A General Way to Fabricate Chain-like Ferrite with Ultralow Conductive Percolation Threshold and Wideband Absorbing Ability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials
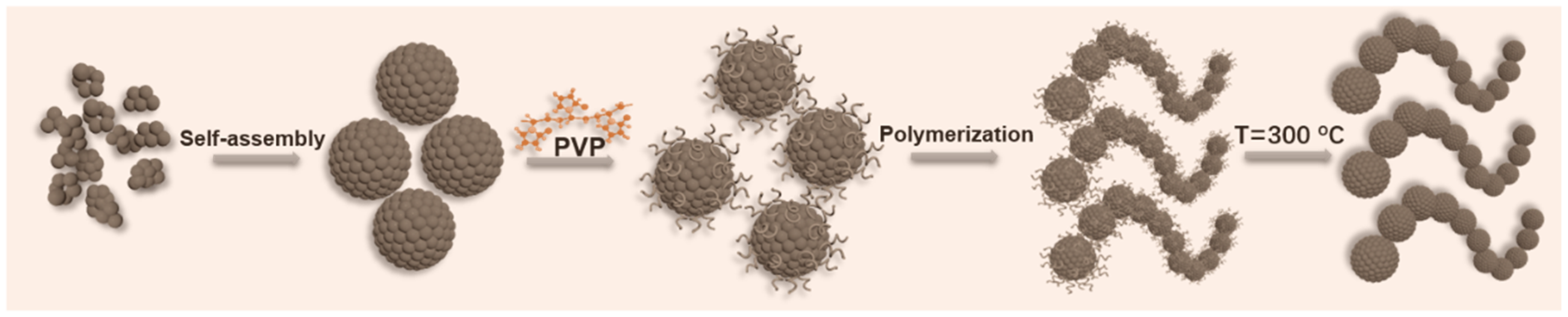
2.2. Preparation of Chain-Shaped Ferrites
2.3. Characterization and Measurements
2.4. Electromagnetic Parameters
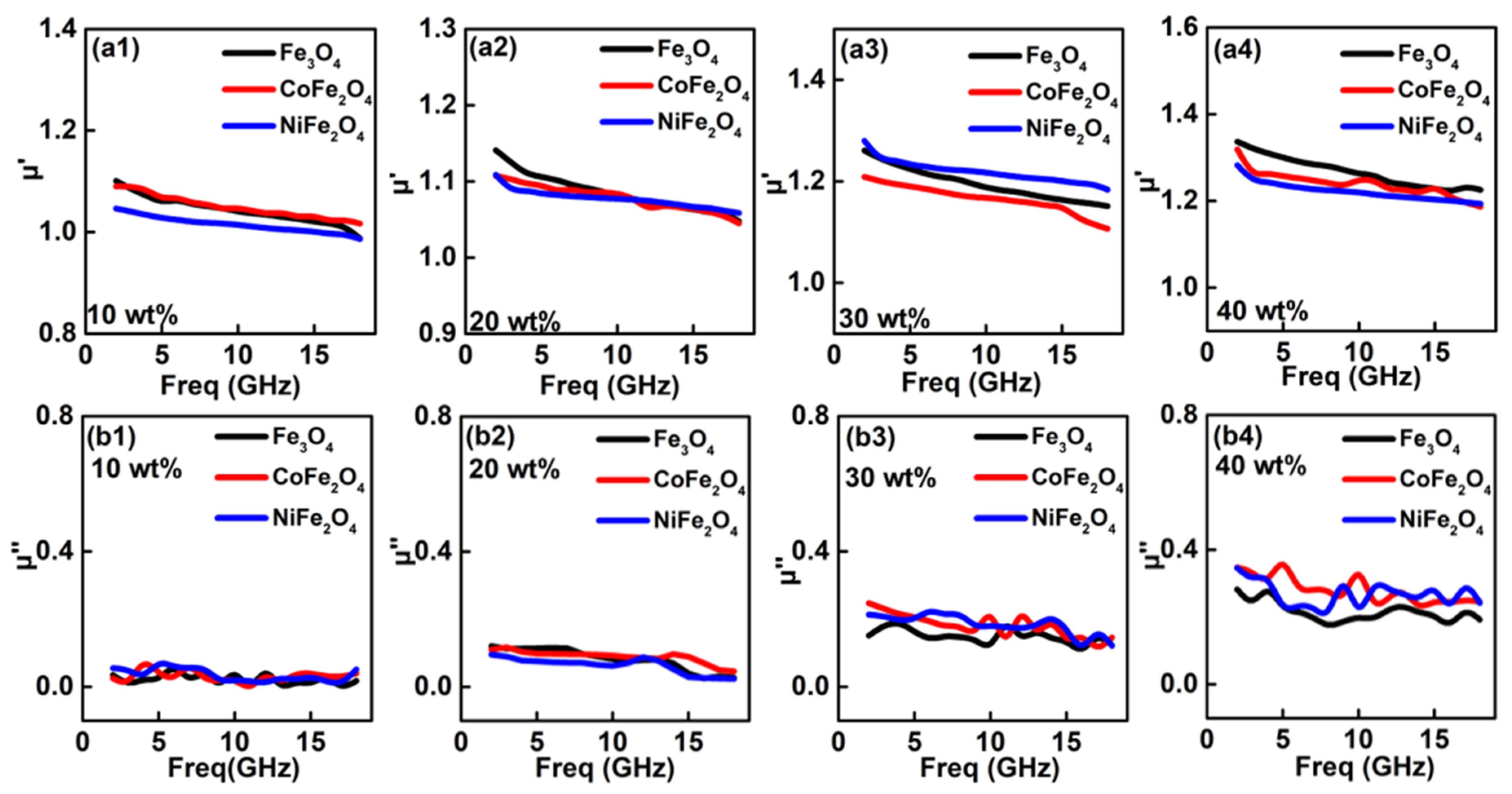
3. Results and Discussion
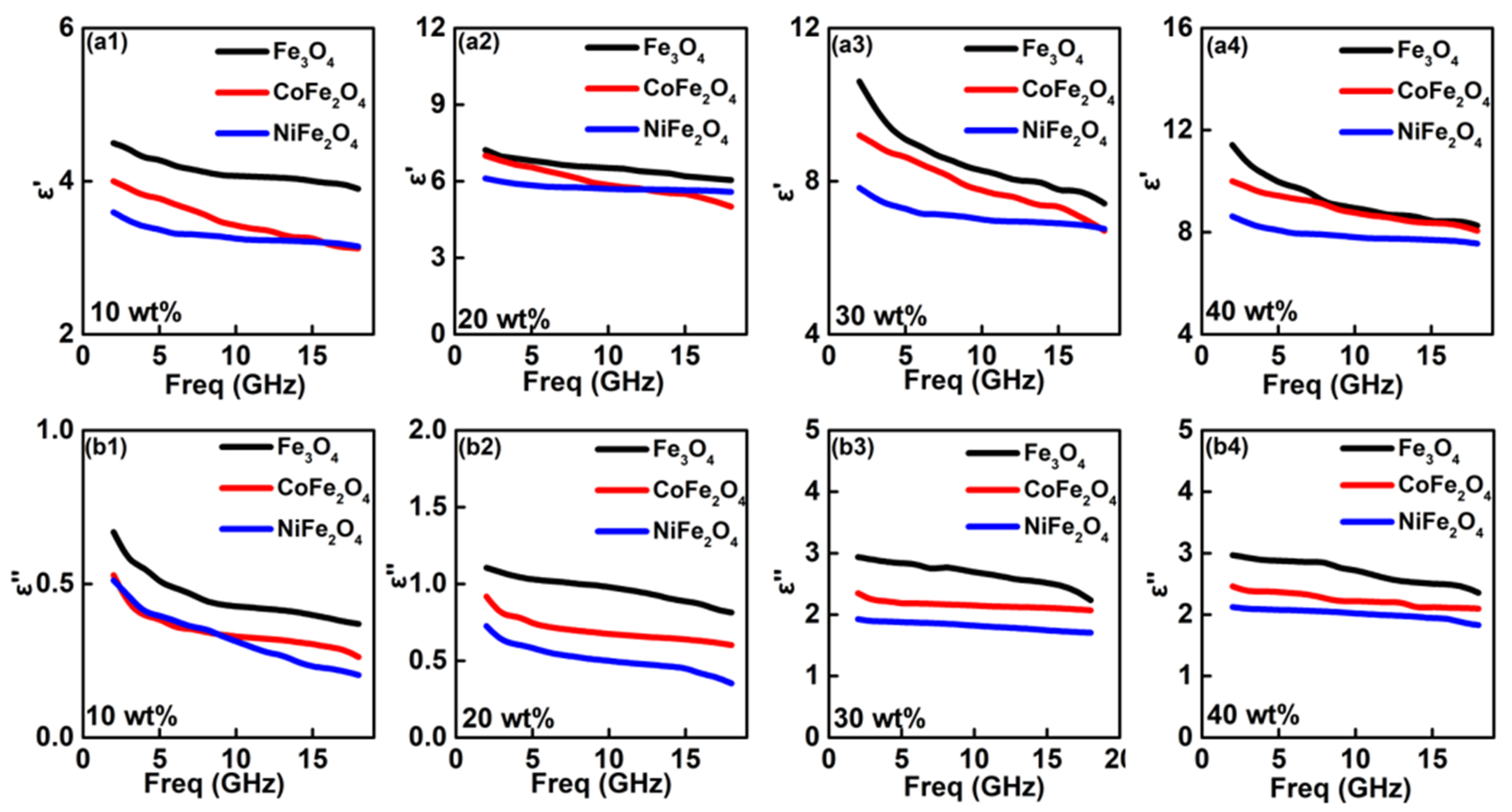
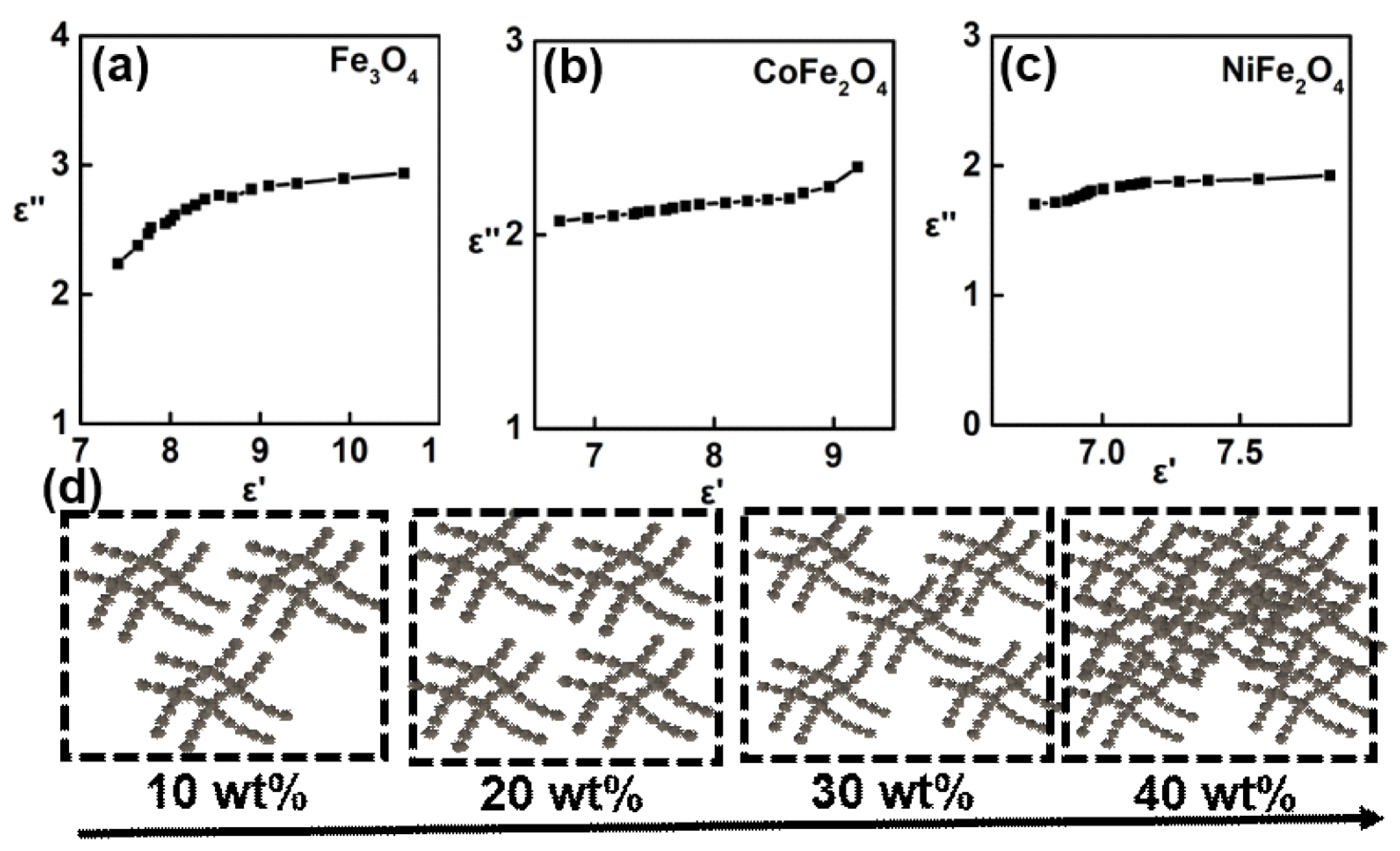
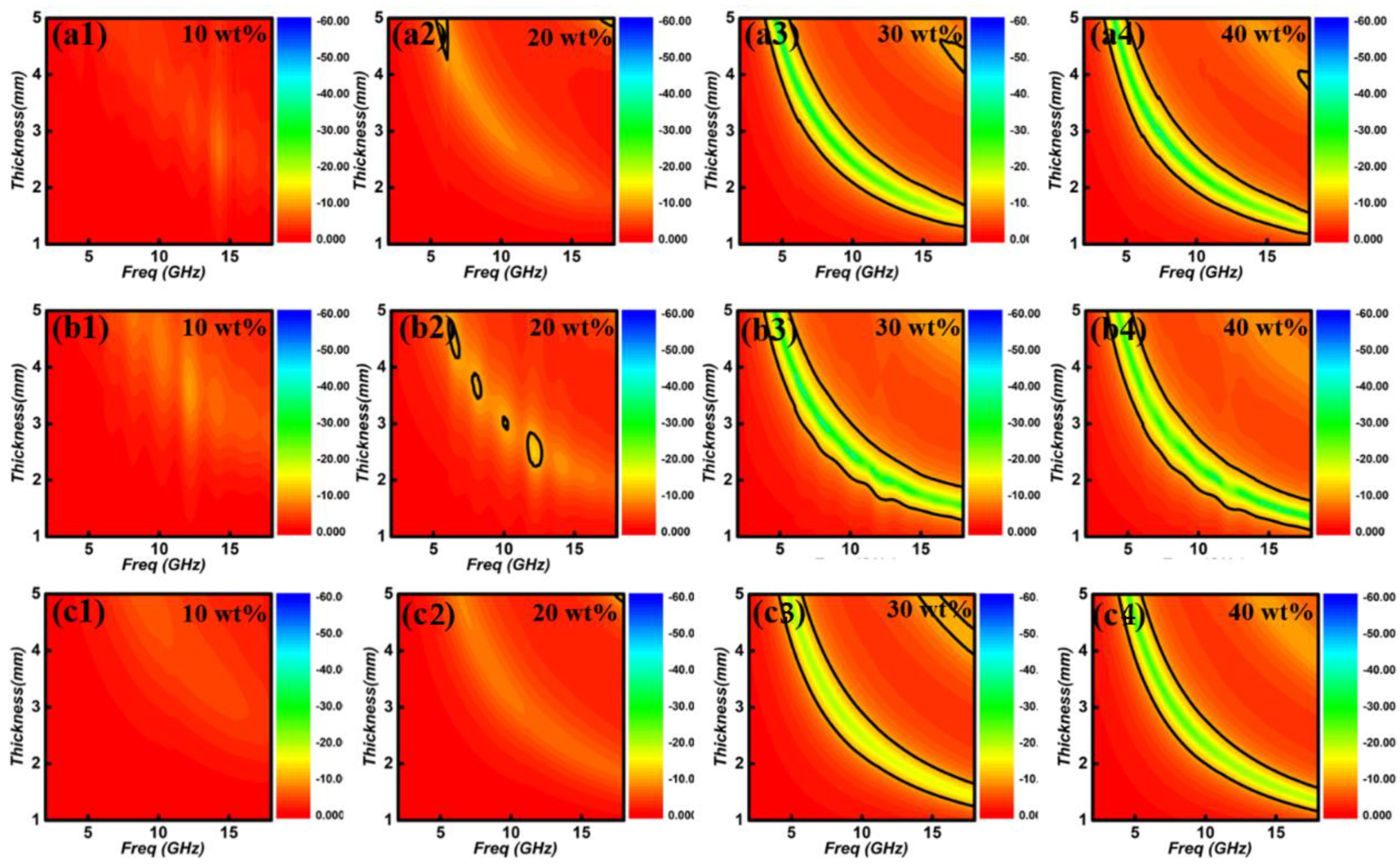
- A higher content of ferrite would lead to the strong dielectric loss ability. Besides, the distinct enhancement of ε″ can be observed at ferrite weight regions of 10~30 wt%, but slowly increases between 30~40 wt%.
- Fe3O4 is easier to present the strongest dielectric loss behavior than CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, Z.R.; Wang, B.B.; Feng, A.L.; Liu, J.J.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.Y.; Wu, G.L. Development of spindle-cone shaped of Fe/α-Fe2O3 hybrids and their superior wideband electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 799, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yang, Z.H.; Pan, H.G.; Wu, R.B. Electromagnetic absorption materials: Current progress and new frontiers. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 127, 100946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.C.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhou, X.D.; Kara, U.I.; Mamtani, R.S.; Lv, H.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.H.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, C.X.; et al. An angle-insensitive electromagnetic absorber enabling a wideband absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 113, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, Y.C.; Huang, L.L.; Ma, H.; Cheng, Q. BST-silicon hybrid terahertz meta-modulator for dual-stimuli-triggered opposite transmission amplitude control. Nanophotonics 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.L.; Yang, Z.H.; Ong, S.J.H.; Wei, C.; Liao, H.B.; Xi, S.B.; Du, Y.H.; Ji, G.B.; Xu, Z.C.J. A flexible microwave shield with tunable frequency-transmission and electromagnetic compatibility. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Cao, M.S.; Shu, J.C.; Cai, Y.Z.; Wang, X.X.; Zhao, Q.L. Atomic layer tailoring titanium carbide MXene to tune transport and polarization for utilization of electromagnetic energy beyond solar and chemical energy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12535–12543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.L.; Zhang, H.X.; Luo, X.X.; Yang, L.J.; Lv, H.L. Investigation and optimization of Fe/ZnFe2O4 as a wide-band electromagnetic absorber. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 536, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.W.; Li, W.J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhang, G.Y. Nitrogen-doped Co-C/MWCNTs nanocomposites derived from bimetallic metal-organic frameworks for electromagnetic wave absorption in the X-band. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.B.; Qiu, H.; Song, P.; Shi, X.T.; Kong, J.; Gu, J.W. Ultra-light MXene aerogel/wood-derived porous carbon composites with wall-like “mortal/brick” structures for electromagnetic interference shielding. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, H.L.; Yang, Z.H.; Liu, B.; Wu, G.L.; Lou, Z.C.; Fei, B.; Wu, R.B. A flexible electromagnetic wave-electricity harvester. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zong, M.; Liu, P. Synthesis of polypyrrole decorated FeCo@SiO2 as a high-performance electromagnetic absorption material. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 774, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Wang, B.B.; Feng, A.L.; Zhang, N.; Jia, Z.R.; Huang, Z.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Wu, G.L. Mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres with tunable pore size and shell thickness as efficient electromagnetic wave absorbers. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2019, 167, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Shu, R.W.; Guo, C.L.; Sun, R.R.; Chen, Y.N.; Yuan, J. Fabrication of nickel ferrite micropsheres decorated multi-walled carbon nanotubes hybrid composites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 784, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.M.; Yao, Z.J.; Li, S.Z.; Zou, J.T.; Haidry, A.A.; Liu, P.J. Broadband high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption of Co-doped NiZn ferrite/polyaniline on MXenes. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 10006–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Lu, Y.K.; Zhu, T.; Chang, S.C.; Wang, W. CoFe2O4/N-doped reduced graphene oxide aerogels for high-performance microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhu, T.; Chang, S.C.; Lu, Y.; Mi, W.B.; Wang, W., 3rd. Nest-like architecture of core-shell CoFe2O4@1T/2H-MoS2 composites with tunable microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 11252–11264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.L.; Zhao, H.Q.; Ji, G.B.; Du, Y.W. Achieving excellent bandwidth absorption by a mirror growth process of magnetic porous polyhedron structures. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.; Singh, K.; Ohlan, A.; Singh, D.P.; Dhawan, S.K. Thermal, dielectric and microwave absorption properties of polyaniline-CoFe2O4 nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, J.J.; Wang, Z.J.; Li, Y.B.; He, X.D.; Yuan, Y. Microwave absorption enhancement of porous C@CoFe2O4 nanocomposites derived from eggshell membrane. Carbon 2019, 143, 507–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Chang, S.C.; Song, Y.F.; Lahoubi, M.; Wang, W. PVP-encapsulated CoFe2O4/rGO composites with controllable electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamastra, F.R.; Nanni, F.; Camilli, L.; Matassa, R.; Carbone, M.; Gusmano, G. Morphology and structure of electrospun CoFe2O4/multi-wall carbon nanotubes composite nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.; Afghahi, S.; Jafarian, M.; Stergiou, C.A. Multicomponent nanocomposites with carbonyl Fe-CoFe2O4-CaTiO3 fillers for microwave absorption applications. Mater. Des. 2016, 112, 462–468. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.L.; Jiao, Q.Z.; Hu, J.; Li, J.J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.S.; Wu, Q. Vapor diffusion synthesis of rugby-shaped CoFe2O4/graphene composites as absorbing materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 630, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.T.; Tan, R.; Yao, Z.J.; Li, Z. Preparation of CoFe2O4 hollow spheres with carbon sphere templates and their wave absorption performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 244, 122697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golchinvafa, S.; Masoudpanah, S.M.; Jazirehpour, M. Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of FeCo/CoFe2O4 composite powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 809, 151746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.X.; Huo, S.; Chen, W.; Dai, W.; Zhang, B. One-step preparation of CoFe2O4/FeCo/graphite nanosheets hybrid composites with tunable microwave absorption performance. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 12353–12363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdikhah, V.; Ataie, A.; Babaei, A.; Sheibani, S.; Yang, C.W.O.; Abkenar, S.K. CoFe2O4/Fe magnetic nanocomposites: Exchange coupling behavior and microwave absorbing property. Ceram. Int. 2020, 21, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.Q.; Wang, B.B.; Jia, Z.R.; Wu, H.J.; Lan, D.; Huang, Z.Y.; Feng, A.L.; Ma, M.L.; Wu, G.L. A review of metal-oxide-related microwave absorbing materials from the dimension and morphology perspective. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 10961–10984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.L.; Guo, Y.H.; Wu, G.L.; Ji, G.; Zhao, Y. Interface polarization strategy to solve electromagnetic wave interference issue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5660–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Hamidinejad, M.; Zhao, C.X.; Li, R.S.; Wang, S.; Kazemi, Y.; Park, C.B. A versatile foaming platform to fabricate polymer/carbon composites with high dielectric permittivity and ultra-low dielectric loss. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Q.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, H.L.; Ji, G.B.; Du, Y.W. A novel hierarchically porous magnetic carbon derived from biomass for strong lightweight microwave absorption. Carbon 2019, 142, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Han, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lv, H.; Lou, Z. Multi-interface self-assembling on MXenes skeleton towards wideband electromagnetic dissipation. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 24, 100685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.D.; Han, H.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, C.; Lv, H.L.; Lou, Z.C. Silicon-coated fibrous network of carbon nanotube/iron towards stable and wideband electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 121, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.T.; Dong, T.; Zhang, S.J. Improved electrochemical performance in nanoengineered pomegranate-shaped Fe3O4/RGO nanohybrids anode material. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zeng, S.P.; Li, X.P.; Guo, X.Q.; Bai, Z.Y.; Fan, B.B.; Zhang, R. Flexible PVDF/carbon materials/Ni composite films maintaining strong electromagnetic shielding under cyclic microwave irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 2, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wu, X.M.; Luo, C.Y. Facile synthesis of Mn3O4 hollow polyhedron wrapped by multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a high-efficiency microwave absorber. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.S.; Zhu, J.J.; Wang, S.N.; Liu, Q.C.; Kong, X.K. Microwave absorption on a bare biomass derived holey silica-hybridized carbon absorbent. Carbon 2020, 161, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Long, C.; Yin, S.; Song, R.G.; Zhang, B.H.; Zhang, J.W.; He, D.P.; Cheng, Q. Graphene-based anisotropic polarization meta-filter. Mater. Des. 2021, 206, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, R.B. An electrical switch-driven flexible electromagnetic absorber. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.L.; Zhou, X.D.; Wu, G.L.; Kara, U.I.; Wang, X.G. Engineering defects in 2D g-C3N4 for wideband, efficient electromagnetic absorption at elevated temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 19710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yang, Z.H.; Wang, P.L.Y.; Ji, G.B.; Song, J.Z.; Zheng, L.R.; Zeng, H.B.; Xu, Z.C.J. A voltage-boosting strategy enabling a low-frequency, flexible electromagnetic wave absorption device. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Guo, X.Q.; Zhao, W.Y.; Deng, J.S.; Shao, G.; Fan, B.B.; Bai, Z.Y.; Zhang, R. Yolk-shell Ni@SnO2 composites with a designable interspace to improve the electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 28917–28925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.L.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, S.C.; Sun, T.J.; Zhang, B.; Cao, M.S.; Qin, Y. Wire-in-tube ZnO@carbon by molecular later deposition: Accurately tunable electromagnetic parameters and remarkable microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.T.; Zha, J.W.; You, Y.B.; Yan, X.B.; Dang, Z.M. Barium titanate@polyaniline core-shell semiconducting particles reinforced poly(vinylidene fluoride) flexible films with a percolation threshold and high dielectric constant. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 3325–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.L.; Gao, H.G.; Yang, M.W.H.; Liu, P.; Zhu, H.W. Shape anisotropic Fe3O4 nanotubes for efficient microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, R.; Chen, B.B.; Li, H.G.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Song, L.X. MXene/Co3O4 composite material: Stable synthesis and its enhanced broadband microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 488, 921–930. [Google Scholar]
- Yousuf, M.A.; Baig, M.M.; Khalli, N.F.A.; Khan, M.A.; Abound, M.F.A.; Shakir, I.; Warsi, M.F. The impact of yttrium cations (Y3+) on structural, spectral and dielectric properties of spinel manganese ferrite nanoparticle. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 10936–10942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Che, R.C. Hollow porous Fe2O3 microspheres wrapped by reduced graphene oxides with high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 36, 11167–11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wu, X.M.; Zhang, W.Z.; Luo, C.Y.; Liu, P.B. Facile design of 3D hierarchical NiFe2O4/N-GN/ZnO composite as a high performance electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.N.; Liu, C.; Xu, D.M.; Liu, J.R.; Liu, W.; Shao, Q.; Guo, Z.H. Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of Three-Dimensional Porous Fe3O4/C Composite Flowers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12471–12480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.T.; Hou, Y.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, L.C. Synthesis of Hierarchical ZnFe2O4@SiO2@RGO Core−Shell Microspheres for Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14103–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.M.; Yang, R.L.; Mo, Z.C.; Lu, D.W.; Yang, L.L.; He, Z.F.; Zhu, H.; Tang, Z.K.; Gui, X.C. Nitrogen-doped and Fe-filled CNTs/NiCo2O4 porous sponge with tunable microwave absorption performance. Carbon 2019, 153, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.L.; Zeng, M.; Yin, Y.H.; Zeng, X.J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, W.K.; Wang, Y.; An, J.; He, J.; et al. MWCNTs as Conductive Network for Monodispersed Fe3O4 Nanoparticles to Enhance the Wave Absorption Performances. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 20, 1700543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Jiang, J.T.; Xu, C.Y.; Yuan, Y.; Gong, Y.X.; Zhen, L. Co7Fe3 and Co7Fe3@SiO2 Nanospheres with Tunable Diameters for High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21933–21941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Song, Y.M.; Xiong, J.; Pan, Z.B.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, R.; Yang, H.W.; Lu, W. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of nanoporous Fe3O4@ carbon composites derived from metal-organic frameworks. Carbon 2019, 142, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Thickness (mm) | Filler Ratio (wt%) | Mini. Reflection Loss Value (dB) | Effective Absorption Region (GHz) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiFe2O4 | 2.7 | 20 | −70.7 | 3.5 | [49] |
| Fe3O4/C | 2.1 | 50 | −54.6 | 6.0 | [50] |
| G–4 | 1.5 | 50 | −43.9 | 6.0 | [51] |
| NiCo2O4/CNTs | 4.0 | 30 | −45.1 | 4.0 | [52] |
| Fe3O4/MWCNTs | 2.0 | 50 | −63.6 | 3.0 | [53] |
| Co7Fe3 | 2.0 | 20 | −78.4 | 6.7 | [54] |
| Fe3O4@NPC | 3.0 | 30 | −65.5 | 4.5 | [55] |
| Chain-like-Fe3O4 | 1.8 | 30 wt% | −25.5 | 6.4 GHz | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Dong, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Li, D.; Cai, M.; Zhou, K. A General Way to Fabricate Chain-like Ferrite with Ultralow Conductive Percolation Threshold and Wideband Absorbing Ability. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091603
Chen C, Dong H, Wang J, Chen W, Li D, Cai M, Zhou K. A General Way to Fabricate Chain-like Ferrite with Ultralow Conductive Percolation Threshold and Wideband Absorbing Ability. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(9):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091603
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Cong, Haitao Dong, Jiayuan Wang, Wen Chen, Denghui Li, Meng Cai, and Kun Zhou. 2022. "A General Way to Fabricate Chain-like Ferrite with Ultralow Conductive Percolation Threshold and Wideband Absorbing Ability" Nanomaterials 12, no. 9: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091603
APA StyleChen, C., Dong, H., Wang, J., Chen, W., Li, D., Cai, M., & Zhou, K. (2022). A General Way to Fabricate Chain-like Ferrite with Ultralow Conductive Percolation Threshold and Wideband Absorbing Ability. Nanomaterials, 12(9), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091603





