Doxorubicin-Loaded Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Capsules Modified with Antitumor DR5-Specific TRAIL Variant for Targeted Drug Delivery to Tumor Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Expression and Purification of the Recombinant DR5-B Protein
2.3. Preparation of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Capsules Loaded with Doxorubicin and Functionalized with the DR5-B Protein
2.4. Characterization of the Polyelectrolyte Capsules
2.5. Cell Culture and Multicellular Tumor Spheroid Formation
2.6. Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Flow Cytometry and Fluorimetry
2.7.1. Flow Cytometry
2.7.2. Fluorimetry
2.8. Cytotoxicity Study In Vitro (MTT-Test)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
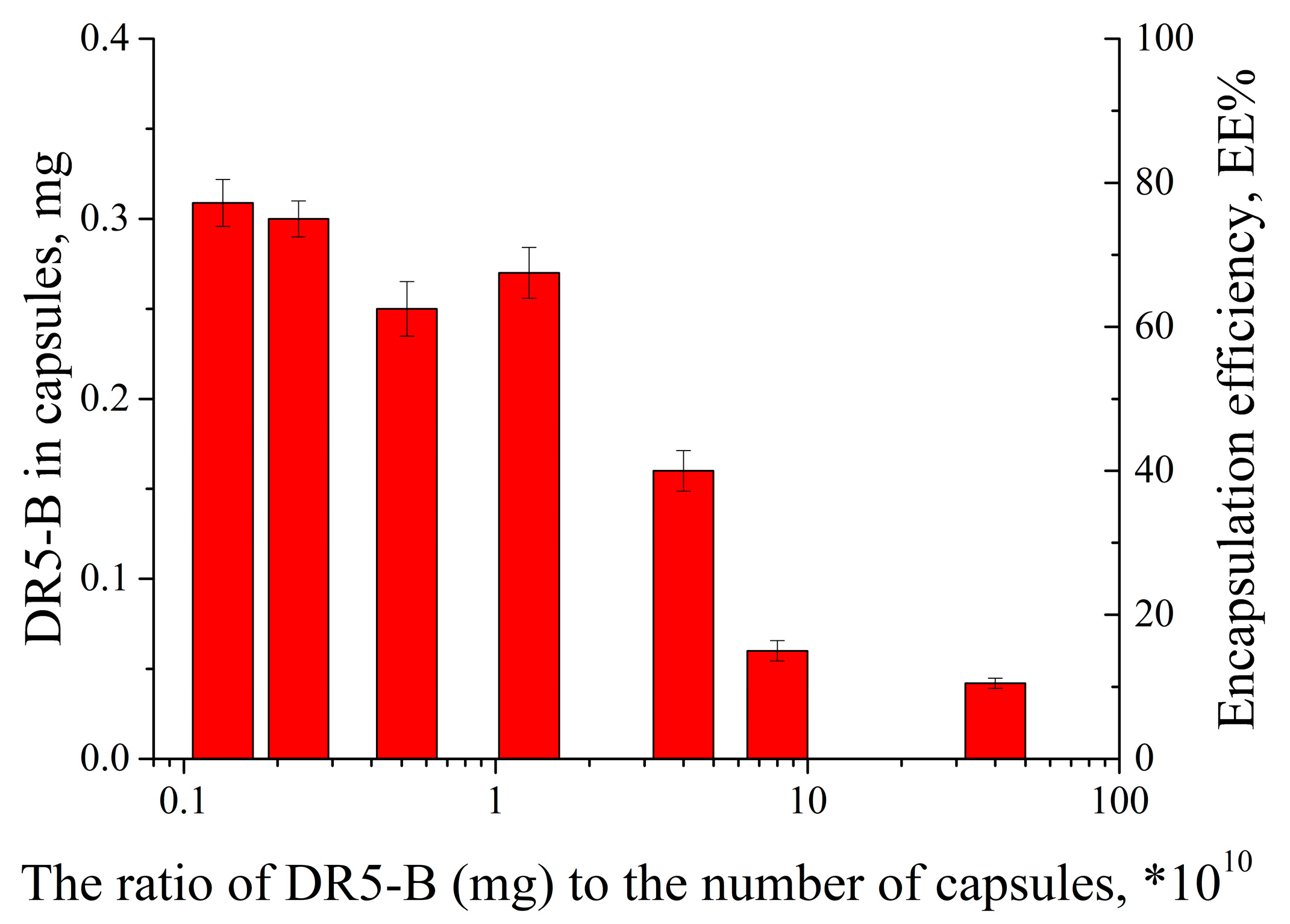
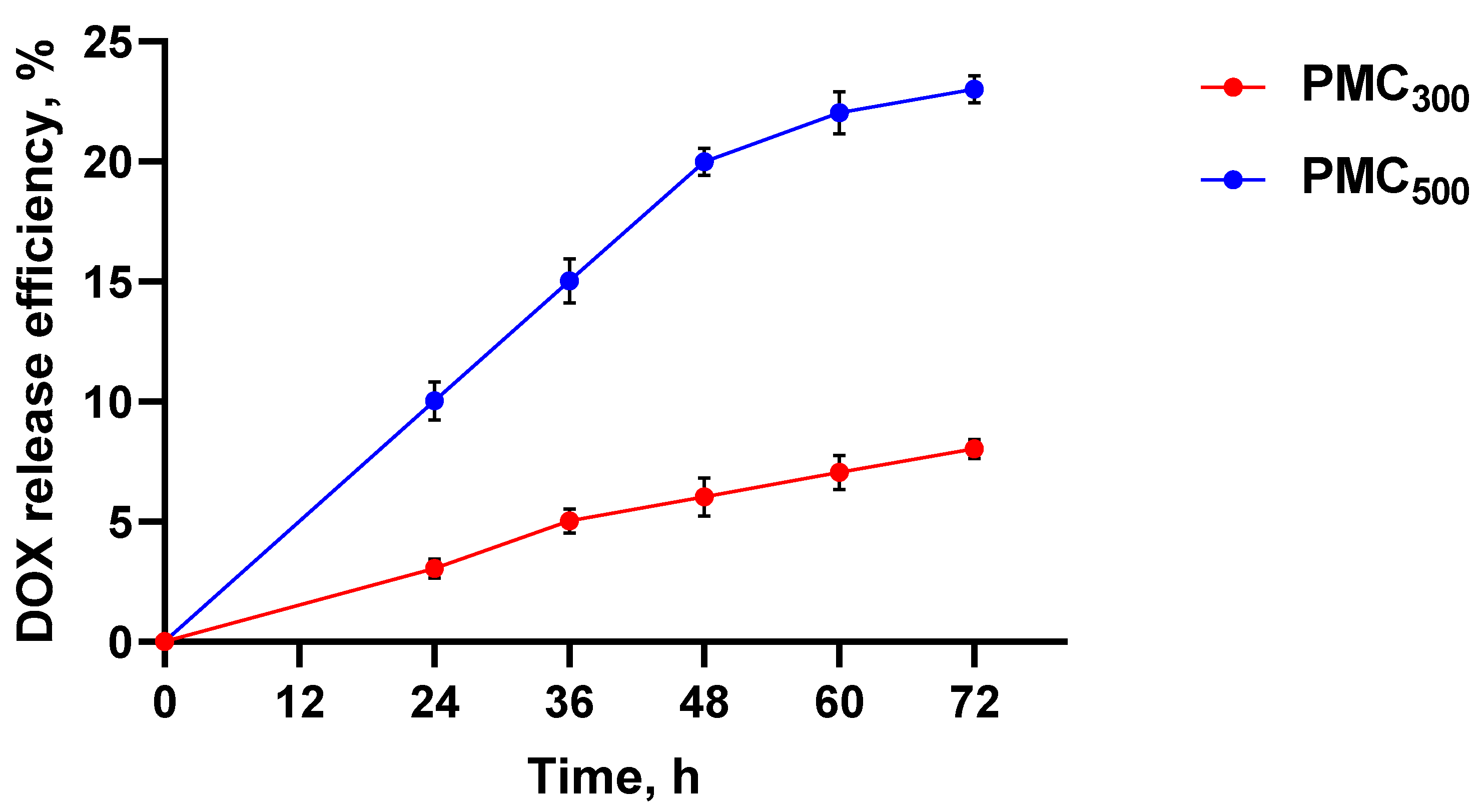
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Polyelectrolyte Multicellular Capsules Loaded with Doxorubicin and Modified with the DR5-B Protein
3.2. Modification of PMC with Fluorescently Labeled DR5-B
3.3. Study of Capsule Accumulation and Localization in the Cells
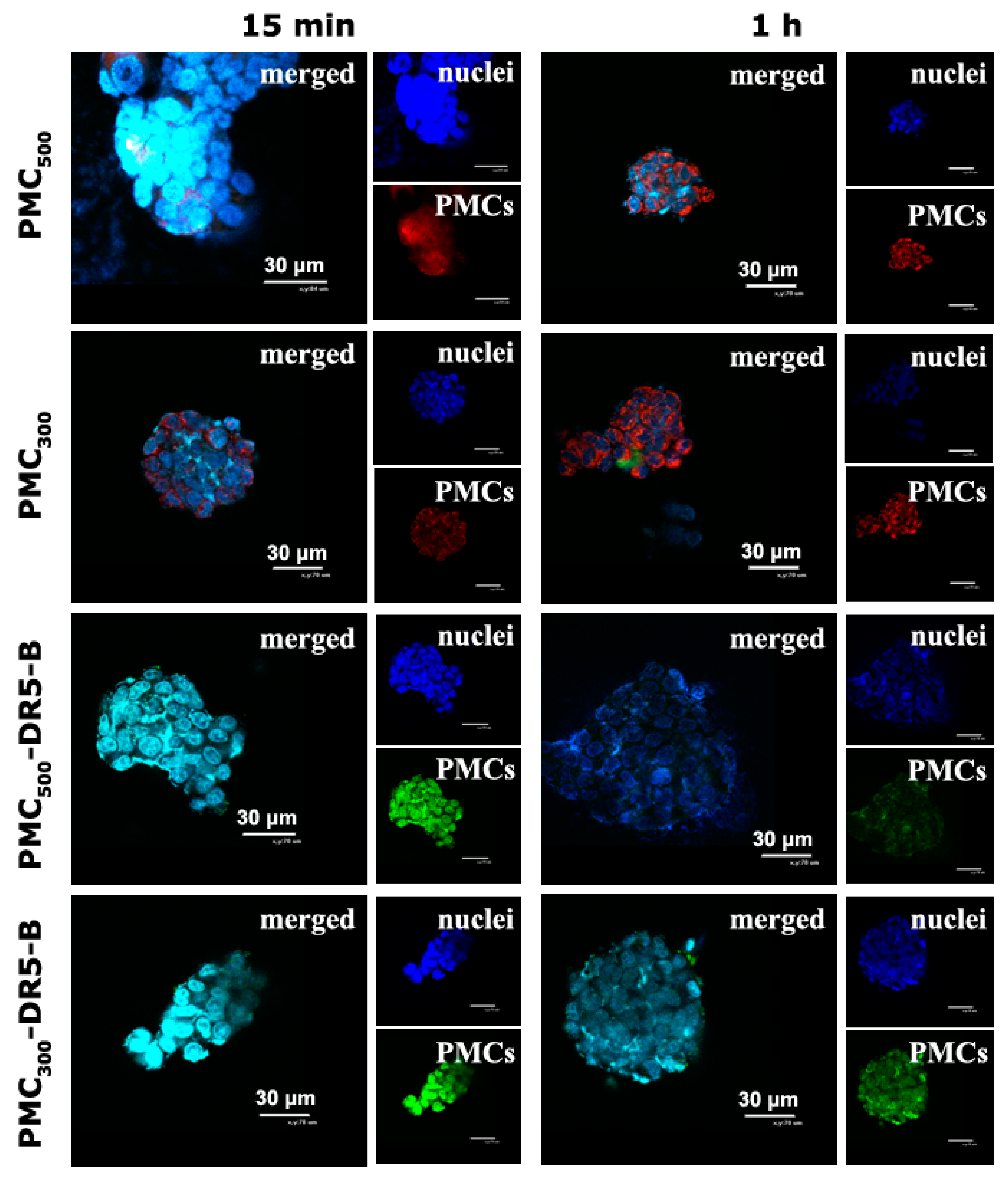
3.3.1. Study of Cellular Uptake of the Capsules by Confocal Microscopy
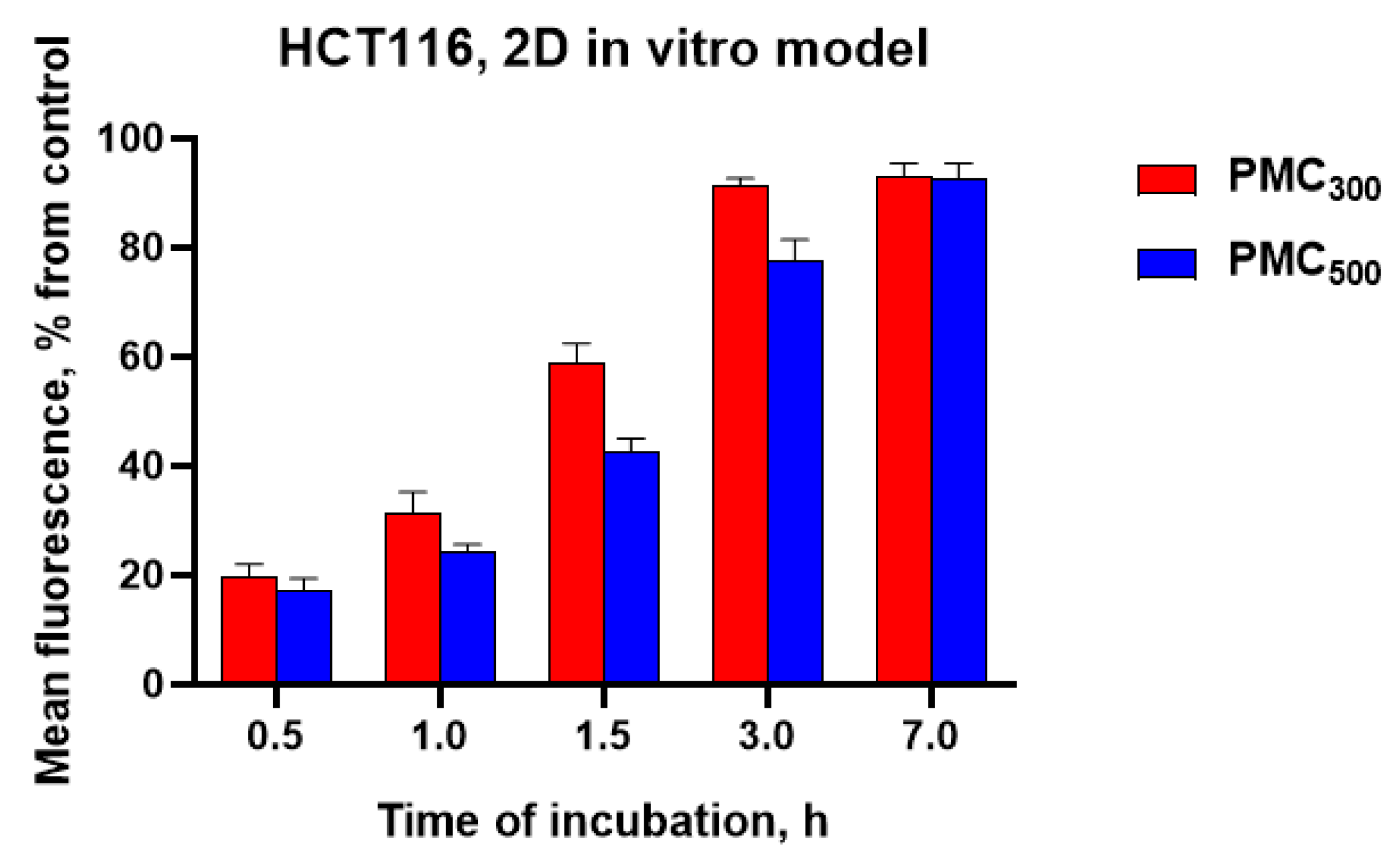
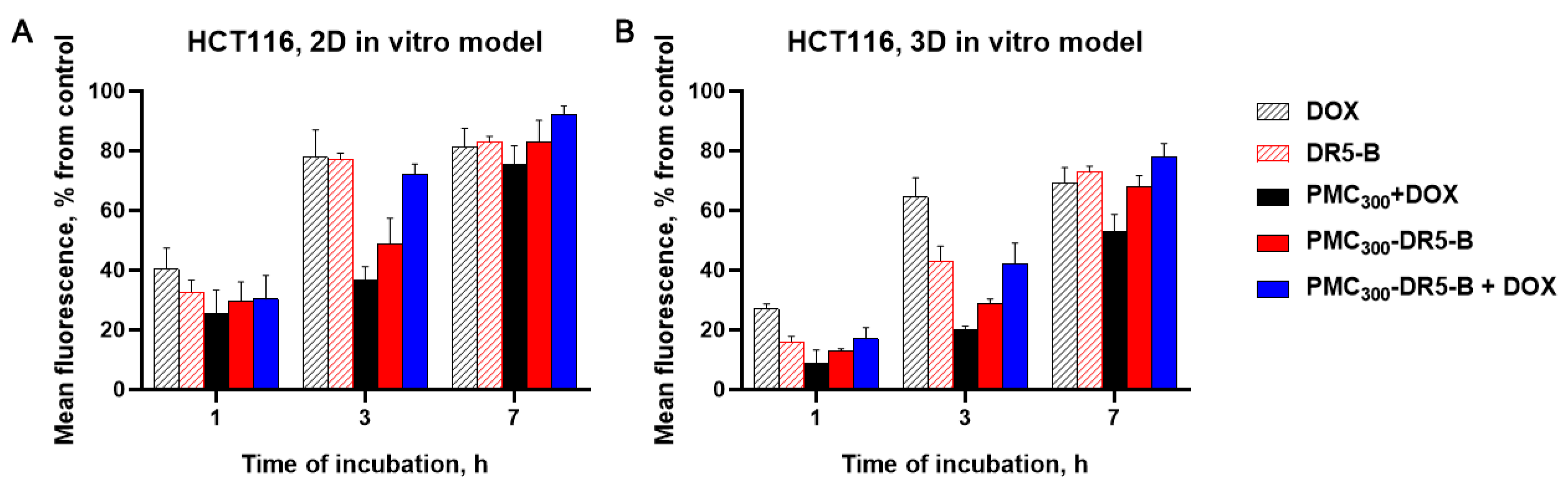
3.3.2. Study of Cellular Uptake of the Capsules by Flow Cytometry and Fluorimetry
3.4. Study of In Vitro Cytotoxicity Effects of the Capsules
4. Conclusions
List of Acronyms
| DOX | doxorubicin |
| DR4 | death receptor 4 |
| DR5 | death receptor 5 |
| DS | dextran sulfate sodium salt (MW 50 kDa) |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| HCT-116 | human colorectal carcinoma cell line |
| LbL | layer-by-layer |
| MTT | thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide, 98% |
| Parg | poly-L-arginine hydrochloride (MW 15–70 kDa) |
| PMC | polyelectrolyte multilayer capsules |
| TB medium | Terrific Broth medium |
| TRAIL | tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand |
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mateos-Maroto, A.; Fernández-Peña, L.; Abelenda-Núñez, I.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G.; Guzmán, E. Polyelectrolyte Multilayered Capsules as Biomedical Tools. Polymers 2022, 14, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, E.; Tapeinos, C.; Sarasua, J.R.; Larrañaga, A. Exploiting the layer-by-layer nanoarchitectonics for the fabrication of polymer capsules: A toolbox to provide multifunctional properties to target complex pathologies. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 304, 102680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Van Koeverden, M.P.; Müllner, M.; Kempe, K.; Caruso, F. Emerging methods for the fabrication of polymer capsules. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 207, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linnik, D.S.; Tarakanchikova, Y.V.; Zyuzin, M.V.; Lepik, K.V.; Aerts, J.L.; Sukhorukov, G.; Timin, A.S. Layer-by-Layer technique as a versatile tool for gene delivery applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 1047–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Mercato, L.L.; Rivera-Gil, P.; Abbasi, A.Z.; Ochs, M.; Ganas, C.; Zins, I.; Sönnichsen, C.; Parak, W.J. LbL multilayer capsules: Recent progress and future outlook for their use in life sciences. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhong, S.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X. Advances in polysaccharide-based nano/microcapsules for biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronin, D.V.; Sindeeva, O.A.; Kurochkin, M.A.; Mayorova, O.; Fedosov, I.V.; Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, O.; Gorin, D.A.; Tuchin, V.V.; Sukhorukov, G.B. In Vitro and in Vivo Visualization and Trapping of Fluorescent Magnetic Microcapsules in a Bloodstream. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6885–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselova, M.V.; German, S.V.; Sindeeva, O.A.; Kulikov, O.A.; Minaeva, O.V.; Brodovskaya, E.P.; Ageev, V.P.; Zharkov, M.N.; Pyataev, N.A.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; et al. Submicron-Sized Nanocomposite Magnetic-Sensitive Carriers: Controllable Organ Distribution and Biological Effects. Polymers 2019, 11, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhovskii, R.; Ermakov, A.; Sindeeva, O.; Prikhozhdenko, E.; Kozlova, A.; Grishin, O.; Makarkin, M.; Gorin, D.; Bratashov, D. Effect of Size on Magnetic Polyelectrolyte Microcapsules Behavior: Biodistribution, Circulation Time, Interactions with Blood Cells and Immune System. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, A.M.; Gabriel, S.A.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Gould, D.J. Improved and targeted delivery of bioactive molecules to cells with magnetic layer-by-layer assembled microcapsules. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9686–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenskaya, Y.; Garello, F.; Lengert, E.; Kozlova, A.; Verkhovskii, R.; Bitonto, V.; Ruggiero, M.R.; German, S.; Gorin, D.; Terreno, E. Biodegradable polyelectrolyte/magnetite capsules for MR imaging and magnetic targeting of tumors. Nanotheranostics 2021, 5, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebli, B.; Susha, A.S.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Rogach, A.L.; Parak, W.J. Magnetic Targeting and Cellular Uptake of Polymer Microcapsules Simultaneously Functionalized with Magnetic and Luminescent Nanocrystals. Langmuir 2005, 21, 4262–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdepérez, D.; del Pino, P.; Sánchez, L.; Parak, W.J.; Pelaz, B. Highly active antibody-modified magnetic polyelectrolyte capsules. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 474, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Li, Q.; Al-Rehili, S.; Omar, H.; Almalik, A.; Alshamsan, A.; Zhang, J.; Khashab, N.M. Hybrid Iron Oxide-Graphene Oxide-Polysaccharides Microcapsule: A Micro-Matryoshka for On-Demand Drug Release and Antitumor Therapy in Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6859–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, D.I.; Gautrot, J.E.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Wang, W. Biofunctionalization of PEGylated Microcapsules for Exclusive Binding to Protein Substrates. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nifontova, G.; Kalenichenko, D.; Baryshnikova, M.; Ramos Gomes, F.; Alves, F.; Karaulov, A.; Nabiev, I.; Sukhanova, A. Biofunctionalized Polyelectrolyte Microcapsules Encoded with Fluorescent Semiconductor Nanocrystals for Highly Specific Targeting and Imaging of Cancer Cells. Photonics 2019, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnikova, T.A.; Kiragosyan, G.; Le, T.H.N.; Springer, S.; Winterhalter, M. Protein A Functionalized Polyelectrolyte Microcapsules as a Universal Platform for Enhanced Targeting of Cell Surface Receptors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11506–11517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, C.; Tomaskovic-Crook, E.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Radt, B.; Cody, S.H.; Scott, A.M.; Nice, E.C.; Heath, J.K.; Caruso, F. Targeting and Uptake of Multilayered Particles to Colorectal Cancer Cells. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1998–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, C.; Tomaskovic-Crook, E.; Johnston, A.P.R.; Scott, A.M.; Nice, E.C.; Heath, J.K.; Caruso, F. Influence of Size, Surface, Cell Line, and Kinetic Properties on the Specific Binding of A33 Antigen-Targeted Multilayered Particles and Capsules to Colorectal Cancer Cells. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.Y.; Correa, S.; Min, J.; Li, J.; Roy, S.; Laccetti, K.H.; Dreaden, E.; Kong, S.; Heo, R.; Roh, Y.H.; et al. Binary Targeting of siRNA to Hematologic Cancer Cells In Vivo Using Layer-by-Layer Nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianat-Moghadam, H.; Heidarifard, M.; Mahari, A.; Shahgolzari, M.; Keshavarz, M.; Nouri, M.; Amoozgar, Z. TRAIL in oncology: From recombinant TRAIL to nano- and self-targeted TRAIL-based therapies. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparian, M.E.; Chernyak, B.V.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Yagolovich, A.V.; Popova, E.N.; Sycheva, A.M.; Moshkovskii, S.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.P. Generation of new TRAIL mutants DR5-A and DR5-B with improved selectivity to death receptor 5. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.M.; Sznol, M.; DiVito, K.A.; Camp, R.L.; Rimm, D.L.; Kluger, H.M. Evaluating the Expression and Prognostic Value of TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 in Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5188–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, M.T.; Lowenthal, R.M.; Venn, A.; Marwick, T.H. Chemotherapy-related cardiomyopathy: A neglected aspect of cancer survivorship. Intern. Med. J. 2014, 44, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagolovich, A.V.; Artykov, A.A.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Gasparian, M.E. A New Efficient Method for Production of Recombinant Antitumor Cytokine TRAIL and Its Receptor-Selective Variant DR5-B. Biochem. 2019, 84, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagolovich, A.; Kuskov, A.; Kulikov, P.; Kurbanova, L.; Bagrov, D.; Artykov, A.; Gasparian, M.; Sizova, S.; Oleinikov, V.; Gileva, A.; et al. Amphiphilic Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) Nanoparticles Conjugated with DR5-Specific Antitumor Cytokine DR5-B for Targeted Delivery to Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trushina, D.B.; Bukreeva, T.V.; Antipina, M.N. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Vaterite Calcium Carbonate by the Mixing Method: Aiming for Nanosized Particles. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trushina, D.B.; Bukreeva, T.V.; Borodina, T.N.; Belova, D.D.; Belyakov, S.; Antipina, M.N. Heat-driven size reduction of biodegradable polyelectrolyte multilayer hollow capsules assembled on CaCO3 template. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasov, R.; Zaytseva-Zotova, D.; Burov, S.; Leko, M.; Dontenwill, M.; Chiper, M.; Vandamme, T.; Markvicheva, E. Formation of multicellular tumor spheroids induced by cyclic RGD-peptides and use for anticancer drug testing in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodina, T.; Gileva, A.; Akasov, R.; Trushina, D.; Burov, S.; Klyachko, N.; González-Alfaro, Y.; Bukreeva, T.; Markvicheva, E. Fabrication and evaluation of nanocontainers for lipophilic anticancer drug delivery in 3D in vitro model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gileva, A.; Sarychev, G.; Kondrya, U.; Mironova, M.; Sapach, A.; Selina, O.; Budanova, U.; Burov, S.; Sebyakin, Y.; Markvicheva, E. Lipoamino acid-based cerasomes for doxorubicin delivery: Preparation and in vitro evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koloskova, O.O.; Gileva, A.M.; Drozdova, M.G.; Grechihina, M.V.; Suzina, N.E.; Budanova, U.A.; Sebyakin, Y.L.; Kudlay, D.A.; Shilovskiy, I.P.; Sapozhnikov, A.M.; et al. Effect of lipopeptide structure on gene delivery system properties: Evaluation in 2D and 3D in vitro models. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K. Transport of Molecules, Particles, and Cells in Solid Tumors. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 1, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euliss, L.E.; DuPont, J.A.; Gratton, S.; DeSimone, J. Imparting size, shape, and composition control of materials for nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhao, X.; Lin, Y.; Su, Z. Polydopamine-Based Nanoparticles for an Antibiofilm Platform: Influence of Size and Surface Charge on Their Penetration and Accumulation in S. aureus Biofilms. Langmuir 2022, 38, 10662–10671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Yao, X.; Sung, S.; Pang, Z.; Yang, W. Erythrocyte-cancer hybrid membrane-camouflaged melanin nanoparticles for enhancing photothermal therapy efficacy in tumors. Biomaterials 2019, 192, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schädlich, A.; Caysa, H.; Mueller, T.; Tenambergen, F.; Rose, C.; Göpferich, A.; Kuntsche, J.; Mäder, K. Tumor Accumulation of NIR Fluorescent PEG–PLA Nanoparticles: Impact of Particle Size and Human Xenograft Tumor Model. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8710–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trushina, D.B.; Akasov, R.A.; Khovankina, A.V.; Borodina, T.N.; Bukreeva, T.V.; Markvicheva, E.A. Doxorubicin-loaded biodegradable capsules: Temperature induced shrinking and study of cytotoxicity in vitro. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 284, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, Q.; Chen, S.; Yi, C.; Gong, C. TRAIL and curcumin codelivery nanoparticles enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis through upregulation of death receptors. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jwa, Y.; Hong, J.; Kim, K. Inhibition of Colon Cancer Recurrence via Exogenous TRAIL Delivery Using Gel-like Coacervate Microdroplets. Gels 2022, 8, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


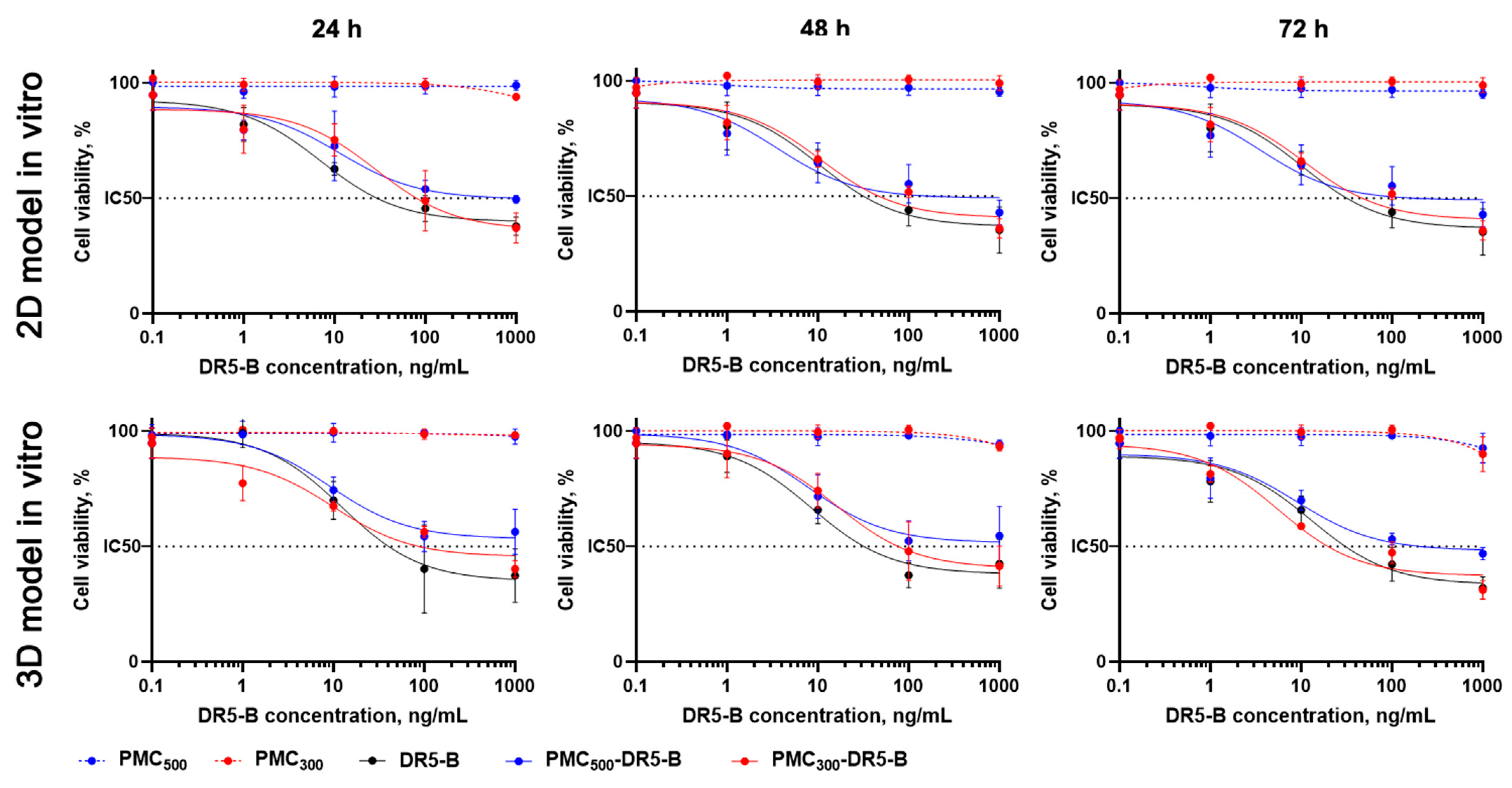

| Samples | IC50 * Values, ng/mL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D In Vitro Model | 3D In Vitro Model | |||||
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| PMC300 | >1000 | |||||
| PMC500 | ||||||
| DR5-B | 31 ± 2.6 | 27 ± 3.2 | 10 ± 0.7 | 39 ± 4.0 | 33 ± 2.4 | 28 ± 5.1 |
| PMC300-DR5-B | 72 ± 8.3 | 42 ± 3.8 | 10 ± 3.4 | 96 ± 7.7 | 77 ± 5.2 | 19 ± 1.6 |
| PMC500-DR5-B | 519 ± 38.5 | 111 ± 10.9 | 24 ± 3.1 | >1000 | 109 ± 18.2 | |
| Samples | IC50 * Values, ng/mL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D In Vitro Model | 3D In Vitro Model | |||||
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| PMC300 | >1000 | |||||
| DR5-B | 40 ± 5.8 | 31 ± 4.2 | 12 ± 2.2 | 56 ± 8.0 | 40 ± 8.8 | 31 ± 5.1 |
| DOX + DR5-B | 19 ± 2.4 | 7 ± 3.0 | 3 ± 0.9 | 53 ± 7.6 | 31 ± 4.3 | 10 ± 2.0 |
| DOX | >1000 | 809 ± 31.3 | 665 ± 27.3 | >1000 | 847 ± 65.3 | |
| PMC300 + DOX | >1000 | 593 ± 43.8 | >1000 | |||
| PMC300-DR5-B | 101 ± 9.6 | 38 ± 6.2 | 6 ± 1.2 | 107 ± 25.5 | 84 ± 10.4 | 19 ± 6.0 |
| PMC300-DR5-B+DOX | 52 ± 3.9 | 30 ± 3.7 | 7 ± 0.8 | 78 ± 8.1 | 47 ± 4.5 | 11 ± 3.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gileva, A.; Trushina, D.; Yagolovich, A.; Gasparian, M.; Kurbanova, L.; Smirnov, I.; Burov, S.; Markvicheva, E. Doxorubicin-Loaded Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Capsules Modified with Antitumor DR5-Specific TRAIL Variant for Targeted Drug Delivery to Tumor Cells. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050902
Gileva A, Trushina D, Yagolovich A, Gasparian M, Kurbanova L, Smirnov I, Burov S, Markvicheva E. Doxorubicin-Loaded Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Capsules Modified with Antitumor DR5-Specific TRAIL Variant for Targeted Drug Delivery to Tumor Cells. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(5):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050902
Chicago/Turabian StyleGileva, Anastasia, Daria Trushina, Anne Yagolovich, Marine Gasparian, Leyli Kurbanova, Ivan Smirnov, Sergey Burov, and Elena Markvicheva. 2023. "Doxorubicin-Loaded Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Capsules Modified with Antitumor DR5-Specific TRAIL Variant for Targeted Drug Delivery to Tumor Cells" Nanomaterials 13, no. 5: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050902
APA StyleGileva, A., Trushina, D., Yagolovich, A., Gasparian, M., Kurbanova, L., Smirnov, I., Burov, S., & Markvicheva, E. (2023). Doxorubicin-Loaded Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Capsules Modified with Antitumor DR5-Specific TRAIL Variant for Targeted Drug Delivery to Tumor Cells. Nanomaterials, 13(5), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050902








