Effect of Nanoparticles on Rheological Properties of Water-Based Drilling Fluid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Preparation Method for NWBDF
2.2. Experimental Method
3. Results and Discussion
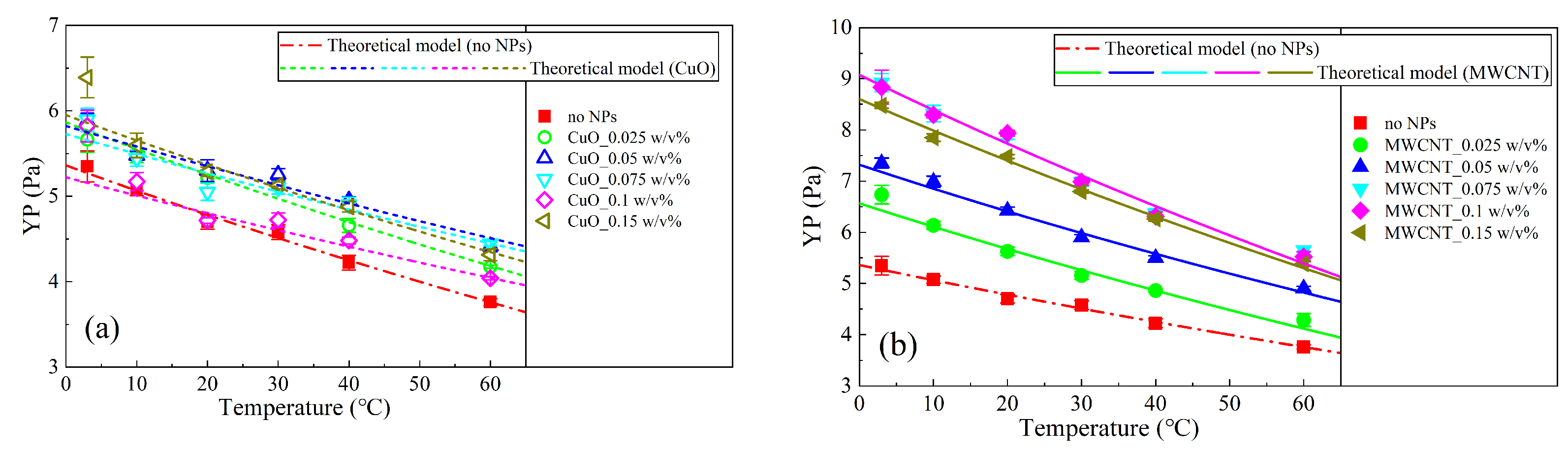
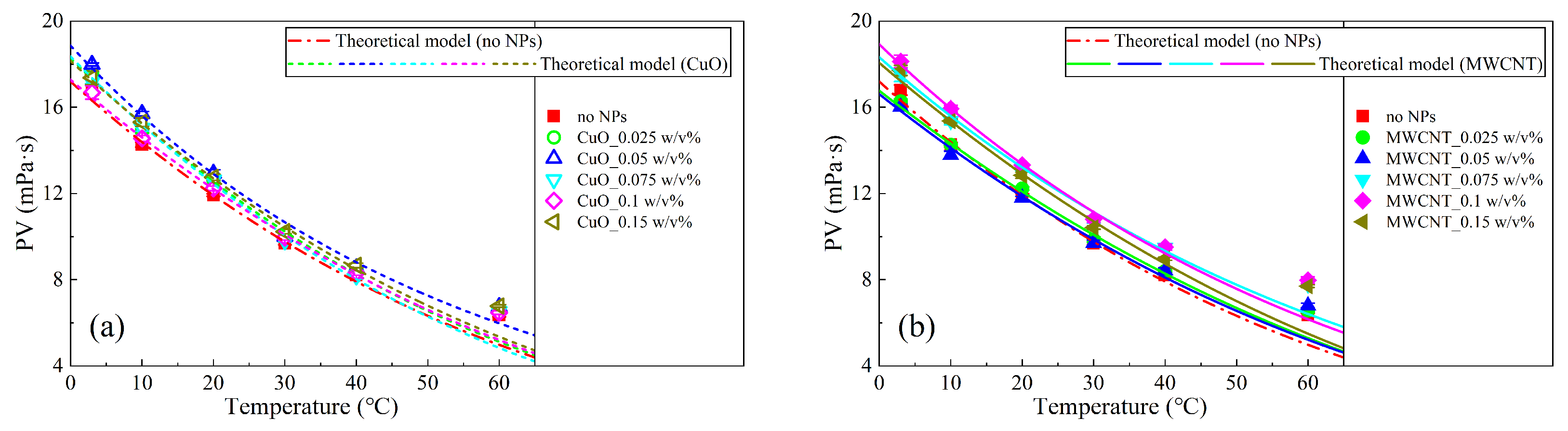
3.1. Analysis of the Rheological Behavior under Steady Shear
3.2. Analysis of the Rheological Behavior during a SAOS Experiment
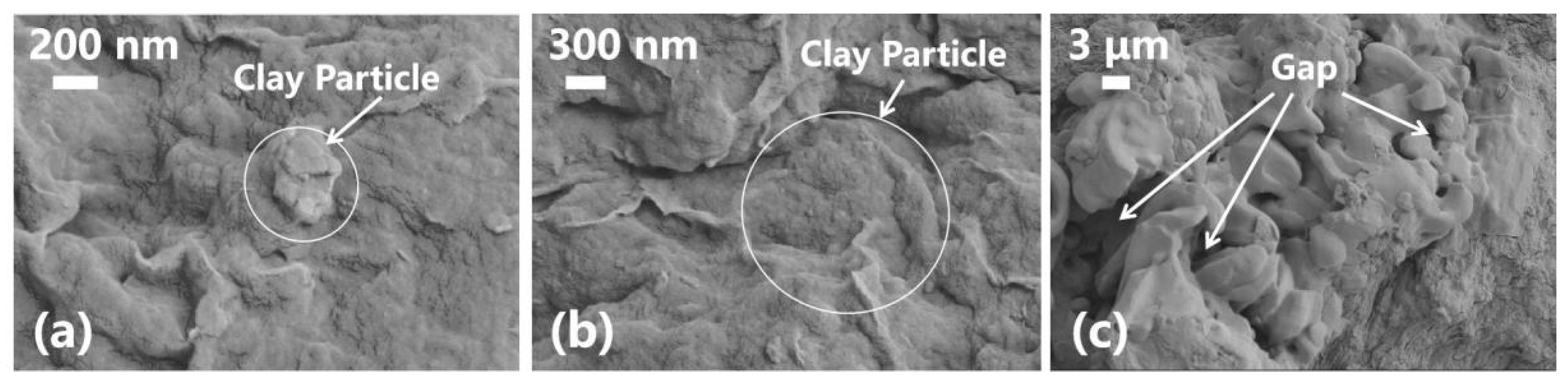
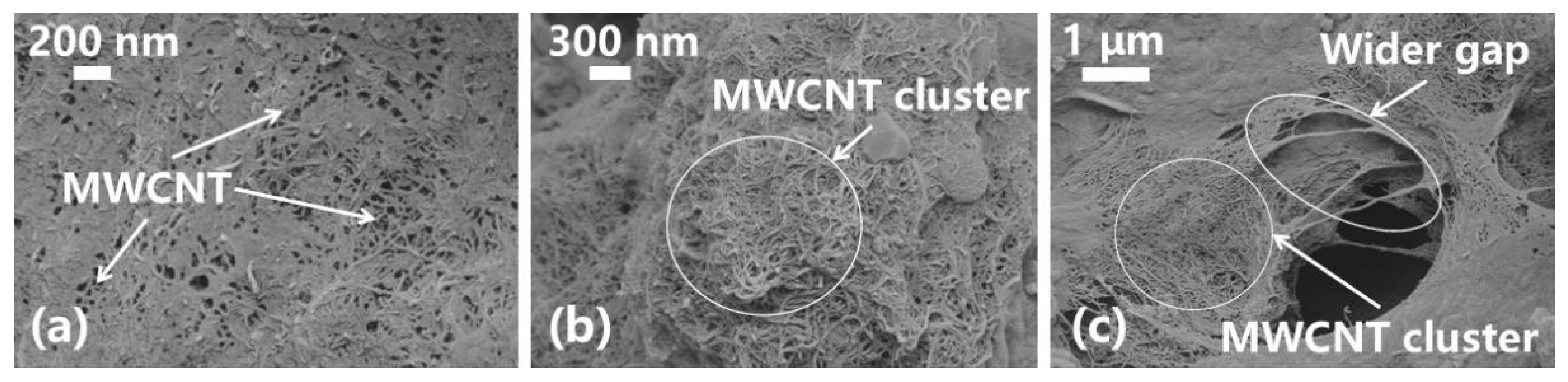
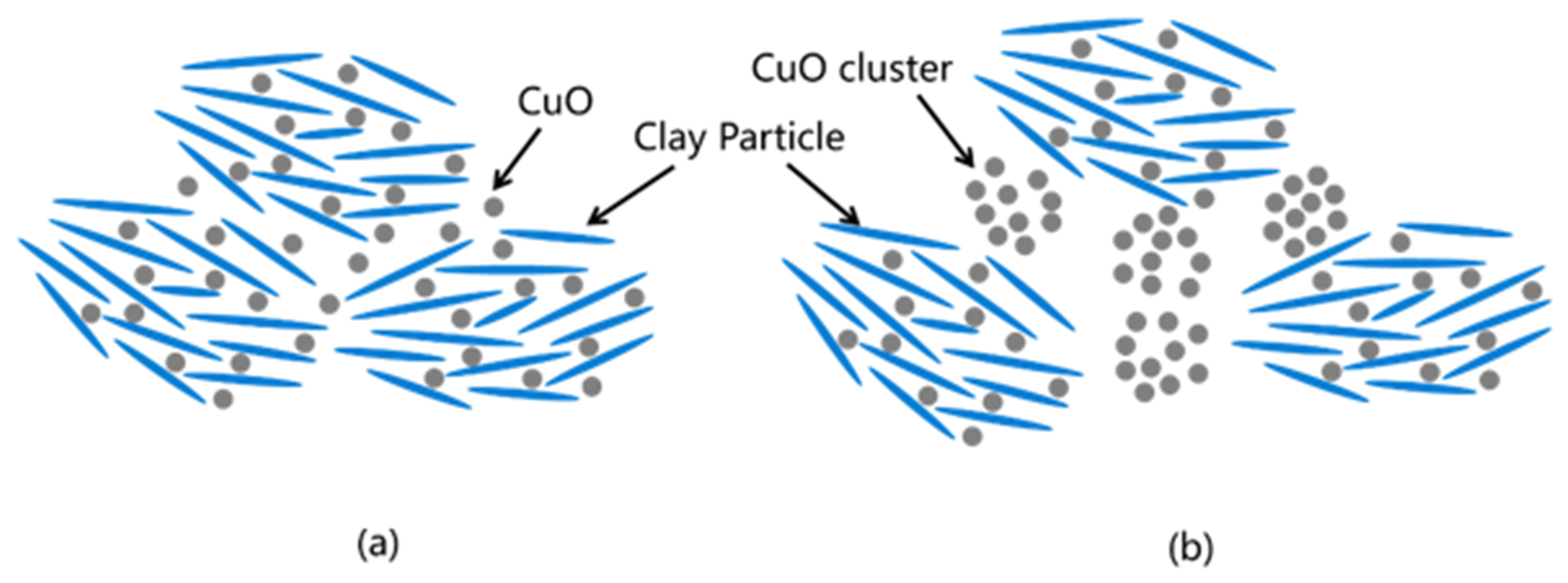
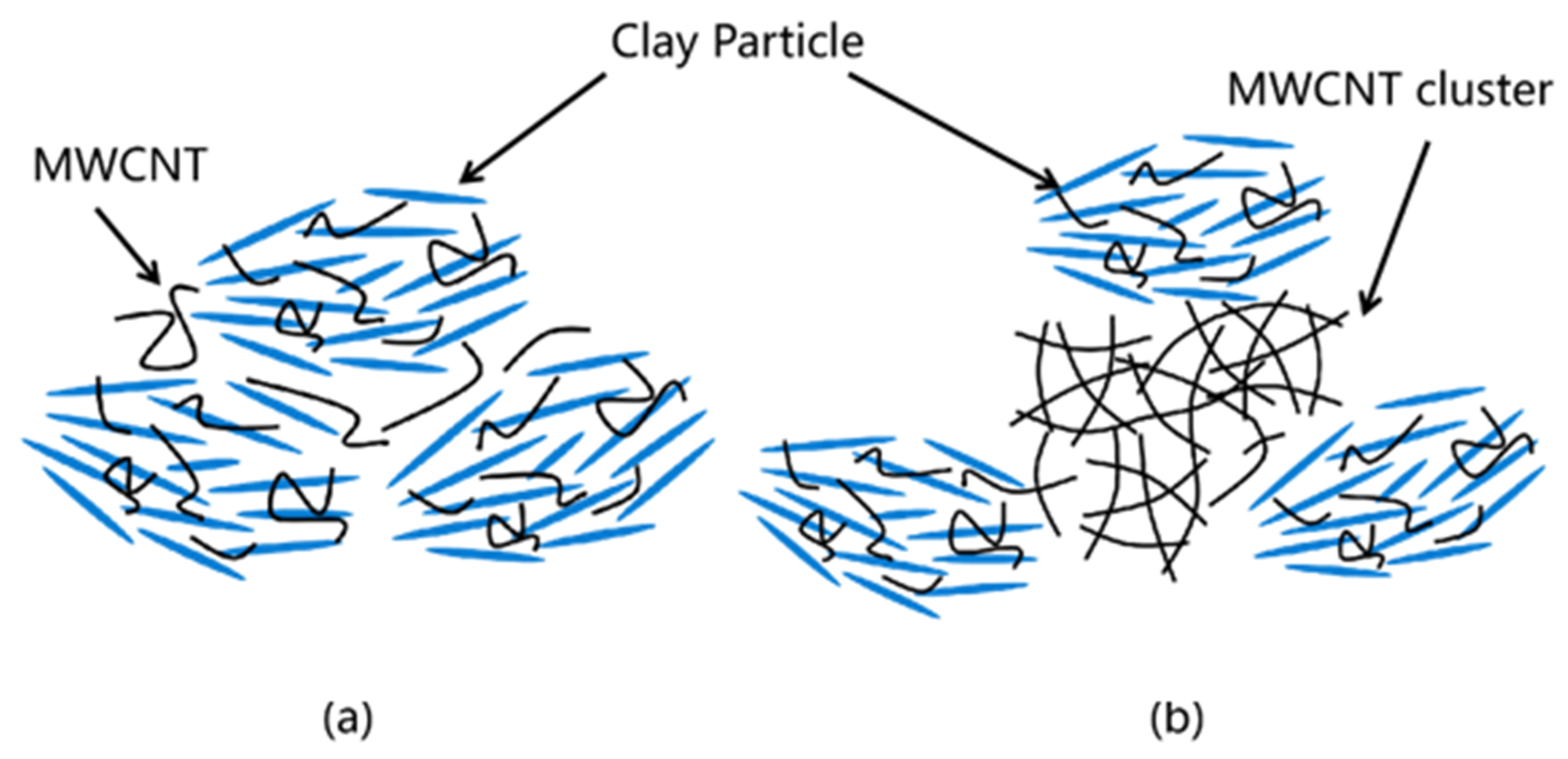
3.3. Analysis of the Microstructure
3.4. Theoretical Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bekkour, K.; Leyama, M.; Benchabane, A.; Scrivener, O. Time-dependent rheological behavior of bentonite suspensions: An experimental study. J. Rheol. 2005, 49, 1329–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paineau, E.; Michot, L.J.; Bihannic, I.; Baravian, C. Aqueous Suspensions of Natural Swelling Clay Minerals. 2. Rheological Characterization. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7806–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignon, F.; Magnin, A.; Piau, J.M. Thixotropic colloidal suspensions and flow curves with minimum: Identification of flow regimes and rheometric consequences. J. Rheol. 1996, 40, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakairi, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Adachi, Y. Effects of salt concentration on the yield stress of sodium montmorillonite suspension. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 283, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, A.; Kirichek, A.; Chassagne, C. Rheology and yielding transitions in mixed kaolinite/bentonite suspensions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 211, 106206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignon, F.; Magnin, A.; Piau, J.M. Thixotropic behavior of clay dispersions: Combinations of scattering and rheometric techniques. J. Rheol. 1998, 42, 1349–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Phan-Thien, N.; Pan, D. Rheological behavior for laponite and bentonite suspensions in shear flow. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 125233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qin, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, J. Study on the Rheological Behavior of a Model Clay Sediment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, A.M.; Baravian, C.; Imperor-Clerc, M.; De Silva, J.; Paineau, E.; Bihannic, I.; Davidson, P.; Meneau, F.; Levitz, P.; Michot, L.J. Rheo-SAXS investigation of shear-thinning behaviour of very anisometric repulsive disc-like clay suspensions. J. Phys. Condens. Mat. 2011, 23, 194112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Cheah, L.K.J.; Phan-Thien, N.; Khoo, B.C. Effect of temperature on rheological behavior of kaolinite and bentonite suspensions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 506, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qin, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, J. Rheology of bentonite dispersions: Role of ionic strength and solid content. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 214, 106275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.K.; Teo, J.; Teh, E.; Smith, J.; Widjaja, J.; Lee, J.X.; Fourie, A.; Fahey, M.; Chen, R. Controlling attractive interparticle forces via small anionic and cationic additives in kaolin clay slurries. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Luo, M. Application a novel thermo-sensitive copolymer as a potential rheological modifier for deepwater water-based drilling fluids. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 581, 123848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.J.; Deville, J.P.; Araujo, C.S.; Li, S.; Rojas, O.J. Nanocellulose and Its Derivatives for High-Performance Water-Based Fluids. In Proceedings of the SPE International Conference on Oilfield Chemistry, Montgomery, TX, USA, 3–5 April 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.; Kesarwani, H.; Sharma, S. Effect of CuO and ZnO Nanoparticles on Efficacy of Poly 4-Styrenesulfonic Acid-Co-Maleic Acid Sodium Salt for Controlling HPHT Filtration. In Proceedings of the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition & Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 11–14 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.R.; Rashid, N.M.; Jaafar, M.Z.; Sulaiman, W.R.W.; Buang, N.A. Effect of Nanomaterial on the Rheology of Drilling Fluids. J. Appl. Sci. 2014, 14, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaasadi, M.; Zarei, V.; Elveny, M.; Alizadeh, S.M.; Alizadeh, V.; Khan, A. Improving the rheological properties and thermal stability of water-based drilling fluid using biogenic silica nanoparticles. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 6162–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosynkin, D.V.; Ceriotti, G.; Wilson, K.C.; Lomeda, J.R.; Scorsone, J.T.; Patel, A.D.; Friedheim, J.E.; Tour, J.M. Graphene Oxide as a High-Performance Fluid-Loss-Control Additive in Water-Based Drilling Fluids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, J.; Haneef, M.D. Clay nanoparticles modified drilling fluids for drilling of deep hydrocarbon wells. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 86, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, J.K.M.; Ponmani, S.; Samuel, R.; Nagarajan, R.; Sangwai, J.S. Effect of CuO and ZnO nanofluids in xanthan gum on thermal, electrical and high pressure rheology of water-based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 117, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, M.M.; Jung, Y.; Lee, J.K.; Phuoc, T.X.; Chyu, M.K. Fluid filtration and rheological properties of nanoparticle additive and intercalated clay hybrid bentonite drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 127, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.R.; Aftab, A.; Ibupoto, Z.H.; Zolkifile, N. The novel approach for the enhancement of rheological properties of water-based drilling fluids by using multi-walled carbon nanotube, nanosilica and glass beads. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 139, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi-Zaboli, M.; Sahraei, E.; Pourabbas, B. Hydrophobic silica nanoparticle-stabilized invert emulsion as drilling fluid for deep drilling. Pet. Sci. 2017, 14, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perween, S.; Beg, M.; Shankar, R.; Sharma, S.; Ranjan, A. Effect of zinc titanate nanoparticles on rheological and filtration properties of water based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 170, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Luo, P.; Tian, Y.; Lin, Y.; Guo, Q. Poly (sodium p-styrene sulfonate) modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles as effective additives in water-based drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 165, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, N.; Mirzaee, M.; Aghayari, R.; Maddah, H. Investigating Created Properties of Nanoparticles Based Drilling Mud. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 54, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elochukwu, H.; Sia, L.K.S.; Gholami, R.; Hamid, M.A. Data on experimental investigation of Methyl Ester Sulphonate and nanopolystyrene for rheology improvement and filtration loss control of water-based drilling fluid. Data Brief 2018, 21, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejtaradon, P.; Hamidi, H.; Chuks, M.H.; Wilkinson, D.; Rafati, R. Impact of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles on the rheological and filtration properties of water-based drilling fluid. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 570, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, R.; Sabbaghi, S.; Kalantariasl, A. Improvement of rheological, filtration and thermal conductivity of bentonite drilling fluid using copper oxide/polyacrylamide nanocomposite. Powder Technol. 2019, 353, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadian, M.; Sajjadian, V.A.; Rashidi, A. The effect of nanoparticles with KCL salt on rheological and filtrate properties of water-based drilling fluid: Experimental analysis. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 18, 1804014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, R.; Rafati, R.; Haddad, A.S. Rheological and filtration property evaluations of the nano-based muds for drilling applications in low temperature environments. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 622, 126632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhienkova, E.I.; Lysakov, S.V.; Neverov, A.L.; Zhigarev, V.A.; Minakov, A.V.; Rudyak, V.Y. Experimental study on the influence of nanoparticles on oil-based drilling fluid properties. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, M.; Hajipour, M.; Emamzadeh, A. Enhancement of the heat capacity of water-based drilling fluids for deep drilling applications. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, E.U.; Enyi, G.C.; Nasr, G.G. Enhancing the performance of xanthan gum in water-based mud systems using an environmentally friendly biopolymer. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 1933–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guria, C.; Kumar, R.; Mishra, P. Rheological analysis of drilling fluid using Marsh Funnel. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 105, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi-Beydokhti, A.; Hajiabadi, S.H.; Sanati, A. Surface modification of carbon nanotubes as a key factor on rheological characteristics of water-based drilling muds. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2018, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.R.; Rafati, R.; Haddad, A.S.; Cooper, A.; Hamidi, H. Application of aluminium oxide nanoparticles to enhance rheological and filtration properties of water based muds at HPHT conditions. Colloid Surf. A 2018, 537, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhi, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Gupta, D.K.; Mazumdar, A. An investigation on the effects of silica and copper oxide nanoparticles on rheological and fluid loss property of drilling fluids. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2019, 10, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.G. The Structure and Rheology of Complex Fluids; Oxford University Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Laxton, P.B.; Berg, J.C. Relating clay yield stress to colloidal parameters. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 296, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Phan-Thien, N.; Lee, J.B.P.; Khoo, B.C. Concentration Dependence of Yield Stress and Dynamic Moduli of Kaolinite Suspensions. Langmuir 2015, 31, 4791–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombacz, E.; Szekeres, M. Colloidal behavior of aqueous montmorillonite suspensions: The specific role of pH in the presence of indifferent electrolytes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 27, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
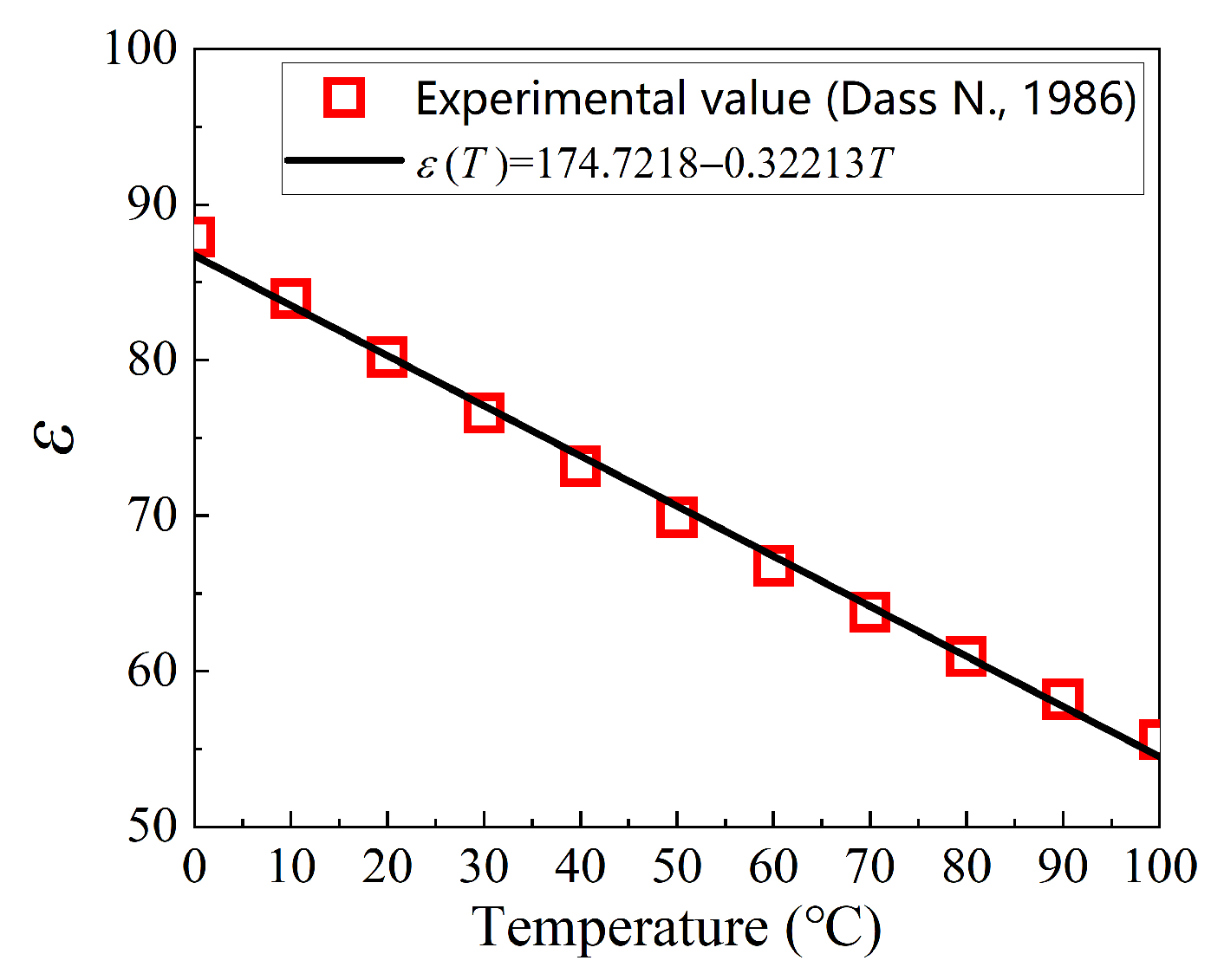
- Dass, N. Temperature Dependence of Dielectric Constant in Light and Heavy Water. Phys. Chem. Liq. 1986, 15, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
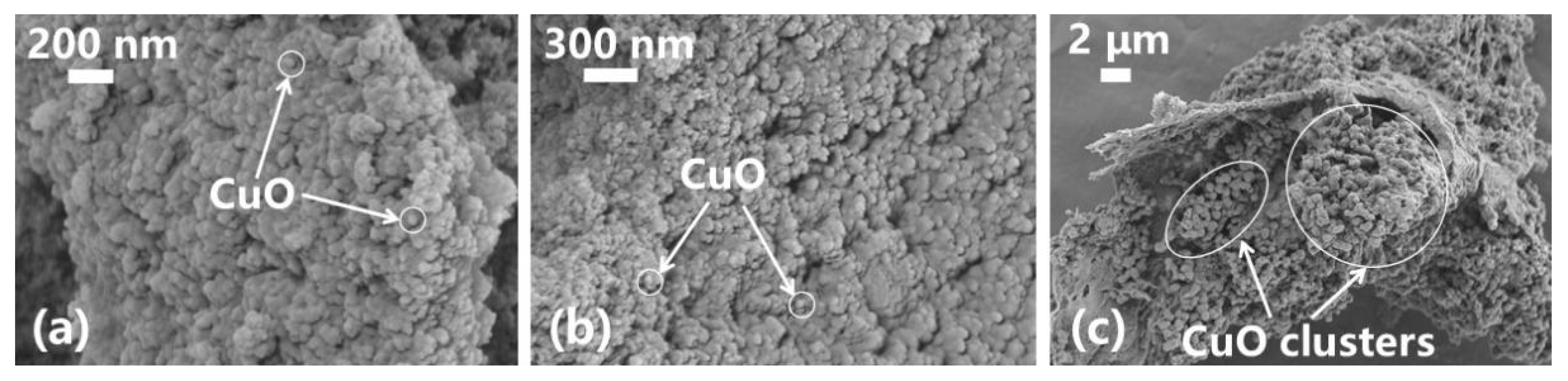
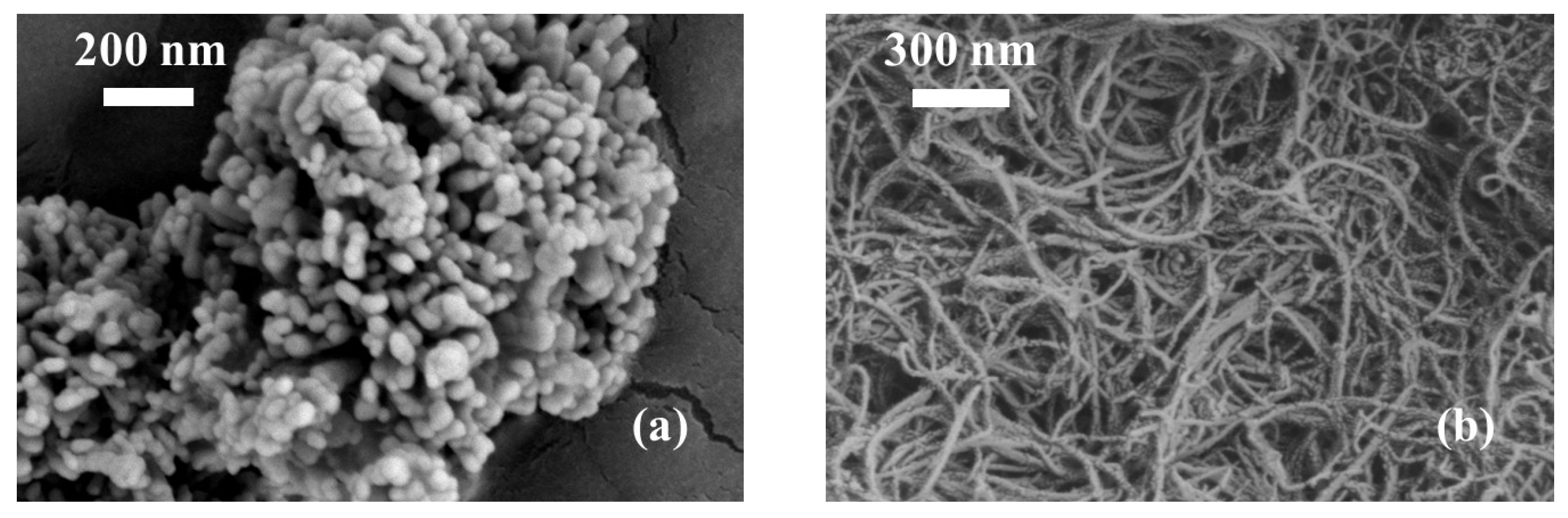
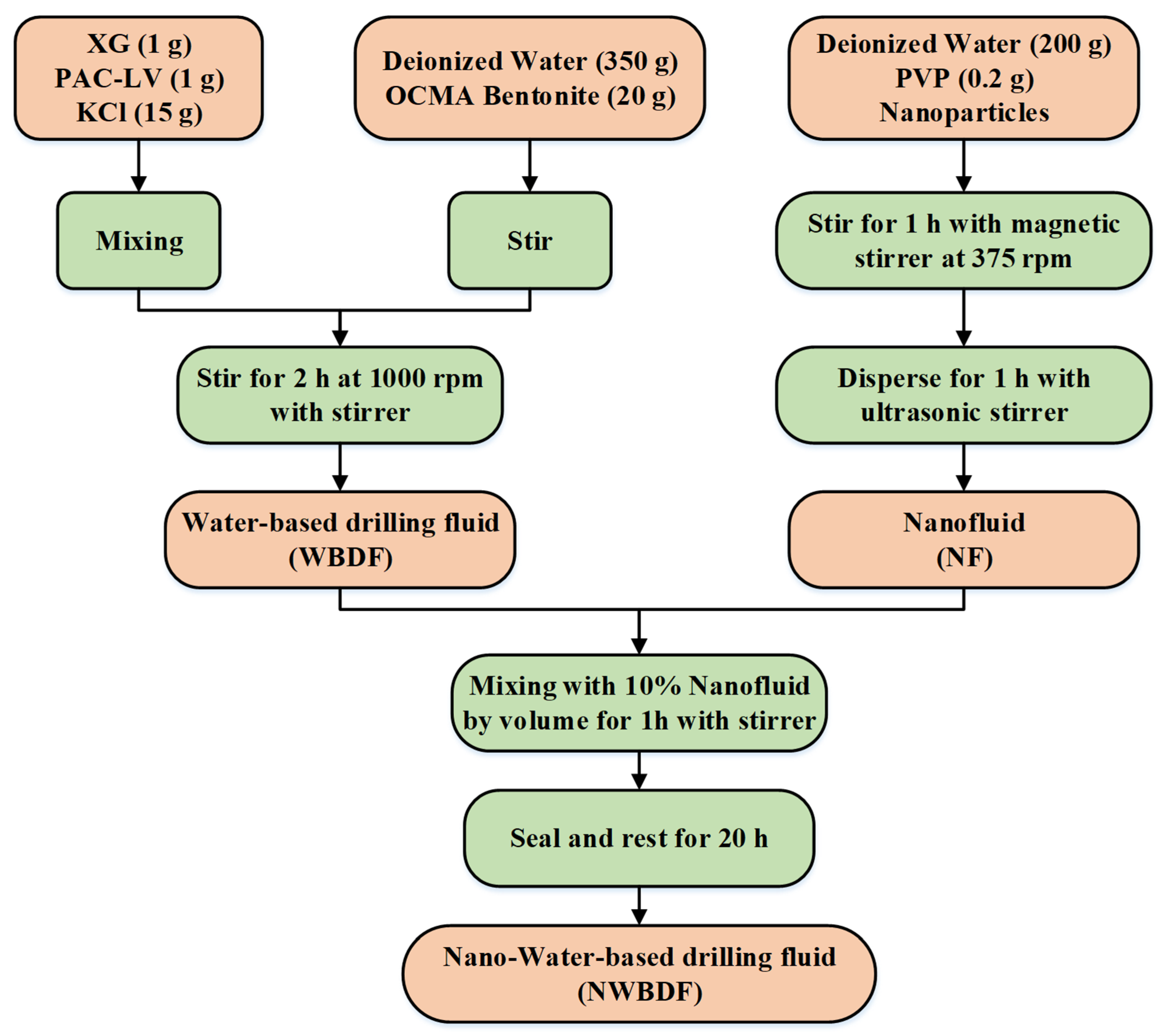
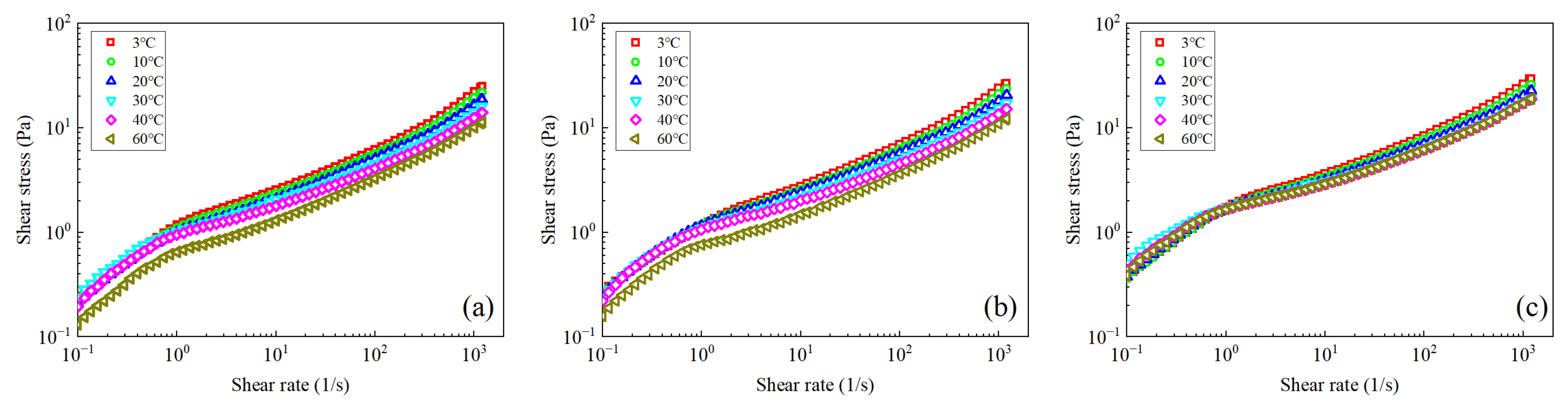

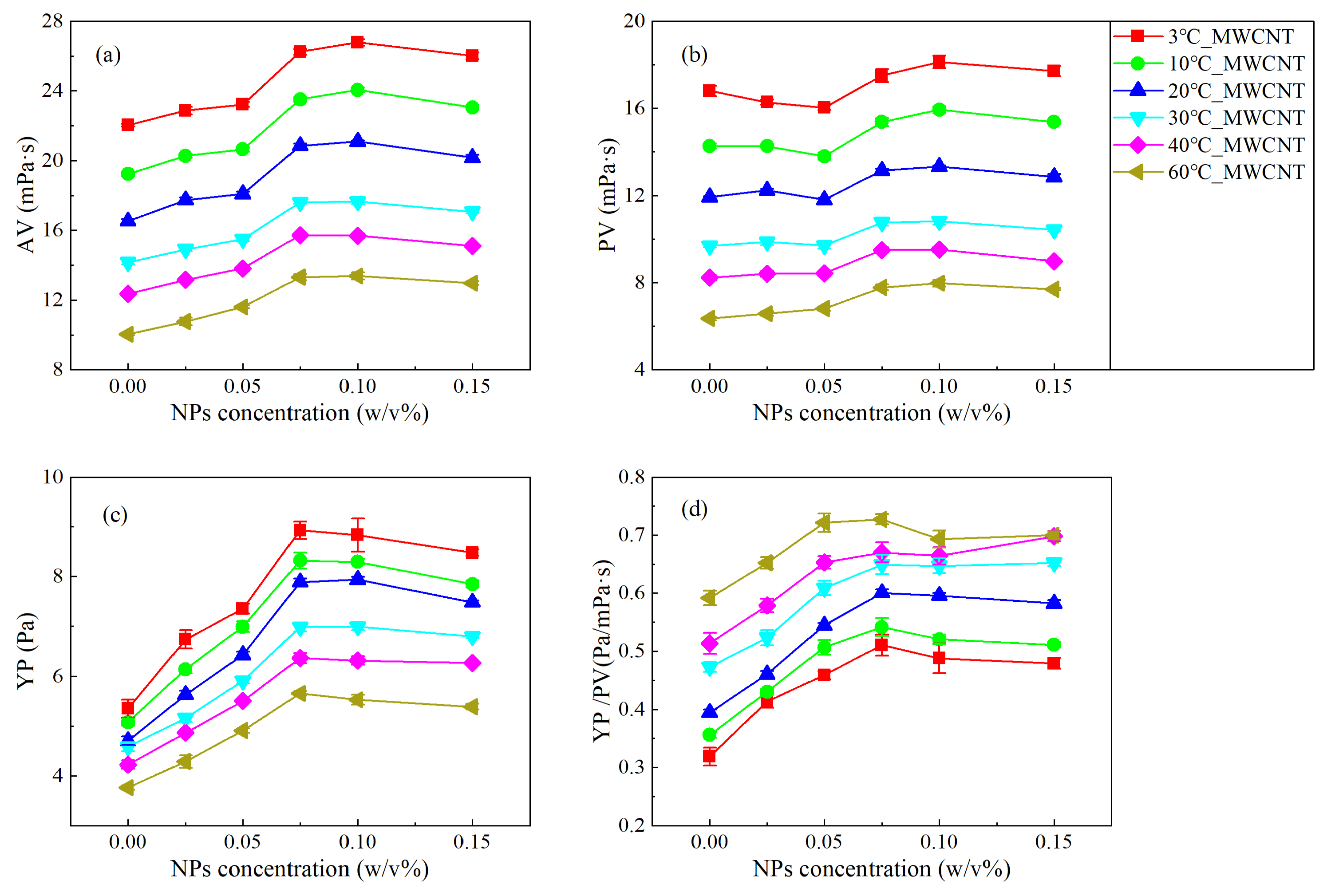
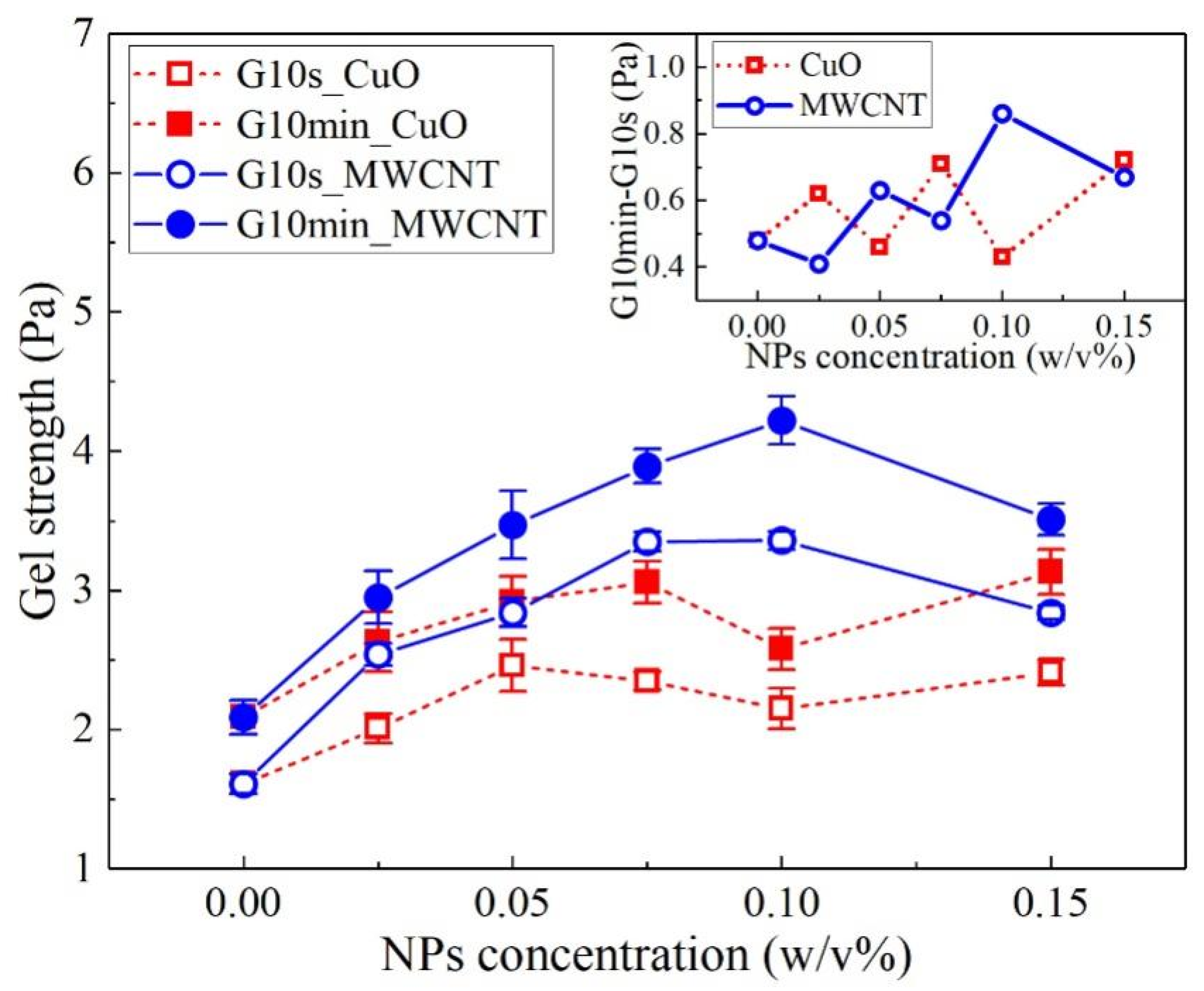
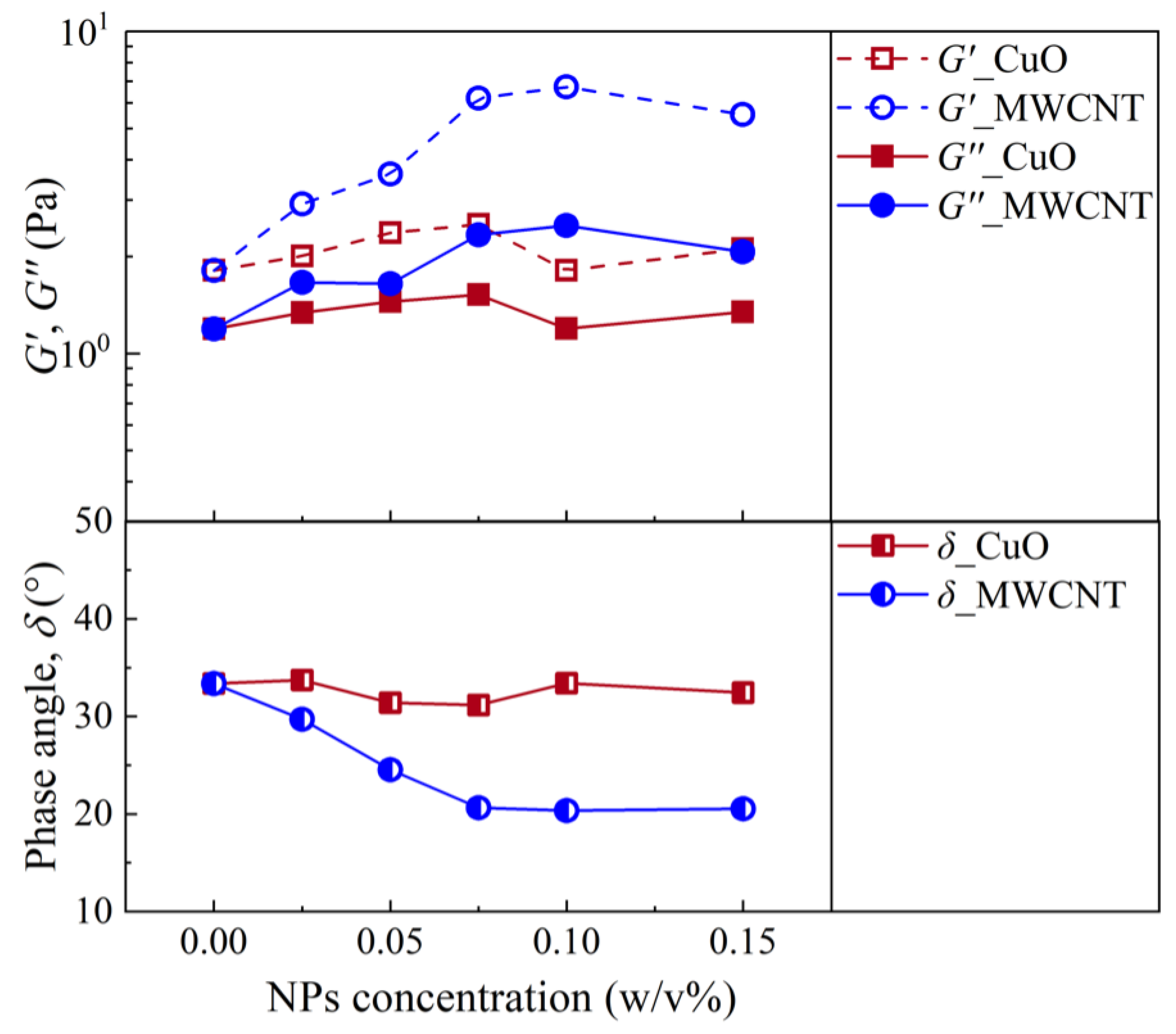
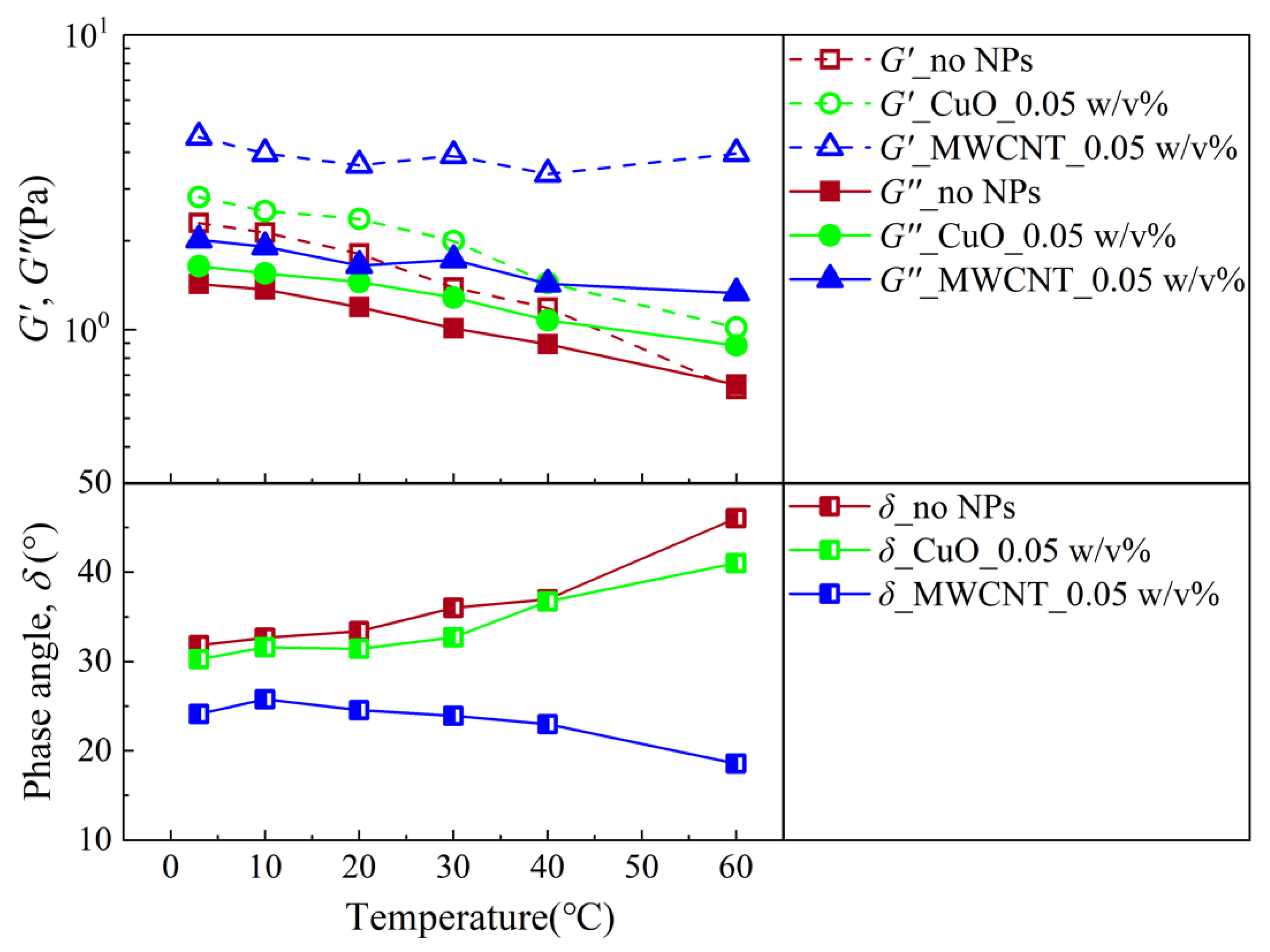
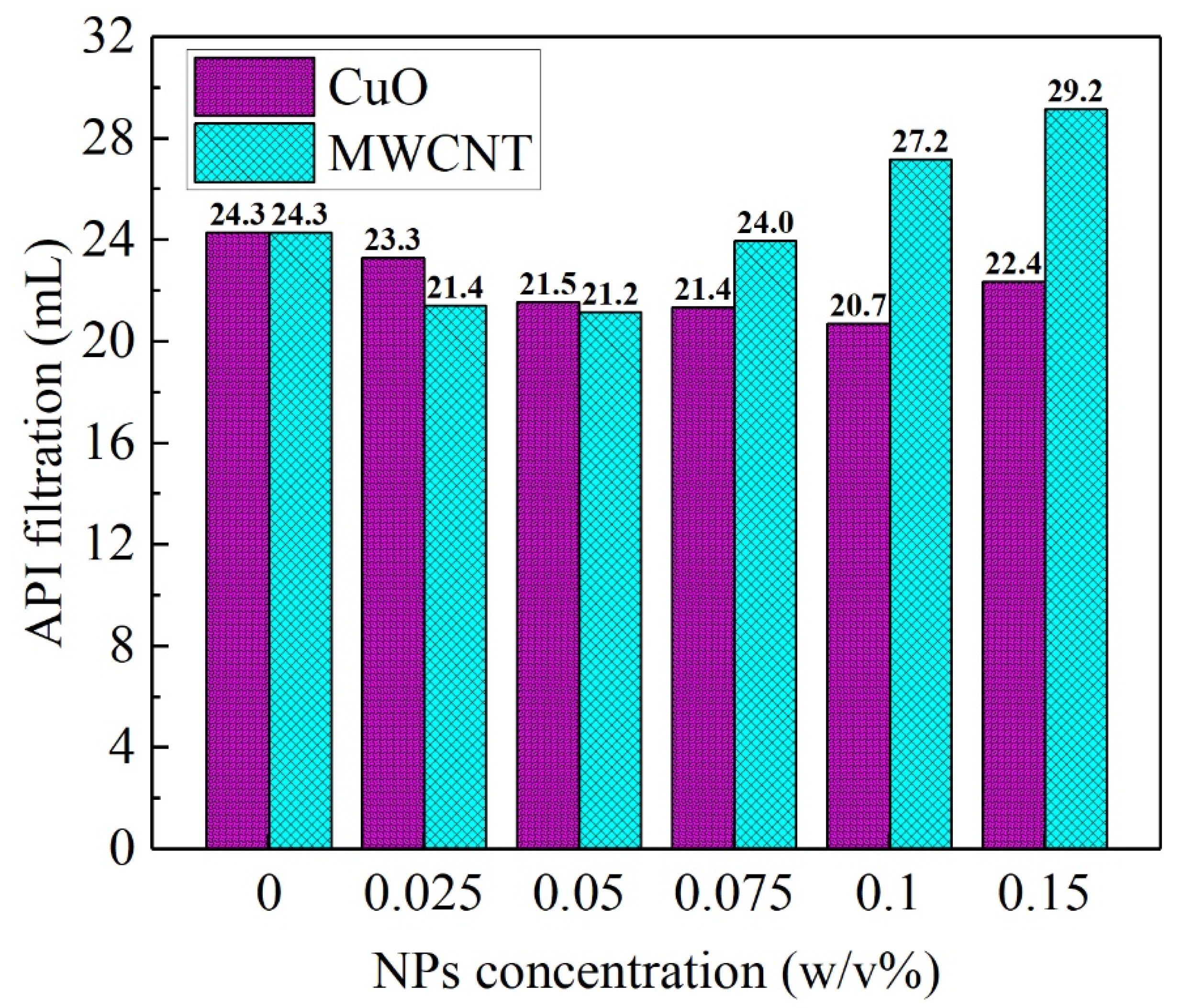
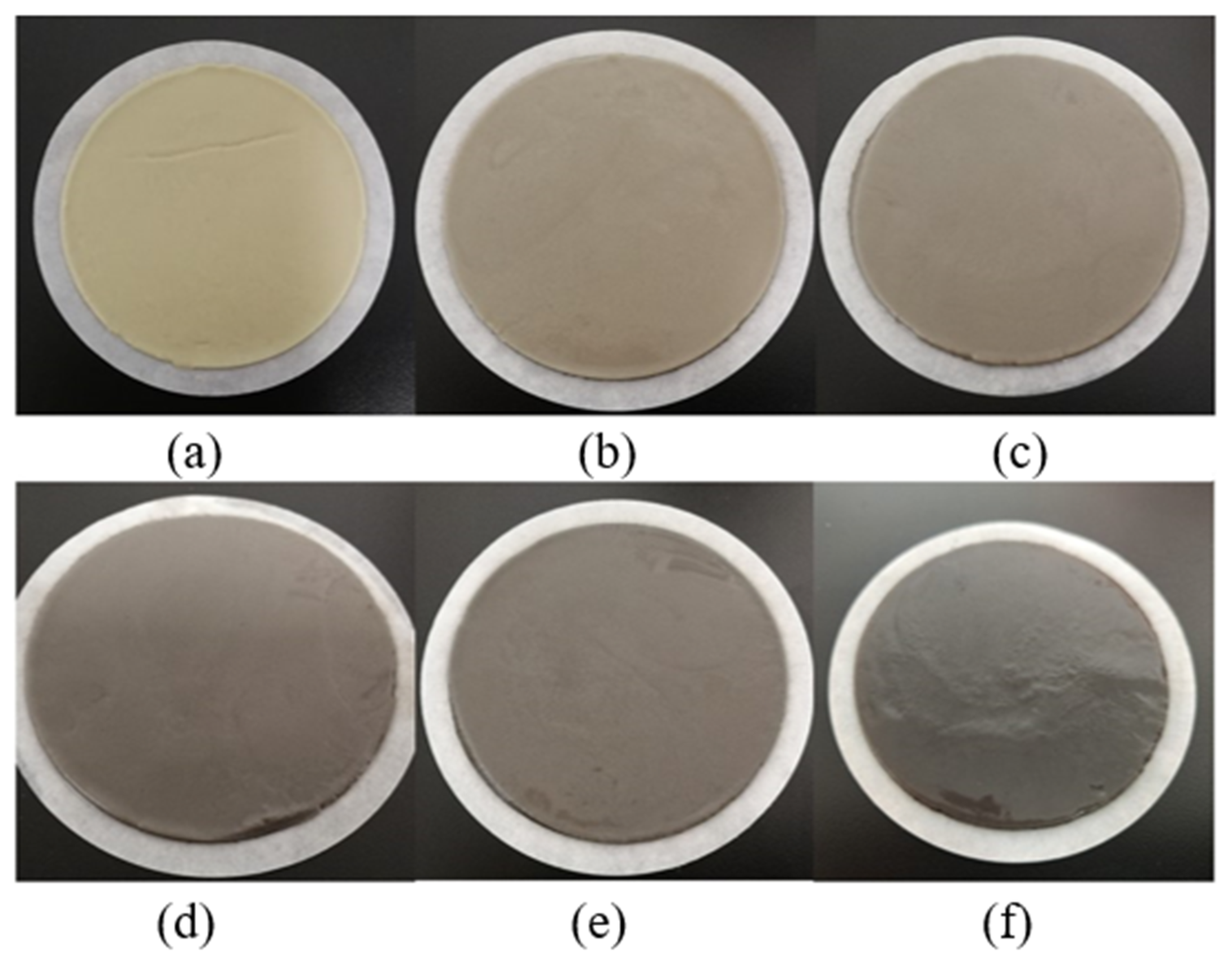



| Author | Year | Drilling Fluid Type | Type and Size of NPs | Modification Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kosynkin et al. | 2012 | WBDF (Bentonite) | Graphene Oxide | Improved filtration property | [18] |
| Abdo et al. | 2013 | WBDF (Montmorillonite) | ) | Improved rheological properties | [19] |
| William et al. | 2014 | WBDF (Bentonite) | ) | Improved temperature and pressure resistance, increased viscosity | [20] |
| Barry et al. | 2015 | WBDF (Bentonite) | ) | Improved rheological and filtration properties | [21] |
| Ismail et al. | 2016 | WBDF | ) ) | Improved rheological and filtration properties | [22] |
| Dargahi-Zaboli et al. | 2017 | OBDF (Oil–Water Ratio 70:30) | ) | Improved thermal stability | [23] |
| Perween et al. | 2018 | WBDF (Bentonite) | ) | Improved heat resistance and filtration properties | [24] |
| Wang et al. | 2018 | WBDF (Bentonite) | ) | Improved rheological and filtration properties | [25] |
| Ghasemi et al. | 2018 | OBDF (Oil–Water Ratio 10:90) | ) ) | Improved rheological and filtration properties | [26] |
| Elochukwu et al. | 2018 | WBDF (Bentonite) | ) | Improved rheological and filtration properties | [27] |
| Dejtaradon et al. | 2019 | WBDF (Bentonite) | ) | Improved rheological and filtration properties | [28] |
| Saboori et al. | 2019 | WBDF (Bentonite) | CuO/PAM | Improved rheological and filtration properties | [29] |
| Sajjadian et al. | 2020 | WBDF (Bentonite) | ) ) ) | Improved rheological and filtration properties | [30] |
| Novara et al. | 2021 | WBDF (Bentonite) | SiO2 and Al2O3 | Improved rheological and filtration properties | [31] |
| Mirzaasadi et al. | 2021 | WBDF | SiO2 | Improved rheological properties | [17] |
| Mikhienkova et al. | 2022 | OBDF (Oil–Water Ratio 70:30) | ) | Improved rheological and filtration properties | [32] |
| Cheraghi et al. | 2022 | WBDF | ) ) ) | Improved thermal stability | [33] |
| Deionized Water | OCMA-Grade Bentonite | XG | PAC-LV | KCl |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Deionized Water (g) | PVP (g) | CuO (g) | MWCNTs (g) | Concentration of NPs (w/v%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type and Concentration of NPs | R2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1307 × 107 | 110.091 | 0.01 | 0.99115 | |
| 1.2290 × 107 | 114.649 | 0.01 | 0.98433 | |
| 1.6089 × 107 | 117.405 | 0.01 | 0.85988 | |
| 1.6162 × 107 | 118.500 | 0.01 | 0.8083 | |
| 1.6242 × 107 | 110.078 | 0.01 | 0.77229 | |
| 1.4828 × 107 | 116.694 | 0.01 | 0.93545 | |
| 3.0072 × 107 | 172.386 | 0.01 | 0.9798 | |
| 2.4284 × 107 | 170.259 | 0.01 | 0.97329 | |
| 3.8621 × 107 | 229.217 | 0.01 | 0.97259 | |
| 4.9517 × 107 | 256.460 | 0.01 | 0.95113 | |
| 4.1711 × 107 | 231.160 | 0.01 | 0.98832 |
| Type and Concentration of NPs | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.07654 | 3.22918 | 0.8665 | |
| 0.01308 | 4.14329 | 0.91483 | |
| 0.00293 | 4.92964 | 0.88079 | |
| 0.04204 | 3.42462 | 0.84135 | |
| 0.14190 | 2.72975 | 0.98357 | |
| 0.24815 | 2.28716 | 0.88557 | |
| 0.45040 | 1.90060 | 0.96969 | |
| 0.21757 | 2.14809 | 0.9961 | |
| 0.35275 | 1.76141 | 0.96033 | |
| 0.44156 | 1.65033 | 0.91679 | |
| 0.27534 | 1.93192 | 0.94567 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Tian, Q.; Lin, P.; Tan, X.; Qin, H.; Chen, J. Effect of Nanoparticles on Rheological Properties of Water-Based Drilling Fluid. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142092
Lin Y, Tian Q, Lin P, Tan X, Qin H, Chen J. Effect of Nanoparticles on Rheological Properties of Water-Based Drilling Fluid. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(14):2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142092
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yuan, Qizhong Tian, Peiwen Lin, Xinghui Tan, Huaitao Qin, and Jiawang Chen. 2023. "Effect of Nanoparticles on Rheological Properties of Water-Based Drilling Fluid" Nanomaterials 13, no. 14: 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142092
APA StyleLin, Y., Tian, Q., Lin, P., Tan, X., Qin, H., & Chen, J. (2023). Effect of Nanoparticles on Rheological Properties of Water-Based Drilling Fluid. Nanomaterials, 13(14), 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142092







