Fixation and Visualization of Full Protein Corona on Lipid Surface of Composite Nanoconstruction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Assembly of the MLNC
2.3. Modification of FBS or BSA Proteins with PACL
2.4. Incubation of MLNCs with Solutions of FBS or BSA
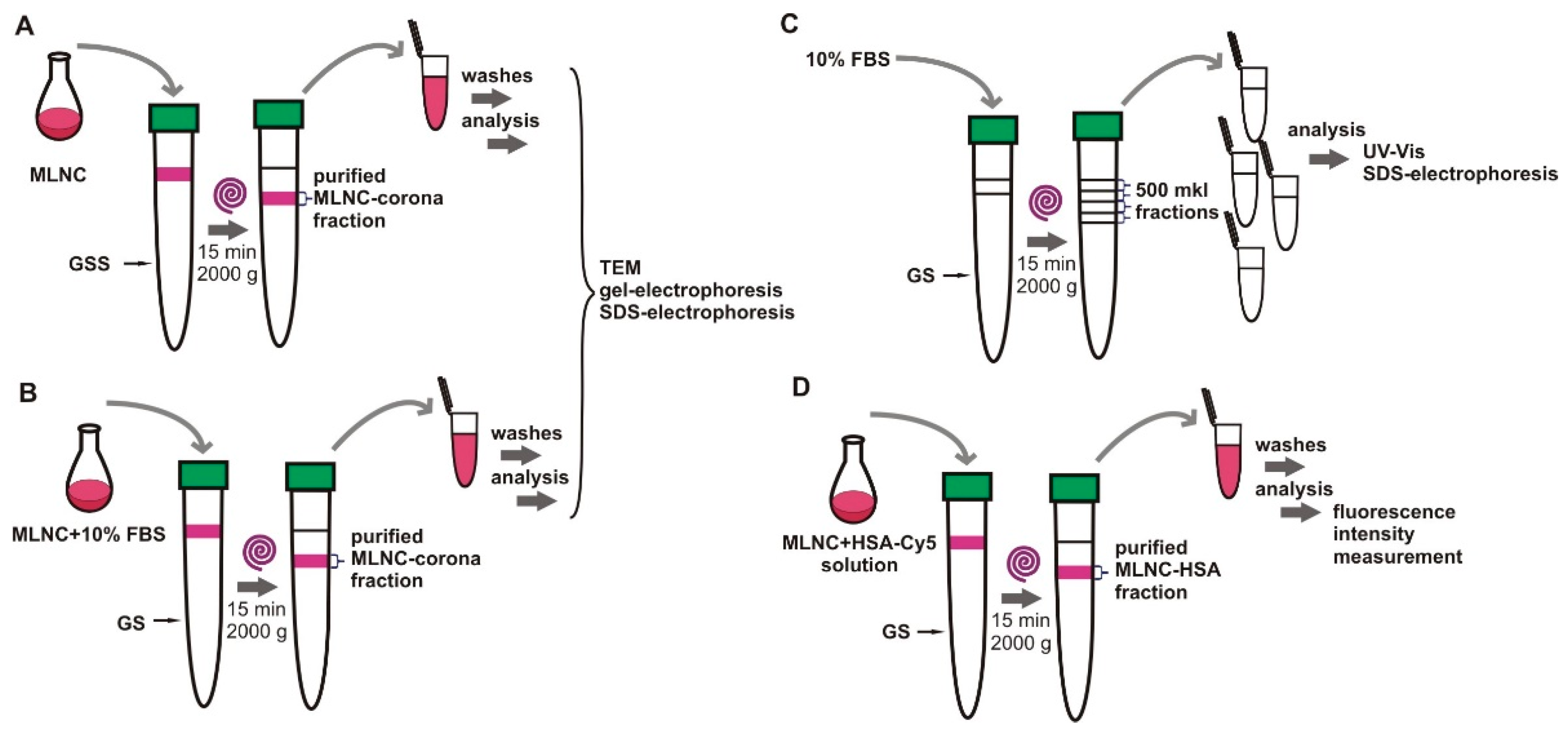
2.5. Isolation of MLNCs
2.6. Washing and Concentration of Isolated MNLCs
2.7. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.8. Optical Extinction Spectra
2.9. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.10. Electrophoresis
2.11. MALDI Mass Spectrometry
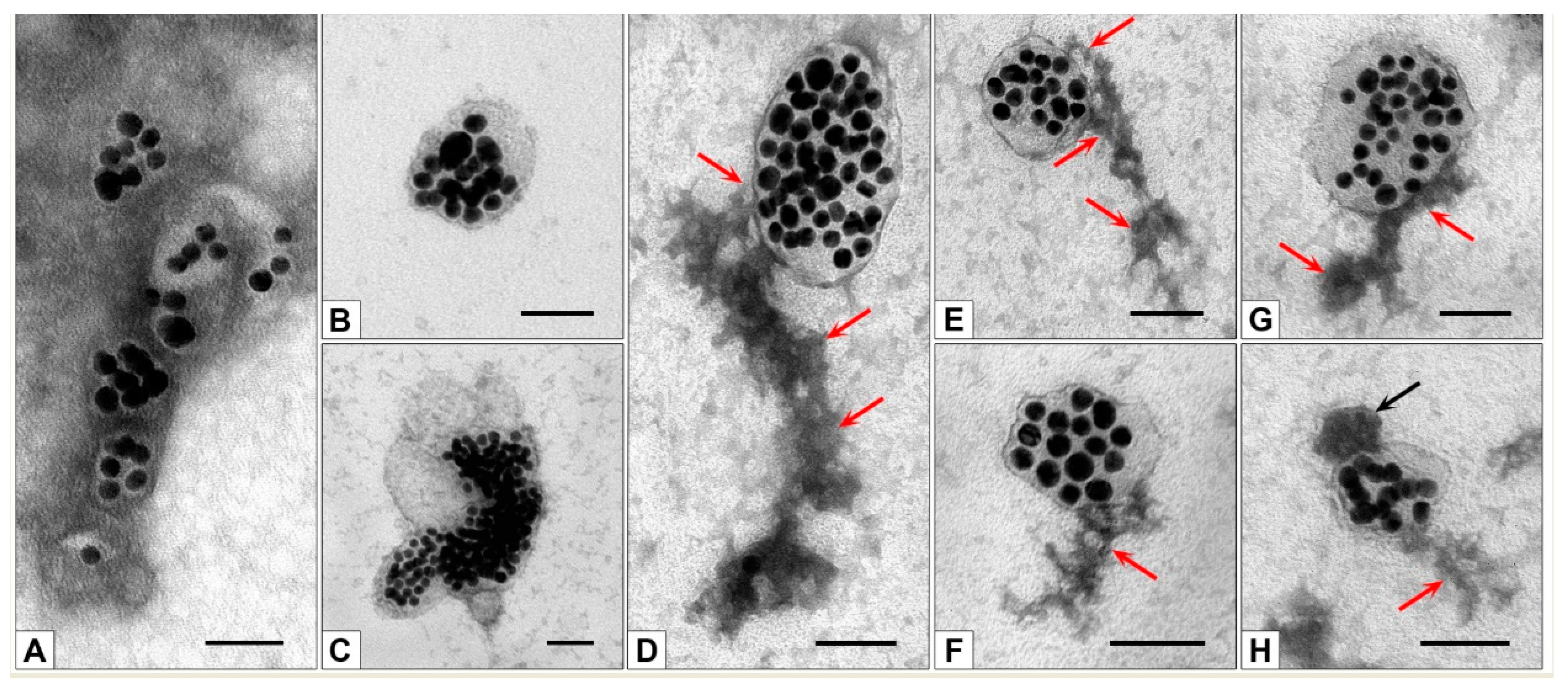
2.12. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3. Results
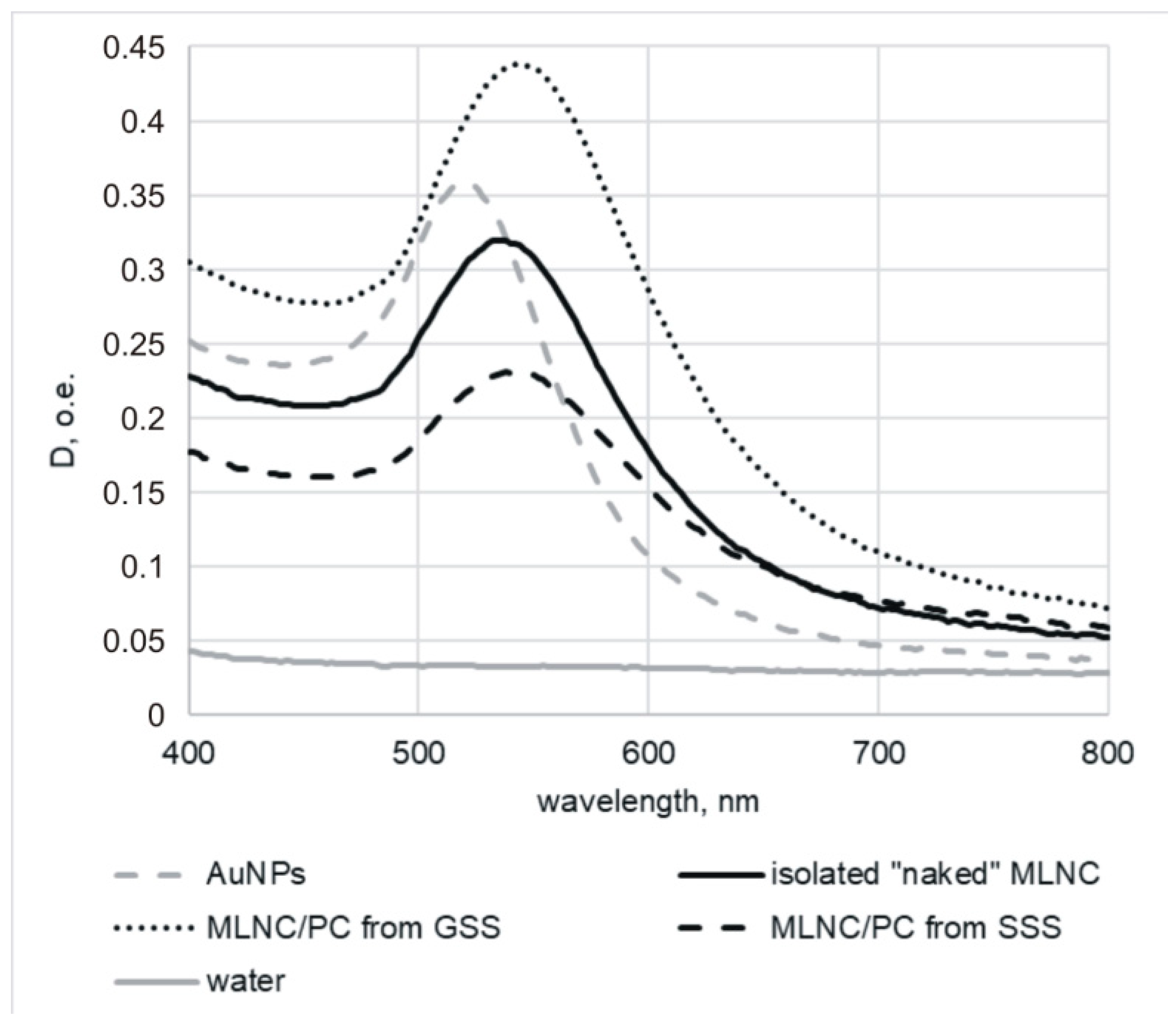
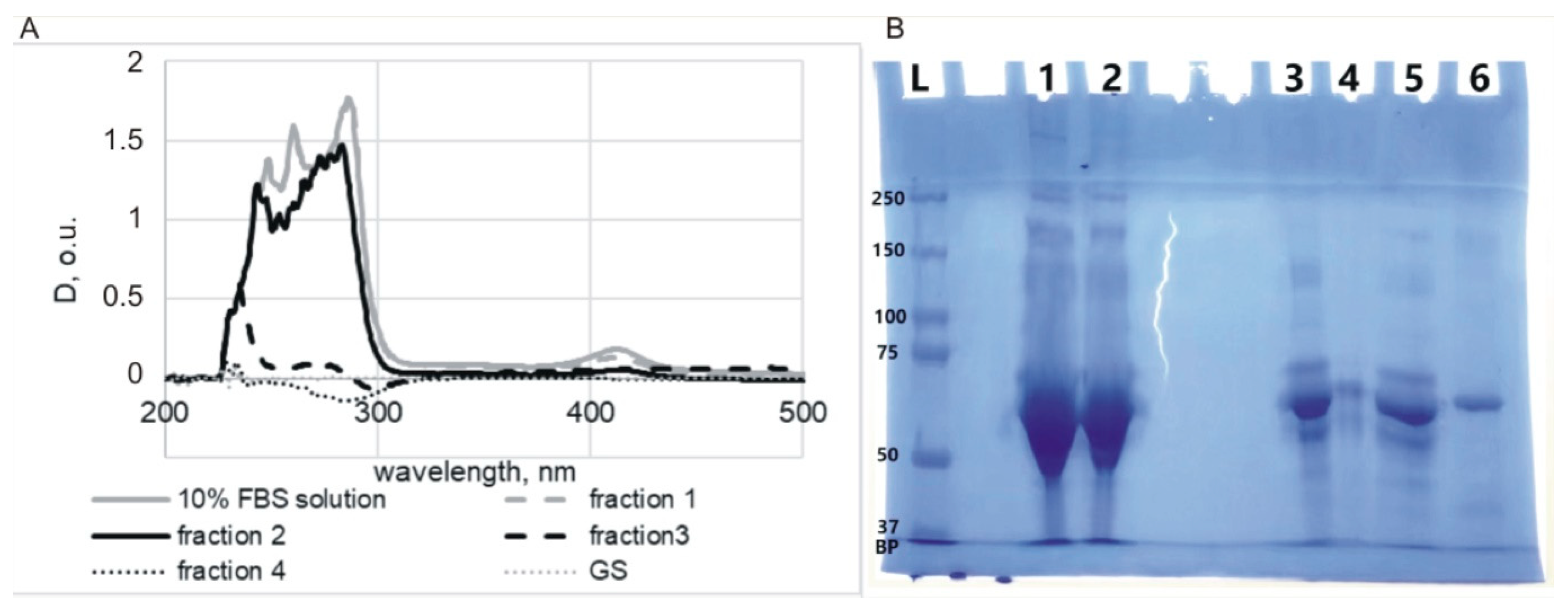
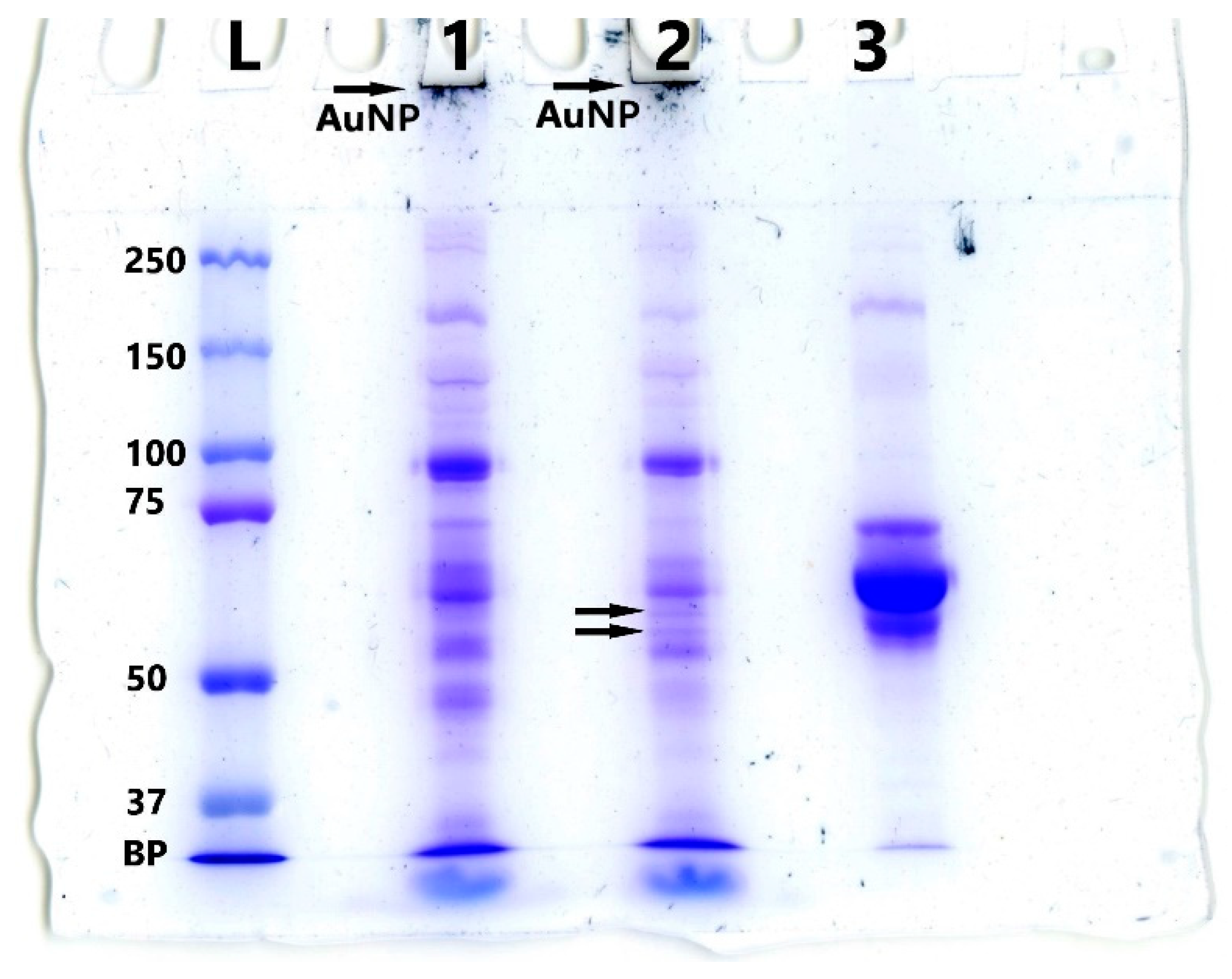
3.1. Confirmation of the Formation of a Protein Corona on the Surface of MLNCs
3.2. Isolation of MLNCs Bearing a Hard Protein Corona
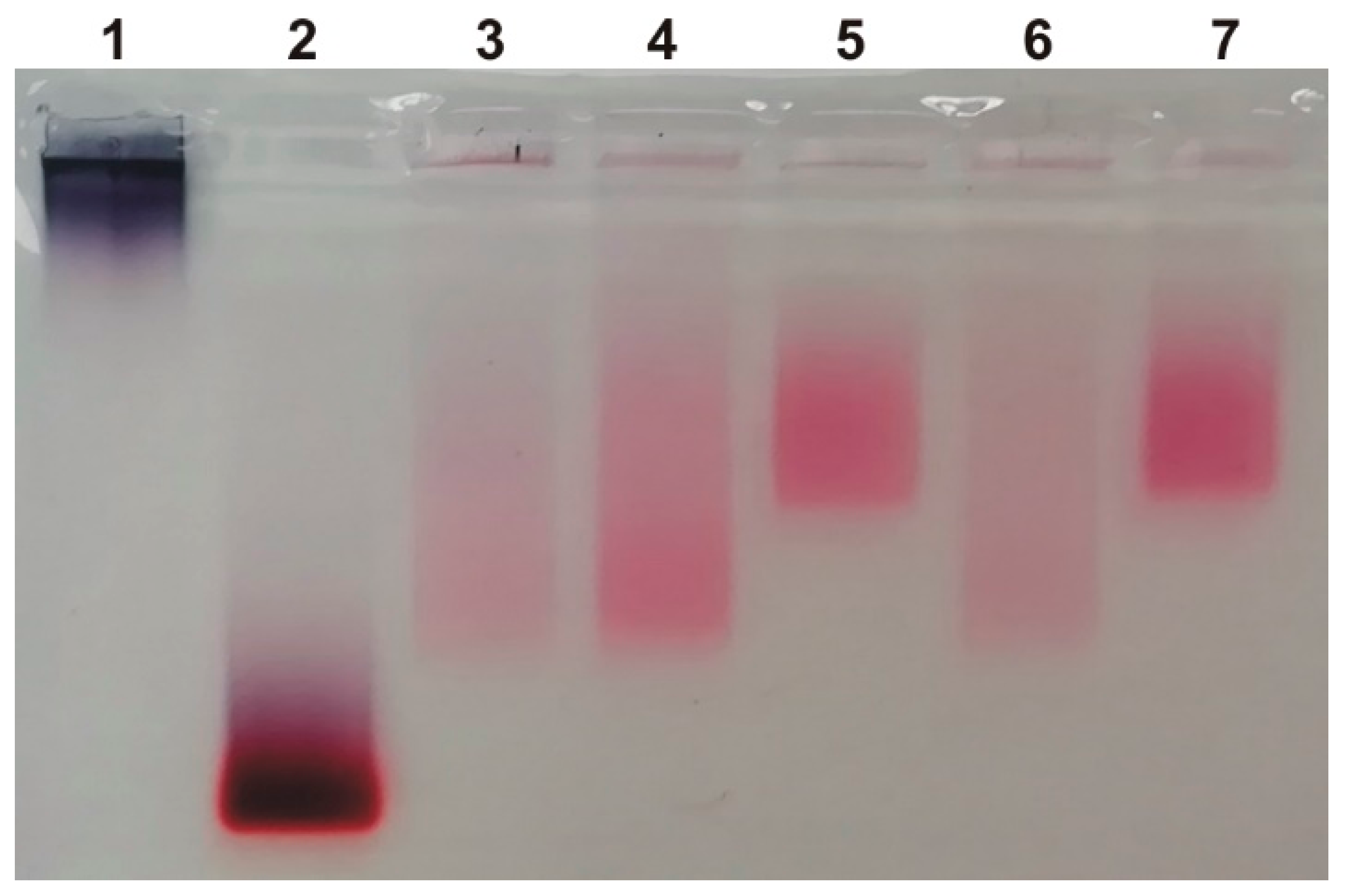
3.2.1. Selection of Conditions for Purification of MLNC/HCs from Unbound Serum Proteins
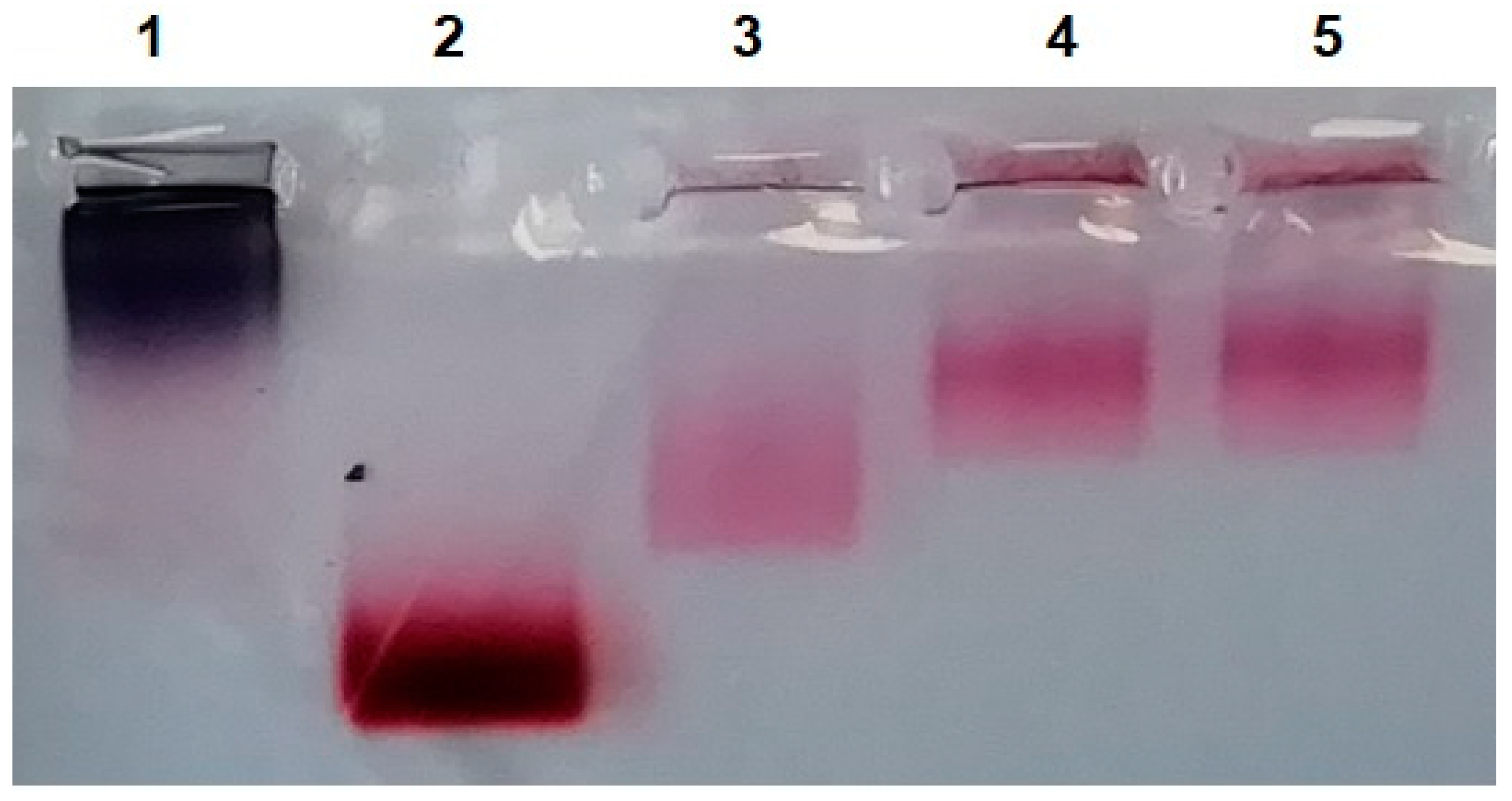
3.2.2. Determining the Quantity of MLNCs Needed to Study Hard Corona
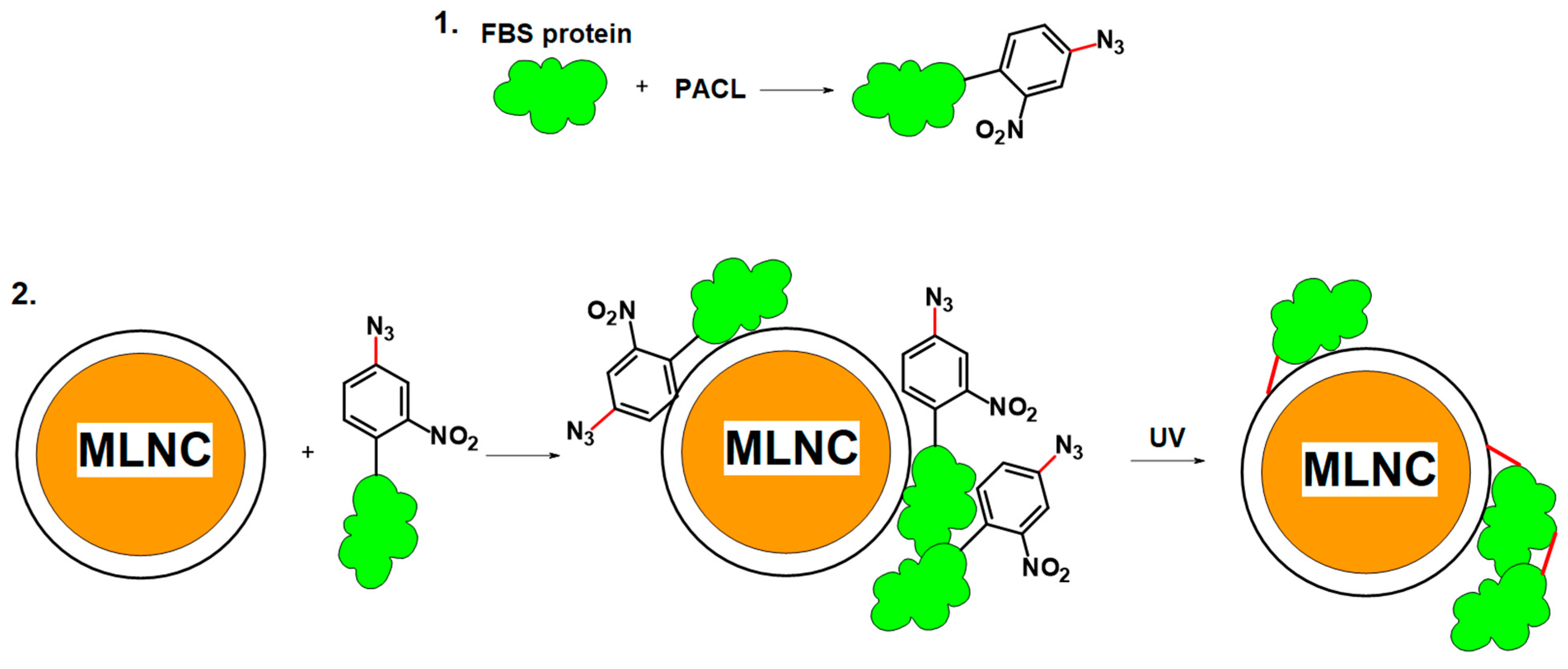
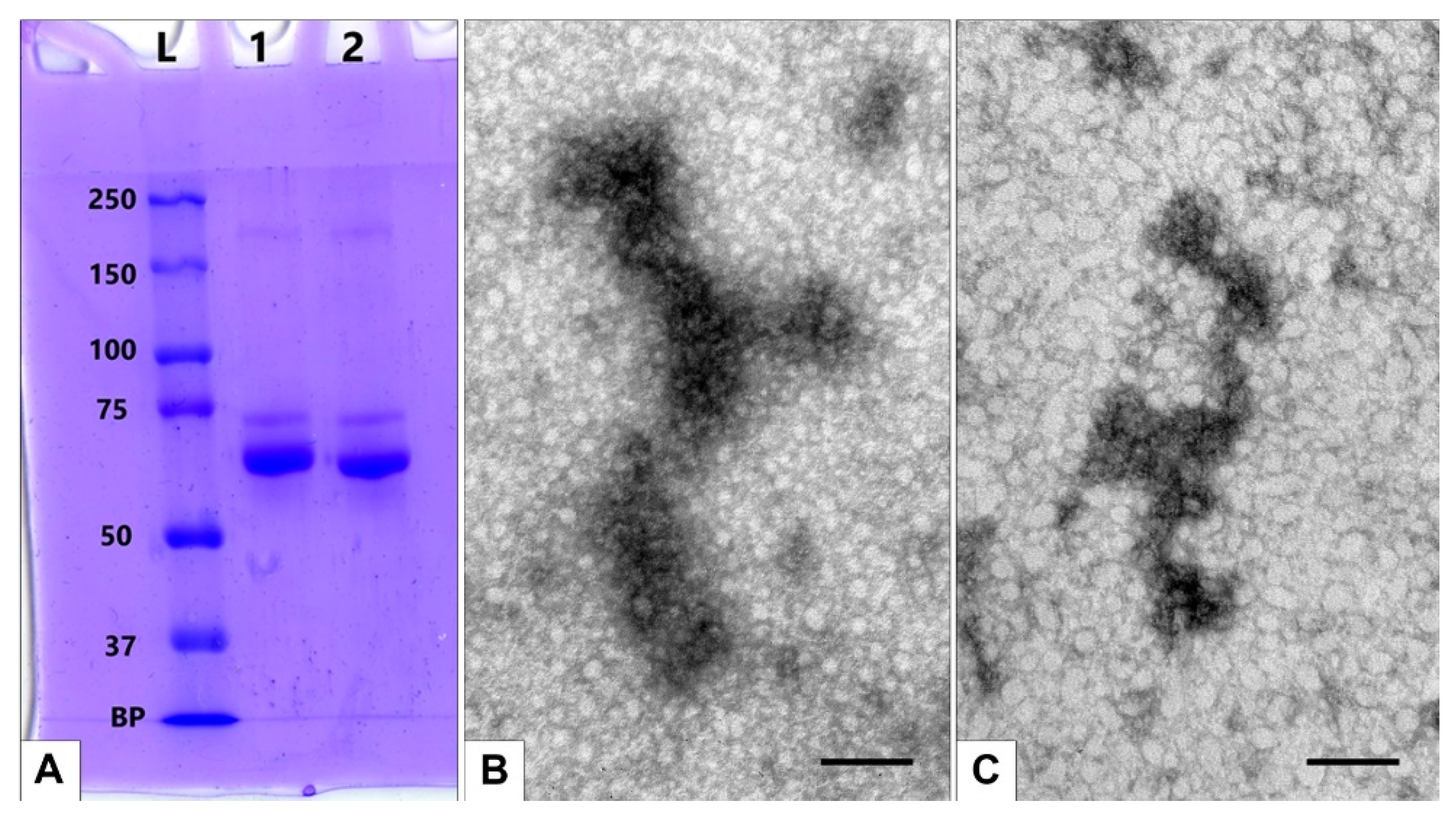
3.3. Obtaining MLNCs with Full Protein Corona
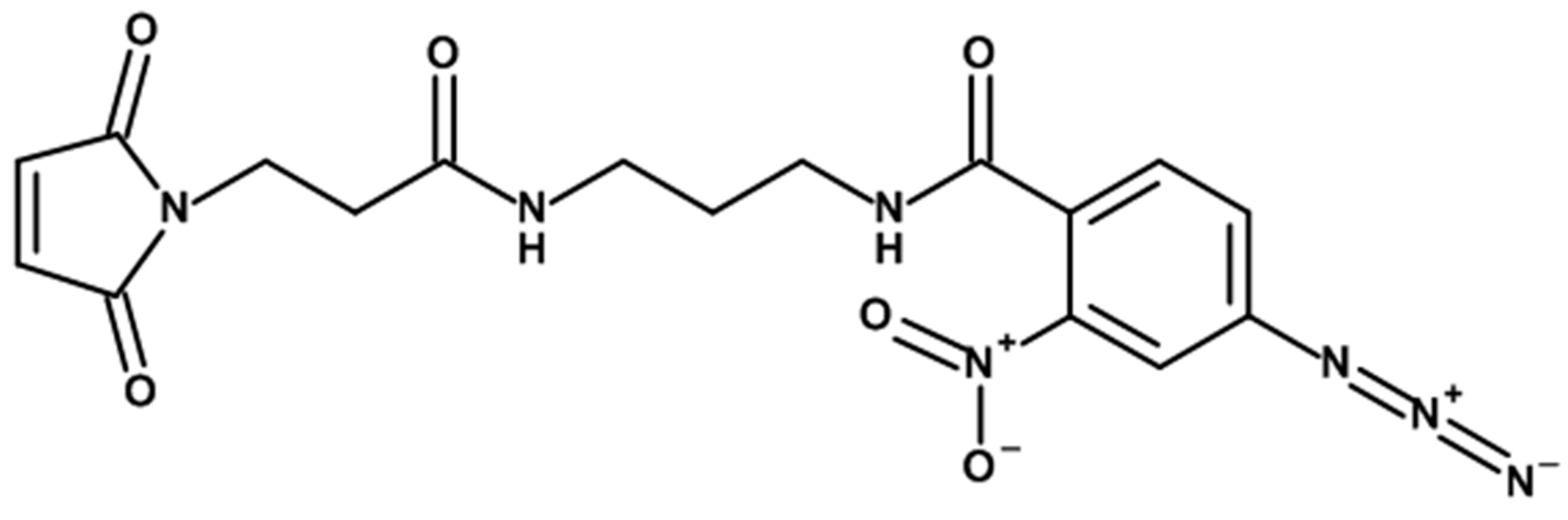
3.3.1. Cross-Linker Design
3.3.2. Modification of Serum Proteins
3.3.3. Interaction of Modified Serum with MLNCs
3.3.4. Detection of Full Corona Formation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Álvarez, R.; Vallet-Regí, M. Hard and Soft Protein Corona of Nanomaterials: Analysis and Relevance. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruszewska, J.; Zajda, J.; Matczuk, M. How to effectively prepare a sample for bottom-up proteomic analysis of nanoparticle protein corona? A critical review. Talanta 2021, 226, 122153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawan, C.; Lim, M.; Marquis, C.P.; Amal, R. Nanoparticle–protein corona complexes govern the biological fates and functions of nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 21, 2060–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Andrikopoulos, N.; Velonia, K.; Tang, H.; Cai, R.; Ding, F.; Ke, P.C.; Chen, C. Chemical and Biophysical Signatures of the Protein Corona in Nanomedicine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 9184–9205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Zoulikha, M.; Qiu, M.; Teng, C.; Lin, C.; Li, X.; Sallam, M.A.; Xu, Q.; He, W. The effects of protein corona on in vivo fate of nanocarriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 186, 114356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienhaus, K.; Nienhaus, G.U. Mechanistic Understanding of Protein Corona Formation around Nanoparticles: Old Puzzles and New Insights. Small 2023, 19, e2301663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, J.E.; Manning, W.C.; Troiano, G.; Hornburg, D.; Figa, M.; Hesterberg, L.; Platt, T.L.; Zhao, X.; Cuaresma, R.A.; Everley, P.A.; et al. Rapid, deep and precise profiling of the plasma proteome with multi-nanoparticle protein corona. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Qian, J.; Wei, X.; Ying, T.; Lu, W.; Zhan, C. Deciphering Protein Corona by scFv-Based Affinity Chromatography. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Simon, J.; Mailänder, V.; Morsbach, S.; Landfester, K. Preservation of the soft protein corona in distinct flow allows identification of weakly bound proteins. Acta Biomater. 2018, 76, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Beigi, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Zeuthen, C.M.; Eskandari, H.; Scavenius, C.; Juul-Madsen, K.; Vorup-Jensen, T.; Enghild, J.J.; Sutherland, D.S. Mapping and identification of soft corona proteins at nanoparticles and their impact on cellular association. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epanchintseva, A.V.; Poletaeva, J.E.; Dovydenko, I.S.; Chelobanov, B.P.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Pyshnaya, I.A. A Lipid-Coated Nanoconstruct Composed of Gold Nanoparticles Noncovalently Coated with Small Interfering RNA: Preparation, Purification and Characterization. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epanchintseva, A.V.; Poletaeva, J.E.; Dome, A.S.; Dovydenko, I.S.; Pyshnaya, I.A.; Ryabchikova, E.I. Chemical Modifications Influence the Number of siRNA Molecules Adsorbed on Gold Nanoparticles and the Efficiency of Downregulation of a Target Protein. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashkova, V.V.; Epanchintseva, A.V.; Vorobjev, P.E.; Razum, K.V.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Pyshnaya, I.A. Multilayer associates based on oligonucleotides and gold nanoparticles. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 43, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, K.M.; Payne, C.K. Concentration and composition of the protein corona as a function of incubation time and serum concentration: An automated approach to the protein corona. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 7265–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, S.; Baldelli Bombelli, F.; Pitek, A.S.; Dawson, K.A.; Rädler, J. Reversible versus Irreversible Binding of Transferrin to Polystyrene Nanoparticles: Soft and Hard Corona. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2532–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winzen, S.; Schoettler, S.; Baier, G.; Rosenauer, C.; Mailaender, V.; Landfester, K.; Mohr, K. Complementary analysis of the hard and soft protein corona: Sample preparation critically effects corona composition. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2992–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Landry, M.P.; Moore, A.; Coreas, R. The protein corona from nanomedicine to environmental science. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 422–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinz, A. Chemical cross-linking and mass spectrometry to map three-dimensional protein structures and protein–protein interactions. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2006, 25, 663–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.E.B.; Caspersen, M.B.; Robinson, E.; Morais, M.; Maruani, A.; Nunes, J.P.M.; Nicholls, K.; Saxton, M.J.; Caddick, S.; Baker, J.R.; et al. A platform for efficient, thiol-stable conjugation to albumin’s native single accessible cysteine. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 7946–7949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murale, D.P.; Hong, S.C.; Haque, M.; Lee, J.-S. Photo-affinity labeling (PAL) in chemical proteomics: A handy tool to investigate protein-protein interactions (PPIs). Proteome Sci. 2017, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, G.W.; Wilson, A.J. Photo-induced covalent cross-linking for the analysis of biomolecular interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3289–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldi, M.; Baldassarre, M.; Nati, M.; Laggetta, M.; Giannone, F.A.; Domenicali, M.; Bernardi, M.; Caraceni, P.; Bertucci, C. Mass spectrometric characterization of human serum albumin dimer: A new potential biomarker in chronic liver diseases. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 112, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izak-Nau, E.; Voetz, M.; Eiden, S.; Dusch, A.; Puntes, V. Altered characteristics of silica nanoparticles in bovine and human serum: The importance of nanomaterial characterization prior to its toxicological evaluation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Chantada-Vázquez, M.P.; López, A.C.; García-Vence, M.; Acea-Nebril, A.; Bravo, S.; Núñez, C. Protein Corona Gold Nanoparticles Fingerprinting Reveals a Profile of Blood Coagulation Proteins in the Serum of HER2- Overexpressing Breast Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M.; Mulenos, M.R.; Steele, L.R.; Sayes, C.M. Differences among Unique Nanoparticle Protein Corona Constructs: A Case Study Using Data Analytics and Multi-Variant Visualization to Describe Physicochemical Characteristics. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Poupardin, R.W.; Ebner-Peking, P.; Andrade, A.C.; Blochl, C.; Obermayer, A.; Gomes, F.G.; Vari, B.; Maeding, N.; Eminger, E.; et al. A functional corona around extracellular vesicles enhances angiogenesis, skin regeneration and immunomodulation. J. Extracell. Vesicl. 2022, 11, e12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, E.Á.; Turiák, L.; Visnovitz, T.; Cserép, C.; Mázló, A.; Sódar, B.W.; Försönits, A.I.; Petővári, G.; Sebestyén, A.; Komlósi, Z.; et al. Formation of a protein corona on the surface of extracellular vesicles in blood plasma. J. Extracell. Vesic. 2021, 10, e12140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigor’eva, A.E.; Dyrkheeva, N.S.; Bryzgunova, O.E.; Tamkovich, S.N.; Chelobanov, B.P.; Ryabchikova, E.I. Contamination of exosome preparations, isolated from biological fluids. Biomed. Khim. 2017, 63, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristo, E.; Hazizaj, A.; Corredig, M. Structural Changes Imposed on Whey Proteins by UV Irradiation in a Continuous UV Light Reactor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6204–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Number of Washes | RFU(Cy5)/RFU(albumin+Cy5-albumin) × 100% |
|---|---|
| Supernatant after MLNC isolation | 0.686 ± 0.059 |
| 1st wash | 0.021 ± 0.012 |
| 2nd wash | 0.015 ± 0.014 |
| 3rd wash | 0.002 ± 0.001 |
| 4th wash | not detected |
| Line | Sample | Size ± SD (d.nm) | ζ-Potential ± SD (mV) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MLNC | 210.4 ± 86.79 | −35.3 ± 5.6 | 0.148 |
| 2 | MLNC + FBS | 249.9 ± 124.2 | −43.0 ± 5.2 | 0.176 |
| 3 | MLNC + FBS UV-irradiated | 225 ± 97.83 | −38.5 ± 5.2 | 0.193 |
| 4 | MLNC&FBS/PACL/UV | 288.4 ± 116,8 | −37.2 ± 5.1 | 0.193 |
| 5 | MLNC + FBS/PACL | 242.3 ± 120.0 | −41.2 ± 5.8 | 0.175 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Epanchintseva, A.V.; Poletaeva, J.E.; Bakhno, I.A.; Belov, V.V.; Grigor’eva, A.E.; Baranova, S.V.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Dovydenko, I.S. Fixation and Visualization of Full Protein Corona on Lipid Surface of Composite Nanoconstruction. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243094
Epanchintseva AV, Poletaeva JE, Bakhno IA, Belov VV, Grigor’eva AE, Baranova SV, Ryabchikova EI, Dovydenko IS. Fixation and Visualization of Full Protein Corona on Lipid Surface of Composite Nanoconstruction. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(24):3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243094
Chicago/Turabian StyleEpanchintseva, Anna V., Julia E. Poletaeva, Irina A. Bakhno, Vladimir V. Belov, Alina E. Grigor’eva, Svetlana V. Baranova, Elena I. Ryabchikova, and Ilya S. Dovydenko. 2023. "Fixation and Visualization of Full Protein Corona on Lipid Surface of Composite Nanoconstruction" Nanomaterials 13, no. 24: 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243094
APA StyleEpanchintseva, A. V., Poletaeva, J. E., Bakhno, I. A., Belov, V. V., Grigor’eva, A. E., Baranova, S. V., Ryabchikova, E. I., & Dovydenko, I. S. (2023). Fixation and Visualization of Full Protein Corona on Lipid Surface of Composite Nanoconstruction. Nanomaterials, 13(24), 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243094








