Modulating the Surface Properties of Lithium Niobate Nanoparticles by Multifunctional Coatings Using Water-in-Oil Microemulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
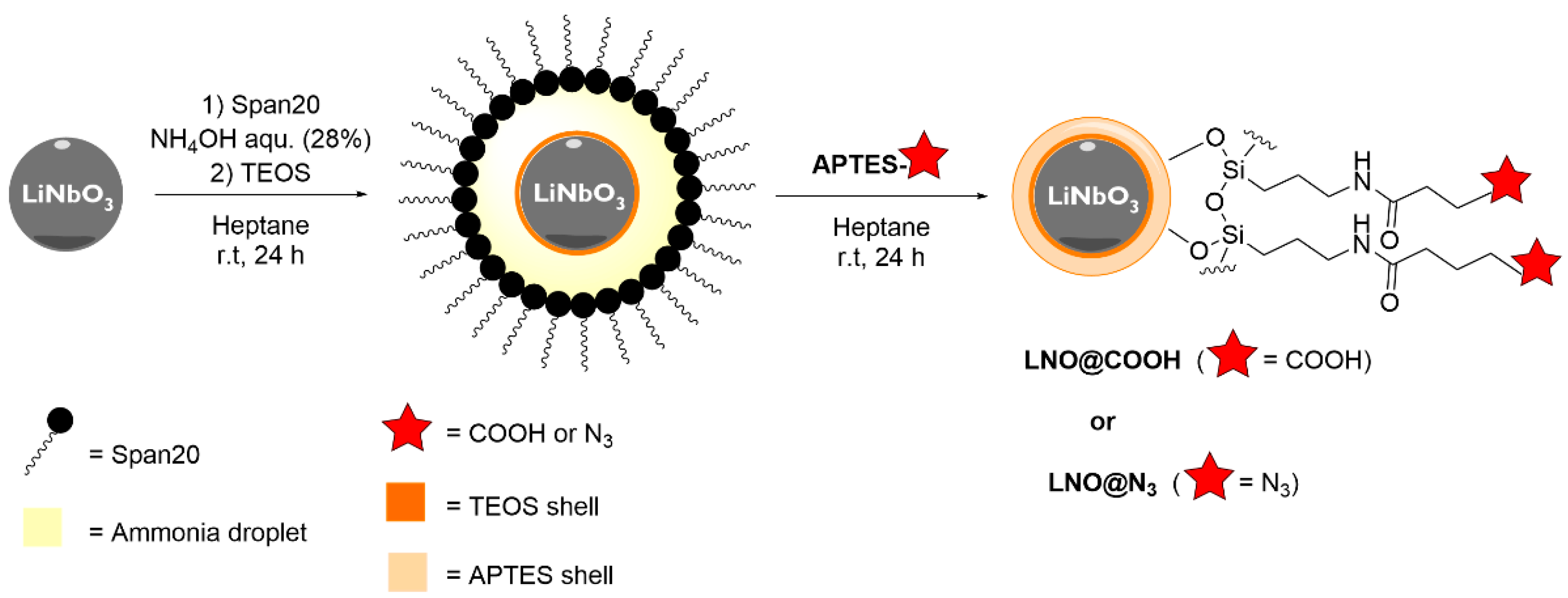
2.1. General Procedure for Coating LNO NPs Using a Reverse Micro-Emulsion Method
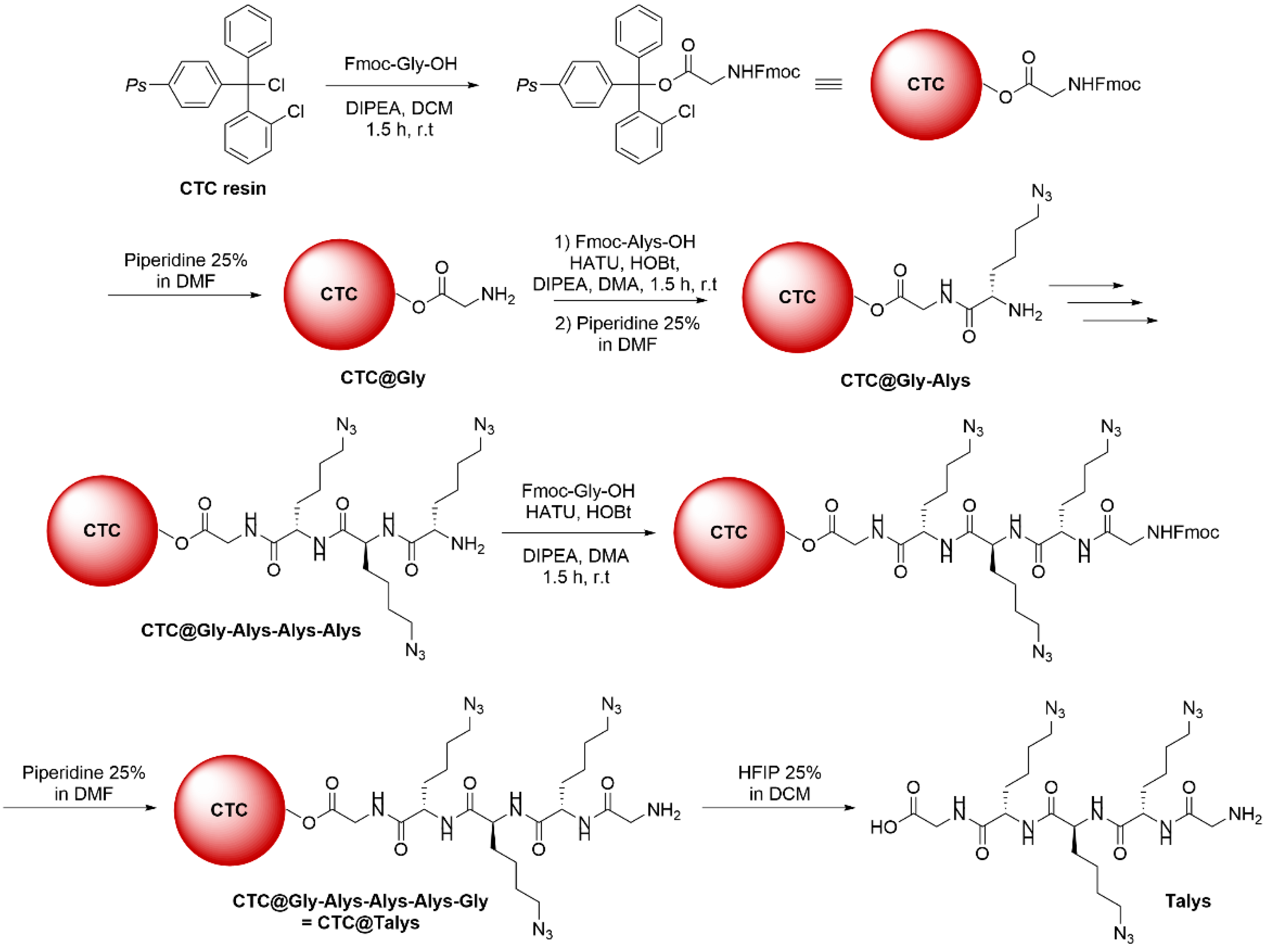
2.2. Synthesis of Tri-Azidolysine (Talys)
2.2.1. Glycine Loading on 2-Chlorotrityl Chloride Resin
2.2.2. Azidolysine (Alys) Successive Coupling
2.2.3. Final Glycine Coupling
2.2.4. Peptide Cleavage from Resin
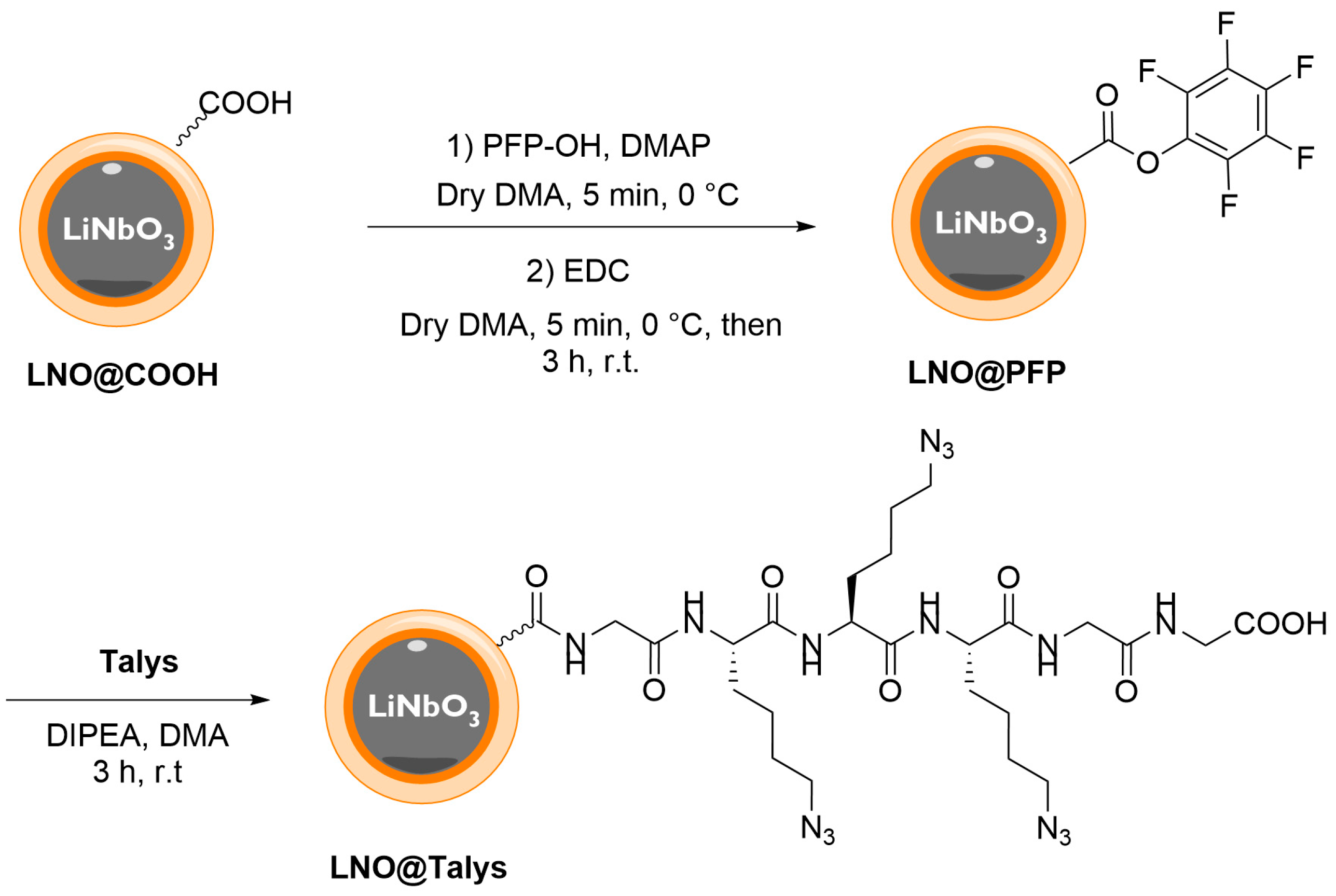
2.3. Functionalization of Coated LNO NPs with Peptide Derivative
2.4. Protein Adsorption on LNO@Talys
3. Results
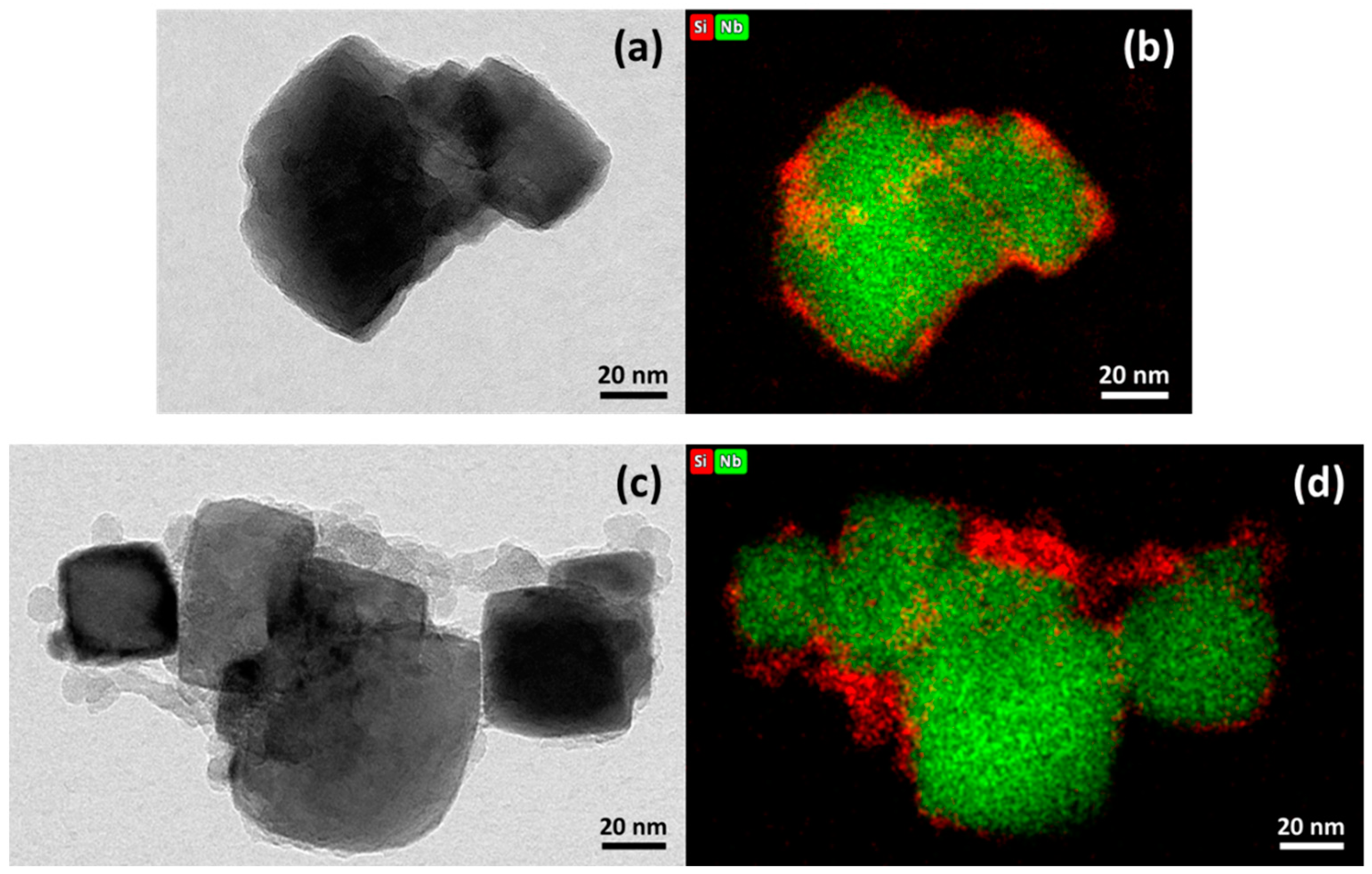
3.1. Coating of LNO NPs by W/O Microemulsion
3.2. Functionalization of LNO@COOH NPs with Peptide Derivative
3.2.1. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Talys
3.2.2. Conjugation of Talys to LNO@COOH NPs
3.2.3. Protein Adsorption on LNO@Talys
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De, M.; Ghosh, P.S.; Rotello, V.M. Applications of Nanoparticles in Biology. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4225–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, X.; Li, Y. Physicochemical Characteristics of Nanoparticles Affect Circulation, Biodistribution, Cellular Internalization, and Trafficking. Small 2013, 9, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Crozals, G.; Bonnet, R.; Farre, C.; Chaix, C. Nanoparticles with multiple properties for biomedical applications: A strategic guide. Nano Today 2016, 11, 435–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.K.; Yun, Y.H.; Park, K. Smart nanoparticles for drug delivery: Boundaries and opportunities. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 125, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramasamy, T.; Ramasamy, H.B.; Gupta, B.; Gupta, B.K.; Choi, H.-G.; Yong, C.S. Smart chemistry-based nanosized drug delivery systems for systemic applications: A comprehensive review. J. Control. Release 2017, 258, 226–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, T.; Ruttala, H.B.; Gupta, B.; Poudel, B.K.; Choi, H.-G.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O. Biofunctionalized targeted nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2008, 8, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Xu, K.; Taratula, O.; Farsad, K. Applications of Nanoparticles in Biomedical Imaging. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ge, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Cui, J.; Zeng, J.; Gao, M. Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: A next generation contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 14, e1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wiśniowska, A.; Fan, J.; Harvey, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, V.; Hansen, E.C.; Zhang, J.; Kaul, M.G.; Frey, A.M.; et al. Single-nanometer iron oxide nanoparticles as tissue-permeable MRI contrast agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102340118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wen, S.; Han, Q.; Fu, L.; Yan, L.; Jin, D.; Bünzli, J.-C.G.; Bao, G. Magnetic regulation of the luminescence of hybrid lanthanide-doped nanoparticles. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 469, 214653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.Y.; Yue, H.; Tegafaw, T.; Liu, S.; Ho, S.L.; Lee, G.H.; Nam, S.-W.; Chang, Y. Functionalized Lanthanide Oxide Nanoparticles for Tumor Targeting, Medical Imaging, and Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morselli, G.; Villa, M.; Fermi, A.; Critchley, K.; Ceroni, P. Luminescent copper indium sulfide (CIS) quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Nanoscale Horiz. 2021, 6, 676–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, F.; Liu, J. Engineered lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles for biosensing and bioimaging application. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passemard, S.; Staedler, D.; Sonego, G.; Magouroux, T.; Schneiter, G.S.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Bonacina, L.; Gerber-Lemaire, S. Functionalized bismuth ferrite harmonic nanoparticles for cancer cells labeling and imaging. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.G.; Marino, A.; Rocca, A.; Mattoli, V.; Ciofani, G. Barium titanate nanoparticles: Promising multitasking vectors in nanomedicine. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 232001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantelle, G.; Beauquis, S.; Le Dantec, R.; Monnier, V.; Galez, C.; Mugnier, Y. Solution-Based Synthesis Routes for the Preparation of Noncentrosymmetric 0-D Oxide Nanocrystals with Perovskite and Nonperovskite Structures (Small 30/2022). Small 2022, 18, 2270161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacina, L. Nonlinear Nanomedecine: Harmonic Nanoparticles toward Targeted Diagnosis and Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staedler, D.; Magouroux, T.; Rachid, H.; Joulaud, C.; Extermann, J.; Schwung, S.; Passemard, S.; Kasparian, C.; Clarke, G.; Gerrmann, M.; et al. Harmonic Nanocrystals for Biolabeling: A Survey of Optical Properties and Biocompatibility. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2542–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campargue, G.; La Volpe, L.; Giardina, G.; Gaulier, G.; Lucarini, F.; Gautschi, I.; Le Dantec, R.; Staedler, D.; Diviani, D.; Mugnier, Y.; et al. Multiorder Nonlinear Mixing in Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 8725–8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, W.P.; Fraser, S.E.; Pantazis, P. SHG nanoprobes: Advancing harmonic imaging in biology. BioEssays 2012, 34, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, R.; Lanvin, T.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Pu, Y.; Psaltis, D. Imaging with second-harmonic radiation probes in living tissue. Biomed. Opt. Express 2011, 2, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vittadello, L.; Klenen, J.; Koempe, K.; Kocsor, L.; Szaller, Z.; Imlau, M. NIR-to-NIR Imaging: Extended Excitation Up to 2.2 μm Using Harmonic Nanoparticles with a Tunable hIGh EneRgy (TIGER) Widefield Microscope. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, P.; Wills, J.W.; Brown, M.R.; Barnes, C.M.; Summers, H.D. The origin of heterogeneous nanoparticle uptake by cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos-Rasera, J.R.; Neto, A.S.; Monteiro, R.T.R.; van Gestel, C.A.M.; de Carvalho, H.W.P. Toxicity, bioaccumulation and biotransformation of Cu oxide nanoparticles in Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 2897–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, J.; Tian, F.; Li, L.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Shi, X.; Lu, H. Regulation of the cellular uptake of nanoparticles by the orientation of helical polypeptides. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S. Understanding and overcoming major barriers in cancer nanomedicine. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.-D.; Huang, L. Nanoparticles Evading the Reticuloendothelial System: Role of The Supported Bilayer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gatoo, M.A.; Naseem, S.; Arfat, M.Y.; Dar, A.M.; Qasim, K.; Zubair, S. Physicochemical Properties of Nanomaterials: Implication in Associated Toxic Manifestations. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 498420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luyts, K.; Napierska, D.; Nemery, B.; Hoet, P.H.M. How physico-chemical characteristics of nanoparticles cause their toxicity: Complex and unresolved interrelations. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2012, 15, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Shi, Y.; Qi, T.; Qiu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Q.; Lin, G. Precise design strategies of nanomedicine for improving cancer therapeutic efficacy using subcellular targeting. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Weng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, S. Improved In Vitro and In Vivo Biocompatibility of Graphene Oxide through Surface Modification: Poly(Acrylic Acid)-Functionalization is Superior to PEGylation. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3267–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kim, W.; Kim, J. Surface Modification of Functional Nanoparticles for Controlled Drug Delivery. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2003, 24, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malachowski, T.; Hassel, A. Engineering nanoparticles to overcome immunological barriers for enhanced drug delivery. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, Y.; Yuan, H.; von Roemeling, C.A.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Shih, K.D.; Knight, J.A.; Tun, H.W.; Wharen, R.E.; Jiang, W.; et al. Surface modification of nanoparticles enables selective evasion of phagocytic clearance by distinct macrophage phenotypes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanità, G.; Carrese, B.; Lamberti, A. Nanoparticle Surface Functionalization: How to Improve Biocompatibility and Cellular Internalization. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 587012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobs, L.; Buchegger, F.; Gurny, R.; Allémann, E. Current methods for attaching targeting ligands to liposomes and nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 1980–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Gao, H.; Yang, C.; Chu, L.; Cheng, T.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Fan, S.; Shi, L.; Meng, A. The impact of PEGylation patterns on the in vivo biodistribution of mixed shell micelles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4229–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerrero-Martínez, A.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Recent Progress on Silica Coating of Nanoparticles and Related Nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, T.; Le, Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Chu, G.-W.; Chen, J.-F.; Shao, L. Cu nanoparticle preparation in a tube-in-tube microchannel reactor and encapsulation by silica. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1717–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-F.; Wang, Y.-F.; Yan, X.-P. Amine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for rapid capture and removal of bacterial pathogens. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7908–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaura, M.; Camilo, R.L.; Sampaio, L.C.; Macêdo, M.A.; Nakamura, M.; Toma, H.E. Preparation and characterization of (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 279, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Shen, H.; Zhang, H.; Gu, N. Preparation and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles coated by amino silane. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 212, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuning the Surface Chemistry of Second-Harmonic-Active Lithium Niobate Nanoprobes Using a Silanol–Alcohol Condensation Reaction|Langmuir. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c00645 (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Sodipo, B.K.; Aziz, A.A. One minute synthesis of amino-silane functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by sonochemical method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodipo, B.K.; Aziz, A.A. A sonochemical approach to the direct surface functionalization of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sodipo, B.K.; Aziz, A.A. Optimization of sonochemical method of functionalizing Amino-Silane on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles using Central Composite Design. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 64, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Qutubuddin, S. Synthesis of titania-coated silica nanoparticles using a nonionic water-in-oil microemulsion. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 179, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, L.; Thomas, T.; Pichumani, M. Do depletant stabilized water-in-oil microemulsions have implications for nanoencapsulation? Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.M.; Xu, S.C.; Li, G.H. Fe3O4@SiO2 Core/Shell Nanoparticles: The Silica Coating Regulations with a Single Core for Different Core Sizes and Shell Thicknesses. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 4572–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.K.; Selvan, S.T.; Lee, S.S.; Papaefthymiou, G.C.; Kundaliya, D.; Ying, J.Y. Silica-Coated Nanocomposites of Magnetic Nanoparticles and Quantum Dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4990–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Tapec, R.; Theodoropoulou, N.; Dobson, J.; Hebard, A.; Tan, W. Synthesis and Characterization of Silica-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Microemulsion: The Effect of Nonionic Surfactants. Langmuir 2001, 17, 2900–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, T.; Grasset, F.; Mornet, S.; Duguet, E.; Cador, O.; Cordier, S.; Molard, Y.; Demange, V.; Mortier, M.; Haneda, H. Functional silica nanoparticles synthesized by water-in-oil microemulsion processes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Jiang, J.; Lee, S.S.; Ying, J.Y. Reverse microemulsion-mediated synthesis of silica-coated gold and silver nanoparticles. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2008, 24, 5842–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, P.P.; Jaroniec, M. Renaissance of Stöber method for synthesis of colloidal particles: New developments and opportunities. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 584, 838–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardikar, V.V.; Matijević, E. Coating of Nanosize Silver Particles with Silica. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 221, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Dickinson, E.; Dungan, S.R.; Kinsella, J.E.; Ma, J.G.; Povey, M.J.W. Effect of Emulsifier Type on the Crystallization Kinetics of Oil-in-Water Emulsions Containing a Mixture of Solid and Liquid Droplets. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 160, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbandi, M.; Thomann, R.; Nann, T. Single Quantum Dots in Silica Spheres by Microemulsion Synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 5720–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koole, R.; van Schooneveld, M.M.; Hilhorst, J.; Donegá, C.D.M.; Hart, D.C.; van Blaaderen, A.; Vanmaekelbergh, D.; Meijerink, A. On the Incorporation Mechanism of Hydrophobic Quantum Dots in Silica Spheres by a Reverse Microemulsion Method. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earhart, C.; Jana, N.R.; Erathodiyil, N.; Ying, J.Y. Synthesis of Carbohydrate-Conjugated Nanoparticles and Quantum Dots. Langmuir 2008, 24, 6215–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Yang, K.; Boye, D.M.; Sigmon, T.; Malloy, K.J.; Xu, H.; López, G.P.; Brinker, C.J. Self-assembly of ordered, robust, three-dimensional gold nanocrystal/silica arrays. Science 2004, 304, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestal, C.R.; Zhang, Z.J. Effects of Surface Coordination Chemistry on the Magnetic Properties of MnFe2O4 Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9828–9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullivant, J.P.; Zhao, S.; Willenberg, B.J.; Kozissnik, B.; Batich, C.D.; Dobson, J. Materials Characterization of Feraheme/Ferumoxytol and Preliminary Evaluation of Its Potential for Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17501–17510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Cui, L.; Tong, N.; Gu, H. Development of High Magnetization Fe3O4/Polystyrene/Silica Nanospheres via Combined Miniemulsion/Emulsion Polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15582–15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuilleumier, J.; Gaulier, G.; De Matos, R.; Ortiz, D.; Menin, L.; Campargue, G.; Mas, C.; Constant, S.; Le Dantec, R.; Mugnier, Y.; et al. Two-Photon-Triggered Photorelease of Caged Compounds from Multifunctional Harmonic Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 27443–27452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.F.; Gates, B.D. Synthesis of Lithium Niobate Nanocrystals with Size Focusing through an Ostwald Ripening Process. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 2028–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbain, M.; Riporto, F.; Beauquis, S.; Monnier, V.; Marty, J.-C.; Galez, C.; Durand, C.; Chevolot, Y.; Dantec, R.; Mugnier, Y. On the Reaction Pathways and Growth Mechanisms of LiNbO3 Nanocrystals from the Non-Aqueous Solvothermal Alkoxide Route. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantão, F.; Melo, W.; Oliveira, L.; Passos, A.; Silva, A. Utilization of Sn/Nb2O5 composite for the removal of methylene blue. Quim. Nova 2010, 33, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, S. Facile preparation of C, N co-modified Nb2O5 nanoneedles with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 16519–16525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaraah, F.; Mahyoub, S.; Hafez, M.; Xiu, G. Facile route for C–N/Nb 2 O 5 nanonet synthesis based on 2-methylimidazole for visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 39561–39571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nienhaus, K.; Xue, Y.; Shang, L.; Nienhaus, G.U. Protein adsorption onto nanomaterials engineered for theranostic applications. Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 262001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Stellacci, F. Effect of Surface Properties on Nanoparticle–Cell Interactions. Small 2010, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yu, M.; Ning, X.; Zhou, C.; Yang, S.; Zheng, J. PEGylation and Zwitterionization: Pros and Cons in the Renal Clearance and Tumor Targeting of Near-IR-Emitting Gold Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 12804–12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirshafiee, V.; Kim, R.; Park, S.; Mahmoudi, M.; Kraft, M.L. Impact of protein pre-coating on the protein corona composition and nanoparticle cellular uptake. Biomaterials 2016, 75, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.I.; Abidi, S.M.S.; Randhawa, S.; Joshi, R.; Kumar, R.; Acharya, A. Protein-Cloaked Nanoparticles for Enhanced Cellular Association and Controlled Pathophysiology via Immunosurveillance Escape. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittig, G.; Krebs, A. Zur Existenz niedergliedriger Cycloalkine, I. Chem. Ber. 1961, 94, 3260–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewett, J.C.; Bertozzi, C.R. Cu-free click cycloaddition reactions in chemical biology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskin, J.M.; Prescher, J.A.; Laughlin, S.T.; Agard, N.J.; Chang, P.V.; Miller, I.A.; Lo, A.; Codelli, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. Copper-free click chemistry for dynamic in vivo imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16793–16797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vuilleumier, J. Functionalization of Second Harmonic Generation Nanoparticles for Theranostic Applications; EPFL: Lausanne, Switzeraland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, N.; Goddard-Borger, E.; Greiner, R.; Klapötke, T.; Skelton, B.; Stierstorfer, J. Sensitivities of some imidazole-1-sulfonyl azide salts. J. Org. Chem 2012, 77, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSminia, J.; Pedersen, D. Azide- and alkyne-functionalized α and β3-amino acids. Synlett 2012, 23, 2643–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


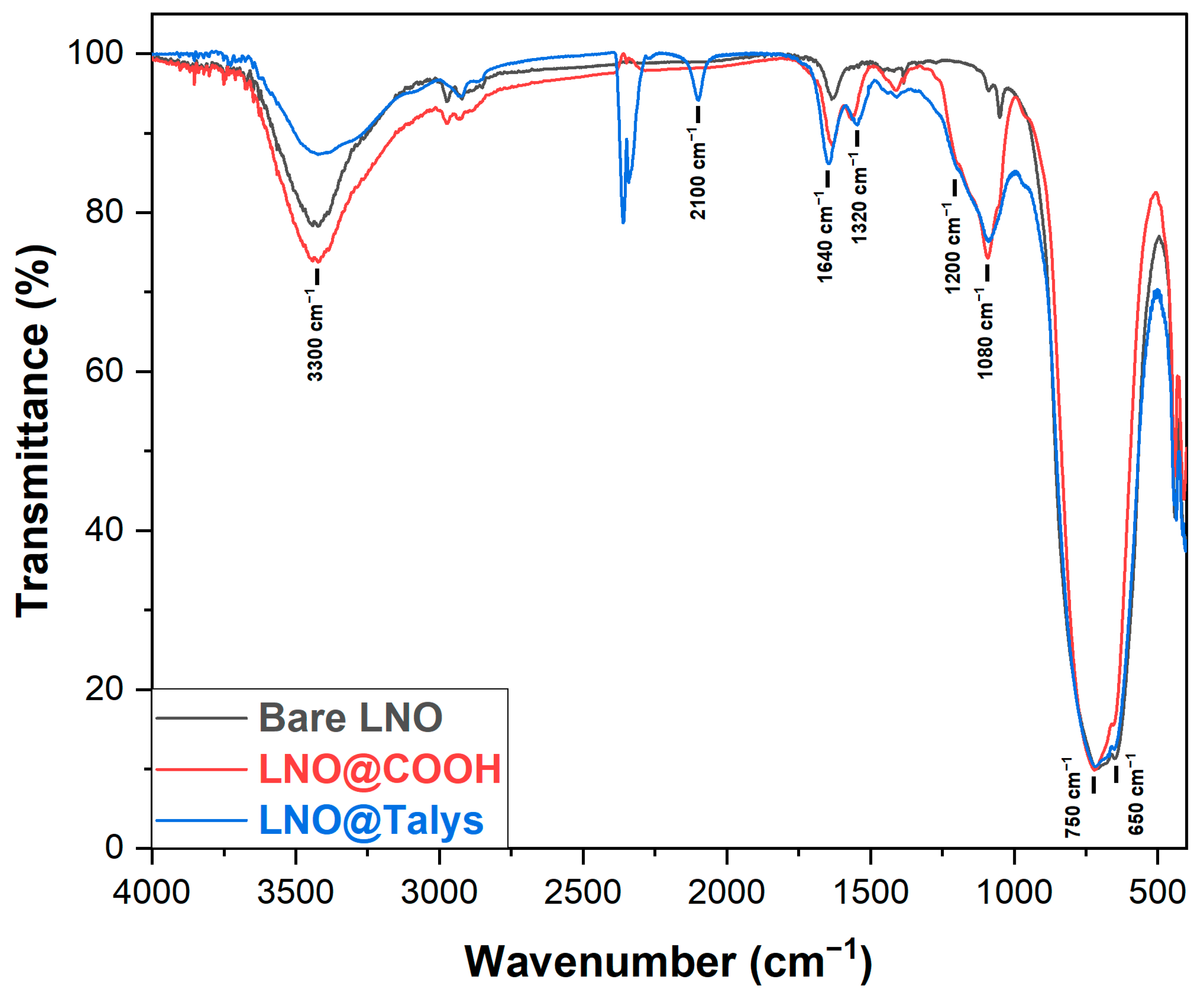
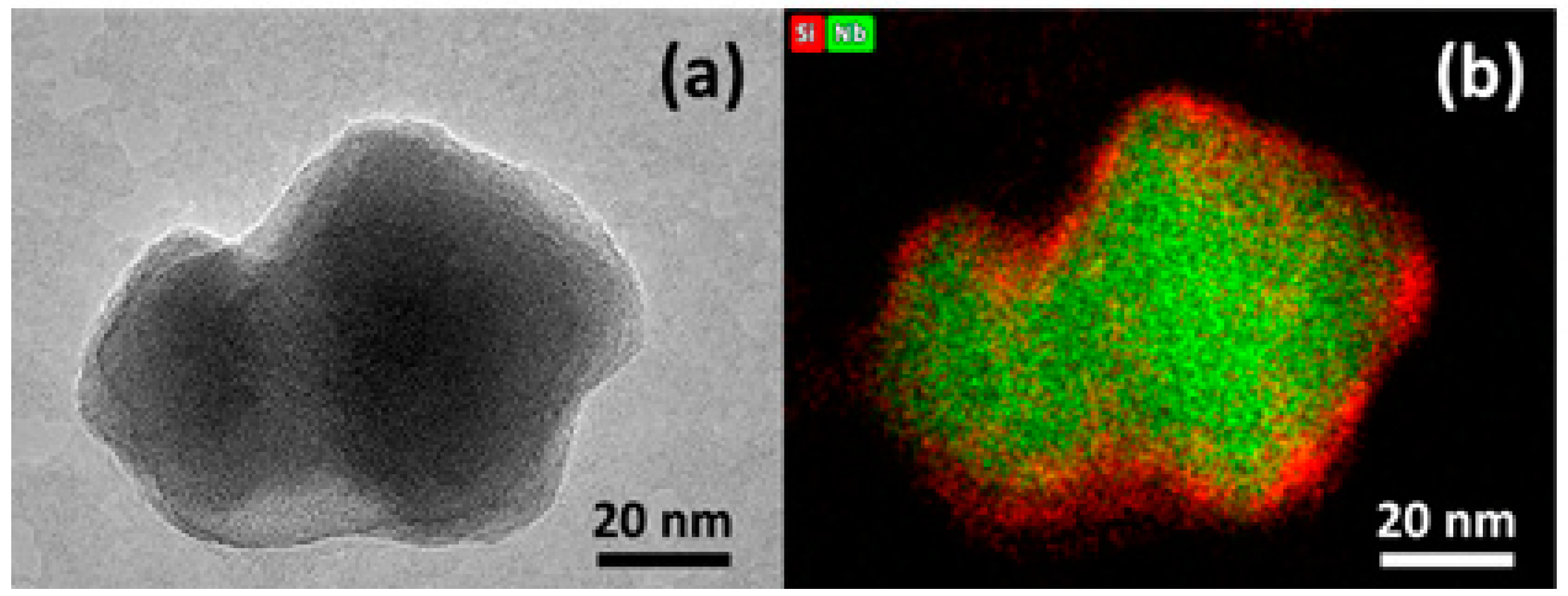
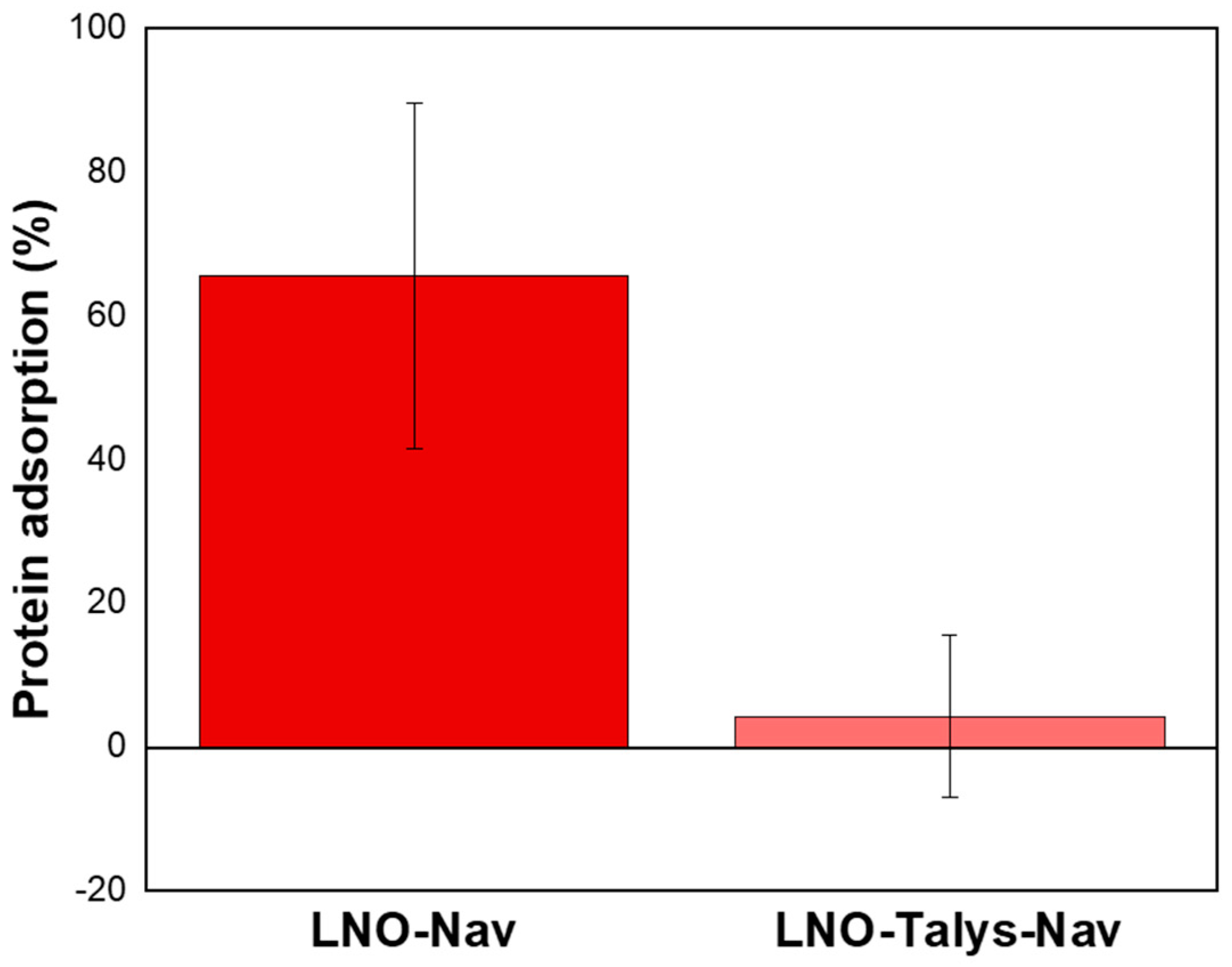
| NPs | Bare LNO | LNO@COOH (1) | LNO@COOH (2) | LNO@N3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrodynamic diameter a [nm] | 120.1 ± 1.8 | Not measured | Not measured | 233.2 ± 0.5 |
| PDI a | 0.03 | Not measured | Not measured | 0.07 |
| Hydrodynamic diameter b [nm] | 78.2 ± 29.6 | 175.2 ± 2.2 | 152.1 ± 3.6 | 864.2 ± 37.6 |
| PDI b | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.29 |
| Zeta potential, pH 7.4 b [mV] | −34.8 ± 1.4 | −42.8 ± 0.5 | −44.8 ± 1.1 | −27.6 ± 4.1 |
| Zeta potential, pH 3.0 c [mV] | −33.8 ± 0.4 | −12.2 ± 0.5 | −11.4 ± 2.3 | −9.0 ± 1.5 |
| NPs | LNO@COOH | LNO@Talys |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrodynamic diameter a [nm] | Not measured | 184.5 ± 8.8 |
| PDI a | Not measured | 0.10 |
| Hydrodynamic diameter b [nm] | 152.1 ± 3.6 | 169.5 ± 2.5 |
| PDI b | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| Zeta potential, pH 7.4 b [mV] | −44.8 ± 1.1 | −35.8 ± 0.4 |
| Zeta potential, pH 3.0 c [mV] | −11.4 ± 2.3 | −10.6 ± 2.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gheata, A.; Spada, A.; Wittwer, M.; Dhouib, A.; Molina, E.; Mugnier, Y.; Gerber-Lemaire, S. Modulating the Surface Properties of Lithium Niobate Nanoparticles by Multifunctional Coatings Using Water-in-Oil Microemulsions. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030522
Gheata A, Spada A, Wittwer M, Dhouib A, Molina E, Mugnier Y, Gerber-Lemaire S. Modulating the Surface Properties of Lithium Niobate Nanoparticles by Multifunctional Coatings Using Water-in-Oil Microemulsions. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(3):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030522
Chicago/Turabian StyleGheata, Adrian, Alessandra Spada, Manon Wittwer, Ameni Dhouib, Emilie Molina, Yannick Mugnier, and Sandrine Gerber-Lemaire. 2023. "Modulating the Surface Properties of Lithium Niobate Nanoparticles by Multifunctional Coatings Using Water-in-Oil Microemulsions" Nanomaterials 13, no. 3: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030522
APA StyleGheata, A., Spada, A., Wittwer, M., Dhouib, A., Molina, E., Mugnier, Y., & Gerber-Lemaire, S. (2023). Modulating the Surface Properties of Lithium Niobate Nanoparticles by Multifunctional Coatings Using Water-in-Oil Microemulsions. Nanomaterials, 13(3), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030522









