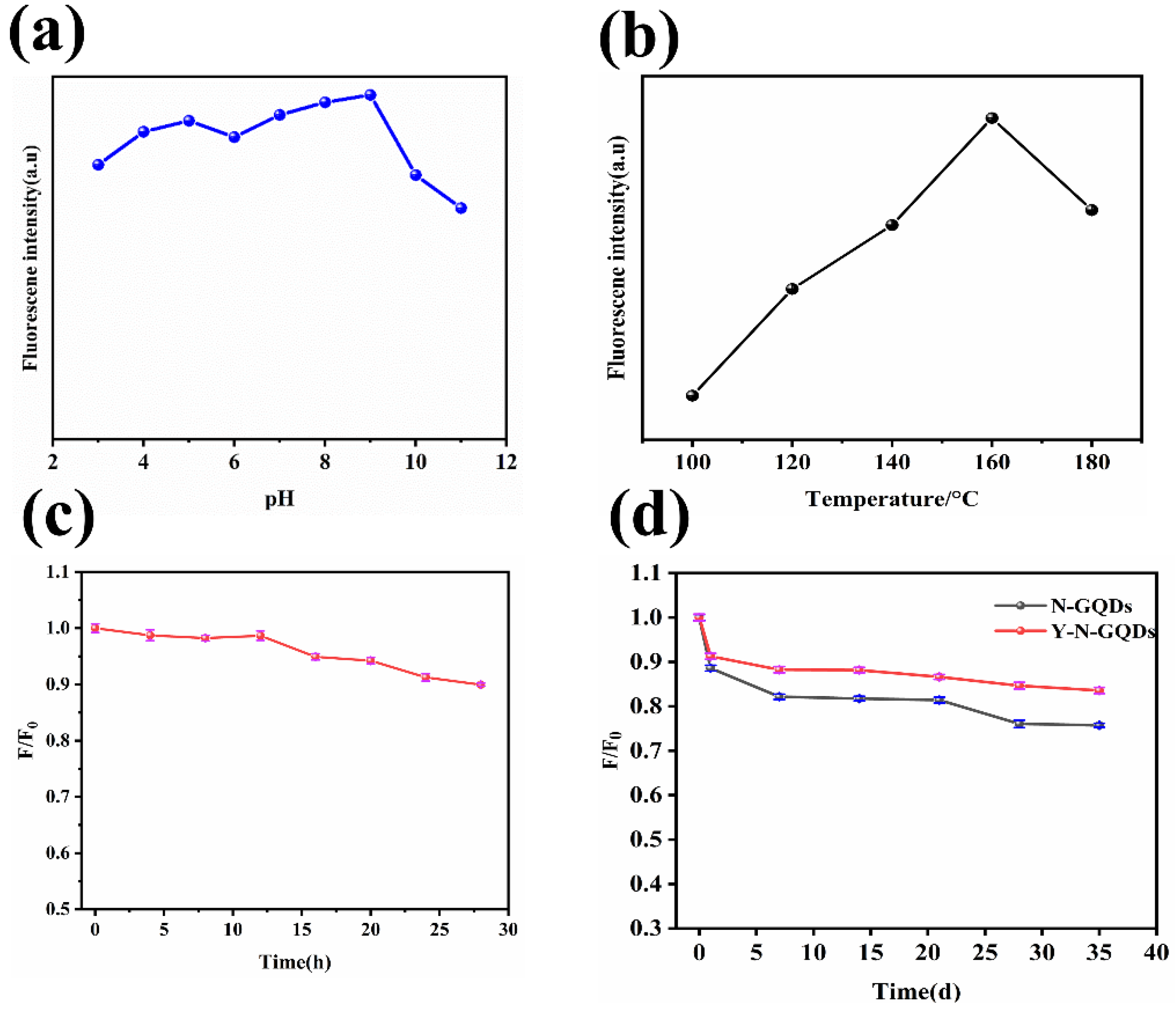
3.3. Effect of pH and Temperature on the Fluorescence Intensity of N-GQDs
3.4. Fluorescence Response of N-GQDs to CLB
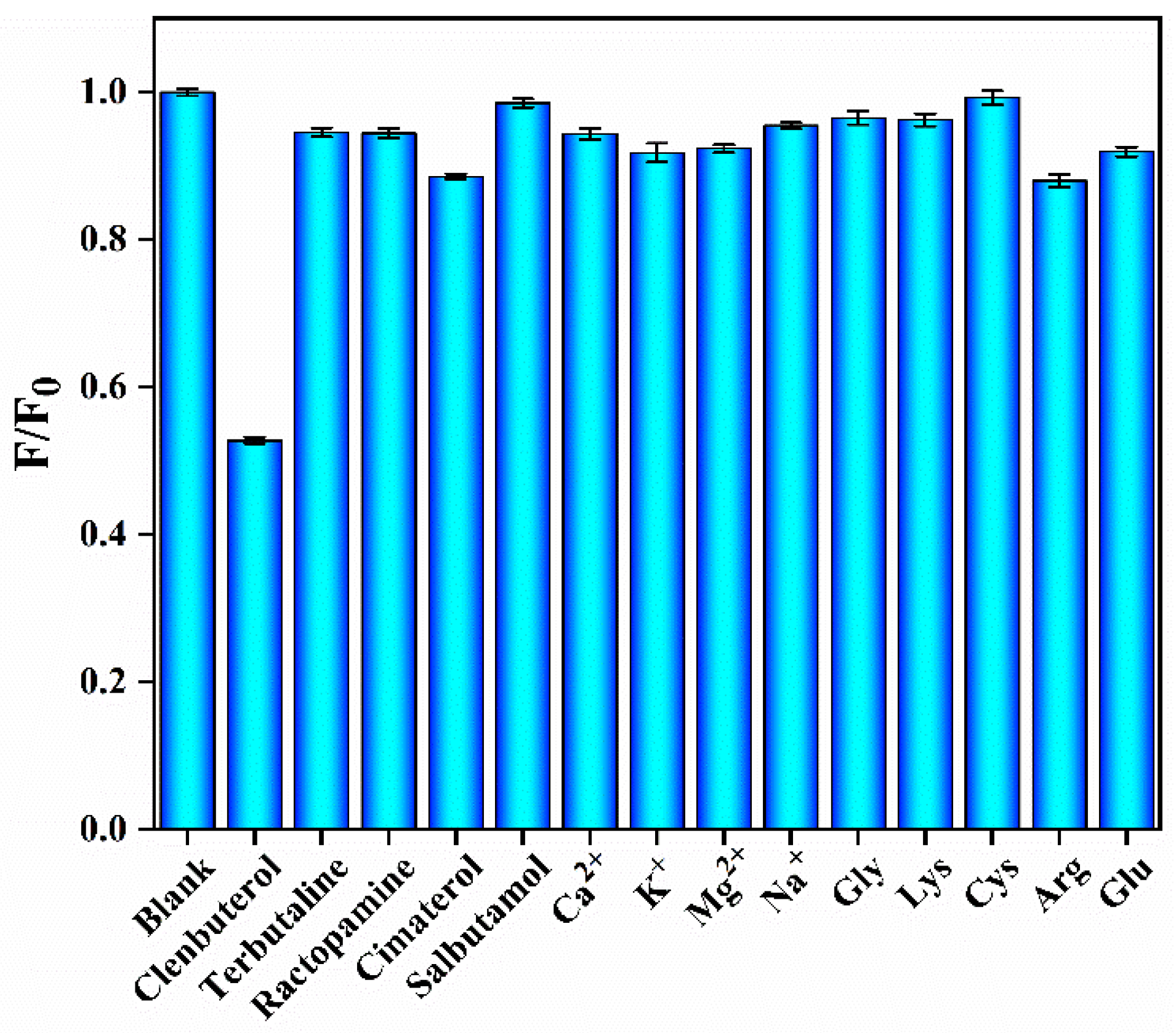
3.5. Assay Selectivity
3.6. Detection for CLB Content in Real Samples
3.7. Potential Quenching Mechanism Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, X.; Pan, W.; Chen, M.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, L. The fabrication of a thiol-modified chitosan magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite and its adsorption performance towards the illegal drug clenbuterol in pork samples. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 6097–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, F.; Du, J. Rapid screening of clenbuterol hydrochloride in chicken samples by molecularly imprinted matrix solid-phase dispersion coupled with liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 923, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Du, B.; Ma, H.; Wu, D.; Wei, Q. A silver–palladium alloy nanoparticle-based electrochemical biosensor for simultaneous detection of ractopamine, clenbuterol and salbutamol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Zhi, A.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Jia, G.; Shervin, J.; Tang, L.; Hu, X.; Deng, R.; Xu, C. Rapid and sensitive detection of β-agonists using a portable fluorescence biosensor based on fluorescent nanosilica and a lateral flow test strip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.-L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang-Fu, W.-G. Simultaneous determination of clenbuterol, salbutamol and ractopamine in milk by reversed-phase liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with isotope dilution. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7873–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posyniak, A.; Zmudzki, J.; Niedzielska, J. Screening procedures for clenbuterol residue determination in bovine urine and liver matrices using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 483, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Nilghaz, A.; Choi, J.R.; Liu, X.; Lu, X. Rapid detection of clenbuterol in milk using microfluidic paper-based ELISA. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, J.; Huangfu, W.-G.; Wu, Y.-L. Simultaneous determination of melamine and clenbuterol in animal feeds by GC–MS. Chromatographia 2010, 72, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Lorenzo, I.; Sánchez-Cortés, S.; García-Ramos, J.V. Adsorption of beta-adrenergic agonists used in sport doping on metal nanoparticles: A detection study based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14663–14670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zong, Y.; Guo, Q.; Xu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Yao, J. Magnetic separation of clenbuterol based on competitive immunoassay and evaluation by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 3388–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Jin, G.-P.; Chen, L.-L.; Li, Y.; Yu, B. Preparation of molecular imprinted film based on chitosan/nafion/nano-silver/poly quercetin for clenbuterol sensing. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Xi, C.; Xue, Q.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W.; Chen, Z. Cutting sp2 clusters in graphene sheets into colloidal graphene quantum dots with strong green fluorescence. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 3314–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, N.-J.; Chen, Y.-S.; Wu, C.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chan, Y.-H.; Chen, I.-W.P. One-pot synthesis of hydrophilic and hydrophobic n-doped graphene quantum dots via exfoliating and disintegrating graphite flakes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, B.; Yu, K.; Li, H.; Qi, R.; Zhang, Y.; Song, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, M. Coral-shaped MoS2 decorated with graphene quantum dots performing as a highly active electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3653–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Adsetts, J.R.; Nie, Y.; Sun, X.; Ding, Z. Electrochemiluminescence of nitrogen-and sulfur-doped graphene quantum dots. Carbon 2018, 129, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Li, J.; Wang, E. One-pot green synthesis of optically pH-sensitive carbon dots with upconversion luminescence. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5572–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Dai, L.; Li, L.-S. Nitrogen-doped colloidal graphene quantum dots and their size-dependent electrocatalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18932–18935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Kundu, S.; Roy, C.N.; Das, T.K.; Saha, A. Synthesis of excitation independent highly luminescent graphene quantum dots through perchloric acid oxidation. Langmuir 2017, 33, 14634–14642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Ji, J.; Fei, R.; Wang, C.Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J.R.; Jiang, L.P.; Zhu, J.J. A facile microwave avenue to electrochemiluminescent two-color graphene quantum dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wei, J.S.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Gao, Q.Y.; Xiong, H.M. Solvent-controlled synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots with a wide color gamut and narrowed emission peak widths. Small 2018, 14, 1800612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mo, Z.; Liu, N.; Guo, R.; Niu, X.; Zhao, P.; Yang, X. One-pot synthesis of highly fluorescent boron and nitrogen co-doped graphene quantum dots for the highly sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions in aqueous media. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 389, 112255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Peng, C.; Ali, I.; Liu, J. Fabrication and Characterization of Magnetic GQDs Using Green Tea Extract for Environmental Remediation. J. Mater. Appl. 2018, 7, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Akanda, M.R.; Park, B.-Y.; Kim, H.Y. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from carrot juice for in vitro cellular imaging. Carbon Lett. 2017, 21, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahu, S.; Behera, B.; Maiti, T.K.; Mohapatra, S. Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: Application as excellent bio-imaging agents. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8835–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahesh, S.; Lekshmi, C.L.; Renuka, K.D.; Joseph, K. Simple and cost-effective synthesis of fluorescent graphene quantum dots from honey: Application as stable security ink and white-light emission. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2016, 33, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, H.; Mohapatra, J.; Pradhan, L.; Mitra, A.; Bahadur, D.; Aslam, M. Efficient synthesis of rice based graphene quantum dots and their fluorescent properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 23518–23524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.-S.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chen, P.-C.; Hou, Y.-I.; Shao, Y.-T.; Kao, H.-F.; Hsu, C.-L.L.; Chen, Y.-C. Graphene quantum dots with nitrogen-doped content dependence for highly efficient dual-modality photodynamic antimicrobial therapy and bioimaging. Biomaterials 2017, 120, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ming, H.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. One-step ultrasonic synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots from glucose and their visible-light sensitive photocatalytic ability. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganganboina, A.B.; Chowdhury, A.D.; Doong, R.-A. Nano assembly of N-doped graphene quantum dots anchored Fe3O4/halloysite nanotubes for high performance supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 245, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Bao, W.; Liu, T.; Zhang, B.; Huang, S.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Pan, C. Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots prepared by electrolysis of nitrogen-doped nanomesh graphene for the fluorometric determination of ferric ions. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, J.; Xie, G.; Ren, Y.; Zheng, Y.-Q. Ratiometric system based on graphene quantum dots and Eu3+ for selective detection of tetracyclines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1022, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, M.; Doong, R.-A.; Kumar, N.; Tseng, T.Y. Ternary Au/ZnO/rGO nanocomposites electrodes for high performance electrochemical storage devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-X.; Lu, D.; Wang, G.-G.; Huangfu, J.; Wu, Q.-B.; Wang, X.-F.; Liu, L.-F.; Ye, D.-M.; Yan, B.; Han, J. Highly efficient orange emissive graphene quantum dots prepared by acid-free method for white LEDs. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 6657–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Chen, W. Synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for sensitive, label-free detection of Fe (III) in aqueous media. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.; Saievar-Iranizad, E. Synthesis of green-photoluminescent single layer graphene quantum dots: Determination of HOMO and LUMO energy states. J. Lumin. 2017, 192, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanca, J.; Muñoz, P.; Morgado, M.; Méndez, N.; Aranda, A.; Reuvers, T.; Hooghuis, H. Determination of clenbuterol, ractopamine and zilpaterol in liver and urine by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 529, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.-D.; Wu, Y.-L.; Yang, H.-J.; Yang, T. Simultaneous determination of 10 β2-agonists in swine urine using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry and multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a reversed dispersive solid phase extraction sorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1260, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, B.; Jiang, X.; Hsieh, Y.-H.P.; Rao, Q. Matrix effect on food allergen detection–A case study of fish parvalbumin. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.; Shellaiah, M.; Steffi, P.; Sun, K.W.; Ko, F.-H. Development of extremely stable dual functionalized gold nanoparticles for effective colorimetric detection of clenbuterol and ractopamine in human urine samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1023, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, H.T.T.; Hoang, M.H.; Nguyen, P.H.N.; Thi, L.N.; Thi, N.H.; Van, C.D.; Van, T.L.; Nhu, H.L.; Ngoc, D.T.; Dai, L.T. Fabrication of graphene quantum dots based fluorescent sensor for detection of clenbuterol. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 4567–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. A Nanosensor based on carbon dots for recovered fluorescence detection clenbuterol in pork samples. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Na, L.; Jiang, Y.; Lou, D.; Jin, L. Graphene quantum dots as a fluorescence-quenching probe for quantitative analysis of Ponceau 4R solution. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7242–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, M.; Cao, Y.; Li, F.; Jia, P.; Guo, D.; Sun, X.; Wang, L. Ratiometric fluorescent probe based on diazotization-coupling reaction for determination of clenbuterol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11578–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Added (M) | Found (M) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, N = 3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beef | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2.5 × 10−6 | 2.63 × 10−6 | 105.2 | 10.32 | |
| 1.0 × 10−6 | 1.01 × 10−6 | 101.0 | 9.98 | |
| 2.5 × 10−7 | 2.46 × 10−6 | 98.4 | 8.26 | |
| Chicken | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2.5 × 10−6 | 2.72 × 10−6 | 108.8 | 6.90 | |
| 1.0 × 10−6 | 9.92 × 10−7 | 99.2 | 8.36 | |
| 2.5 × 10−7 | 2.68 × 10−7 | 107.2 | 10.25 |
| Analytical Method | Detection Limit | Linear Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquidchromatography–mass | 0.04 g·L–1 | 0.5–5.0 g·L–1 | [36] |
| spectrometry (LC–MS) | |||
| SERS | 17.0 fg·mL−1 | / | [10] |
| HPLC | 12.0 ng∙g−1 | / | [37] |
| 0.6 ng∙g−1 | 5000–80,000 ng∙g−1 | [38] | |
| ELISA | 0.2 ppb | / | [7] |
| Gas chromatography–mass | |||
| spectroscopy (GC–MS) | 2.40 lg·kg−1 | / | [8] |
| Spectrophotometer | 0.93 nM | 0–600 nM | [39] |
| Fluorescence | 10−10 g·mL−1 | 10−4–10−10 g·mL−1 | [40] |
| Fluorescence | 3.0 nM | 8–200 nM | [41] |
| Fluorescence | 2.083 × 10−13 M | 5 × 10−10–5 × 10−7 M | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Chen, C.; Lie, J.; You, R.; Qian, W.; Lin, S.; Lu, Y. Sensitive and Selective Detection of Clenbuterol in Meat Samples by a Graphene Quantum Dot Fluorescent Probe Based on Cationic-Etherified Starch. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040691
Xie H, Chen C, Lie J, You R, Qian W, Lin S, Lu Y. Sensitive and Selective Detection of Clenbuterol in Meat Samples by a Graphene Quantum Dot Fluorescent Probe Based on Cationic-Etherified Starch. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(4):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040691
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Huanyu, Cairou Chen, Jiansen Lie, Ruiyun You, Wei Qian, Shan Lin, and Yudong Lu. 2022. "Sensitive and Selective Detection of Clenbuterol in Meat Samples by a Graphene Quantum Dot Fluorescent Probe Based on Cationic-Etherified Starch" Nanomaterials 12, no. 4: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040691
APA StyleXie, H., Chen, C., Lie, J., You, R., Qian, W., Lin, S., & Lu, Y. (2022). Sensitive and Selective Detection of Clenbuterol in Meat Samples by a Graphene Quantum Dot Fluorescent Probe Based on Cationic-Etherified Starch. Nanomaterials, 12(4), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040691





