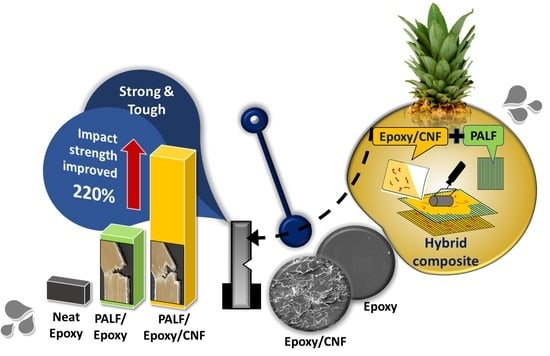
Synergistic Toughening of Epoxy Composite with Cellulose Nanofiber and Continuous Pineapple Leaf Fiber as Sustainable Reinforcements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of CNF Epoxy Composite (CNF-EP)
2.3. Preparation of PALF-Reinforced Epoxy Composite (PALF-EP)
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Electron Microscopy (EM)
2.4.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4.3. Mechanical Characterization
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Some Characteristics of CNF and PALF
3.2. Structural Analysis of the Matrix with DSC
3.3. Flexural Properties
3.4. Impact Property
3.5. Fractography
3.6. Possible Toughening Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ishii, J.; Osuga, M.; Okada, T.; Miyazaki, H.; Koseki, M.; Tanikoshi, K. Reduction of CO2 Emissions for Automotive Systems. Hitachi Revi 2008, 8, 184–191. [Google Scholar]
- Dufluo, J.R.; Deng, Y.; Acker, K.V.; Dewulf, W. Do fiber-reinforced polymer composites provide environmentally benign alternatives? A life-cycle-assessment-based study. MRS Bulletin 2012, 37, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikaya, E.; Çallioğlu, H.; Demirel, H. Production of epoxy composites reinforced by different natural fibers and their mechanical properties. Compos. B. Eng. 2019, 167, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poilâne, C.; Cherif, Z.E.; Richard, F.; Vivet, A.; Ben Doudou, B.; Chen, J. Polymer reinforced by flax fibres as a viscoelastoplastic material. Compos. Struct. 2014, 112, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.-P.; Sain, M. Progress Report on Natural Fiber Reinforced Composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathijsen, D. The renaissance of flax fibers. Reinf. Plast. 2018, 62, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vegt, O.M.; Haije, W.G. Comparative Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Composite Materials; Energy Research Foundation (ECN): Sint Maartensvlotbrug, The Netherlands, 1997; Volume 29, pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Boland, C.S.; De Kleine, R.; Keoleian, G.A.; Lee, E.C.; Kim, H.C.; Wallington, T.J. Life Cycle Impacts of Natural Fiber Composites for Automotive Applications: Effects of Renewable Energy Content and Lightweighting. J. Ind. Ecol. 2016, 20, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangmesh, B.; Patil, N.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Gowrishankar, T.P.; Selvakumar, K.K.; Jyothi, M.S.; Jyothilakshmi, R.; Kumar, S. Development of sustainable alternative materials for the construction of green buildings using agricultural residues: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deputy Permanent Secretary of the Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives Sits at the Head of the Table for the Meeting of the National Pineapple Policy and Development Committee to Consider the Pineapple Development Plan for the Years 2023–2027. Office of Agricultural Economics. 26 May 2022. Available online: https://shorturl.at/ksEFR (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Kengkhetkit, N.; Amornsakchai, T. Utilisation of pineapple leaf waste for plastic reinforcement: A novel extraction method for short pineapple leaf fiber. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2012, 40, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksman, K. High Quality Flax Fibre Composites Manufactured by the Resin Transfer Moulding Process. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2016, 20, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Drzal, L.T.; Misra, M.; Hinrichsen, G. A Review on Pineapple Leaf Fibers, Sisal Fibers and Their Biocomposites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2004, 289, 955–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Dhakal, H.N.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Barouni, A.; Zahari, R. Enhancement of impact toughness and damage behaviour of natural fibre reinforced composites and their hybrids through novel improvement techniques: A critical review. Compos. Struct. 2021, 259, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surajarusarn, B.; Hajjar-Garreau, S.; Schrodj, G.; Mougin, K.; Amornsakchai, T. Comparative study of pineapple leaf microfiber and aramid fiber reinforced natural rubbers using dynamic mechanical analysis. Polym. Test. 2020, 82, 106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisittanawat, U.; Thanawan, S.; Amornsakchai, T. Remarkable improvement of failure strain of preferentially aligned short pineapple leaf fiber reinforced nitrile rubber composites with silica hybridization. Polymer Testing 2014, 38, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nopparut, A.; Amornsakchai, T. Influence of pineapple leaf fiber and it’s surface treatment on molecular orientation in, and mechanical properties of, injection molded nylon composites. Polymer Testing 2016, 52, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyasart, K.; Chaiyut, N.; Amornsakchai, T.; Santawitee, O. Effect of Surface Treatment on the Properties of Pineapple Leaf Fibers Reinforced Polyamide 6 Composites. Energy Procedia 2014, 56, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, J.; Jain, S.; Sinha, S. Characterization and thermal kinetic analysis of pineapple leaf fibers and their reinforcement in epoxy. J. Elastomers Plast. 2018, 51, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Teramoto, Y. Recent Advances in Nanocellulose Composites with Polymers: A Guide for Choosing Partners and How to Incorporate Them. Polymers 2018, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Seo, J.; Kang, Y.-H.; Kim, W.; Kang, T. State-of-the-Art of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Optimal Method for their Dispersion for Construction-Related Applications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Aitomäki, Y.; Berglund, L.A.; Oksman, K.; Bismarck, A. On the use of nanocellulose as reinforcement in polymer matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 105, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Shim, B.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Min, S.-K.; Jang, D.; Abas, Z.; Kim, J. Review of nanocellulose for sustainable future materials. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 2, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudich, A.; Sapru, S.; Shoseyov, O. Biocompatible, Resilient, and Tough Nanocellulose Tunable Hydrogels. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, F.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Haagenson, D.; Wiesenborn, D.P. Cellulose nanocrystals vs. cellulose nanofibrils: A comparative study on their microstructures and effects as polymer reinforcing agents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 2999–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; McGinnis, S.; Sydnor, C.; Wong, A.; Renneckar, S. Nanocellulose Life Cycle Assessment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Paridah, M.T.; Abdan, K.; Ibrahim, N.A. Effect of oil palm nano filler on mechanical and morphological properties of kenaf reinforced epoxy composites. Constr Build Mater. 2016, 123, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Safwan, A.; Sanyang, M.L.; Mohammad, F.; Pervaiz, M.; Jawaid, M.; Alothman, O.Y.; Sain, M. Thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of cellulose nanofibers reinforced epoxy composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, A.; Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S.; Fischer, S. Fully bio-based agro-waste soy stem fiber reinforced bio-epoxy composites for lightweight structural applications: Influence of surface modification techniques. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.; Low, I.M. Characterization of epoxy hybrid composites filled with cellulose fibers and nano-SiC. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, E222–E232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, B.E.B.; Chiromito, E.M.S.; Carvalho, A.J.F.; Arenal, R.; Tarpani, J.R. TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers as interfacial strengthener in continuous-fiber reinforced polymer composites. Mater. Des. 2017, 133, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Paridah, M.T.; Abdan, K.; Ibrahim, N.A. Dynamic mechanical properties of oil palm nano filler/kenaf/epoxy hybrid nanocomposites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Weder, C. Cellulose whisker/epoxy resin nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surajarusarn, B.; Traiperm, P.; Amornsakcha, T. Revisiting the Morphology, Microstructure, and Properties of Cellulose Fiber from Pineapple Leaf so as to Expand Its Utilization. Sains Malaysiana 2019, 48, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Galland, S.; Johansson, M.; Plummer, C.J.G.; Berglund, L.A. Cellulose nanofiber network for moisture stable, strong and ductile biocomposites and increased epoxy curing rate. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 63, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayan, J.S.; Saritha, A.; Deeraj, B.D.S.; Joseph, K. Triblock copolymer grafted Graphene oxide as nanofiller for toughening of epoxy resin. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 248, 122930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.P.B.; dos Reis, J.M.L. A Thermomechanical and Adhesion Analysis of Epoxy/Al2O3 Nanocomposites. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanawijan, W.; Amornsakchai, T.; Amornsakchai, P.; Petiraksakul, P. Influence of compatibilizer on notched impact strength and fractography of HDPE-organoclay composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.; Pappu, A.; Tyagi, P.; Patidar, R.; Khan, A.; Mishra, A.; Gupta, M.K.; Thakur, V.K. Next-generation high-performance sustainable hybrid composite materials from silica-rich granite waste particulates and jute textile fibres in epoxy resin. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2022, 177, 114527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustina, E.; Goak, J.C.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.C.; Seo, Y.; Lee, N. Effect of Graphite Nanoplatelet Size and Dispersion on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy-Based Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.J. Effect of Ambient Plasma Treatments on Thermal Conductivity and Fracture Toughness of Boron Nitride Nanosheets/Epoxy Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2022, 13, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.L. Discontinuous-Fibre Reinforced Composites, 1st ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2017; pp. 1–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Composite System | Tg Onset | Tg (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| 0CNF | 47 | 55 |
| 1CNF | 43 | 49 |
| 3CNF | 46 | 52 |
| 5CNF | 51 | 55 |
| 0CNF/PALF | 56 | 59 |
| 1CNF/PALF | 54 | 59 |
| 3CNF/PALF | 53 | 56 |
| 5CNF/PALF | 56 | 59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klinthoopthamrong, N.; Thanawan, S.; Schrodj, G.; Mougin, K.; Goh, K.-L.; Amornsakchai, T. Synergistic Toughening of Epoxy Composite with Cellulose Nanofiber and Continuous Pineapple Leaf Fiber as Sustainable Reinforcements. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111703
Klinthoopthamrong N, Thanawan S, Schrodj G, Mougin K, Goh K-L, Amornsakchai T. Synergistic Toughening of Epoxy Composite with Cellulose Nanofiber and Continuous Pineapple Leaf Fiber as Sustainable Reinforcements. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(11):1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111703
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlinthoopthamrong, Nichapa, Sombat Thanawan, Gautier Schrodj, Karine Mougin, Kheng-Lim Goh, and Taweechai Amornsakchai. 2023. "Synergistic Toughening of Epoxy Composite with Cellulose Nanofiber and Continuous Pineapple Leaf Fiber as Sustainable Reinforcements" Nanomaterials 13, no. 11: 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111703
APA StyleKlinthoopthamrong, N., Thanawan, S., Schrodj, G., Mougin, K., Goh, K.-L., & Amornsakchai, T. (2023). Synergistic Toughening of Epoxy Composite with Cellulose Nanofiber and Continuous Pineapple Leaf Fiber as Sustainable Reinforcements. Nanomaterials, 13(11), 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111703