Characterization of Electrospinning Prepared Nitrocellulose (NC)-Ammonium Dinitramide (ADN)-Based Composite Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Spinning Solution
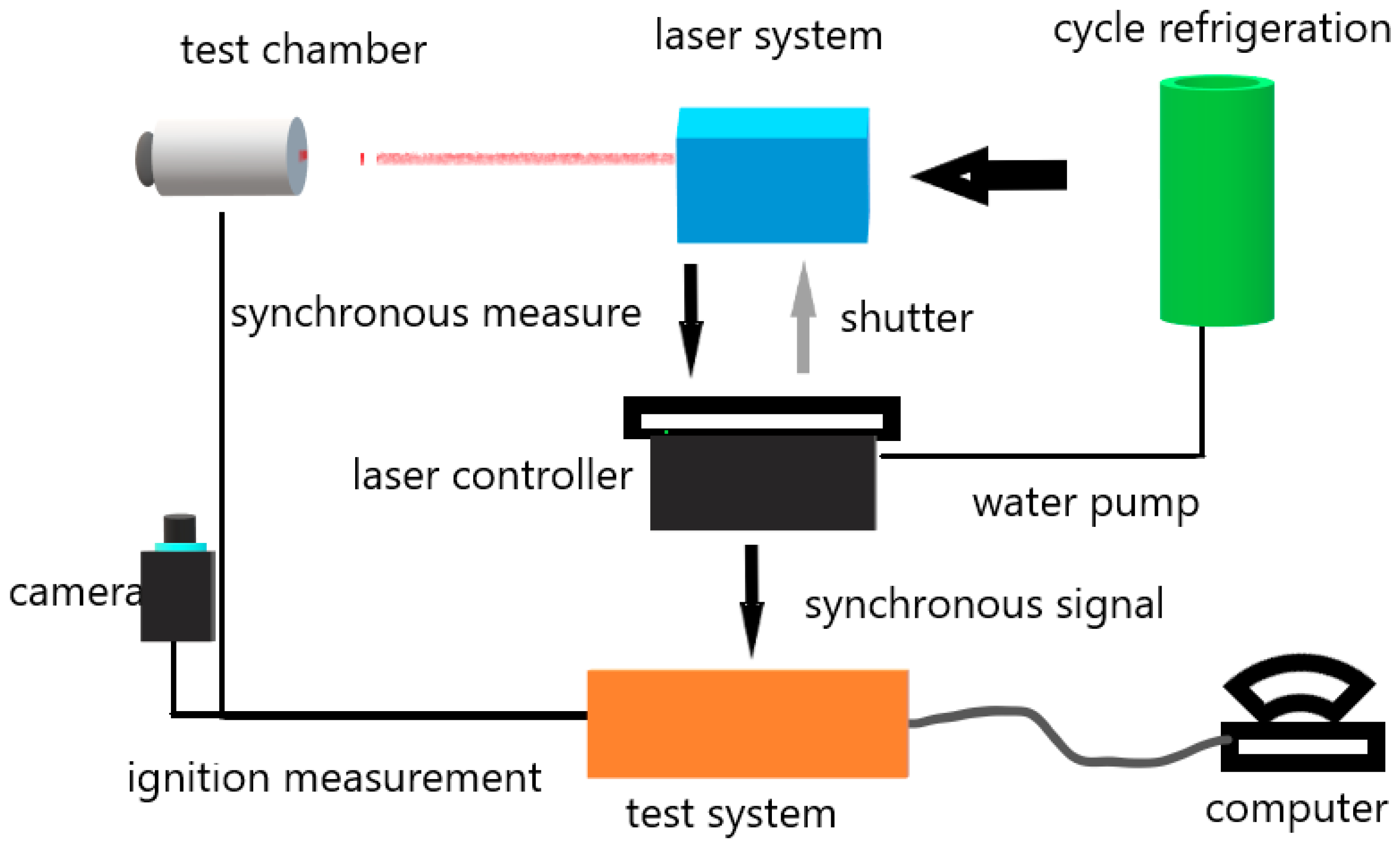
2.3. Electrospinning Process
2.4. Morphology Analysis
2.5. DSC Tests
2.6. Gas Pressure Measurements of Thermostatic Decomposition
2.7. Combustion Tests
2.8. Mechanical Sensitivity
3. Results and Discussions
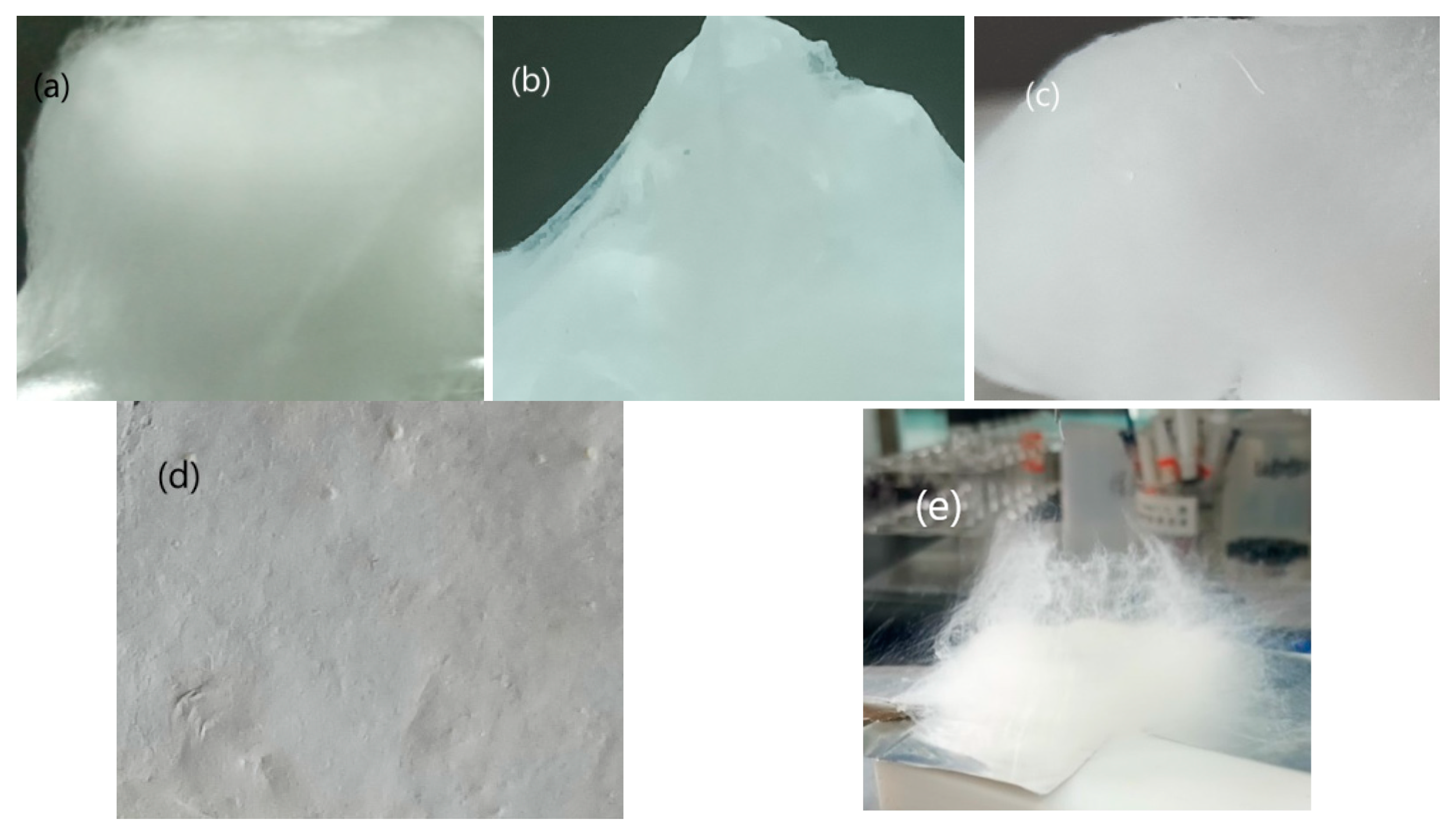
3.1. Morphology Characteristics
3.2. Thermal Behaviors under Linear Heating Conditions
3.3. Thermal Behaviors under Thermostatic Conditions
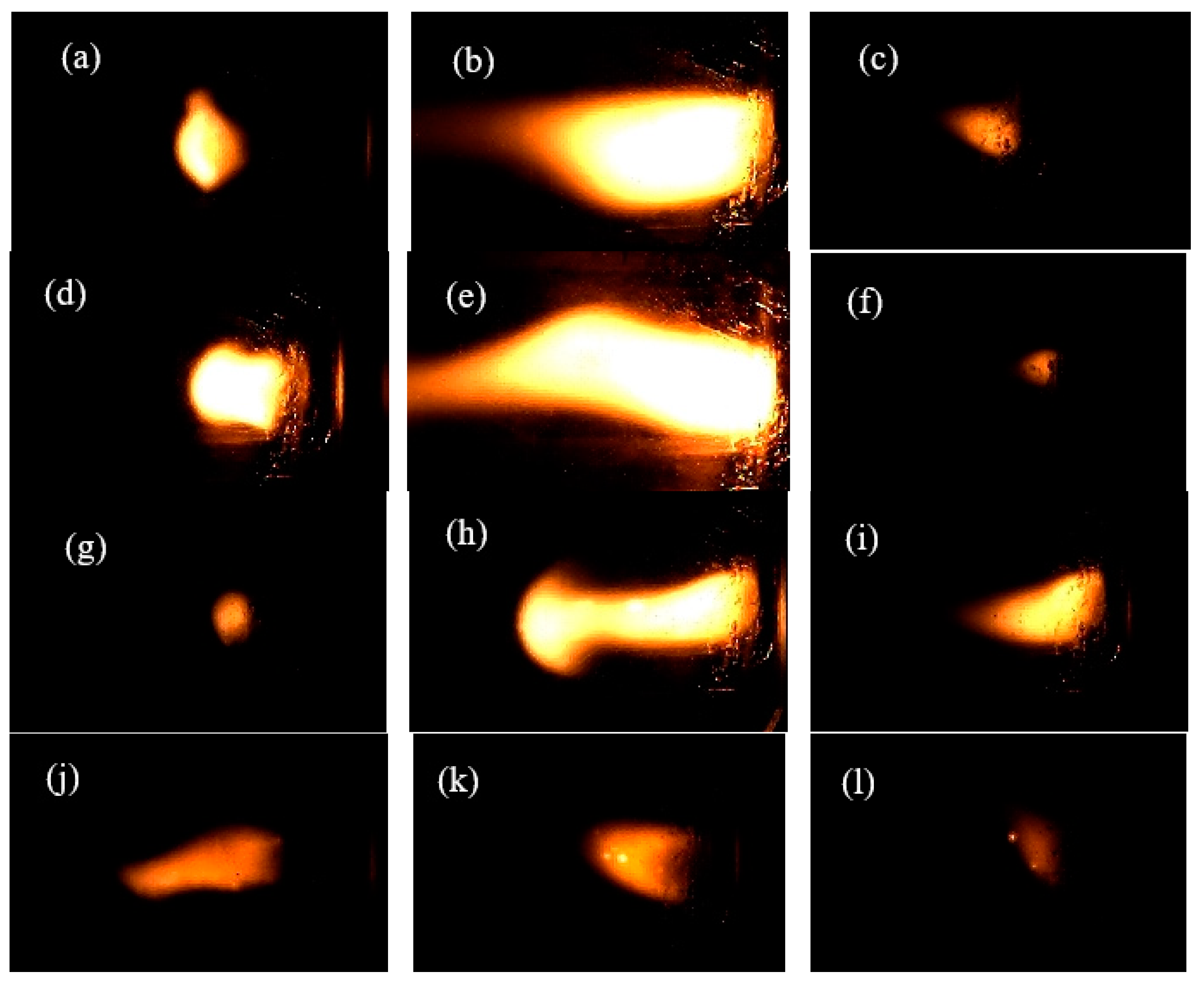
3.4. Combustion Performance
3.5. Mechanical Sensitivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- A Hassan, M. Effect of malonyl malonanilide dimers on the thermal stability of nitrocellulose. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 88, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, R.R.; Makashir, P.S.; Agrawal, J.P. Combustion Behaviour of Nitrocellulose and its Complexes with Copper Oxide. Hot stage microscopic studies. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2001, 65, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Xuan, C.L.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, G.T.; Wang, Q.L. Low-temperature impact strength of nitrocellulose based high energy-low vulnerability gun propellant. Chin. J. Explos. Propell. 2015, 38, 78–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pang, W.Q.; Wang, K.; Xu, H.X.; Li, J.Q.; Xiao, L.Q.; Fan, X.Z.; Li, H. Combustion features of nitrate ester plasticized polyether solid propellants with ADN and Fox-12 particles. Int. J. Energetic Mater. Chem. Propuls. 2020, 19, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Jiang, X.; Lu, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. Study on the catalytic effect of NiO nanoparticles on the thermal decomposition of TEGDN/NC propellant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chajistamatiou, A.S.; Bakeas, E.B. A rapid method for the identification of nitrocellulose in high explosives and smokeless powders using GC–EI–MS. Talanta 2016, 151, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volltrauer, H.N.; Fontijn, A. Low-temperature pyrolysis studies by chemiluminescence techniques real-time nitrocellulose and PBX 9404 decomposition. Combust. Flame 1981, 41, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liang, L.; Luo, Q.; He, Z.; Liang, M.; Shen, H.; Liang, D. Comparison of six ester components in nitrocellulose lacquer thinner from the aspects of dissolution rates, explosion characteristics and environmental influence. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 139, 105426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, A.; Hosseini, S.G.; Bazrgary, M. Improvement of thermal decomposition properties of ammonium perchlorate particles using some polymer coating agents. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 113, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, F.; Khorasani, M.; Ebrahimi, M. Improving the mechanical properties of waterborne nitrocellulose coating using nano-silica particles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 109, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.-Z.; Fu, X.-L.; Yang, Y.-J.; Tang, Q.-F. Energetic nitrocellulose coating: Effective way to decrease sensitivity and modify surface property of HMX particles. J. Energ. Mater. 2019, 37, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, X.X.; Li, Z.L. Research progress in energetic binders. J. Rocket Propuls. 2007, 33, 44–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sudarsana, J.; Ankur, G. Nano-Energetic Materials for Defense Application; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijden, A. Developments and challenges in the manufacturing, characterization and scale-up of energetic nanomaterials–A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Cao, M.-H.; Nie, F.-D.; Huang, H.; Hu, C.-W. Construction and Properties of Structure- and Size-controlled Micro/nano-Energetic Materials. Def. Technol. 2013, 9, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Deng, C.; Li, H.; DeLuca, L.T.; Ouyang, D.; Xu, H.; Fan, X. Effect of Nano-Sized Energetic Materials (nEMs) on the Performance of Solid Propellants: A Review. Nanomaterials 2021, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Saito, Y.; Akiyoshi, M.; Endo, T.; Matsunaga, T. Preparation and Characterization of Nitrocellulose Nanofiber. Propell. Explos. Pyrotech. 2021, 46, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Weeks, B.L. Preparation of sub-micron nitrocellulose particles for improved combustion behavior. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrynin, O.S.; Zharkov, M.N.; Kuchurov, I.V.; Fomenkov, I.V.; Zlotin, S.G.; Monogarov, K.A.; Meerov, D.B.; Pivkina, A.N.; Muravyev, N.V. Supercritical Antisolvent Processing of Nitrocellulose: Downscaling to Nanosize, Reducing Friction Sensitivity and Introducing Burning Rate Catalyst. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Pu, C.; Cui, P.; Xiao, Z. Preparation, Thermal and Sensitivity Properties of Nano-Sized Spherical Nitrocellulose Composite Crystal. Propell. Explos. Pyrotech. 2020, 45, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, A.; Lozier, G.; Haesslein, A.; Kasper, F.; Raphael, R.M.; Baggett, L.S.; Mikos, A.G. Fabrication of Nonwoven Coaxial Fiber Meshes by Electrospinning. Tissue Eng. Methods 2009, 15, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, A.; Wei, L.; Wang, L.; Qin, X.; Yu, J. Mass production of high-quality nanofibers via constructing pre-Taylor cones with high curvature on needleless electrospinning. Mater. Des. 2020, 197, 109247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Hong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, H. Electrospun nanofiber-based nanoboron/nitrocellulose composite and their reactive properties. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Shao, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, F. Preparation of AlNPs/NC Composite Nanofibers by Electrospinning. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2011, 127, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Kohsari, I.; Zandavar, H.; Koudehi, M.F.; Mirsadeghi, S. Electrospinning and thermal characterization of nitrocellulose nanofibers containing a composite of diaminofurazan, aluminum nano-powder and iron oxide nanoparticles. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4405–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, T.; Song, X.; Li, F. Electrospinning Preparation of NC/GAP/Submicron-HNS Energetic Composite Fiber and its Properties. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 14261–14271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Li, H.; Xu, K. Enhanced thermal decomposition, laser ignition and combustion properties of NC/Al/RDX composite fibers fabricated by electrospinning. Cellulose 2021, 28, 6089–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.T.; Xie, W.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X. Preparation and characteristic of NC/RDX nanofibers by electrospinning. Sci. Technol. Energ. Mater. 2020, 81, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Li, H.; Yu, B.; Geng, X.; Wang, J. Preparation and characterization of nano NC/HMX composite particles. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2015, 24, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Song, D.; Liang, L.; An, C.; Wang, J. Synthesis, thermolysis, and sensitivities of HMX/NC energetic nanocomposites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 312, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Brill, T.B. Nanostructured Energetic Composites of CL-20 and Binders Synthesized by Sol Gel Methods. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2006, 31, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanley, E.S.; Melhem, G.A. The oxygen balance criterion for thermal hazards assessment. Process. Saf. Prog. 1995, 14, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Jian, G.; Zachariah, M.R. Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Thermite Textiles and their Reactive Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6432–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, S.; Fischer, S.; Tagliabue, C. ADN Solid Propellants with High Burning Rates as Booster Material for Hypersonic Applications. Propell. Explos. Pyrotech. 2022, 47, e202200028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettwert, V.; Weiser, V.; Tagliabue, C.; Hafner, S.; Fischer, S. Environment-friendly composite propellants based on ammonium dinitramide. Int. J. Energ. Mater. Chem. Propuls. 2019, 18, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhasz, A.G.; Molnar, K.; Idrissi, A.; Jedlovszky-Hajdu, A. Salt induced fluffy structured electrospun fibrous matrix. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bao, X.-Z.; Rong, Y.-B.; Hao, G.-Z.; Xiao, L.; Gao, H.; Ke, X.; Chen, T.; Jiang, W.; Li, F.-S. Preparation of nano-RDX-based PBX and its thermal decomposition properties. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 131, 2693–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ouyang, G.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Gu, Z.; Li, F. Massive Preparation of Reduced-Sensitivity Nano CL-20 and Its Characterization. J. Energ. Mater. 2014, 33, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-C.; Kim, K.-H.; Yoh, J.J. Modeling of high energy laser ignition of energetic materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 083536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.X.; Nan, B.J.; An, T.; Xu, S.; Zhao, F.; Pei, Q.; Gao, H. Laser ignition characteristics of CL-20 composite modified double-based propellants. Chin. J. Lasers 2011, 38, 0502009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.X.; Pei, Q.; Nan, B.J.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, L.B.; Zhao, F.Q. Laser ignition characteristics of RDX-CMDB propellants. Chin. J. Energ. Mater. 2011, 19, 276–281. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lobry, E.; Berthe, J.; Hübner, J.; Schnell, F.; Spitzer, D. Tuning the Oxygen Balance of Energetic Composites: Crystallization of ADN/Secondary Explosives Mixtures by Spray Flash Evaporation. Propell. Explos. Pyrotech. 2021, 46, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Song, D.; An, C.; Wang, J.; Li, F. Mechanism investigation for remarkable decreases in sensitivities from micron to nano nitroamine. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2016, 6, 1847980416663678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G.; Cao, X.; Liu, J.; Nan, F.; He, W. Electrostatic spraying synthesis of energetic RDX@NGEC nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 431, 133718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | NC 10 wt% Solution (mg) | Ethanol (mg) | ADN (mg) | Additive–Weight (mg) | OB (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500 | 100 | 30 | RDX solution–100 | −16.9 |
| 2 | 500 | 100 | 30 | CL-20 solution–100 | −13.3 |
| 3 | 500 | 100 | 30 | 0 | −14.5 |
| 4 | 500 | 100 | 0 | 0 | −38.7 |
| Sample | The First Exothermal Peak Temperature Pertaining to ADN (°C) | The Second Exothermal Peak Temperature Pertaining to NC (°C) | The Third Exothermal Peak Temperature Pertaining to Additives (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | — | 209.0 | — |
| Sample | Impact Sensitivity (%) | Friction Sensitivity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56 | 60 |
| 2 | 56 | 64 |
| 3 | 52 | 60 |
| 4 | 64 | 72 |
| ADN | 48 | 40 |
| RDX | 88 | 84 |
| CL-20 | 100 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Xu, L.-p.; Deng, C.-q.; Yao, E.-g.; Chang, H.; Pang, W.-q. Characterization of Electrospinning Prepared Nitrocellulose (NC)-Ammonium Dinitramide (ADN)-Based Composite Fibers. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040717
Wang Q, Xu L-p, Deng C-q, Yao E-g, Chang H, Pang W-q. Characterization of Electrospinning Prepared Nitrocellulose (NC)-Ammonium Dinitramide (ADN)-Based Composite Fibers. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(4):717. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040717
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiong, Lu-ping Xu, Chong-qing Deng, Er-gang Yao, Hai Chang, and Wei-qiang Pang. 2023. "Characterization of Electrospinning Prepared Nitrocellulose (NC)-Ammonium Dinitramide (ADN)-Based Composite Fibers" Nanomaterials 13, no. 4: 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040717
APA StyleWang, Q., Xu, L. -p., Deng, C. -q., Yao, E. -g., Chang, H., & Pang, W. -q. (2023). Characterization of Electrospinning Prepared Nitrocellulose (NC)-Ammonium Dinitramide (ADN)-Based Composite Fibers. Nanomaterials, 13(4), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040717







