An Externally-Applied, Natural-Mineral-Based Novel Nanomaterial IFMC Improves Cardiopulmonary Function under Aerobic Exercise
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
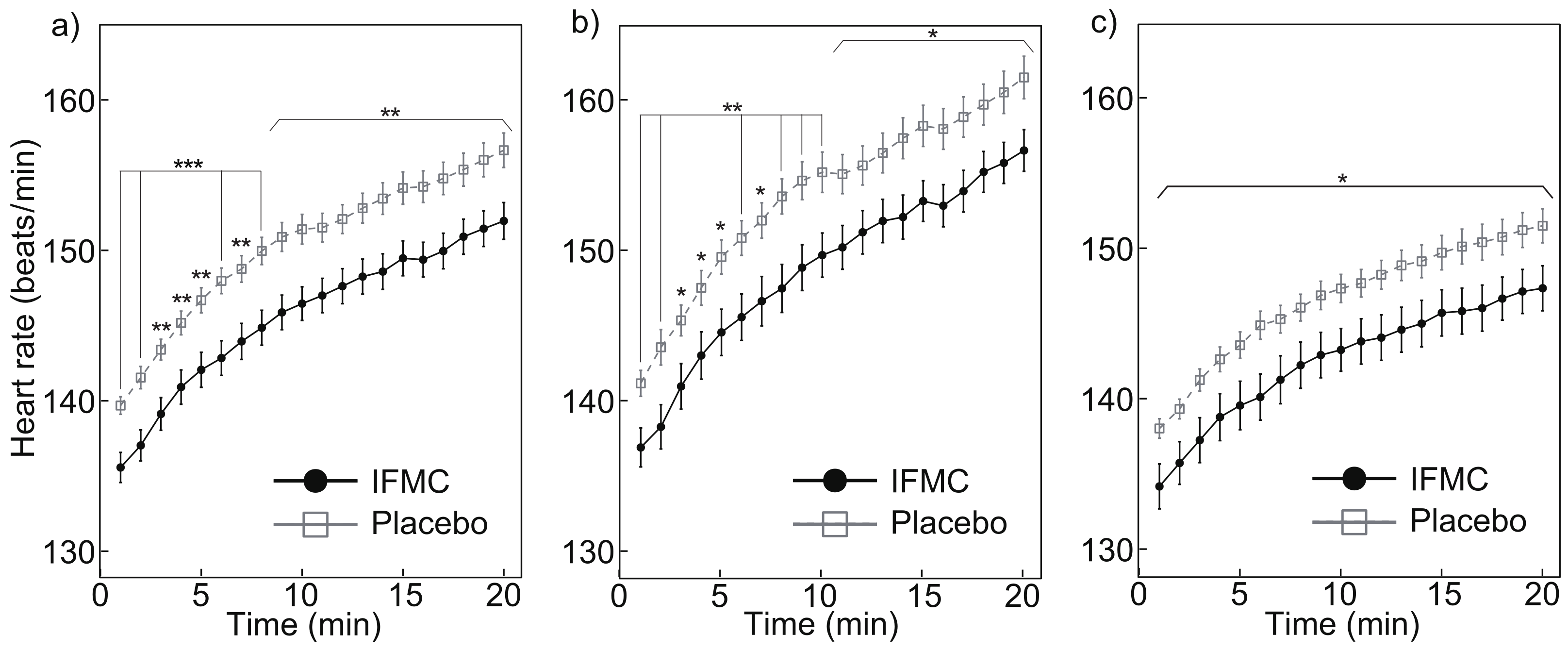
3.1. Heart Rate
3.2. Oxygen Consumption
3.3. Maximal Oxygen Consumption
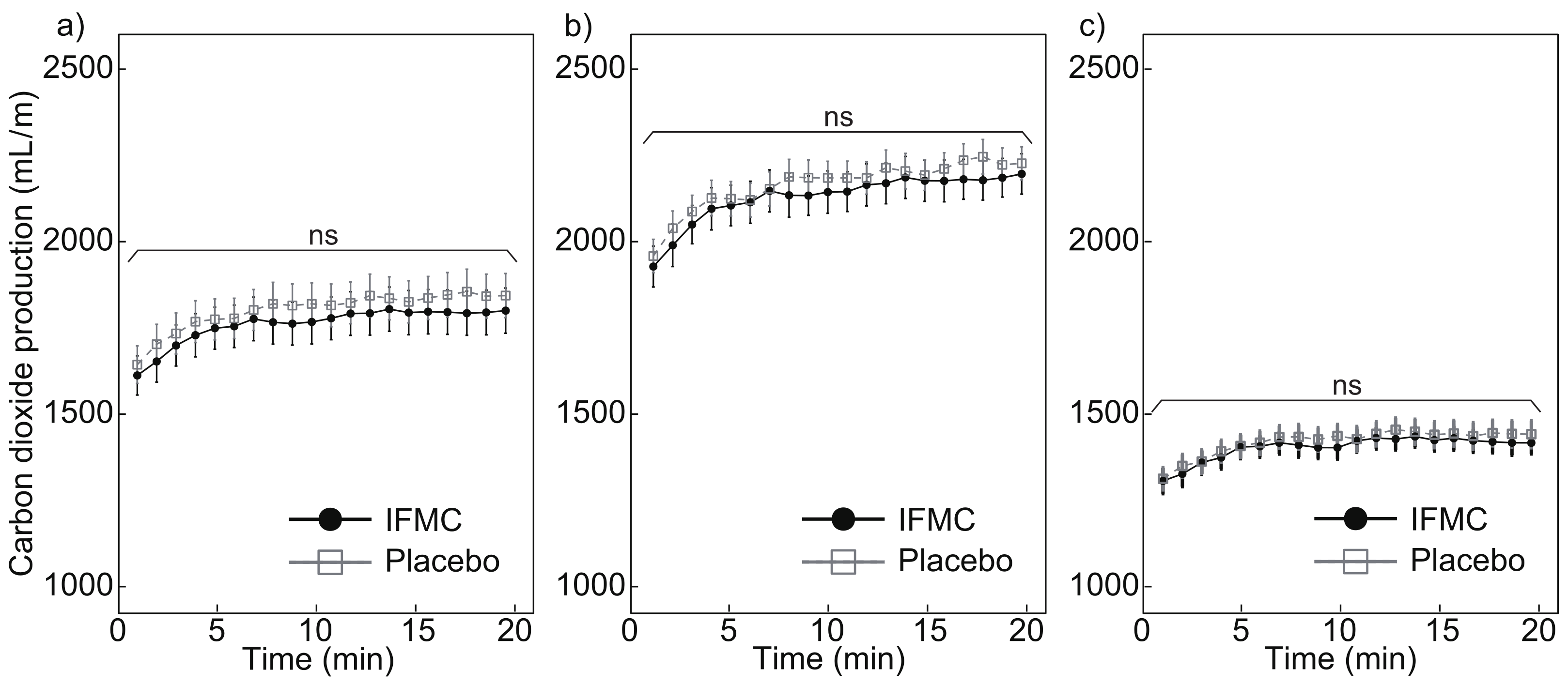
3.4. CO2 Production
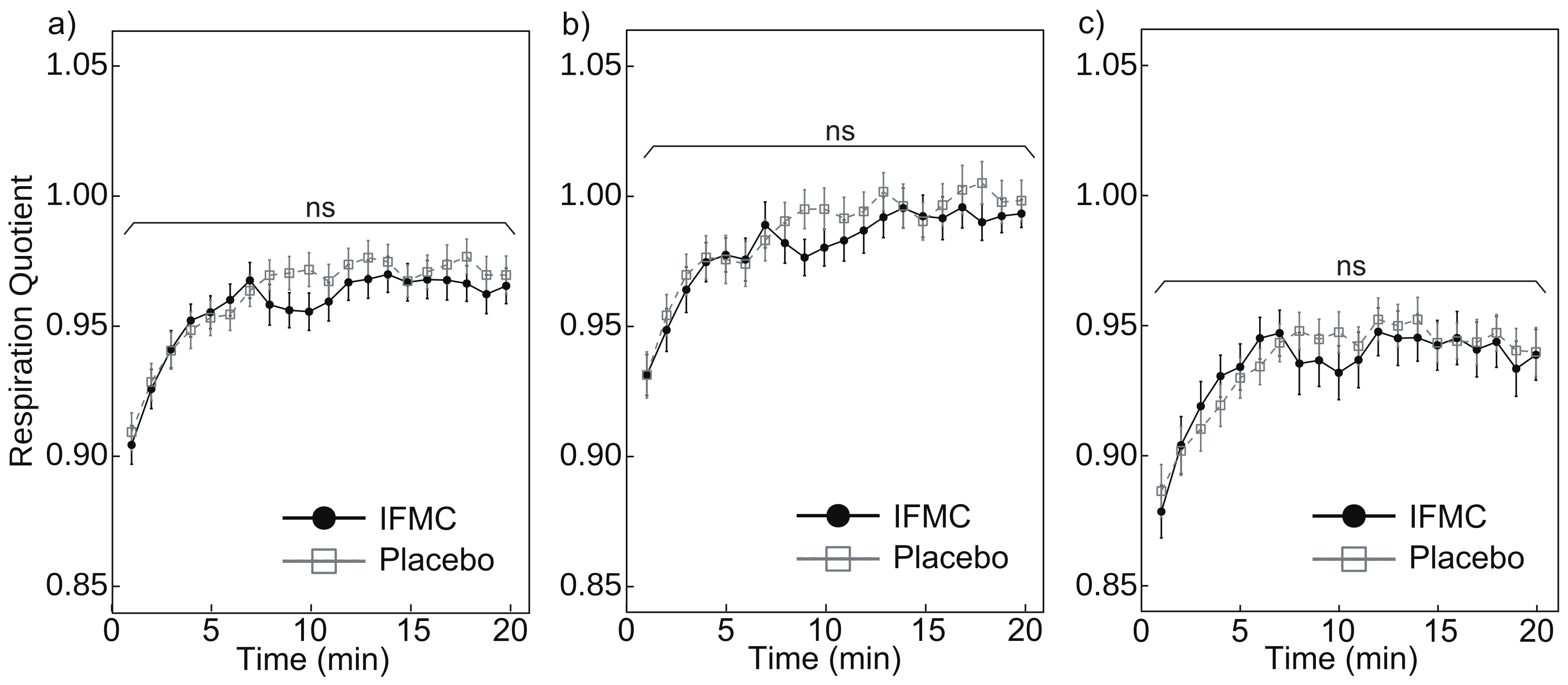
3.5. Respiratory Quotient
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CO | carbon dioxide |
| EDS | energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer |
| FE-SEM | field emission scanning electron microscopy |
| Hb | hemoglobin |
| IFMC | Integrated Functional Mineral Crystal |
| NNI | National Nanotechnology Initiative |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| O | oxygen |
References
- Roco, M.C. The long view of nanotechnology development: The National Nanotechnology Initiative at 10 years. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harifi, T.; Montazer, M. Application of nanotechnology in sports clothing and flooring for enhanced sport activities, performance, efficiency and comfort: A review. J. Ind. Text. 2017, 46, 1147–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.E.; Shen, F. The Applied Research of Nanophase Materials in Sports Engineering. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 496, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.X. Research on Nano Materials Tennis Rackets. Sport, Arts Materials and Management Science. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 507, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawhney, A.; Condon, B.; Singh, K.; Pang, S.; Li, G.; Hui, D. Modern Applications of Nanotechnology in Textiles. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, S.; Wu, Y.; Lau, K.T.; De Rossi, D.; Wallace, G.; Diamond, D. Smart Nanotextiles: A Review of Materials and Applications. MRS Bull. 2007, 32, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onodera, A.; Yayama, K.; Tanaka, A.; Morosawa, H.; Furuta, T.; Takeda, N.; Kakiguchi, K.; Yonemura, S.; Yanagihara, I.; Tsutsumi, Y.; et al. Amorphous nanosilica particles evoke vascular relaxation through PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 30, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renn, O.; Roco, M.C. Nanotechnology and the need for risk governance. J. Nanopart. Res. 2006, 8, 153–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Mädler, L.; Gilbert, B.; Shi, H.; Yeh, J.I.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Comparison of the Mechanism of Toxicity of Zinc Oxide and Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Based on Dissolution and Oxidative Stress Properties. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2121–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabir, F.; Barani, M.; Mukhtar, M.; Rahdar, A.; Cucchiarini, M.; Zafar, M.N.; Behl, T.; Bungau, S. Nanodiagnosis and Nanotreatment of Cardiovascular Diseases: An Overview. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, F.; Qindeel, M.; Zeeshan, M.; Ul Ain, Q.; Rahdar, A.; Barani, M.; González, E.; Aboudzadeh, M.A. Onco-Receptors Targeting in Lung Cancer via Application of Surface-Modified and Hybrid Nanoparticles: A Cross-Disciplinary Review. Processes 2021, 9, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Rutherford, D.; Vuong, T.; Liu, H. Nanomaterials for treating cardiovascular diseases: A review. Bioact. Mater. 2017, 2, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Marei, I.; Crovella, S.; Abou-Saleh, H. Recent Developments in Nanomaterials-Based Drug Delivery and Upgrading Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, J.S.; Greineder, C.; Shuvaev, V.; Muzykantov, V. Endothelial nanomedicine for the treatment of pulmonary disease. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polizzi, M.A.; Stasko, N.A.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Water-Soluble Nitric Oxide-Releasing Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4938–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignarro, L.J. Nitric Oxide: A Unique Endogenous Signaling Molecule in Vascular Biology. Biosci. Rep. 1999, 19, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Bowman, L.; Zhao, J.; Ding, M. Potential applications and human biosafety of nanomaterials used in nanomedicine. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teikoku Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. 2022. Available online: https://ifmc.jp (accessed on 22 February 2022).
- Akiyama, T.; Hirata, T.; Fujimoto, T.; Hatakeyama, S.; Yamazaki, R.; Nomura, T. The Natural-Mineral-Based Novel Nanomaterial IFMC Increases Intravascular Nitric Oxide without Its Intake: Implications for COVID-19 and beyond. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, K. External Composition for Skin. Patent No. 655744, 19 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- The Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study Group. The Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Glucose and Counterregulatory Hormone Concentrations in Children With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.; Paterno, J.; Duscher, D.; Maan, Z.N.; Chen, J.S.; Januszyk, M.; Rodrigues, M.; Rennert, R.C.; Bishop, S.; Whitmore, A.J.; et al. Exercise induces stromal cell-derived factor-1α-mediated release of endothelial progenitor cells with increased vasculogenic function. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 340e–350e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, N.S.; Prentice, S.D.; Callaghan, J.P. Local dynamic stability of the lower extremity in novice and trained runners while running intraditional and minimal footwear. Gait Posture 2019, 68, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, M.; Chua, K.L. A multiple mediation analysis of the association between asynchronous use of music and running performance. J. Sport. Sci. 2021, 39, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.M.J.; Ferrige, A.G.; Moncada, S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature 1987, 327, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, F. Discovery of Some of the Biological Effects of Nitric Oxide and Its Role in Cell Signaling (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1856–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Kuroi, A.; Mochizuki, S.; Goto, M.; Yoshida, K.; Akasaka, T. Effects of Angiotensin II on NO Bioavailability Evaluated Using a Catheter-Type NO Sensor. Hypertension 2006, 48, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsutsui, C.; Lee, M.; Takahashi, G.; Murata, S.; Hirata, T.; Kanai, T.; Mori, A. Treatment of cardiac disease by inhalation of atmospheric pressure plasma. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 060309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, A.C.; Lohman, A.W.; Billaud, M.; Johnstone, S.R.; Dwyer, S.T.; Lee, M.Y.; Bortz, P.S.; Best, A.K.; Columbus, L.; Gaston, B.; et al. Endothelial cell expression of haemoglobin α regulates nitric oxide signalling. Nature 2012, 491, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebrun, R.; Ross, A.; Bender, S.A.; Qaiumzadeh, A.; Baldrati, L.; Cramer, J.; Brataas, A.; Duine, R.A.; Kläui, M. Tunable long-distance spin transport in a crystalline antiferromagnetic iron oxide. Nature 2018, 561, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
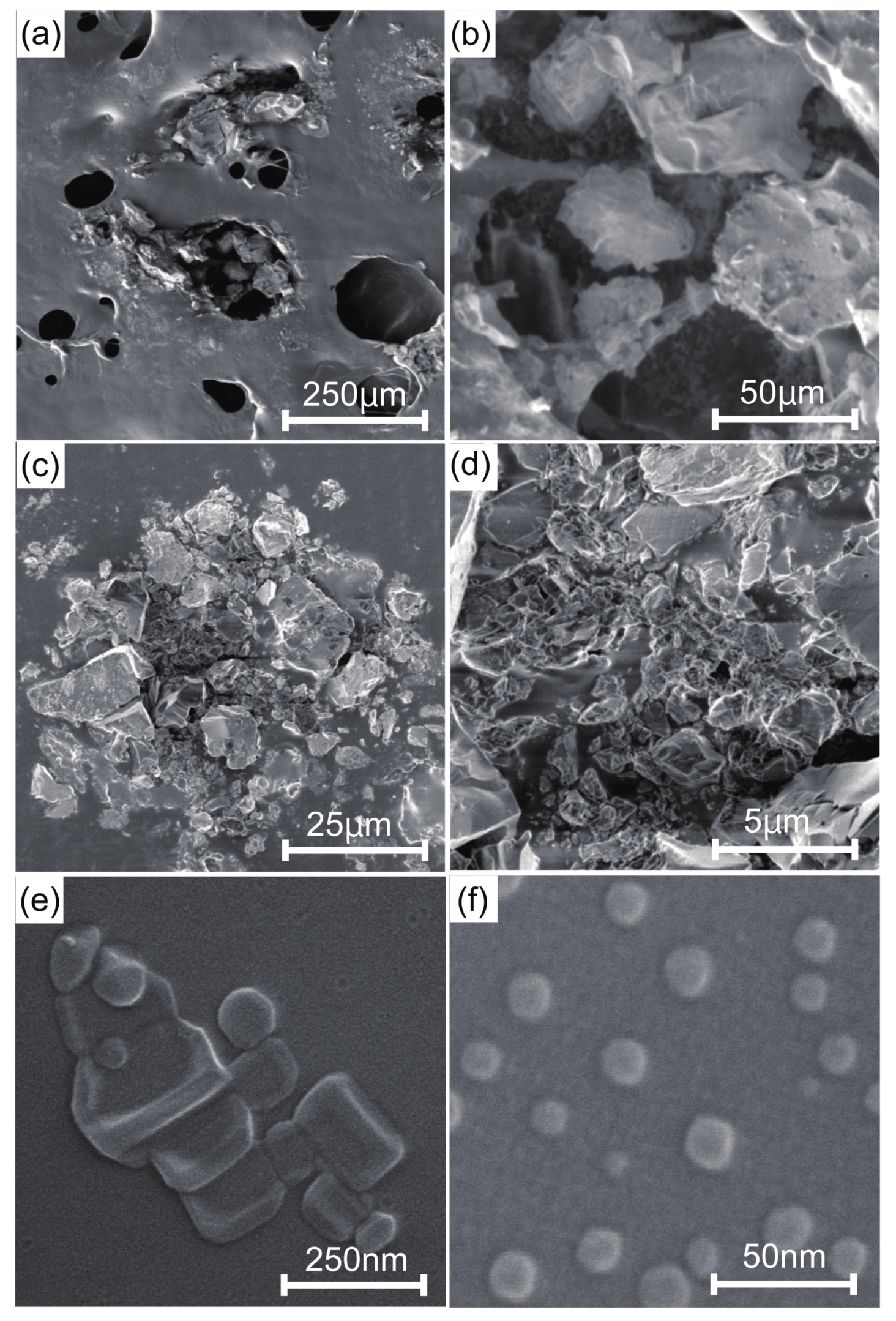
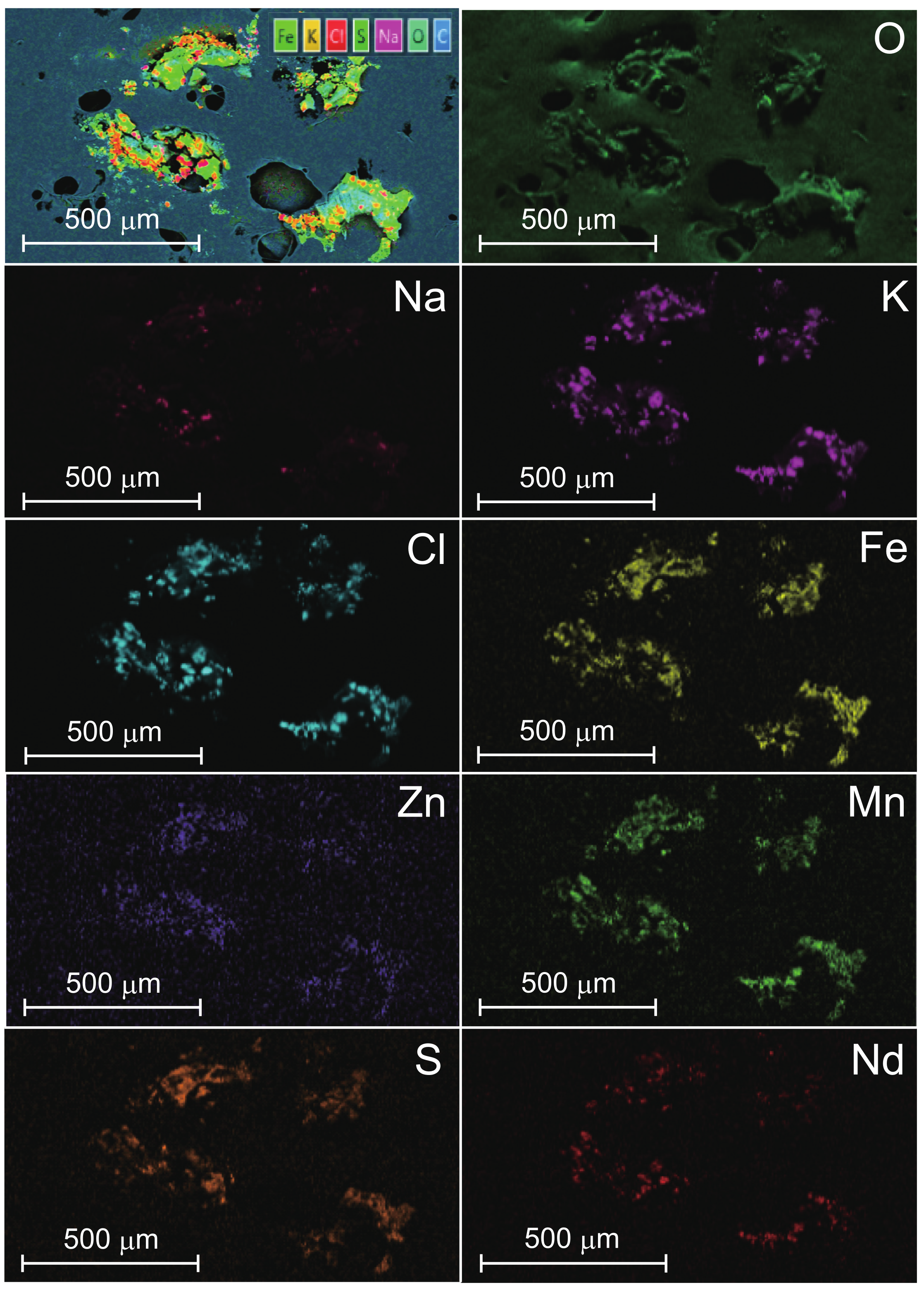


| Subjects | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | M | M | M | M | M | M | M | M | M | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F |
| Age | 21 | 22 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 20 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 23 | 20 |
| Height (cm) | 175 | 174 | 183 | 169 | 173 | 159 | 173 | 169 | 162 | 162 | 161 | 168 | 158 | 165 | 165 | 171 | 168 | 166 |
| Weight (kg) | 87 | 72 | 86 | 62 | 60 | 63 | 63 | 68 | 54 | F | 45 | 65 | 49 | 66 | F | 62 | 56 | 58 |
| Type of athlete | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Smoking habits | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Medication | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akiyama, T.; Hatakeyama, S.; Kawamoto, K.; Nihei, H.; Hirata, T.; Nomura, T. An Externally-Applied, Natural-Mineral-Based Novel Nanomaterial IFMC Improves Cardiopulmonary Function under Aerobic Exercise. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060980
Akiyama T, Hatakeyama S, Kawamoto K, Nihei H, Hirata T, Nomura T. An Externally-Applied, Natural-Mineral-Based Novel Nanomaterial IFMC Improves Cardiopulmonary Function under Aerobic Exercise. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(6):980. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060980
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkiyama, Tomohiro, Shinnosuke Hatakeyama, Kazuhisa Kawamoto, Hideko Nihei, Takamichi Hirata, and Tomohiro Nomura. 2022. "An Externally-Applied, Natural-Mineral-Based Novel Nanomaterial IFMC Improves Cardiopulmonary Function under Aerobic Exercise" Nanomaterials 12, no. 6: 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060980
APA StyleAkiyama, T., Hatakeyama, S., Kawamoto, K., Nihei, H., Hirata, T., & Nomura, T. (2022). An Externally-Applied, Natural-Mineral-Based Novel Nanomaterial IFMC Improves Cardiopulmonary Function under Aerobic Exercise. Nanomaterials, 12(6), 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060980







