Size, Morphology and Crystallinity Control Strategy of Ultrafine HMX by Microfluidic Platform
Abstract
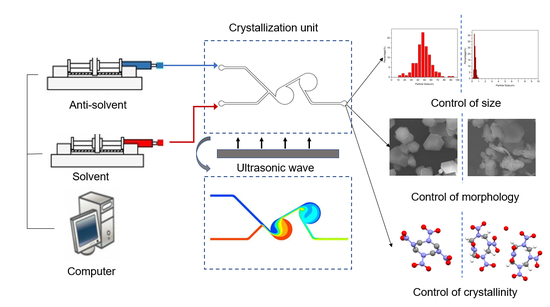
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
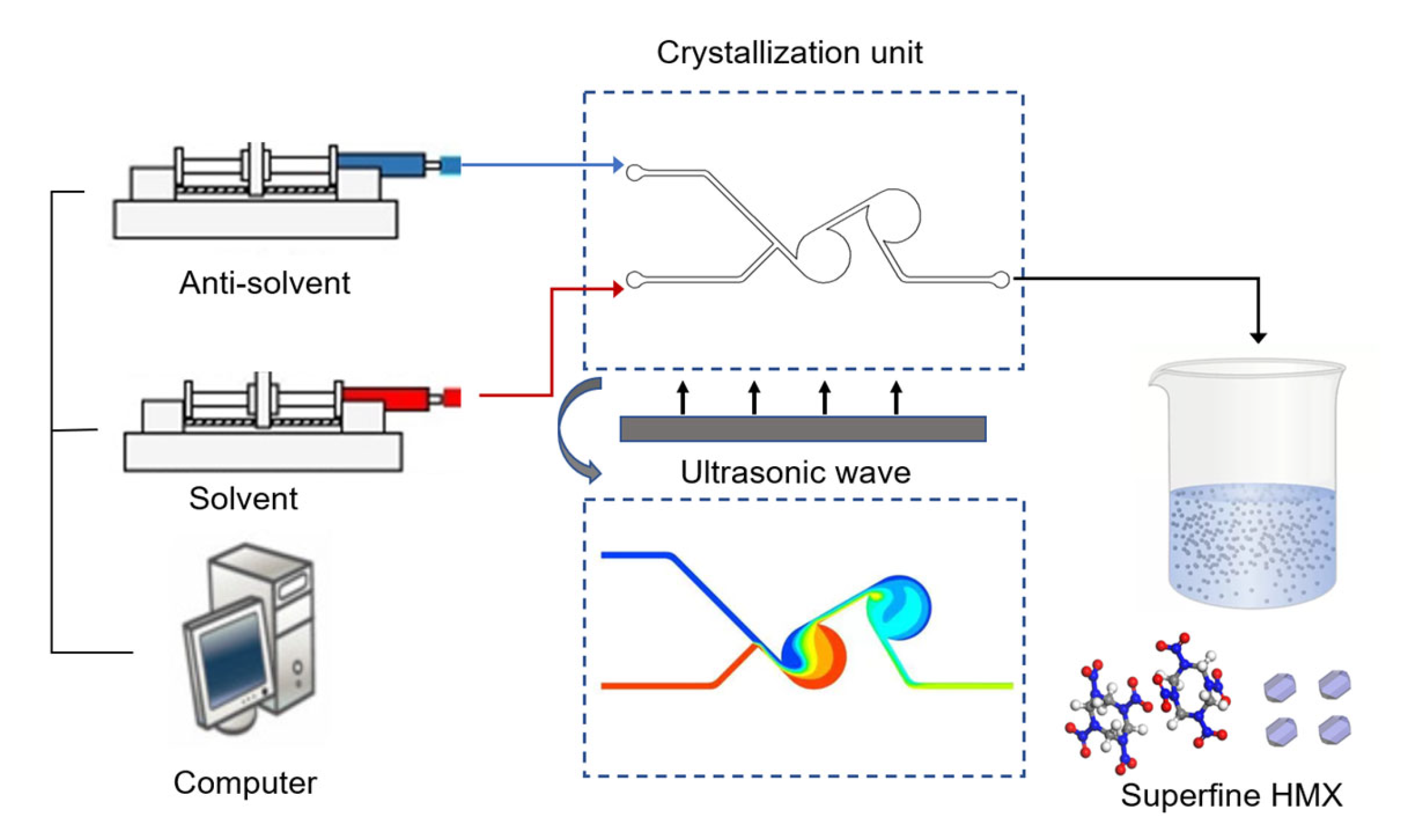
2.2. Preparation of Ultrafine HMX
2.3. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
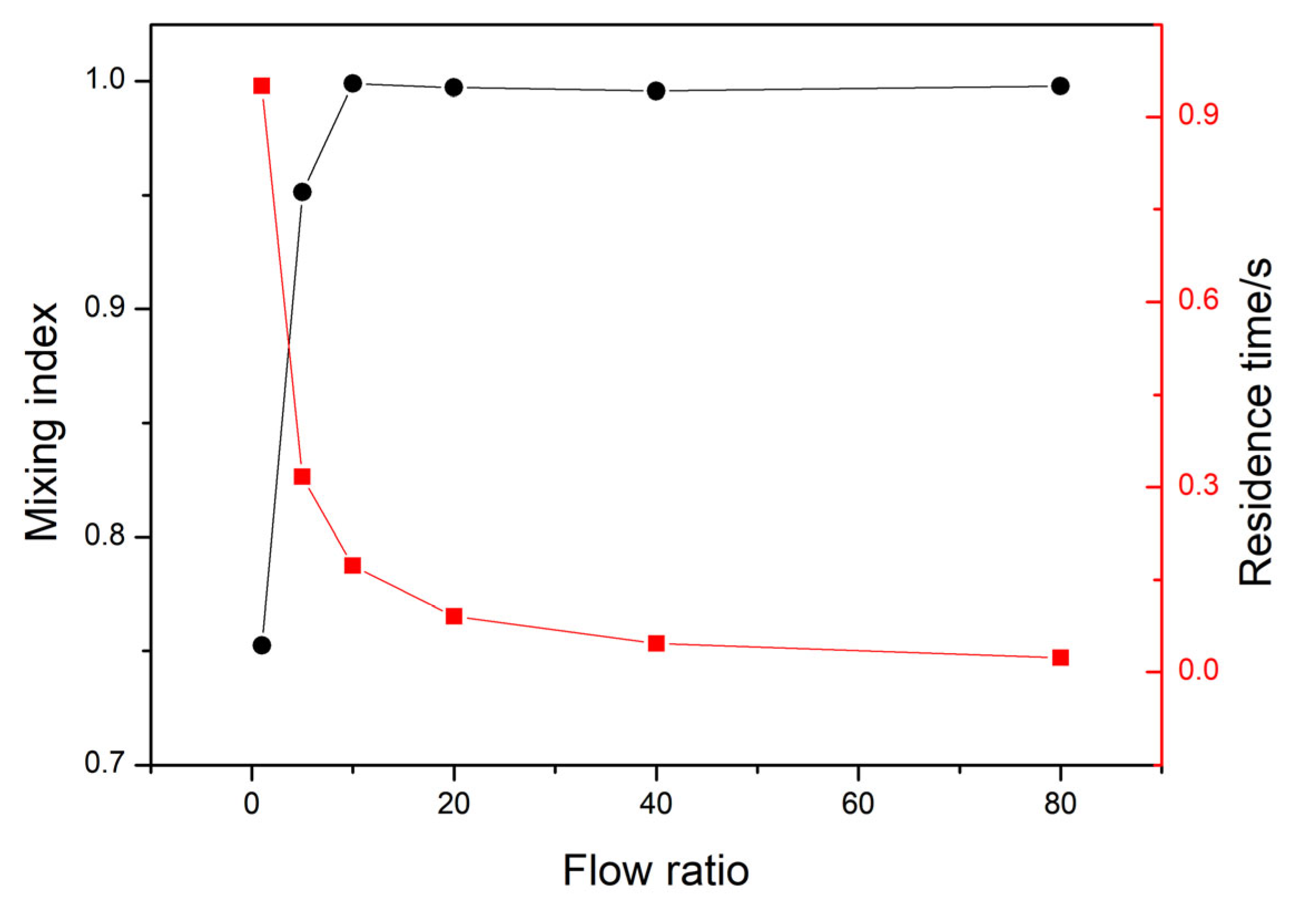
3.1. Flow Characteristics of Micromixer
3.2. Particle Size Control of Ultrafine HMX
3.3. Crystallinity Control of Ultrafine HMX
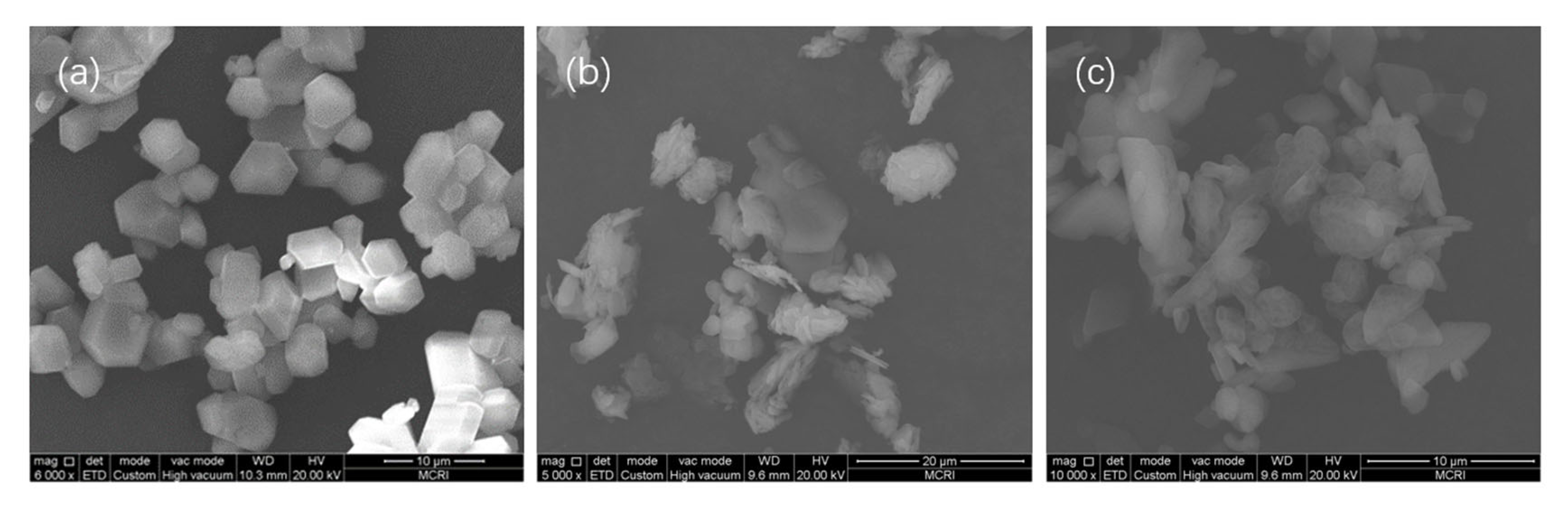
3.4. Crystal Morphology Control of Ultrafine HMX
3.5. Properties of Ultrafine HMX Prepared by Microfluidic Platform
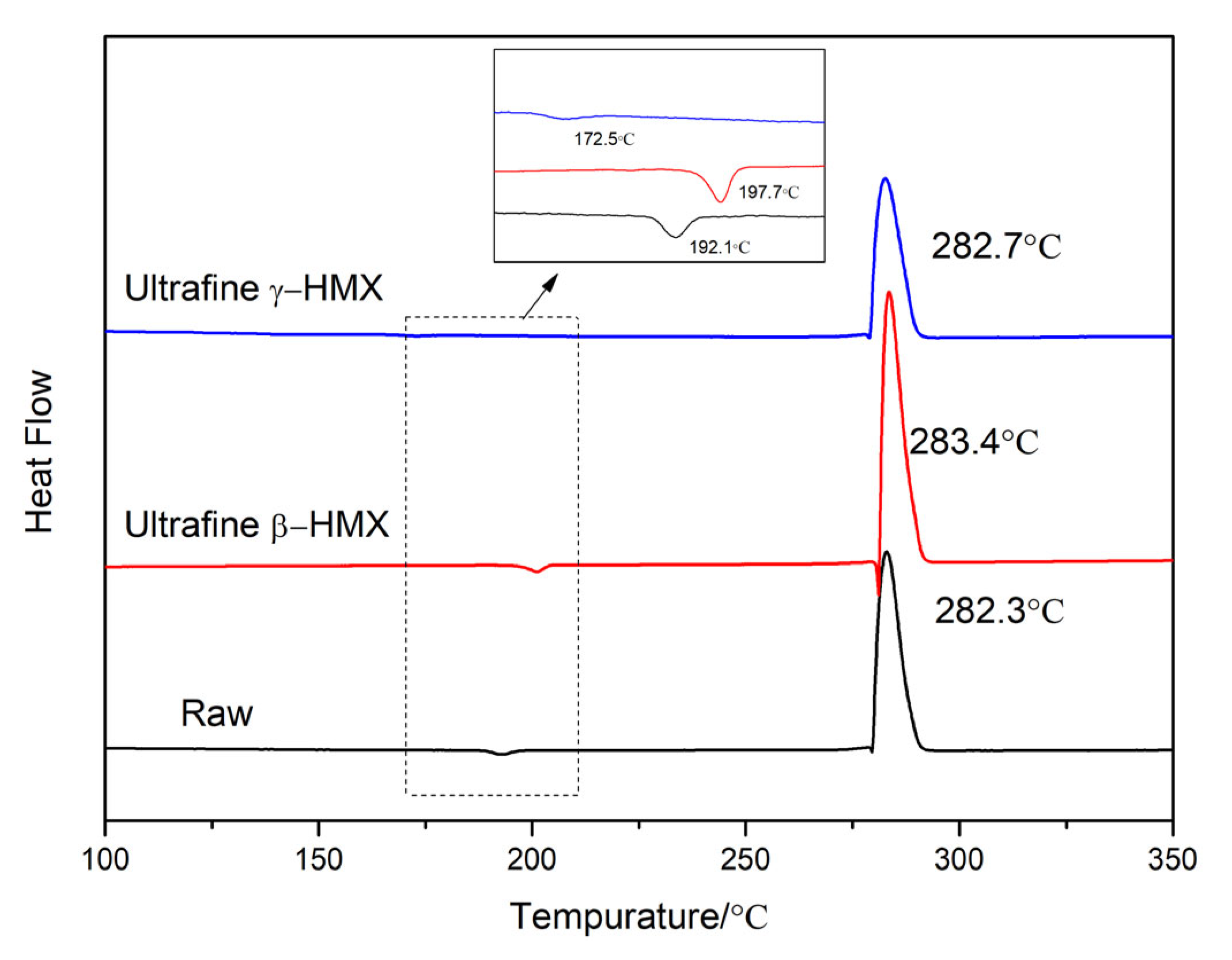
3.5.1. Thermal Behavior
3.5.2. Density and Mechanical Sensitivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akhavan, J. The Chemistry of Explosives; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, H.V.; Rabie, R.L.; Funk, D.J.; Diaz-Acosta, I.; Pulay, P.; Lippert, T.K. Theoretical and Experimental Study of the Vibrational Spectra of the α, β, and δ Phases of Octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine (HMX). J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 10594–10604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zeng, W.; Liu, F.S.; Gan, Y.D.; Tang, B.; Zhu, S.H.; Liu, Q.J. The vibrational, thermodynamic and mechanical properties of four types HMX based on the first-principles study. J. Energ. Mater. 2021, 39, 125–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Li, J.; Han, Z.; Ma, H.; Wang, B. Comparing the impact safety between two HMX-based PBX with different binders. FirePhysChem 2021, 1, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, W.; Yang, Q.; Song, J.; Hao, G.Z.; Li, F.S. Study of nano-nitramine explosives: Preparation, sensitivity and application. Def. Technol. 2014, 10, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.B.; Yang, Z.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Pan, L.P.; Ding, L.; Tian, X.; Zheng, X.; Gong, F.Y. Fabrication and characterization of HMX@TPEE energetic microspheres with reduced sensitivity and superior toughness properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 142, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulenbrugge, J.J.; van der Steen, A.C.; van der Heijden, A.E.D.M. Crystallization of energetic materials: The effect on stability, sensitivity and processing properties. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Energetic Materials Technology (ISEM 1995), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 24–27 September 1995; pp. 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Veltmans, W.H.M.; van der Heijden, A.E.D.M.; Bellerby, J.M.; Rodgers, M.I. The effect of different crystallization techniques on morphology and stability of HNF. In Proceedings of the 31st International Annual Conference of ICT, Karlsruhe, Germany, 27–30 June 2000; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Pang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ping, C. Ultrafine high quality HMX prepared by ultrasonic assisted spray method and its crystal type control. Chin. J. Energ. Mater. 2018, 26, 260–266. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J. Ultrafine HMX prepared by solvent-nonsolvent method. Blasting 2013, 30, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.M.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.W. Preparation of micronized β-HMX using supercritical carbon dioxide as antisolvent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 9107–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ouyang, G.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Gu, Z.; Li, F. Massive preparation of reduced-sensitivity nano CL-20 and its characterization. J. Energ. Mater. 2015, 33, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.W.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.R.; Ye, B.Y.; Geng, X.H.; Wang, J.Y. Nano-HNS particles: Mechanochemical preparation and properties investigation. J. Nanomater. 2018, 20018, 9436089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, A.K.; Thanigaivelan, U.; Pandey, R.K.; Asthana, S.; Khomane, R.B.; Kulkarni, B.D. Preparation of spherical particles of 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethene (FOX-7) using a micellar nanoreactor. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2012, 16, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, Y.; Zarandi, M.; Zarei, M.A.; Soleyman, R.; Zeynali, V. A novel approach for preparation of CL-20 nanoparticles by microemulsion method. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 193, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; An, C.; Hou, C.; Xu, W.; Li, X. Study on ultrasound-and spray-assisted precipitation of CL-20. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 2012, 37, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risse, B.; Spitzer, D.; Hassler, D.; Schnell, F.; Comet, M.; Pichot, V.; Muhr, H. Continuous formation of submicron energetic particles by the flash-evaporation technique. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kumar, P.D.; Jindal, D.; Sharma, S.; Agarwal, A.; Lata, P. Micro nozzle assisted spraying process for re-crystallization of Submicrometer Hexanitrostilbene explosive. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 2018, 43, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Deng, X. Crystal morphology of HMX and its control with supercritical O2 anti-solvent precipitation. J. Synth. Cryst. 2004, 33, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Niehaus, M.; Teipel, U.; Bunte, G.; Krause, H.H. Suitability of modified supercritical carbon dioxide as solvent for polar substances. Propell. Explos. Pyrot. 1997, 22, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Steinbock, O. Materials synthesis and catalysis in microfluidic devices: Prebiotic chemistry in mineral membranes. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, J. Multiphase flow processing in microreactors combined with heterogeneous catalysis for efficient and sustainable chemical synthesis. Catal. Today 2018, 308, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, R.; Sun, Q.; Baby, T.; Wibowo, D.; Middelberg, A.P.; Zhao, C.X. Multiphase microfluidic synthesis of micro-and nanostructures for pharmaceutical applications. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 169, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagus, T.P.; Edd, J.F. A review of the theory, methods and recent applications of high-throughput single-cell droplet microfluidics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 114005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, X.K.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.S.; Wong, C.C.; Fang, Q. Nanoliter-scale oil-air-droplet chip-based single cell proteomic analysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5430–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Xu, S.; Jiang, H. Application and development trend of microfluidic technology in preparation of energetic materials. Chin. J. Explos. Propellants 2022, 41, 439–451. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, R.; Zhu, P.; Ye, Y.; Xia, H.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y. Microflow synthesis and preparation of hazard chemical materials. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2018, 36, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Pan, J.; Fang, Q. Research progress of microfluidic technique in synthesis of micro/nano materials. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, B.; Ding, F.; Ji, Y. Synthesis of insensitive nitrate plasticizers TMETN and PGDN by micro reaction technology. Chin. J. Explos. Propellants 2018, 41, 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, P.; Shi, J.; Yan, F.; Xia, H.; Shen, R. Improvement of silver azide crystal morphology and detonation behavior by fast mixing using a microreaction system with an integrated static micromixer. React. Chem. Eng. 2020, 5, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, J.; Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, J. Study on refining CL-20 by micro-reactor technology. Initiat. Pyrotech. 2020, 6, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Zhu, P.; Zhao, S.; Xu, C.; Yan, F.; Shen, R.; Xia, H.; Jiang, H.; Xu, S.; Zhao, F. Continuous spheroidization strategy for explosives with micro/nano hierarchical structure by coupling microfluidics and spray drying. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, J.; Zhu, P.; Xia, H.; Chen, C.; Shen, R. Microfluidic platform for preparation and screening of narrow size-distributed nanoscale explosives and supermixed composite explosives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 13191–13204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhu, P.; Zhao, S.; Shen, R.; Xia, H.; Jiang, H.; Xu, S. Microfluidic strategy for rapid and high-quality control of crystal morphology of explosives. React. Chem. Eng. 2020, 5, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Chang, C.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Fu, L.M. Microfluidic mixing: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3263–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y. Numerical characterization of simple three-dimensional chaotic micromixers. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 277, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, B.D. Crystal size distribution (CSD) in rocks and the kinetics and dynamics of crystallization. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1988, 99, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Jiao, Q. Micro/Nano Energetic Materials; Beijing Institute of Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Brill, T.B.; Karpowlcz, R.J. Solid phase transition kinetics. The role of intermolecular forces in the condensed-phase decomposition of octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranltro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine. J. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 4260–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, P.; Cobbledick, R.E.; Small, R.W.H. Structure of the fourth form of 1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetraazacyclooctane (γ-HMX), 2C4H8N8O8. 0.5 H2O. Acta Cryst. Sect. C 1985, 41, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wang, X. Crystal structure and morphology of β-HMX in acetone: A molecular dynamics simulation and experimental study. J. Chem. Sci. 2017, 129, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowlan, P.; Henson, B.F.; Smilowitz, L.; Levitas, V.I.; Suvorova, N.; Oschwald, D. Kinetics of the γ–δ phase transition in energetic nitramine-octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 150, 064705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrmann, M.; Engel, W.; Eisenreich, N. Thermal analysis of the phases of HMX using X-ray diffraction. Z. Krist-Cryst. Mater. 1993, 204, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, E.; Zhao, N.; Qin, Z.; Ma, H.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; An, T.; Yi, J.; Zhao, F. Thermal decomposition behavior and thermal safety of nitrocellulose with different shape CuO and Al/CuO nanothermites. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Criado, J.; Sánchez-Jiménez, P.; Pérez-Maqueda, L. Critical study of the isoconversional methods of kinetic analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008, 92, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Features | β-HMX | γ-HMX |
|---|---|---|
| molecular structure | 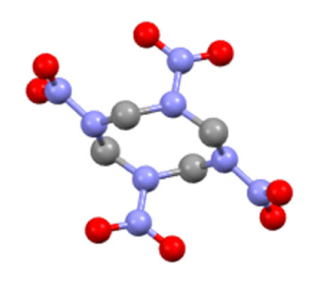 | 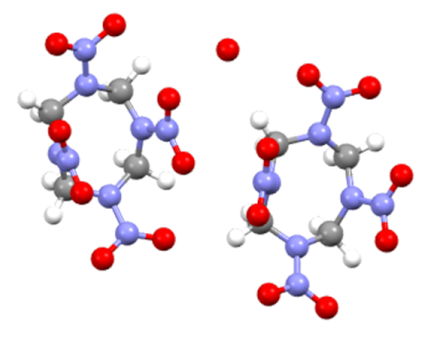 |
| Molecular formula | C4H8N8O8 | 2C4H8N8O8 H2O |
| Conformations | chair | boat |
| Symmetry class | monoclinic | monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/C | Pn |
| Samples | Phase Transition Process | Decomposition Process | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tp1/°C | ΔH1/J g−1 | Tp2/°C | ΔH2/J g−1 | |
| Raw-HMX | 192.1 | 34.2 | 282.3 | −1899.8 |
| ultrafine β-HMX | 197.7 | 35.5 | 283.4 | −1987.3 |
| ultrafine γ-HMX | 172.5 | 13.1 | 282.7 | −1888.2 |
| β/K·min−1 | Tp/°C | Ek/KJ·mol−1 | rk | ln(Ak) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β→δ | 5 | 195.2 | 283.0 ± 2.5 | 0.9234 | 29.8 ± 0.3 |
| 10 | 197.7 | ||||
| 15 | 198.1 | ||||
| 20 | 203.3 | ||||
| γ→δ | 5 | 168.8 | 257.9 ± 2.5 | 0.9840 | 28.6 ± 0.3 |
| 10 | 172.5 | ||||
| 15 | 174.8 | ||||
| 20 | 177.6 |
| Samples | Raw-HMX | Ultrafine β-HMX |
|---|---|---|
| Density/g∙cm−3 | 1.90 | 1.92 |
| Impact sensitivity/% | 84 | 72 |
| Friction sensitivity/% | 88 | 68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, S.; Xu, S.; Zhao, F. Size, Morphology and Crystallinity Control Strategy of Ultrafine HMX by Microfluidic Platform. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030464
Jiang H, Wang X, Yu J, Zhou W, Zhao S, Xu S, Zhao F. Size, Morphology and Crystallinity Control Strategy of Ultrafine HMX by Microfluidic Platform. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(3):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030464
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Hanyu, Xuanjun Wang, Jin Yu, Wenjun Zhou, Shuangfei Zhao, Siyu Xu, and Fengqi Zhao. 2023. "Size, Morphology and Crystallinity Control Strategy of Ultrafine HMX by Microfluidic Platform" Nanomaterials 13, no. 3: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030464
APA StyleJiang, H., Wang, X., Yu, J., Zhou, W., Zhao, S., Xu, S., & Zhao, F. (2023). Size, Morphology and Crystallinity Control Strategy of Ultrafine HMX by Microfluidic Platform. Nanomaterials, 13(3), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030464