The True Nature of Tricalcium Phosphate Used as Food Additive (E341(iii))
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.3. Raman Spectroscopy
2.4. Solid State 31P Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
2.5. Infrared Spectroscopy
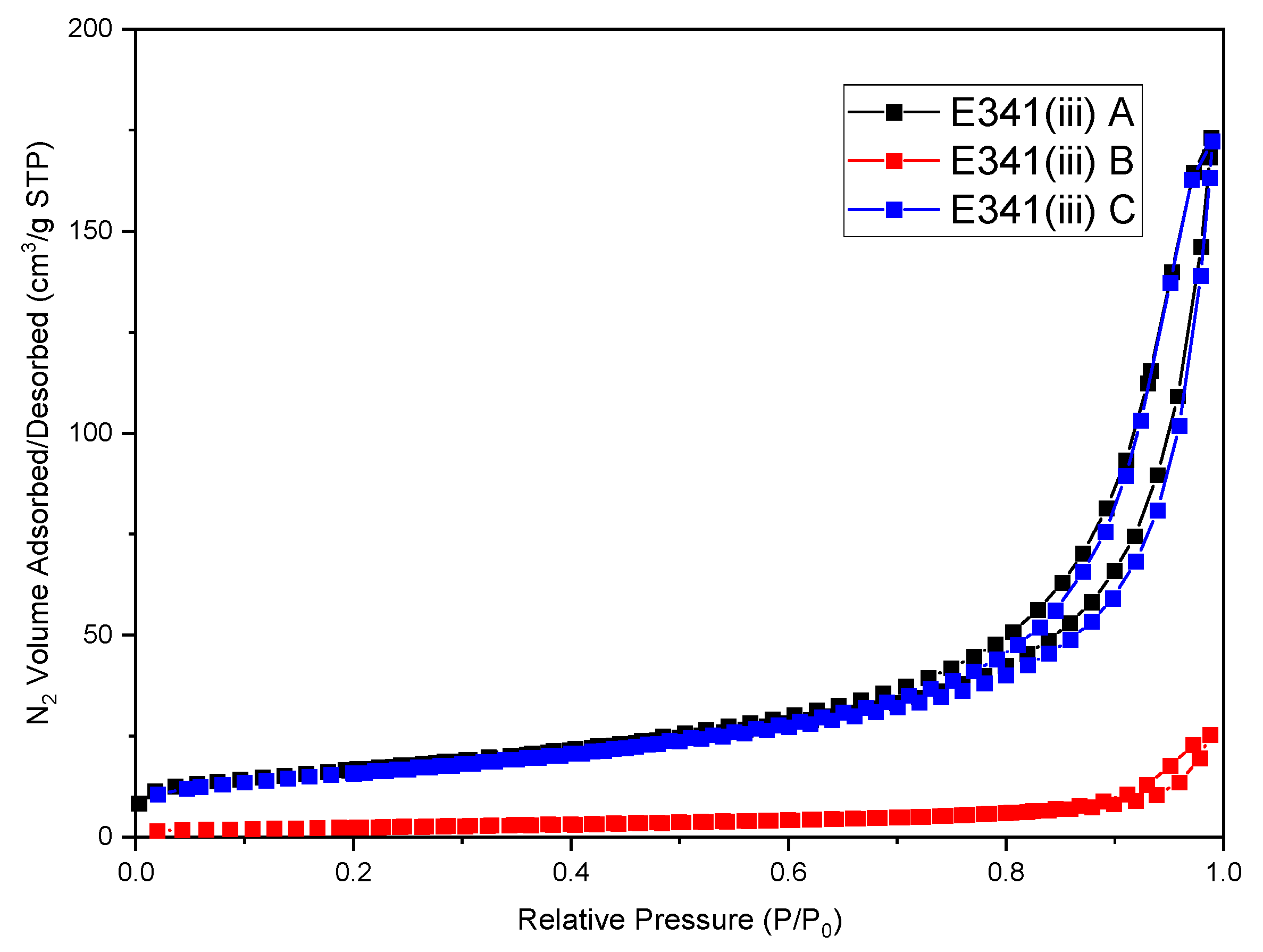
2.6. Specific Surface Determination
2.7. Pycnometry
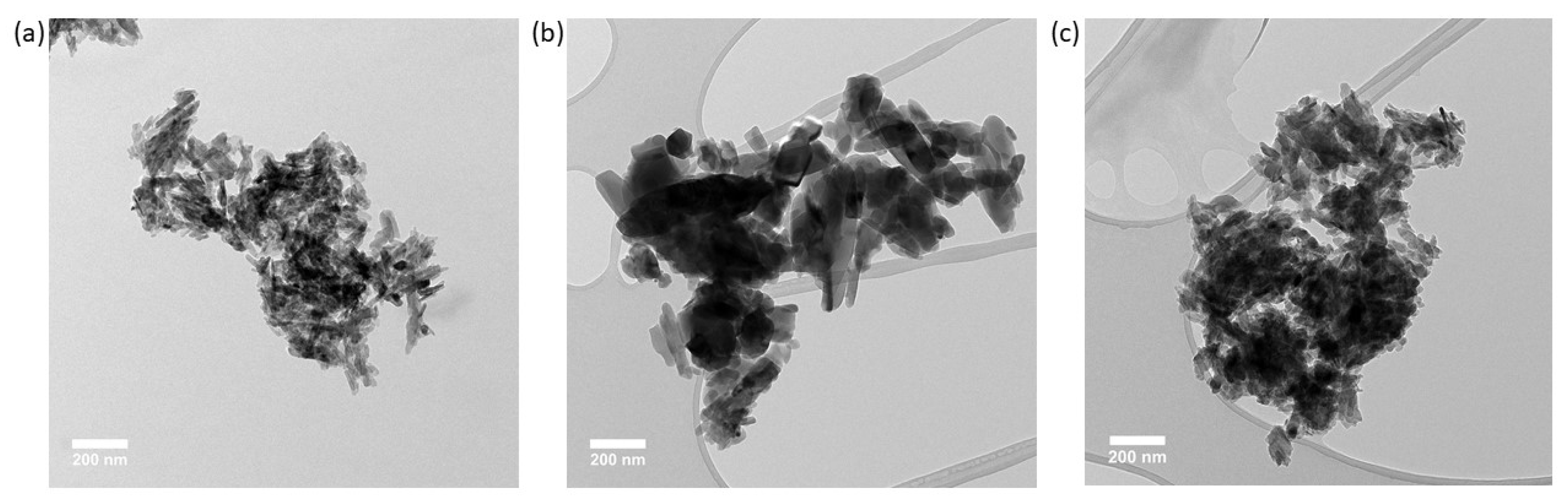
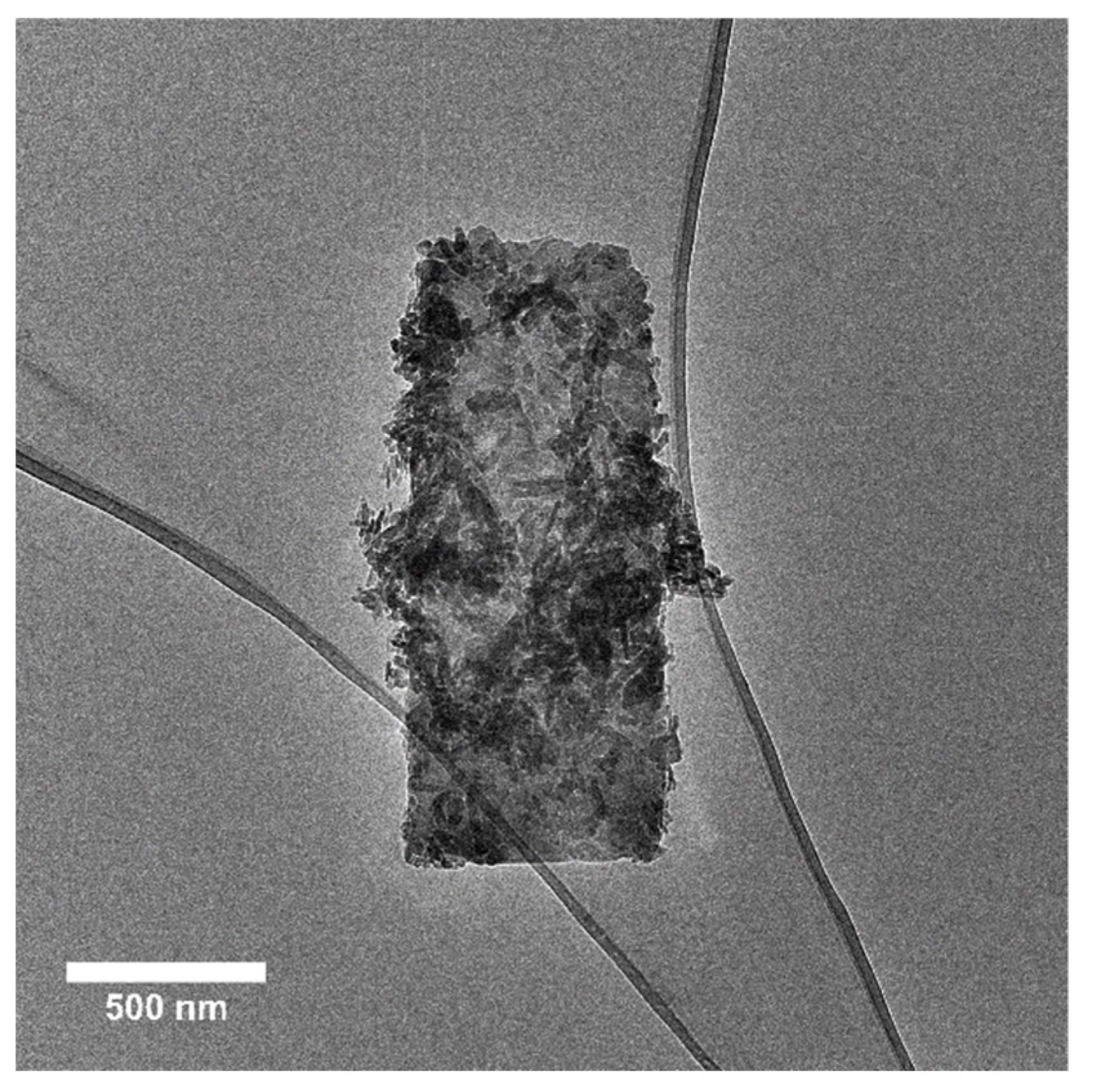
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.9. Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-AES)
2.10. Dissolution Determination
2.11. Granulometry
2.12. Zeta-Potential Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Pristine E341(iii) Food Additive
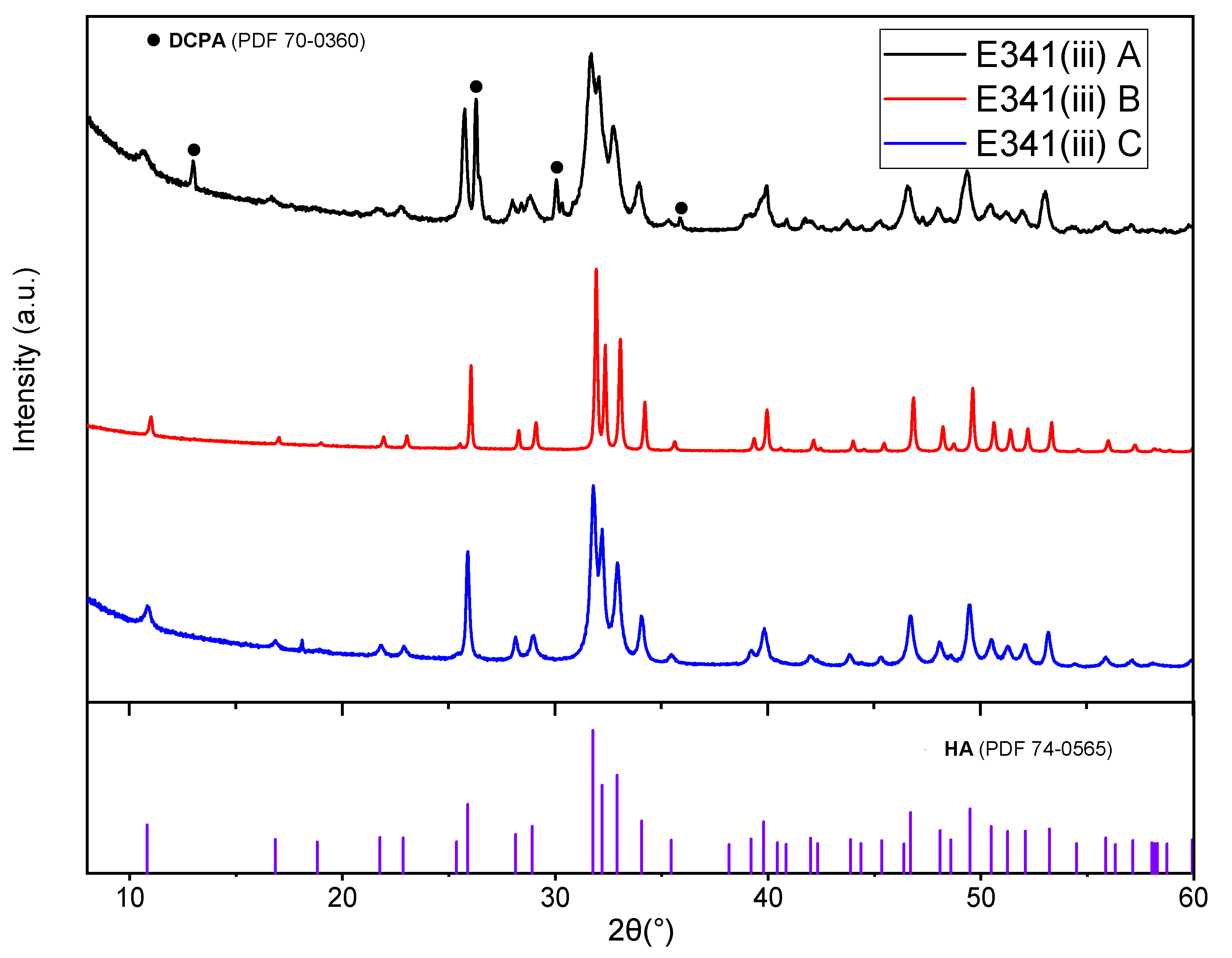
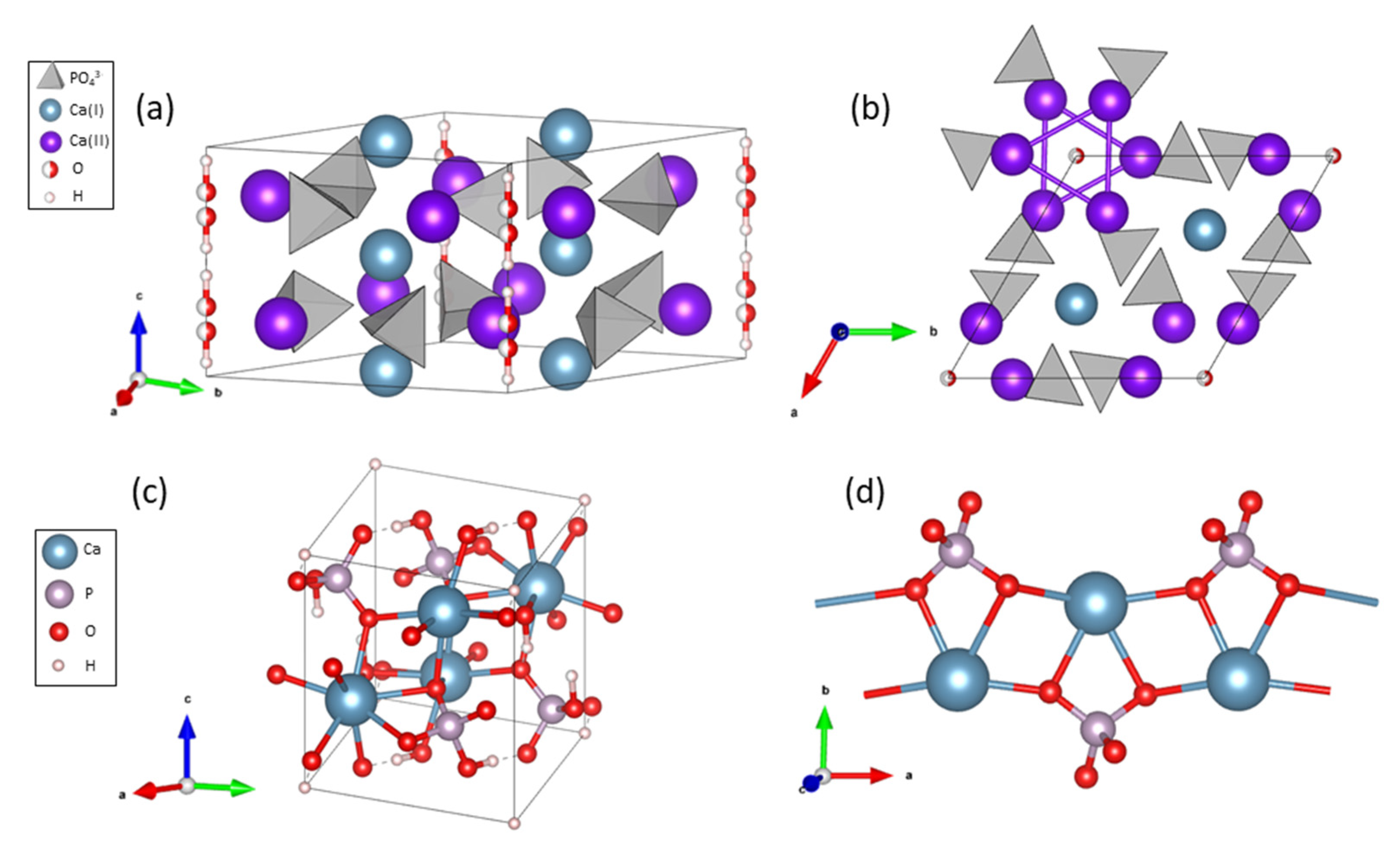
3.1.1. X-ray Diffraction
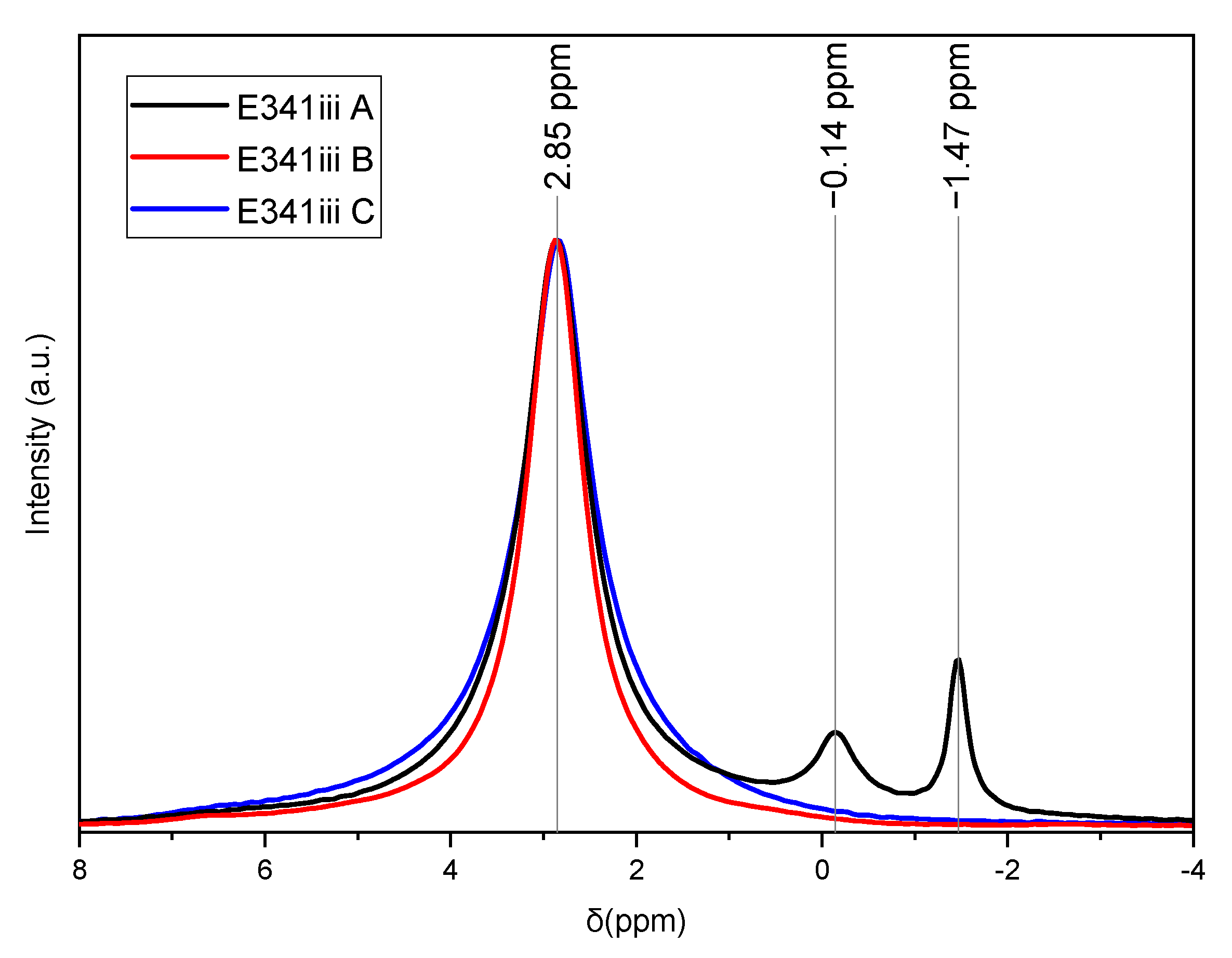
3.1.2. Solid State 31P Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
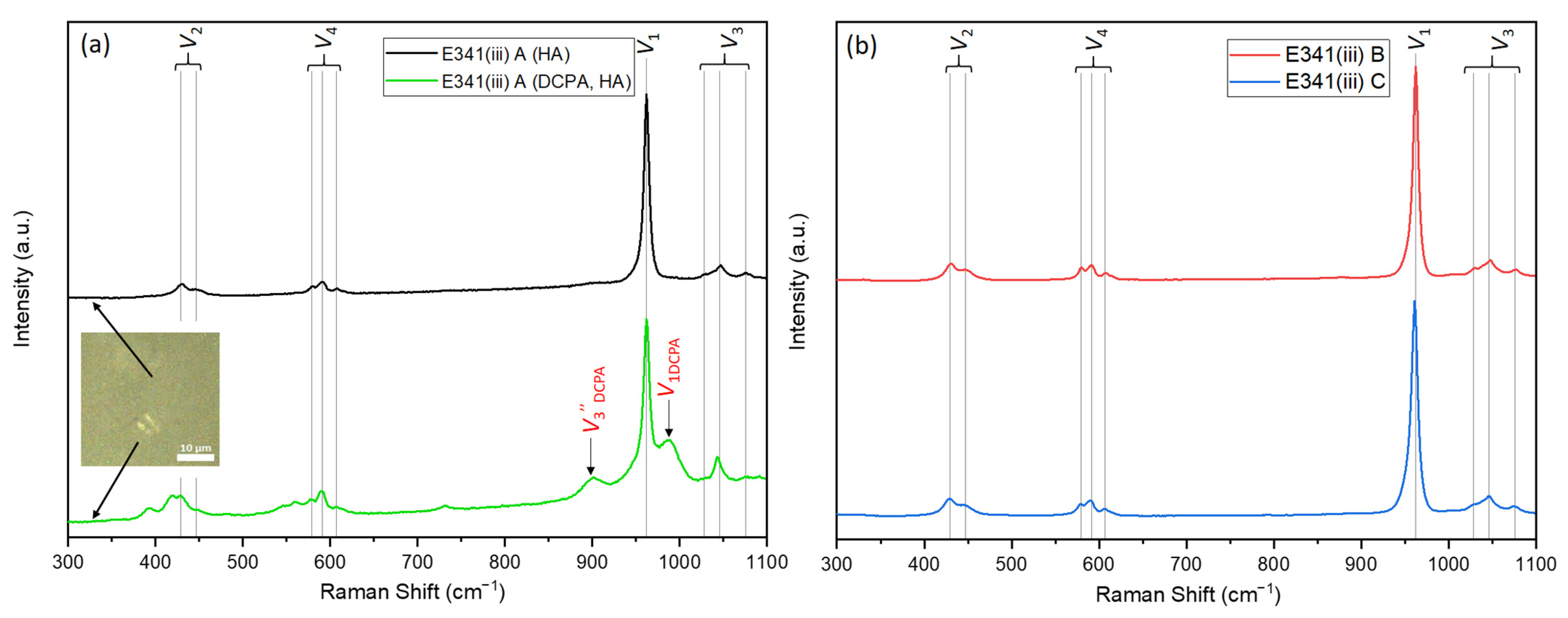
3.1.3. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy
3.1.4. Ca/P Molar Ratio Determined by ICP-AES
3.2. Physicochemical Characteristics (Density and Specific Surface Area) of E341(iii) Powders
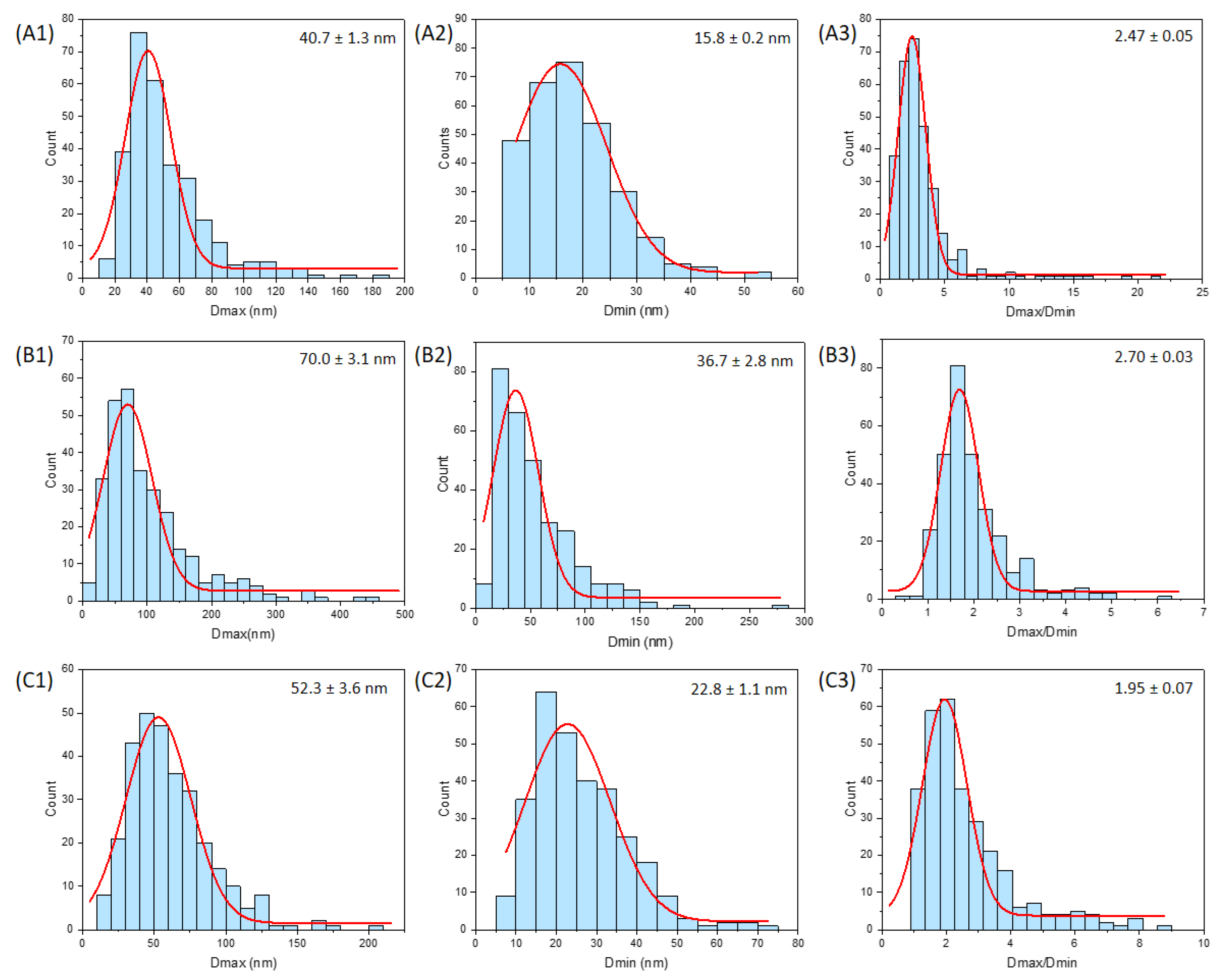
3.3. Nanoparticle Size and Shape from Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.4. Solubility as a Function of pH
3.5. Agglomerates Size
3.6. Surface Charge in Aqueous Solution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joint Research Centre (European Commission); Rauscher, H.; Roebben, G.; Mech, A.; Gibson, N.; Kestens, V.; Linsinger, T.P.J.; Riego Sintes, J. An Overview of Concepts and Terms Used in the European Commission’s Definition of Nanomaterial; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019; ISBN 978-92-79-99660-3. [Google Scholar]
- Yadwade, R.; Gharpure, S.; Ankamwar, B. Nanotechnology in Cosmetics Pros and Cons. Nano Express 2021, 2, 022003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorlander, C.W.; Kooi, M.W.; Oomen, A.G.; Park, M.V.; Vandebriel, R.J.; Geertsma, R.E. Horizon Scan of Nanomedicinal Products. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Qu, H.; Manbachi, A.; Butt, H.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Skorobogatiy, M.; Khademhosseini, A.; Yun, S.H. Nanotechnology in Textiles. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3042–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Deng, H.; Hwang, H. The Current Application of Nanotechnology in Food and Agriculture. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, A.; Ranjan, S.; Dasgupta, N.; Ramalingam, C. Nanomaterials in Food and Agriculture: An Overview on Their Safety Concerns and Regulatory Issues. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlicek, A.; Part, F.; Rose, G.; Praetorius, A.; Miernicki, M.; Gazsó, A.; Huber-Humer, M. A European Nano-Registry as a Reliable Database for Quantitative Risk Assessment of Nanomaterials? A Comparison of National Approaches. NanoImpact 2021, 21, 100276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoepf, J.J.; Bi, Y.; Kidd, J.; Herckes, P.; Hristovski, K.; Westerhoff, P. Detection and Dissolution of Needle-like Hydroxyapatite Nanomaterials in Infant Formula. NanoImpact 2017, 5, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramis, J.M.; Coelho, C.C.; Córdoba, A.; Quadros, P.A.; Monjo, M. Safety Assessment of Nano-Hydroxyapatite as an Oral Care Ingredient According to the EU Cosmetics Regulation. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younes, M.; Aquilina, G.; Castle, L.; Engel, K.-H.; Fowler, P.; Fernandez, M.J.F.; Fürst, P.; Gürtler, R.; Husøy, T.; Mennes, W.; et al. Re-Evaluation of Phosphoric Acid–Phosphates–Di-, Tri- and Polyphosphates (E 338–341, E 343, E 450–452) as Food Additives and the Safety of Proposed Extension of Use. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Amorphous Calcium (Ortho)Phosphates. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4457–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Xiao, H. Is Nano Safe in Foods? Establishing the Factors Impacting the Gastrointestinal Fate and Toxicity of Organic and Inorganic Food-Grade Nanoparticles. NPJ Sci. Food 2017, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EFSA Scientific Committee; Bampidis, V.; Benford, D.; Bragard, C.; Halldorsson, T.; Hernández-Jerez, A.; Hougaard Bennekou, S.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Lambré, C.; Machera, K.; et al. Guidance on Risk Assessment of Nanomaterials to Be Applied in the Food and Feed Chain: Human and Animal Health. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 1–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufort, J.; Ségalen, L.; Gervais, C.; Brouder, C.; Balan, E. Modeling the Attenuated Total Reflectance Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectrum of Apatite. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2016, 43, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leinekugel-le-Cocq-Errien, A.Y.; Deniard, P.; Jobic, S.; Gautier, E.; Evain, M.; Aubin, V.; Bart, F. Structural Characterization of the Hollandite Host Lattice for the Confinement of Radioactive Cesium: Quantification of the Amorphous Phase Taking into Account the Incommensurate Modulated Character of the Crystallized Part. J. Solid State Chem. 2007, 180, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.C. Structure and Chemistry of the Apatites and Other Calcium Orthophosphates; Studies in Inorganic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 18, pp. 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Miquel, J.L.; Facchini, L.; Legrand, A.P.; Rey, C.; Lemaitre, J. Solid State NMR to Study Calcium Phosphate Ceramics. Colloids Surf. 1990, 45, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcock, C.J.; Gentile, P.; Hatton, P.V.; Miller, C.A. Rapid Mix Preparation of Bioinspired Nanoscale Hydroxyapatite for Biomedical Applications. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 120, e55343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrov, I.; Šoptrajanov, B.; Fuson, N.; Lawson, J.R. Infra-Red Investigation of Dicalcium Phosphates. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Spectrosc. 1967, 23, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleshko, N.; Boskey, A.; Mendelsohn, R. Novel Infrared Spectroscopic Method for the Determination of Crystallinity of Hydroxyapatite Minerals. Biophys. J. 1991, 60, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blakeslee, K.C.; Condrate, R.A., Sr. Vibrational Spectra of Hydrothermally Prepared Hydroxyapatites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1971, 54, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casciani, F.; Condrate, R.A. The Raman Spectrum of Monetite, CaHPO4. J. Solid State Chem. 1980, 34, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekmene, O.; Quillard, S.; Rouillon, T.; Bouler, J.-M.; Piot, M.; Gaucheron, F. Effects of PH and Ca/P Molar Ratio on the Quantity and Crystalline Structure of Calcium Phosphates Obtained from Aqueous Solutions. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2009, 89, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Chemicals Agency. Appendix for Nanoforms Applicable to the Guidance on Registration and Substance Identification; European Chemical Agency: Helsinki, Finland, 2022.
- Mostafa, N.Y. Characterization, Thermal Stability and Sintering of Hydroxyapatite Powders Prepared by Different Routes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 94, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresch, H.; Hodoroaba, V.-D.; Schmidt, A.; Rasmussen, K.; Rauscher, H. Counting Small Particles in Electron Microscopy Images—Proposal for Rules and Their Application in Practice. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrich, D.S.; Smith, M.A. Pharmaceutical Applications of Infrared Microspectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 1999, 34, 275–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.K.; Dybowska, A.; Berhanu, D.; Luoma, S.N.; Valsami-Jones, E. The Complexity of Nanoparticle Dissolution and Its Importance in Nanotoxicological Studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffini, A.; Sprio, S.; Preti, L.; Tampieri, A. Synthesis of Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite via Controlled Hydrothermal Route. In Biomaterial-Supported Tissue Reconstruction or Regeneration; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lecloux, A.J.; Atluri, R.; Kolen’ko, Y.V.; Deepak, F.L. Discussion about the Use of the Volume Specific Surface Area (VSSA) as a Criterion to Identify Nanomaterials According to the EU Definition. Part Two: Experimental Approach. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14952–14966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choki, K.; Li, S.; Ye, A.; Jameson, G.B.; Singh, H. Fate of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles during Dynamic in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion: The Impact of Milk as a Matrix. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 2760–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, E.; Roblegg, E. Models for Oral Uptake of Nanoparticles in Consumer Products. Toxicology 2012, 291, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tercinier, L.; Ye, A.; Anema, S.; Singh, A.; Singh, H. Adsorption of Milk Proteins on to Calcium Phosphate Particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 394, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




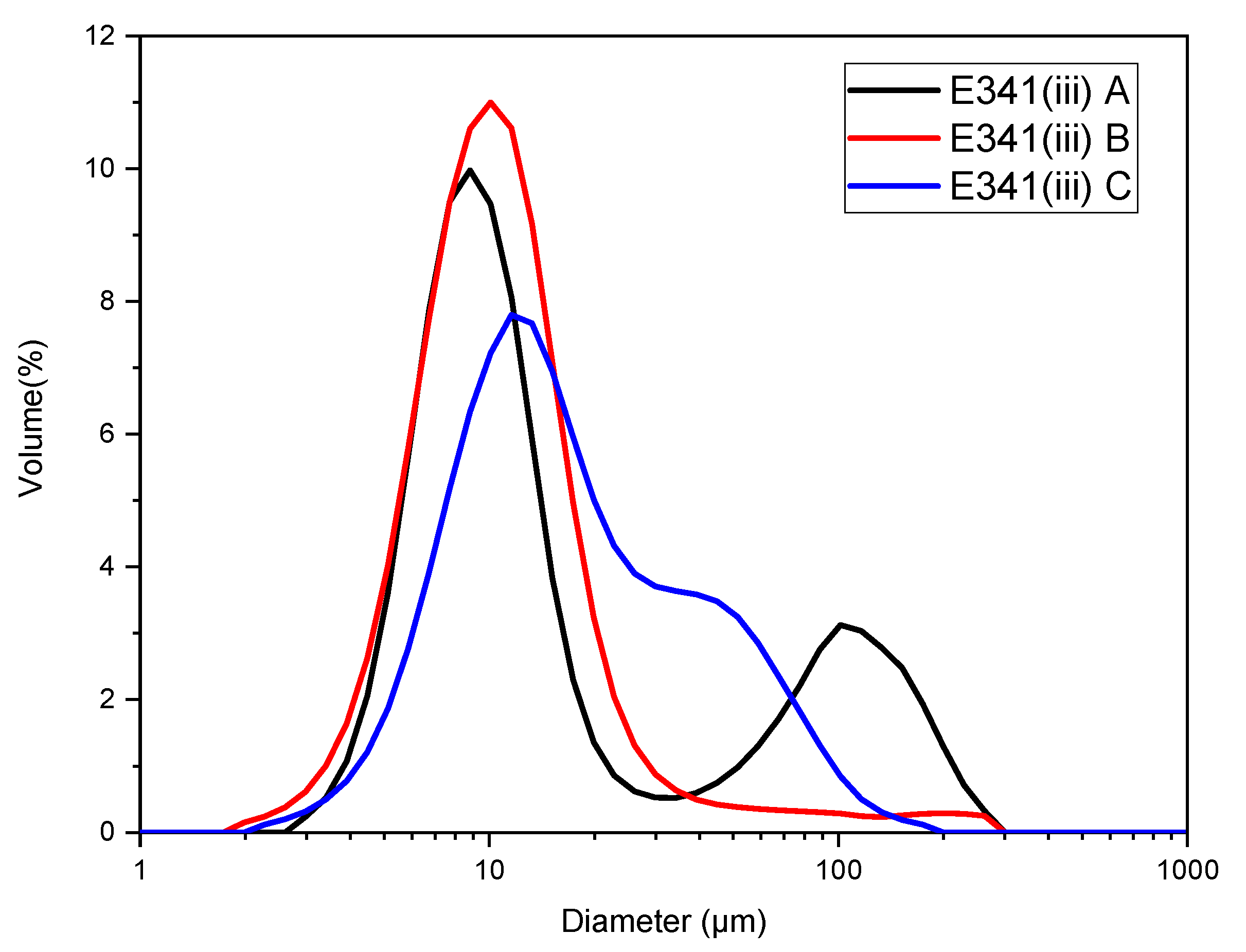
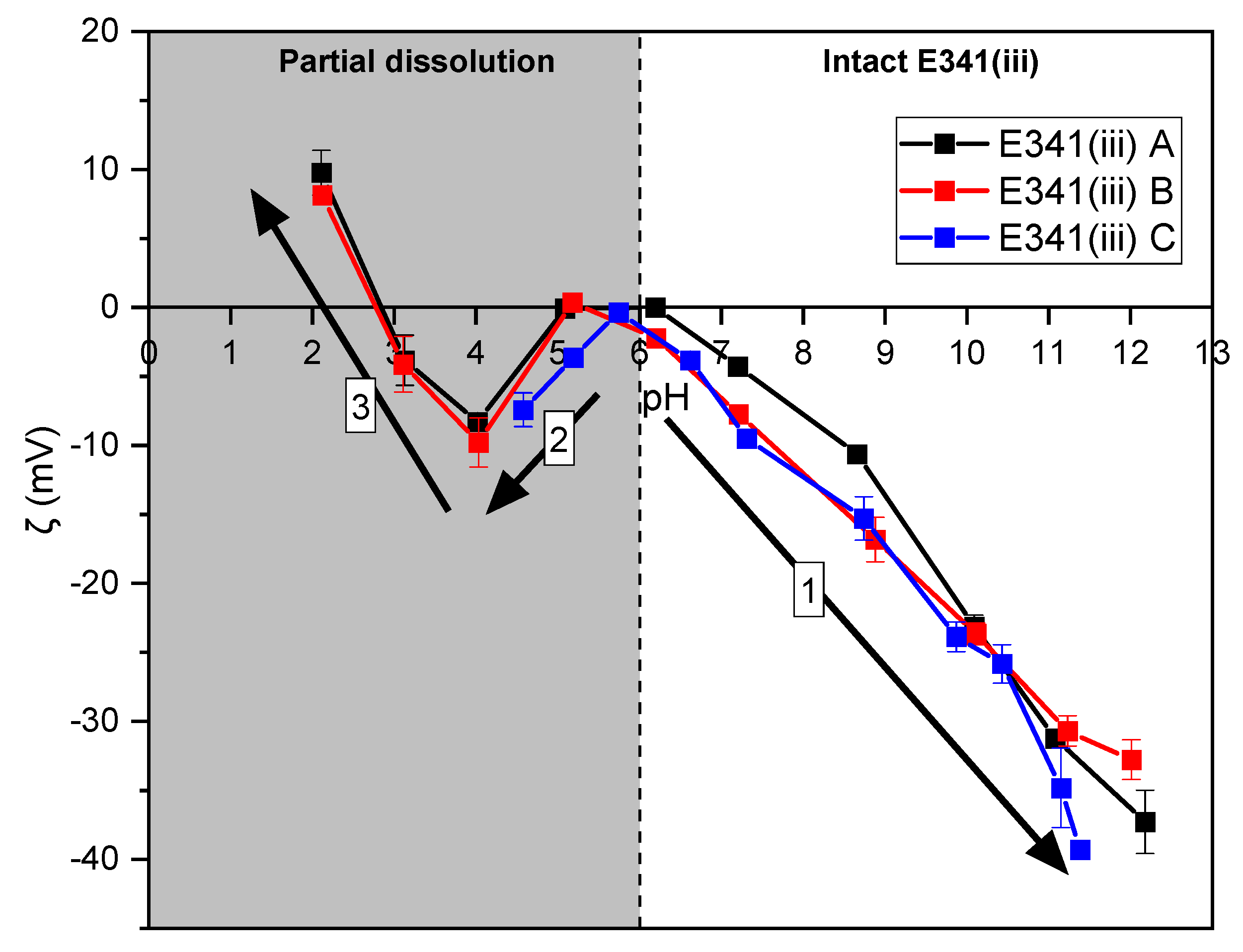
| Sample | Ca/P (Atomic) | Ca/P (Mass) |
|---|---|---|
| E341(iii) A | 1.52 ± 0.02 | 1.97 ± 0.03 |
| E341(iii) B | 1.71 ± 0.02 | 2.21 ± 0.03 |
| E341(iii) C | 1.71 ± 0.03 | 2.21 ± 0.04 |
| Sample | Specific Surface Area Sw (m2/g) | CBET (N2) | (g/cm3) | VSSA (m2/cm3) | dBET,App (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E341(iii) A | 58 | 229 | 2.9 | 166 | 35 |
| E341(iii) B | 9 | 113 | 3.0 | 27 | 220 |
| E341(iii) C | 60 | 150 | 2.9 | 178 | 35 |
| Parameter | E341(iii) A | E341(iii) B | E341(iii) C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dmax | Average (nm) | 52 ± 26 | 102 ± 73 | 62 ± 29 |
| Median (nm) | 44 | 81 | 56 | |
| Q1 (nm)–Q3 (nm) | 33–62 | 52–128 | 40–77 | |
| N (D < 100 nm) (%) | 94 | 61 | 90 | |
| Dmin | Average (nm) | 18 ± 8 | 54 ± 35 | 26 ± 12 |
| Median (nm) | 18 | 43 | 23 | |
| Q1 (nm)–Q3 (nm) | 12–23 | 28–69 | 18–33 | |
| N (D < 100 nm) (%) | 100 | 89 | 100 | |
| Dmax/Dmin | Average | 3.3 ± 2.7 | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 2.6 ± 1.4 |
| Median | 2.8 | 1.8 | 2.2 | |
| Q1–Q3 | 1.9–3.7 | 1.5–2.3 | 1.6–3.1 | |
| Associated shape | Needle-like | Pseudo-spherical | Rod |
| Parameter | E341(iii) A | E341(iii) B | E341(iii) C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase | HA and DCPA | HA | HA |
| Average Dmax (nm); Dmin (nm) | 52 ± 26; 18 ± 8 | 102 ± 73; 54 ± 35 | 62 ± 29; 26 ± 12 |
| HA particle shape (Average Dmax/Dmin) | Needle-like (3.3 ± 2.7) | Pseudo-spherical (2.0 ± 0.8) | Rod (2.6 ± 1.4) |
| CBET (N2) | 229 | 113 | 150 |
| VSSA (m2/cm3) | 166 | 27 | 178 |
| Sw (m2/g) | 58 | 9 | 60 |
| Properties | Technique | E341(iii) Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical composition/identity |
| Ca and P elements with a Ca/P ratio consistent with hydroxyapatite |
| Shape |
| Different possible shapes (needle, rod, spherical) |
| Particle size and size distribution; Agglomeration/Aggregation state |
| Primary nanometric particles in mostly 10 µm agglomerates |
| Crystal form and phase |
| E341(iii) is mainly HA |
| Surface area (volume, mass specific) |
| Moderate (58–60 m2/g) to possibly low values (9 m2/g) |
| Surface chemistry |
| CBET constant dependent on surface affinity for N2 (function of size and particle shape) |
| Surface charge |
| Negatively charged above a pH of 6 |
| Degradation/ Dissolution/Solubility |
| Dissolution under a pH of 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Moussaoui, Y.; Terrisse, H.; Quillard, S.; Ropers, M.-H.; Humbert, B. The True Nature of Tricalcium Phosphate Used as Food Additive (E341(iii)). Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13121823
El Moussaoui Y, Terrisse H, Quillard S, Ropers M-H, Humbert B. The True Nature of Tricalcium Phosphate Used as Food Additive (E341(iii)). Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(12):1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13121823
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Moussaoui, Youssef, Hélène Terrisse, Sophie Quillard, Marie-Hélène Ropers, and Bernard Humbert. 2023. "The True Nature of Tricalcium Phosphate Used as Food Additive (E341(iii))" Nanomaterials 13, no. 12: 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13121823
APA StyleEl Moussaoui, Y., Terrisse, H., Quillard, S., Ropers, M.-H., & Humbert, B. (2023). The True Nature of Tricalcium Phosphate Used as Food Additive (E341(iii)). Nanomaterials, 13(12), 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13121823








