Sensing Approaches Exploiting Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles and Lossy Mode Resonance in Polymer Optical Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of nanoMIPs
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Optical Characterization
2.5. HTR Detection: Binding Measurement Protocol
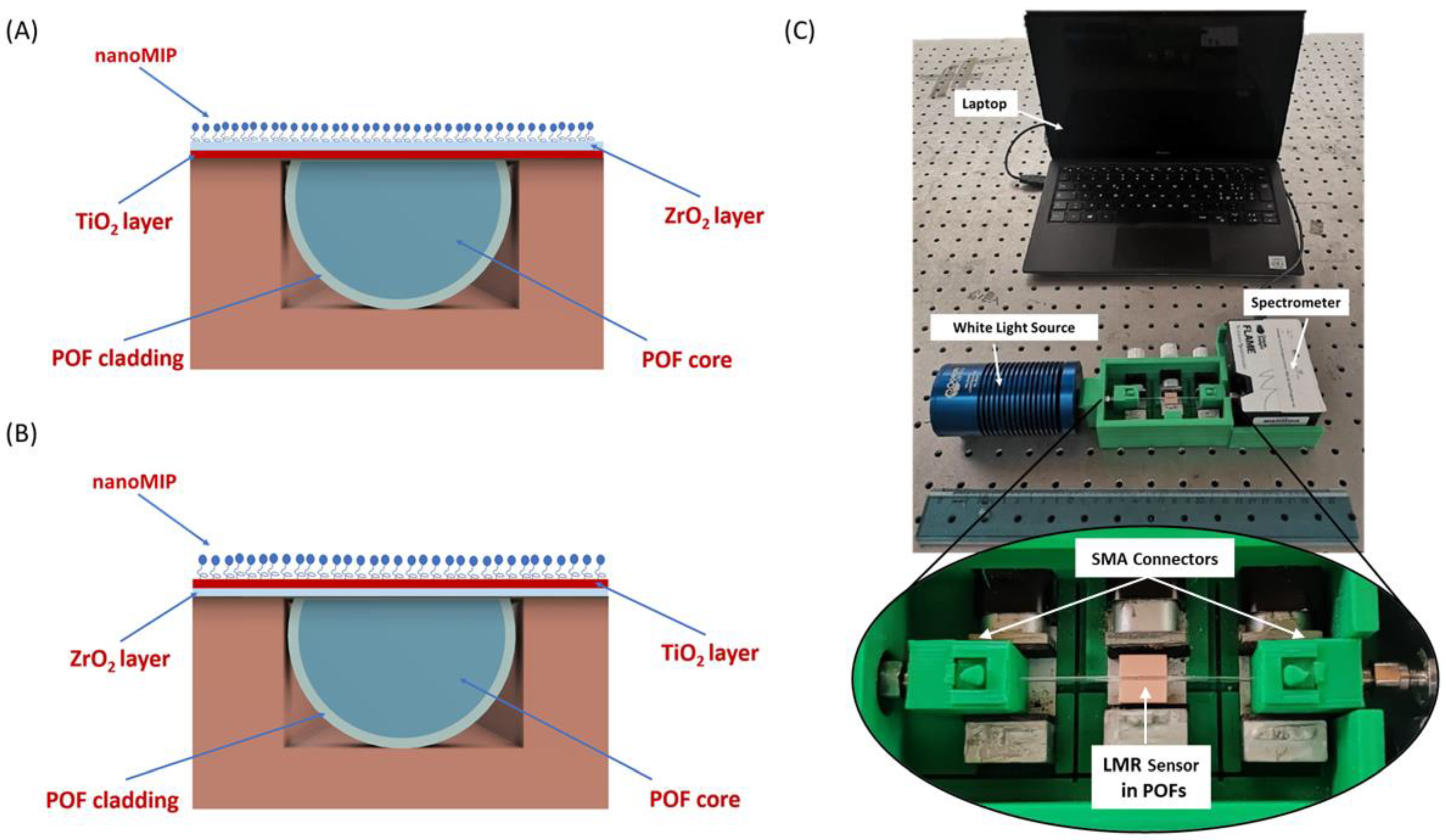
3. LMR-Based HTR Sensors: POF–LMR Platforms and nanoMIPs
3.1. POF–LMR Sensors Fabrication
3.2. POF-LMR Functionalization Process
4. Results
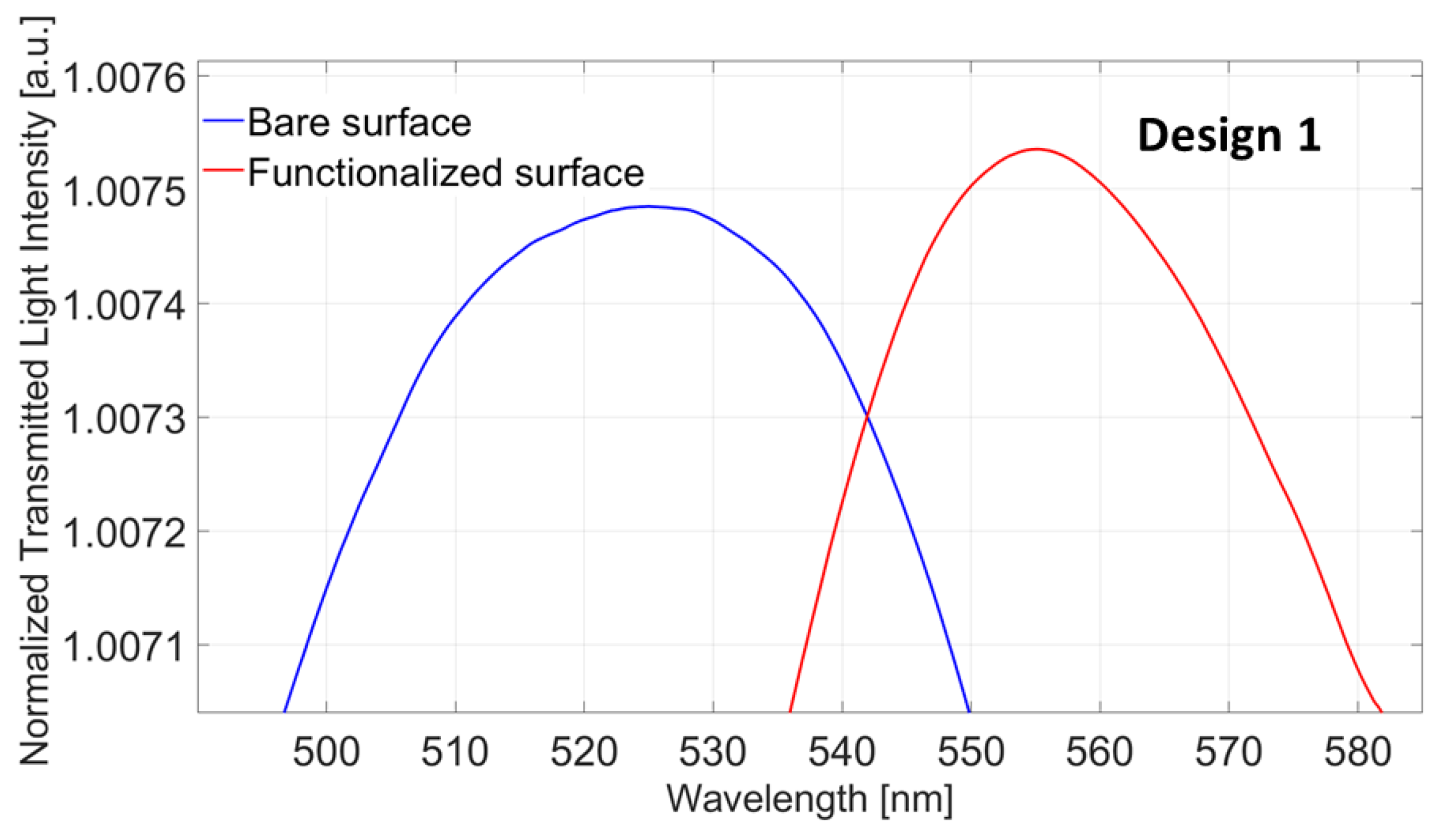
4.1. Design 1 (POF-TiO2-ZrO2)
4.1.1. Bulk Sensitivity for Design 1 (POF-TiO2-ZrO2)
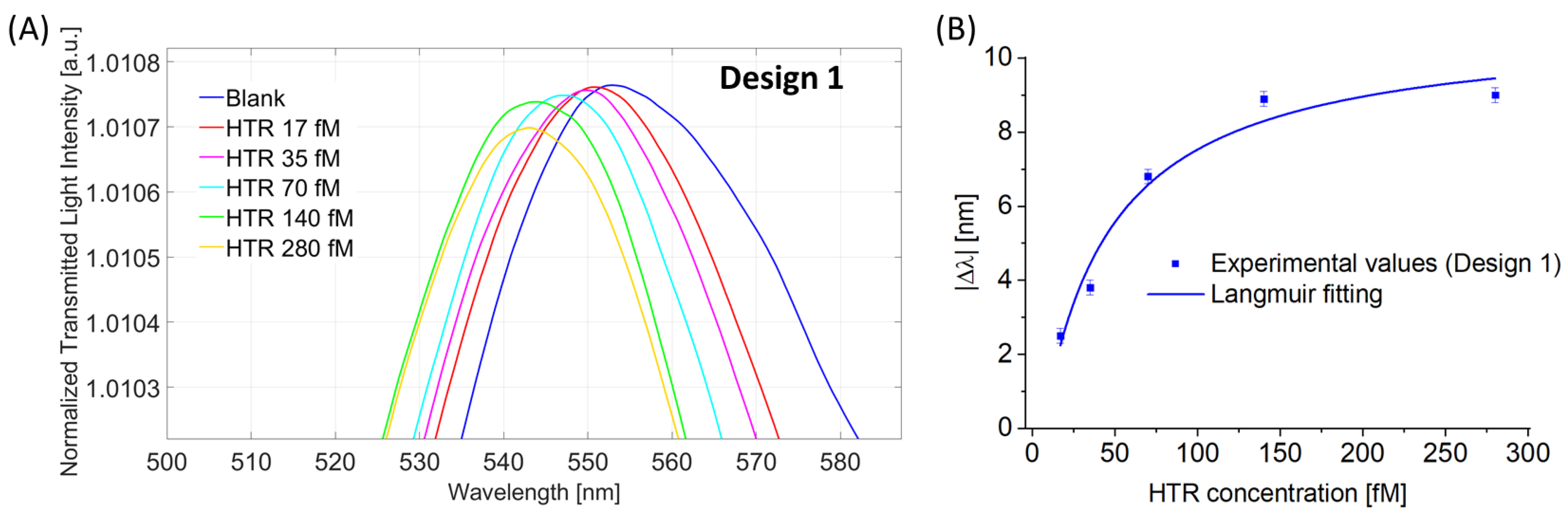
4.1.2. Binding Sensitivity for Design 1 (POF-TiO2-ZrO2-nanoMIPs)
4.2. Design 2 (POF-ZrO2-TiO2)
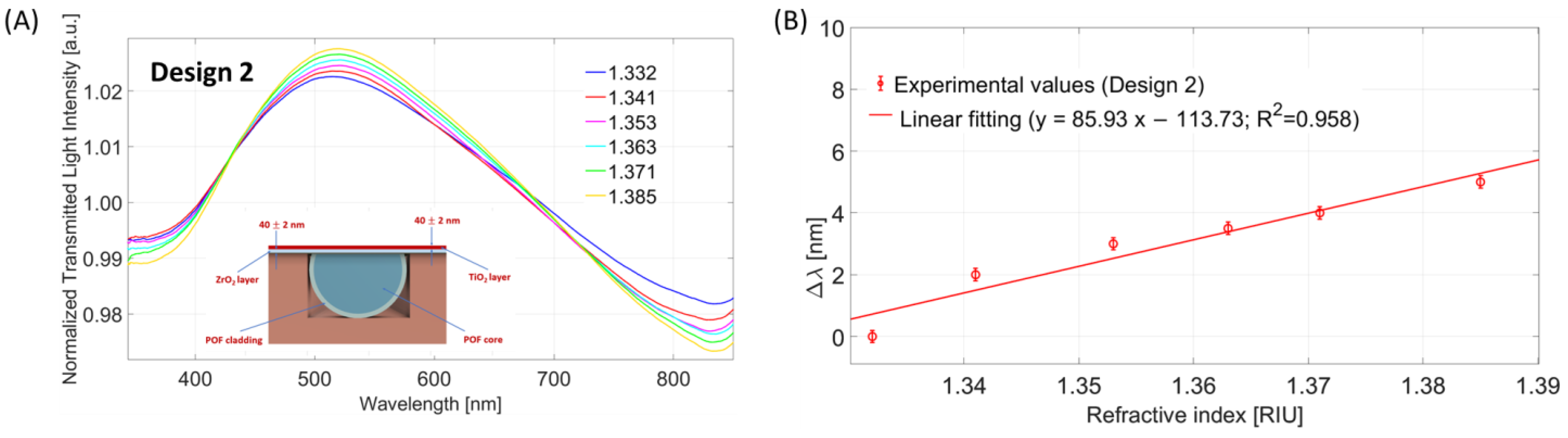
4.2.1. Bulk Sensitivity for Design 2 (POF-ZrO2-TiO2)
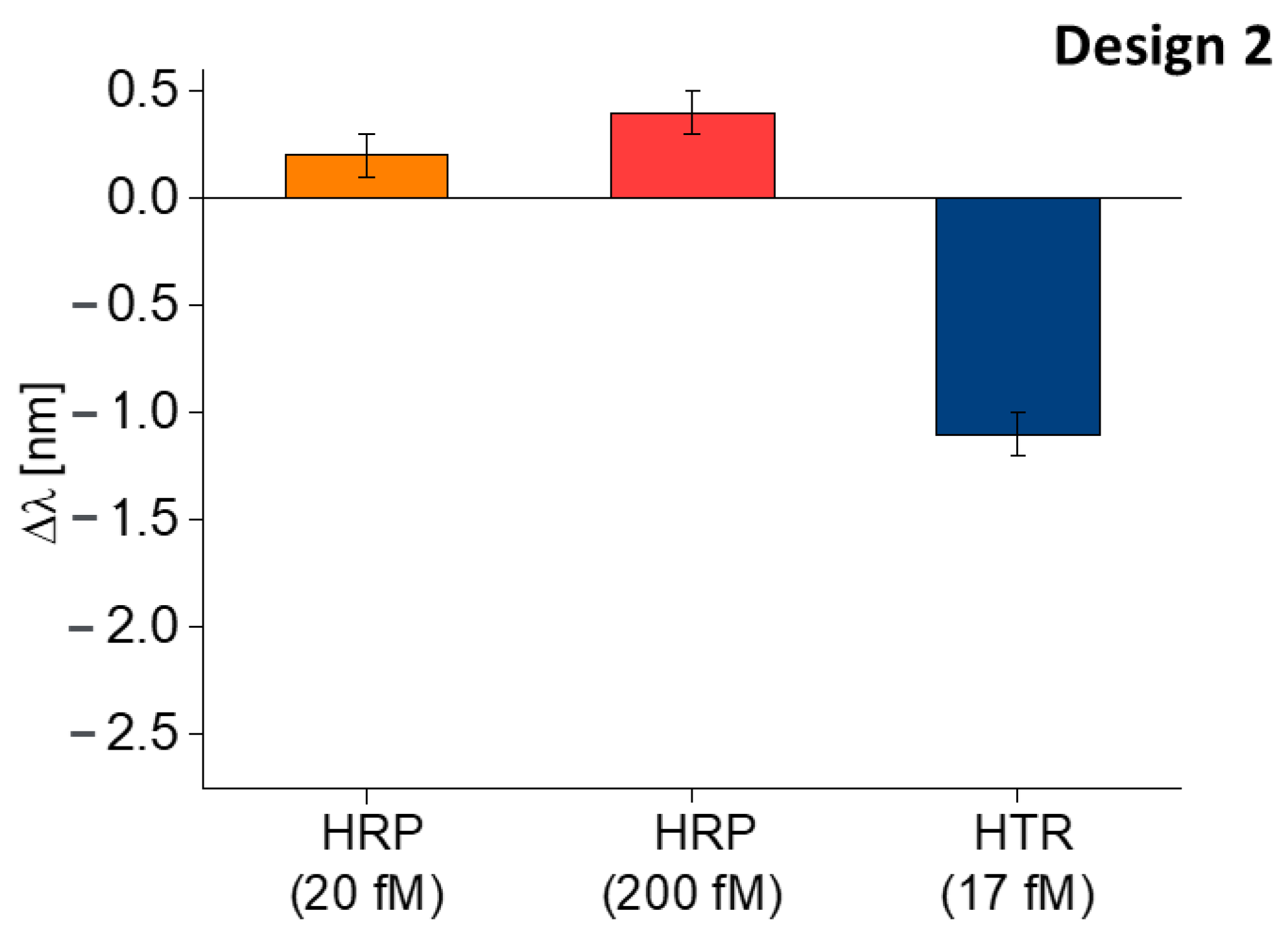
4.2.2. Binding Sensitivity for Design 2 (POF-ZrO2-TiO2-nanoMIPs)
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marciniak, M.; Grzegorzewski, J.; Szustakowski, M. Analysis of lossy mode cut-off conditions in planar waveguides with semiconductor guiding layer. IEEE Proc. J. Optoelectron. 1993, 140, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Villar, I.; Hernaez, M.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Sánchez, P.; Fernández-Valdivielso, C.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Design rules for lossy mode resonance based sensors. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 4298–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelyev, E. Sensitivity of lossy mode resonance-based optical fiber sensors as a function of the coating material refractive index. Eur. Phys. J. D 2021, 75, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Wan-Ming, Z. A comprehensive review of lossy mode resonance-based fiber optic sensors. Opt. Laser Eng. 2018, 100, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Paliwal, N.; John, J. Lossy Mode Resonance (LMR) Based Fiber Optic Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5361–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavaioli, F.; Janner, D. Fiber Optic Sensing With Lossy Mode Resonances: Applications and Perspectives. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 3855–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Villar, I.; Arregui, F.J.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Corres, J.M.; Bariain, C.; Goicoechea, J.; Elosua, C.; Hernaez, M.; Rivero, P.J.; Socorro, A.B.; et al. Optical Sensors Based on Lossy-Mode Resonances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, I.R.; Villar, I.D.; Corres, J.M. Lossy Mode Resonance-Based Sensors in Planar Configuration: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 6397–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcariz, A.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Zubiate, P.; Arregui, F.J. Is There a Frontier in Sensitivity with Lossy Mode Resonance (LMR) Based Refractometers? Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Villar, I.; Zamarreno, C.R.; Hernaez, M.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Lossy mode resonance generation with indium-tin-oxide-coated optical fibers for sensing applications. J. Light. Technol. 2010, 28, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernáez, M.; Del Villar, I.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Optical fiber refractometers based on lossy mode resonances supported by TiO2 coatings. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 3980–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamarreno, C.R.; Sanchez, P.; Hernaez, M.; Del Villar, I.; Fernandez-Valdivielso, C.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Sensing properties of indium oxide coated optical fiber devices based on lossy mode resonances. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 12, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, P.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Hernaez, M.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Optical fiber refractometers based on Lossy Mode Resonances by means of SnO2 sputtered coatings. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2014, 202, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubiate, P.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Del Villar, I.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Tunable Optical Fiber pH Sensors Based on TE and TM Lossy Mode Resonances (LMRs). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascorbe, J.; Corres, J.M.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. High Sensitivity Humidity Sensor Based on Cladding-Etched Optical Fiber and Lossy Mode Resonances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitoria, I.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Ozcariz, A.; Matias, I.R. Fiber Optic Gas Sensors Based on Lossy Mode Resonances and Sensing Materials Used Therefor: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socorro, A.B.; Corres, J.M.; Del Villar, I.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Fiber-optic biosensor based on lossy mode resonances. Sens. Actuators B Chem 2012, 174, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmietana, M.; Koba, M.; Sezemsky, P.; Szot-Karpińska, K.; Burnat, D.; Stranak, V.; Niedziółka-Jönssond, J.; Bogdanowicz, R. Simultaneous optical and electrochemical label-free biosensing with ITO-coated lossy-mode resonance sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 154, 112050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha, S.P.; Gupta, B.D. Urinary p-cresol diagnosis using nanocomposite of ZnO/MoS2 and molecular imprinted polymer on optical fiber based lossy mode resonance sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 101, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Arcadio, F.; Noel, L.; Zeni, L.; Soppera, O. Flexible and Ultrathin Metal-Oxide Films for Multiresonance-Based Sensors in Plastic Optical Fibers. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 10902–10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, O.; Del Villar, I.; Dominguez, I.; Corres, J.M.; Matías, I.R. Simultaneous Generation of Surface Plasmon and Lossy Mode Resonances in the Same Planar Platform. Sensors 2022, 22, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcadio, F.; Noël, L.; Del Prete, D.; Maniglio, D.; Seggio, M.; Soppera, O.; Cennamo, N.; Bossi, A.M.; Zeni, L. Soft Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles with Simultaneous Lossy Mode and Surface Plasmon Multi-Resonances for Femtomolar Sensing of Serum Transferrin Protein. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcadio, F.; Seggio, M.; Del Prete, D.; Buonanno, G.; Mendes, J.; Coelho, L.C.C.; Jorge, P.A.S.; Zeni, L.; Bossi, A.M.; Cennamo, N. A Plasmonic Biosensor Based on Light-Diffusing Fibers Functionalized with Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles for Ultralow Sensing of Proteins. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cennamo, N.; Arcadio, F.; Seggio, M.; Maniglio, D.; Zeni, L.; Bossi, A.M. Spoon-Shaped Polymer Waveguides to Excite Multiple Plasmonic Phenomena: A Multisensor Based on Antibody and Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles to Detect Albumin Concentrations over Eight Orders of Magnitude. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 217, 114707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Özgür, E.; Bereli, N.; Türkmen, D.; Denizli, A. Plastic Antibody Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Nanosensors for Selective Atrazine Detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K. Plastic Antibodies. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, A.M.; Haupt, K. Tailoring a Dress to Single Protein Molecules: Proteins Can Do It Themselves through Localized Photo-Polymerization and Molecular Imprinting. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 14556–14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberzeit, P.A.; Halikias, K.; Afzal, A.; Dickert, F.L. Polymers Imprinted with PAH Mixtures—Comparing Fluorescence and QCM Sensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehlin, F.; Wieder, F.; Spangenberg, A.; Le Meins, J.-M.; Soppera, O. Room-temperature preparation of metal-oxide nanostructures by DUV lithography from metal-oxo clusters. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Maniglio, D.; Tatti, R.; Zeni, L.; Bossi, A.M. Deformable molecularly imprinted nanogels permit sensitivity-gain in plasmonic sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 112126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubiate, P.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Sánchez, P.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. High sensitive and selective C-reactive protein detection by means of lossy mode resonance based optical fiber devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez, M.; Zubiate, P.; Del Villar, I.; Socorro-Leránoz, A.B.; Matías, I.R. Lossy Mode Resonance Based Microfluidic Platform Developed on Planar Waveguide for Biosensing Applications. Biosensors 2022, 12, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razquin, L.; Zamarreno, C.R.; Munoz, F.J.; Matias, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Thrombin detection by means of an aptamer based sensitive coating fabricated onto LMR-based optical fiber refractometer. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Sensors, Taipei, Taiwan, 28–31 October 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]



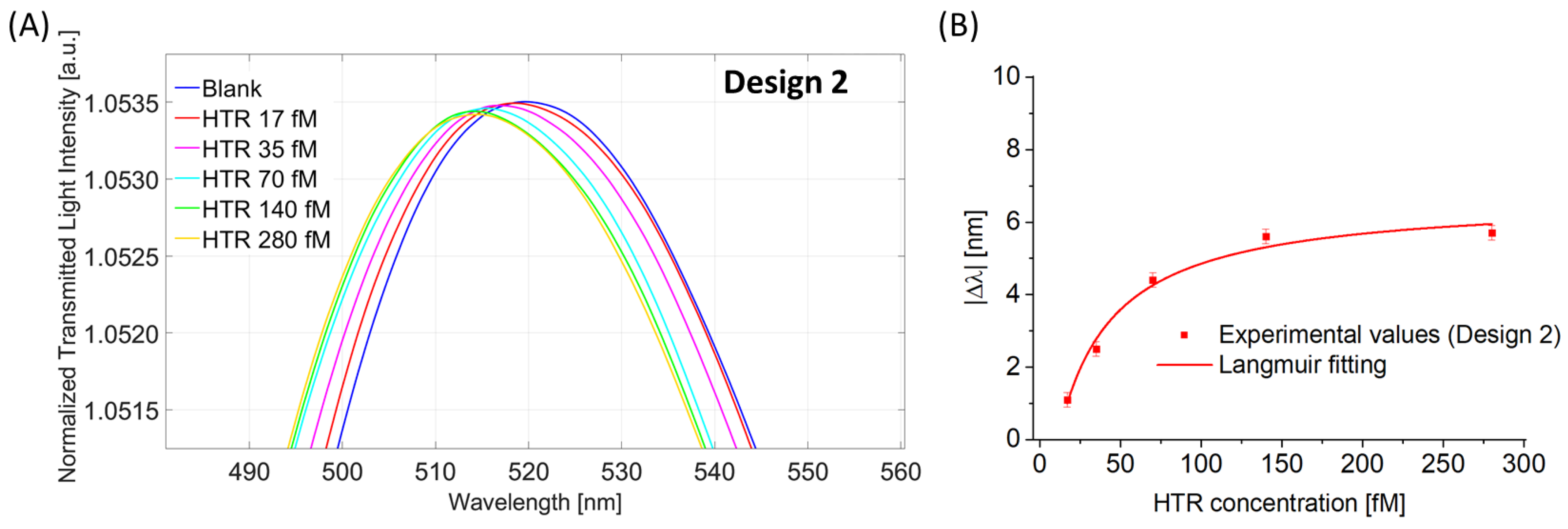

| λ0 [nm] | Δλmax [nm] | K [fM] | Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | St. Error | Value | St. Error | Value | St. Error | Χ2 | R2 |
| −1.855 | 0.453 | 10.899 | 1.351 | 35.918 | 28.672 | 13.676 | 0.937 |
| λ0 [nm] | Δλmax [nm] | K [fM] | Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | St. Error | Value | St. Error | Value | St. Error | Χ2 | R2 |
| −1.265 | 0.785 | 6.692 | 0.542 | 22.631 | 14.493 | 0.128 | 0.968 |
| Configuration | [nm/fM] | [fM] | [fM−1] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design 1 (POF-TiO2-ZrO2-nanoMIPs) | 0.30 | 4.48 | 0.028 |
| Design 2 (POF-ZrO2-TiO2-nanoMIPs) | 0.29 | 7.96 | 0.044 |
| Sensor Configuration | Receptor | LOD | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITO overlayer on multimode optical fiber fused silica core | amine group | avidin | 0.15 [nM] | [18] |
| ITO films on D-shaped optical fiber | aptamer | C-reactive protein (CRP) | 6.20 [nM] | [31] |
| Planar waveguide coated with a titanium dioxide (TiO2) thin-film | antibody | anti-IgG | 10 [nM] | [32] |
| ITO thin layer on uncladded multimode fiber | aptamer | thrombin | 100 [nM] | [33] |
| Design 1 (POF-TiO2-ZrO2) | nanoMIPs | HTR | 4.48 [fM] | This work |
| Design 2 (POF- ZrO2-TiO2) | nanoMIPs | HTR | 7.96 [fM] | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arcadio, F.; Noël, L.; Del Prete, D.; Seggio, M.; Zeni, L.; Bossi, A.M.; Soppera, O.; Cennamo, N. Sensing Approaches Exploiting Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles and Lossy Mode Resonance in Polymer Optical Fibers. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162361
Arcadio F, Noël L, Del Prete D, Seggio M, Zeni L, Bossi AM, Soppera O, Cennamo N. Sensing Approaches Exploiting Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles and Lossy Mode Resonance in Polymer Optical Fibers. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(16):2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162361
Chicago/Turabian StyleArcadio, Francesco, Laurent Noël, Domenico Del Prete, Mimimorena Seggio, Luigi Zeni, Alessandra Maria Bossi, Olivier Soppera, and Nunzio Cennamo. 2023. "Sensing Approaches Exploiting Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles and Lossy Mode Resonance in Polymer Optical Fibers" Nanomaterials 13, no. 16: 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162361
APA StyleArcadio, F., Noël, L., Del Prete, D., Seggio, M., Zeni, L., Bossi, A. M., Soppera, O., & Cennamo, N. (2023). Sensing Approaches Exploiting Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles and Lossy Mode Resonance in Polymer Optical Fibers. Nanomaterials, 13(16), 2361. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162361










