Two-Channel Charge-Kondo Physics in Graphene Quantum Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model, Methods, and Observables
Numerical Renormalization Group
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overview and Phase Diagram
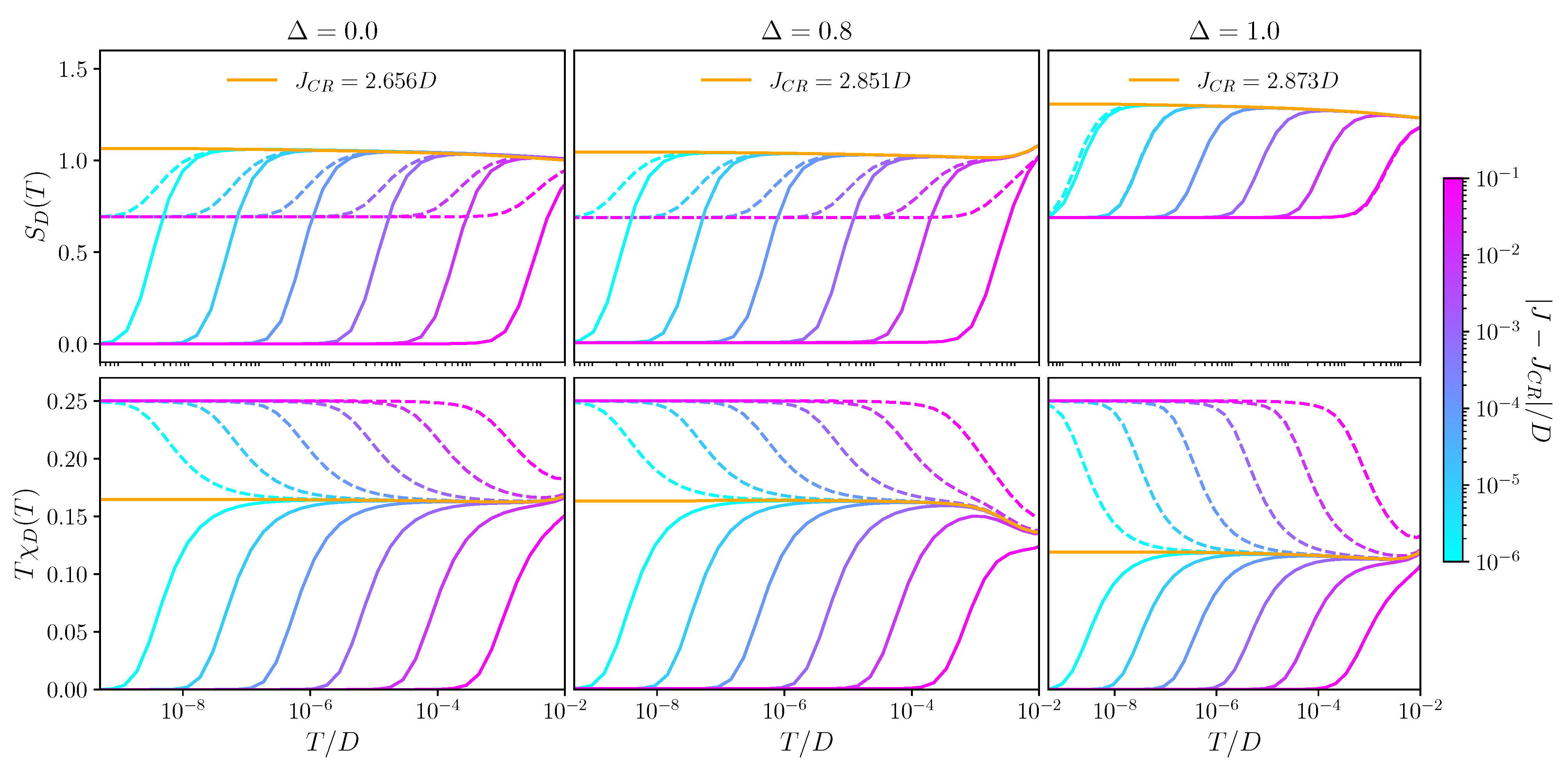
3.2. Thermodynamics and Fixed Points
3.2.1. Frozen Channel Degree of Freedom:
3.2.2. Frustrated Channel Degree of Freedom:
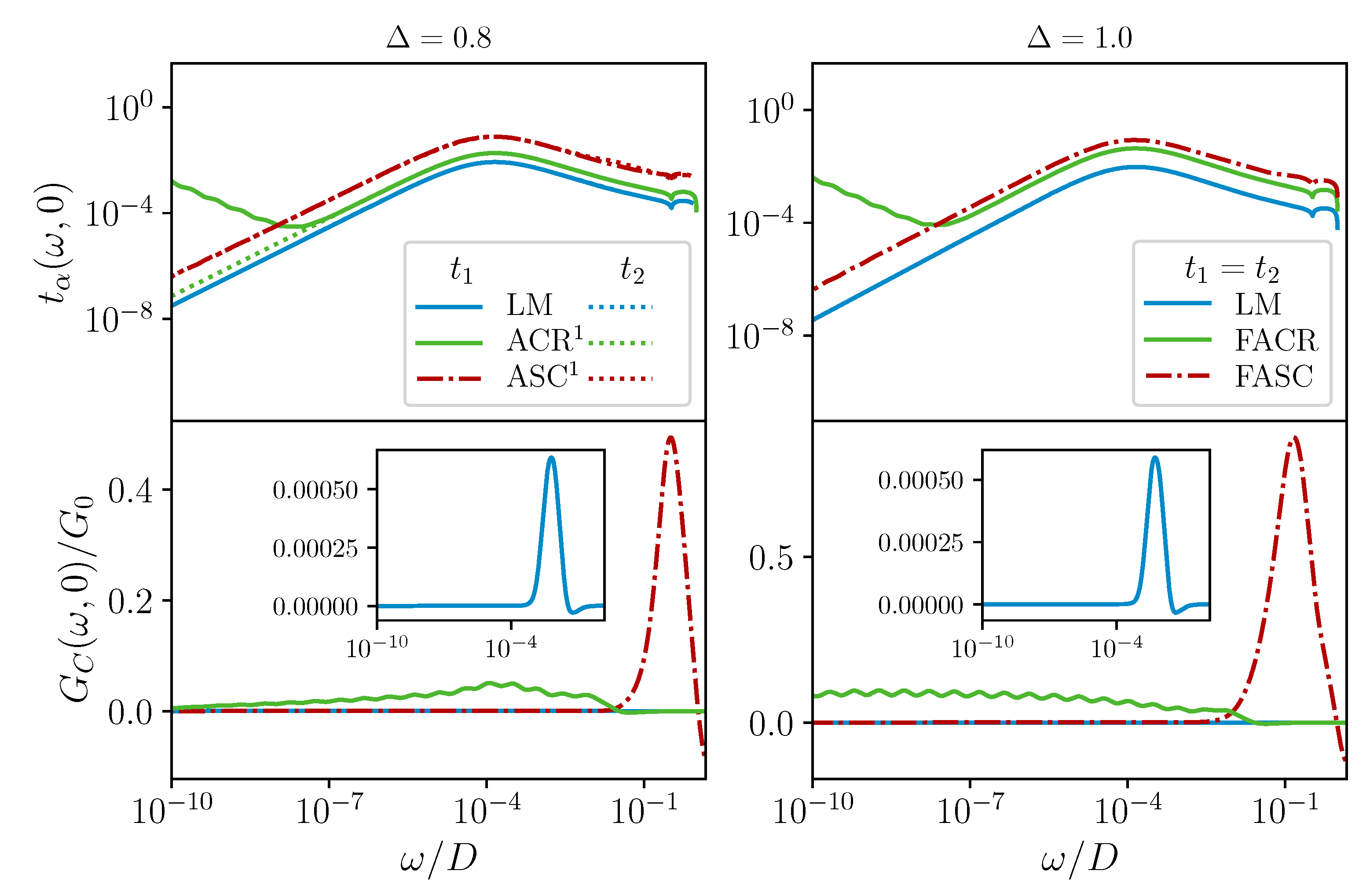
3.3. Dynamics and Transport
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QD | quantum dot |
| QPC | quantum point contact |
| QPT | quantum phase transition |
| QCP | quantum critical point |
| 2CK | two-channel Kondo |
| NRG | Numerical Renormalization Group |
| FL | Fermi liquid |
| NFL | non-Fermi liquid |
| DoS | density of states |
| RG | renormalization group |
| FP | fixed point |
| LM | local moment |
| (F)ALM | (frustrated) asymmetric local moment |
| (F)ASC | (frustrated) asymmetric strong coupling |
| (F)SSC | (frustrated) symmetric strong coupling |
| (F)ACR | (frustrated) asymmetric critical |
References
- Kondo, J. Resistance minimum in dilute magnetic alloys. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1964, 32, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hewson, A.C. The Kondo Problem to Heavy Fermions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, K.G. The renormalization group: Critical phenomena and the Kondo problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1975, 47, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinek, J.; Utsumi, Y.; Imamura, H.; Barnaś, J.; Maekawa, S.; König, J.; Schön, G. Kondo effect in quantum dots coupled to ferromagnetic leads. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 127203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franke, K.; Schulze, G.; Pascual, J. Competition of superconducting phenomena and Kondo screening at the nanoscale. Science 2011, 332, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Schuricht, D.; Vojta, M.; Fritz, L. Kondo effect on the surface of three-dimensional topological insulators: Signatures in scanning tunnelling spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 075430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Fritz, L. Kondo effect in three-dimensional Dirac and Weyl systems. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 121109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.H.; Li, L.; Cullen, W.G.; Williams, E.D.; Fuhrer, M.S. Tunable Kondo effect in graphene with defects. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, L.; Vojta, M. The physics of Kondo impurities in graphene. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2013, 76, 032501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neto, A.C.; Guinea, F.; Peres, N.M.; Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K. The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinrich, A.J.; Oliver, W.D.; Vandersypen, L.M.; Ardavan, A.; Sessoli, R.; Loss, D.; Jayich, A.B.; Fernandez-Rossier, J.; Laucht, A.; Morello, A. Quantum-coherent nanoscience. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, P.; Vandersypen, L.M. Quantum dot systems: A versatile platform for quantum simulations. Ann. Phys. 2013, 525, 808–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kastner, M.A.; Klein, O.; Lyszczarz, T.M.; Mankiewich, P.M.; Shaver, D.C.; Wind, S.; Abusch-Magder, D.; Goldhaber-Gordon, D.J.; Morgan, N.Y. Artificial Atoms; Technical Report; Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE) at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT): Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Goldhaber-Gordon, D.; Shtrikman, H.; Mahalu, D.; Abusch-Magder, D.; Meirav, U.; Kastner, M.A. Kondo effect in a single-electron transistor. Nature 1998, 391, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronenwett, S.M.; Oosterkamp, T.H.; Kouwenhoven, L.P. A tunable Kondo effect in quantum dots. Science 1998, 281, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Wiel, W.; Franceschi, S.D.; Fujisawa, T.; Elzerman, J.; Tarucha, S.; Kouwenhoven, L. The Kondo effect in the unitary limit. Science 2000, 289, 2105–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Becker, M.; Bulla, R. Real-space renormalization group flow in quantum impurity systems: Local moment formation and the Kondo screening cloud. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 115120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, G.; Lee, S.S.; Sim, H.S. Detecting Kondo entanglement by electron conductance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 146801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pustilnik, M.; Glazman, L. Kondo effect in quantum dots. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, R513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vojta, M. Impurity quantum phase transitions. Philos. Mag. 2006, 86, 1807–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Jarrold, T.F.; Logan, D.E. Quantum phase transition in quantum dot trimers. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 085124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, A.; Amasha, S.; Weymann, I.; Moca, C.; Rau, I.; Katine, J.; Shtrikman, H.; Zaránd, G.; Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Emergent SU (4) Kondo physics in a spin–charge-entangled double quantum dot. Nat. Phys. 2014, 10, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Liberman, A.; Sela, E.; Affleck, I. SO (5) non-Fermi liquid in a Coulomb box device. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 147702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potok, R.; Rau, I.; Shtrikman, H.; Oreg, Y.; Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Observation of the two-channel Kondo effect. Nature 2007, 446, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keller, A.; Peeters, L.; Moca, C.; Weymann, I.; Mahalu, D.; Umansky, V.; Zaránd, G.; Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Universal Fermi liquid crossover and quantum criticality in a mesoscopic system. Nature 2015, 526, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Sela, E. Universal low-temperature crossover in two-channel Kondo models. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 235127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Sela, E.; Logan, D.E. Two-channel Kondo physics in two-impurity Kondo models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 086405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nozieres, P.; Blandin, A. Kondo effect in real metals. J. Phys. 1980, 41, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Affleck, I.; Ludwig, A.W. Critical theory of overscreened Kondo fixed points. Nucl. Phys. B 1991, 360, 641–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, Z.; Jezouin, S.; Anthore, A.; Gennser, U.; Parmentier, F.; Cavanna, A.; Pierre, F. Two-channel Kondo effect and renormalization flow with macroscopic quantum charge states. Nature 2015, 526, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Landau, L.; Fritz, L.; Sela, E. Universality and scaling in a charge two-channel Kondo device. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 157202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iftikhar, Z.; Anthore, A.; Mitchell, A.; Parmentier, F.; Gennser, U.; Ouerghi, A.; Cavanna, A.; Mora, C.; Simon, P.; Pierre, F. Tunable quantum criticality and super-ballistic transport in a “charge” Kondo circuit. Science 2018, 360, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, C.; Iftikhar, Z.; Kleeorin, Y.; Anthore, A.; Pierre, F.; Meir, Y.; Mitchell, A.K.; Sela, E. Fractional entropy of multichannel Kondo systems from conductance-charge relations. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.12878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouse, W.; Peeters, L.; Hsueh, C.L.; Gennser, U.; Cavanna, A.; Kastner, M.A.; Mitchell, A.K.; Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Exotic quantum critical point in a two-site charge Kondo circuit. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.12691. [Google Scholar]
- Matveev, K. Coulomb blockade at almost perfect transmission. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 51, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furusaki, A.; Matveev, K. Theory of strong inelastic cotunnelling. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 16676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, I.; Fritz, L.; Anders, F.B.; Benlagra, A.; Vojta, M. Two-channel pseudogap Kondo and Anderson models: Quantum phase transitions and non-Fermi liquids. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 125139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacon, M.; Bradley, S.J.; Nann, T. Graphene quantum dots. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2014, 31, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Gong, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, W.; Pu, K.; Liu, J.; Chen, P. Recent advances on graphene quantum dots: From chemistry and physics to applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Chen, S.; Fu, J. An eco-friendly imprinted polymer based on graphene quantum dots for fluorescent detection of p-nitroaniline. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 41383–41391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebanon, E.; Schiller, A.; Anders, F.B. Coulomb blockade in quantum boxes. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 041311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kogan, E. Poor man’s scaling: Anisotropic Kondo and Coqblin–Schrieffer models. J. Phys. Commun. 2018, 2, 085001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fritz, L.; Vojta, M. Phase transitions in the pseudogap Anderson and Kondo models: Critical dimensions, renormalization group, and local-moment criticality. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 214427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izumida, W.; Sakai, O.; Shimizu, Y. Many body effects on electron tunnelling through quantum dots in an Aharonov-Bohm circuit. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1997, 66, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minarelli, E.L.; Rigo, J.B.; Mitchell, A.K. Linear response quantum transport through interacting multi-orbital nanostructures. 2022; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Meir, Y.; Wingreen, N.S. Landauer formula for the current through an interacting electron region. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Child, T.; Sheekey, O.; Lüscher, S.; Fallahi, S.; Gardner, G.C.; Manfra, M.; Kleeorin, Y.; Meir, Y.; Folk, J. Entropy measurement of a strongly correlated quantum dot. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.14158. [Google Scholar]
- Bulla, R.; Costi, T.A.; Pruschke, T. Numerical renormalization group method for quantum impurity systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 395–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weichselbaum, A.; Von Delft, J. Sum-rule conserving spectral functions from the numerical renormalization group. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 076402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulla, R.; Pruschke, T.; Hewson, A. Anderson impurity in pseudo-gap Fermi systems. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1997, 9, 10463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Pruschke, T.; Anders, F.B. Numerical renormalization group approach to Greenâ’s functions for quantum impurity models. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 245114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anders, F.B.; Schiller, A. Real-time dynamics in quantum-impurity systems: A time-dependent numerical renormalization-group approach. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 196801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Buxton, C.; Ingersent, K. Renormalization-group study of Anderson and Kondo impurities in gapless Fermi systems. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, 14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logan, D.E.; Glossop, M.T. A local moment approach to magnetic impurities in gapless Fermi systems. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2000, 12, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vojta, M.; Fritz, L. Upper critical dimension in a quantum impurity model: Critical theory of the asymmetric pseudogap Kondo problem. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 094502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vojta, M.; Fritz, L.; Bulla, R. Gate-controlled Kondo screening in graphene: Quantum criticality and electron-hole asymmetry. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 2010, 90, 27006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Vojta, M.; Bulla, R.; Fritz, L. Quantum phase transitions and thermodynamics of the power-law Kondo model. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 195119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vojta, M.; Bulla, R. Kondo effect of impurity moments in d-wave superconductors: Quantum phase transition and spectral properties. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 65, 014511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
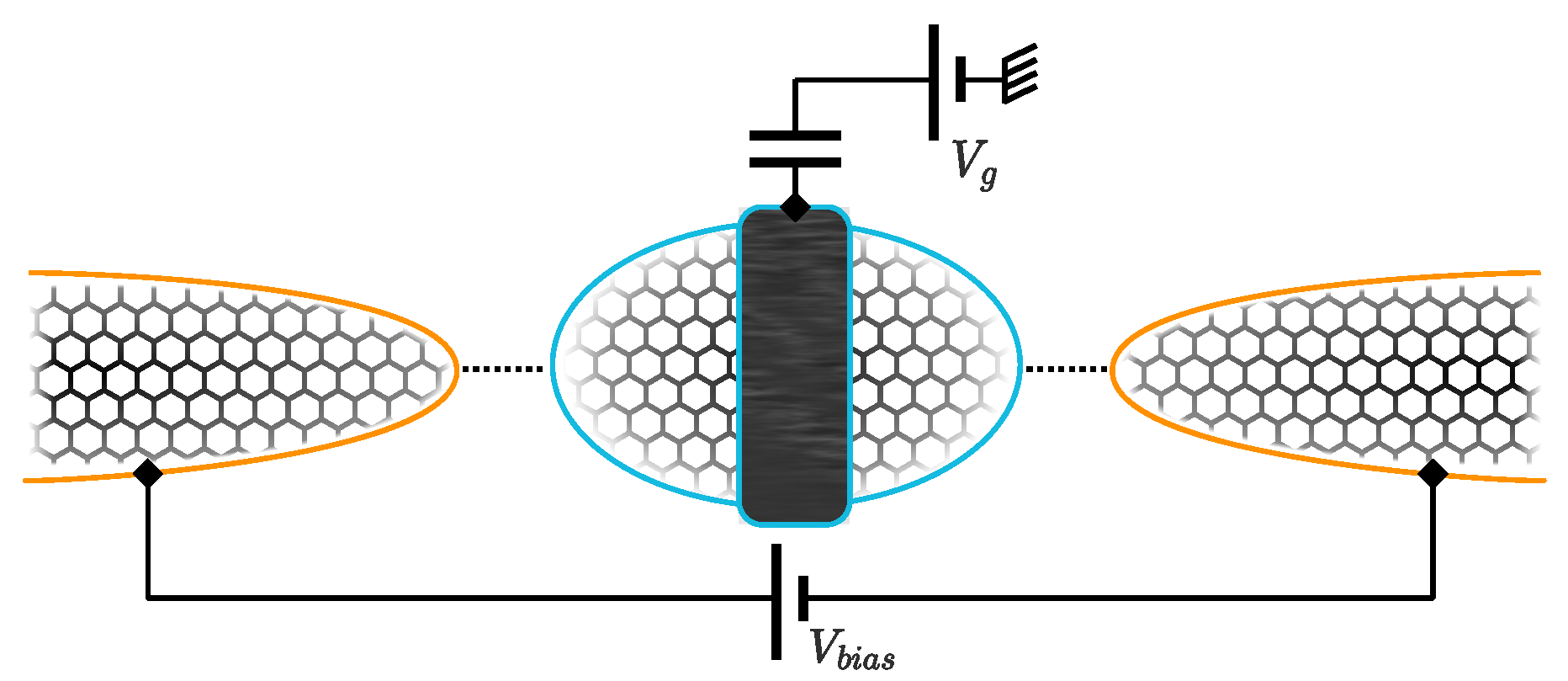

| Asymmetry | Fixed Point | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LM line | 0 | |||||
| ASC | 0 | 0 | ||||
| ACR * | 0 | |||||
| FASC * | 0 | |||||
| FACR * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minarelli, E.L.; Rigo, J.B.; Mitchell, A.K. Two-Channel Charge-Kondo Physics in Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091513
Minarelli EL, Rigo JB, Mitchell AK. Two-Channel Charge-Kondo Physics in Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(9):1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091513
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinarelli, Emma L., Jonas B. Rigo, and Andrew K. Mitchell. 2022. "Two-Channel Charge-Kondo Physics in Graphene Quantum Dots" Nanomaterials 12, no. 9: 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091513
APA StyleMinarelli, E. L., Rigo, J. B., & Mitchell, A. K. (2022). Two-Channel Charge-Kondo Physics in Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials, 12(9), 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091513








