Ball-Mill-Inspired Durable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Collecting and Speed Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of the Composite Triboelectric-Layer
2.3. Fabrication and Design of the Designed BMI-TENG
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Working Principle
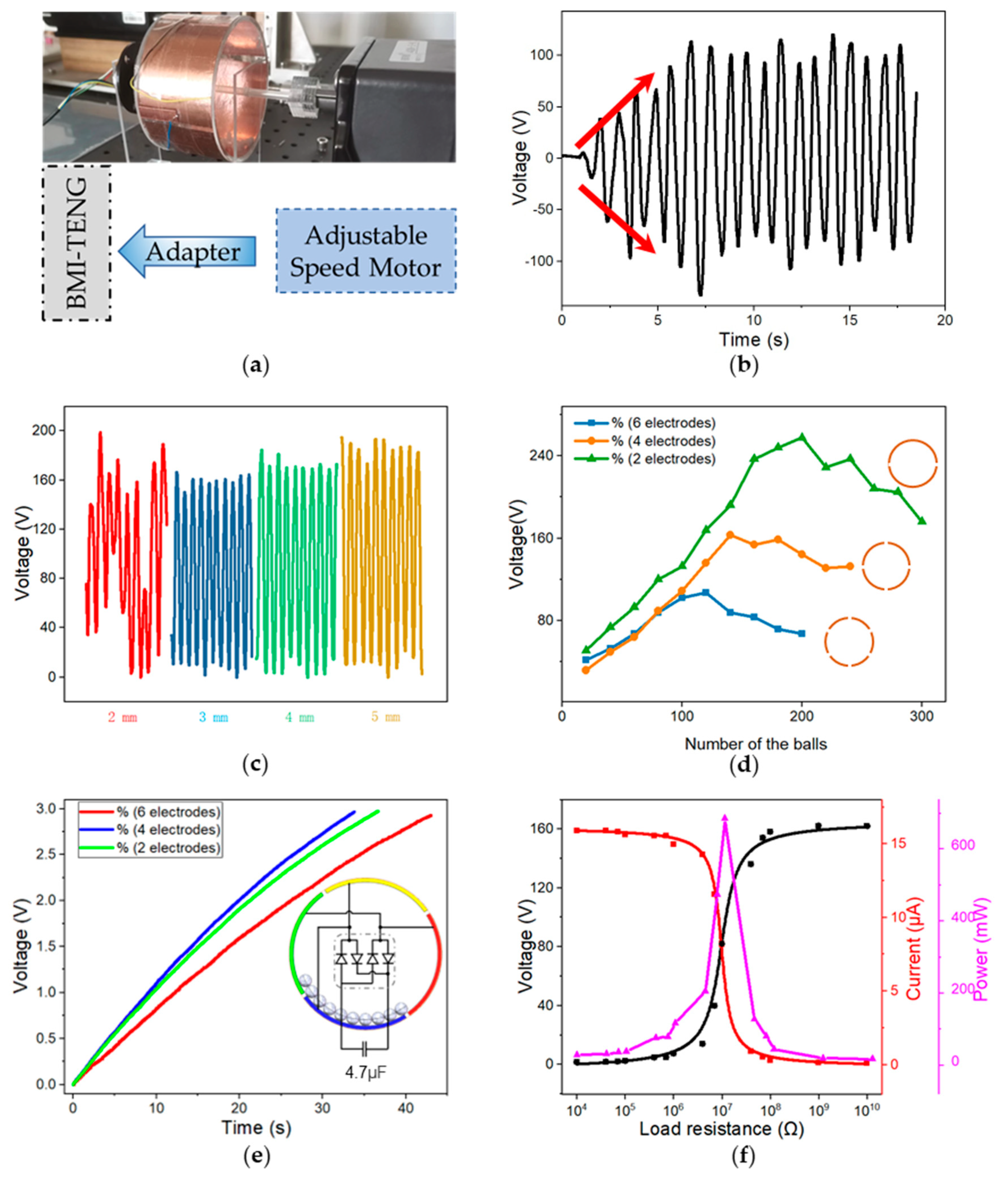
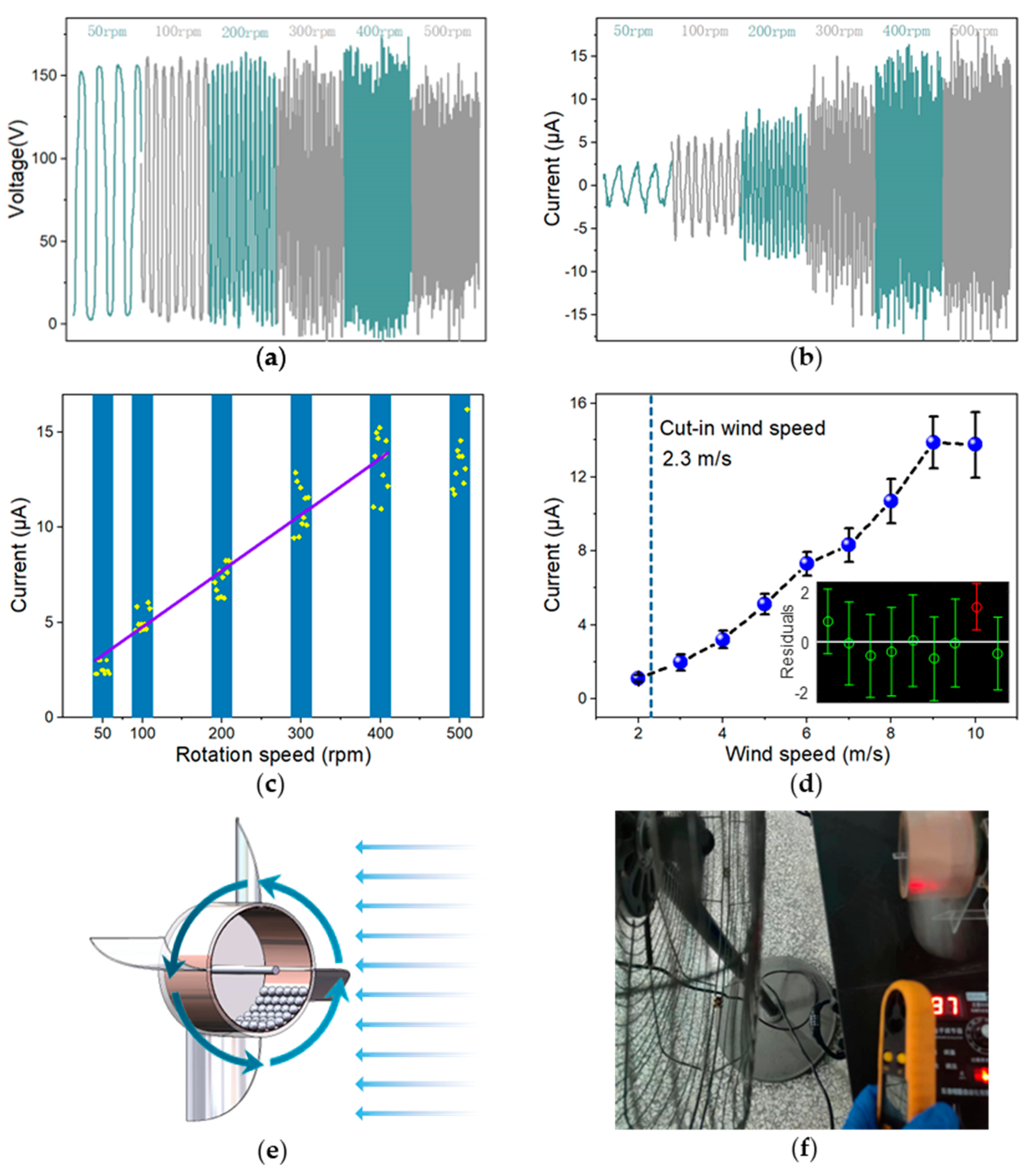
3.2. Measurement and Device Optimization
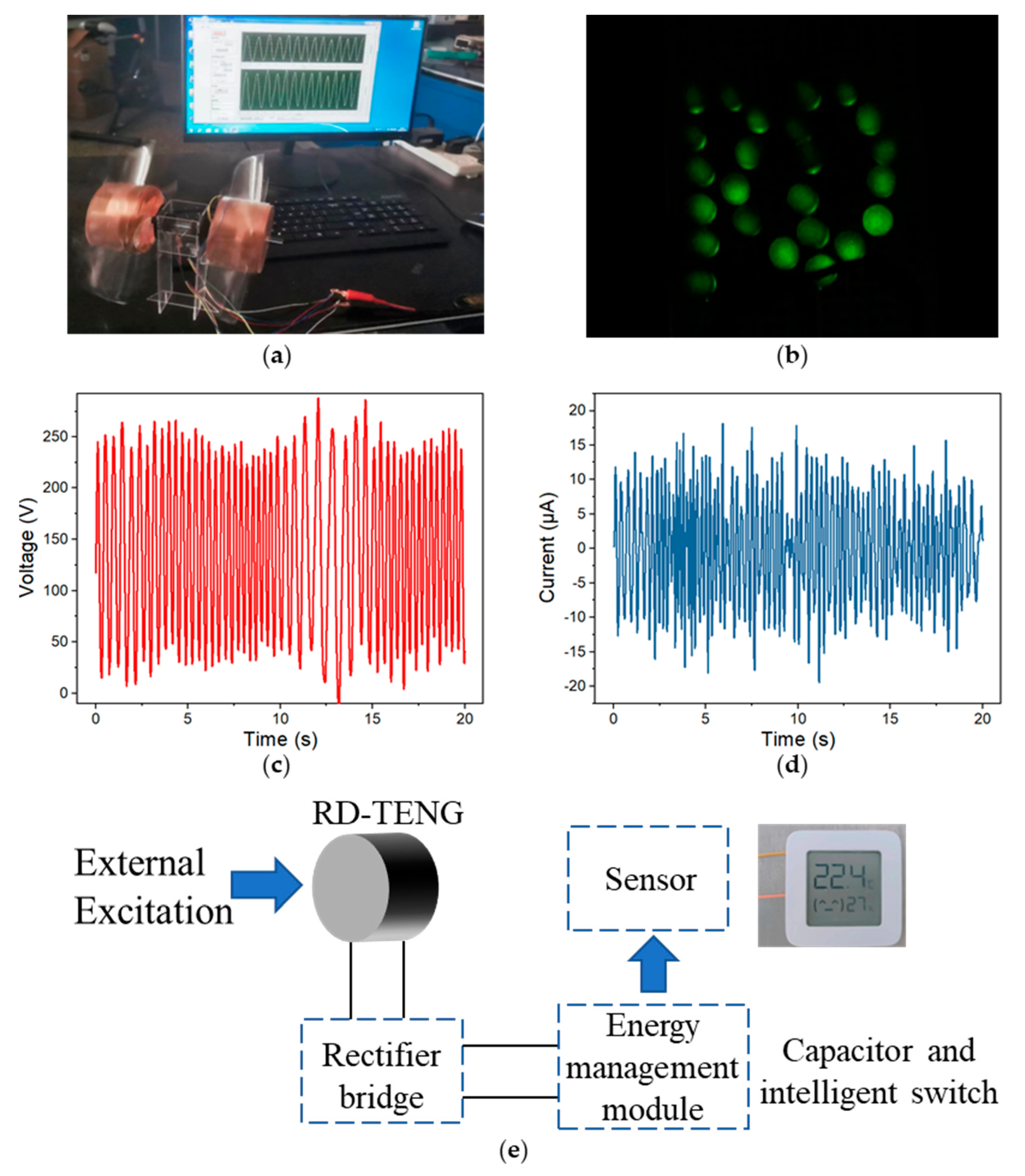
3.3. Performance and Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ackermann, T.; Söder, L. Wind energy technology and current status: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2000, 4, 315–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Scavenging Wind Energy by Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702649. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.L. Entropy theory of distributed energy for internet of things. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, L.; Luo, J.; Yan, Y.; Jia, B.E.; Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Hybrid All-in-One Power Source Based on High-Performance Spherical Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Harvesting Environmental Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.R.; Tian, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator! Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Seol, M.L.; Lee, S.H.; Han, J.W.; Kim, D.; Cho, G.H.; Choi, Y.K. Impact of contact pressure on output voltage of triboelectric nanogenerator based on deformation of interfacial structures. Nano Energy 2015, 17, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.C.; Geng, D.L.; Liang, E.J.; Wang, X.D. Single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator for scavenging friction energy from rolling tires. Nano Energy 2015, 15, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Chung, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Moon, J.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, M.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S. Design and optimization of rotating triboelectric nanogenerator by water electrification and inertia. Nano Energy 2016, 27, 340–351. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Xie, Y.; Jing, Q.; Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Sliding-triboelectric nanogenerators based on in-plane charge-separation mechanism. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2226–2233. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Ding, Z.; Qin, Z.; Chu, F.; Han, Q. Wind energy harvesting based on fluttering double-flag type triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, E.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Mi, J.; Pan, X.; Xu, M. A novel humidity resisting and wind direction adapting flag-type triboelectric nanogenerator for wind energy harvesting and speed sensing. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105279. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, H.; Zhu, C.; Yu, H.; Song, L.; Pan, X.; Mi, J.; Lee, C.; et al. An underwater flag-like triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting ocean current energy under extremely low velocity condition. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106503. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Pang, H.; An, J.; Lu, P.; Feng, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Z.L. Robust Swing-Structured Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Efficient Blue Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 202000064. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Liu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Han, J.; Li, L.; An, J.; Chen, P.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Spherical triboelectric nanogenerator based on spring-assisted swing structure for effective water wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105836. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H.; Feng, Y.; An, J.; Chen, P.; Han, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Segmented Swing-Structured Fur-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Blue Energy toward Marine Environmental Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Wang, P.; Rui, P.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Tu, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; et al. Broadband and Output-Controllable Triboelectric Nanogenerator Enabled by Coupling Swing-Rotation Switching Mechanism with Potential Energy Storage/Release Strategy for Low-Frequency Mechanical Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 202270194. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.; Saadatnia, Z.; Hassan, I.; Zi, Y.; Xi, Y.; He, X.; Zu, J.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Wireless Sensor Node Enabled by a Duck-Shaped Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Water Wave Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 201601705. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; An, J.; Shu, S.; Cheng, R.; Nie, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Super-Durable, Low-Wear, and High-Performance Fur-Brush Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind and Water Energy Harvesting for Smart Agriculture. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 202003066. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, W.; Gu, G.; Zhang, W.; Luo, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Guo, J.; Cui, P.; Yang, F.; Cheng, G.; et al. Rotational pulsed triboelectric nanogenerators integrated with synchronously triggered mechanical switches for high efficiency self-powered systems. Nano Energy 2021, 82, 105725. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.L. Auto-Switching Self-Powered System for Efficient Broad-Band Wind Energy Harvesting Based on Dual-Rotation Shaft Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 202101194. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Guo, H.; Chun, F.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. All-in-one 3D acceleration sensor based on coded liquid-metal triboelectric nanogenerator for vehicle restraint system. Mater. Today 2021, 43, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, O.; Yuan, W.; He, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Wind Energy by a Triboelectric Nanogenerator for an Intelligent High-Speed Train System. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Xi, Y.; Javed, M.S.; Hu, C. A fully-packaged and robust hybridized generator for harvesting vertical rotation energy in broad frequency band and building up self-powered wireless systems. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 508–514. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Meng, L.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Magnetic switch structured triboelectric nanogenerator for continuous and regular harvesting of wind energy. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105851. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Li, Z.; Liao, X.; Qiao, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B. A heaving point absorber-based ocean wave energy convertor hybridizing a multilayered soft-brush cylindrical triboelectric generator and an electromagnetic generator. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106381. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Jiang, T.; Liang, X.; An, J.; Wang, Z.L. Cylindrical triboelectric nanogenerator based on swing structure for efficient harvesting of ultra-low-frequency water wave energy. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 021401. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.H.; Chung, J.; Song, M.; Kim, S.; Shin, D.; Lin, Z.H.; Koo, B.; Kim, D.; Hong, J.; Lee, S. Nonpolar Liquid Lubricant Submerged Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Current Amplification via Direct Electron Flow. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100936. [Google Scholar]
- Long, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; He, W.; Li, G.; Tang, Q.; Guo, H.; Pu, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C. High performance floating self-excited sliding triboelectric nanogenerator for micro mechanical energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Freestanding triboelectric-layer-based nanogenerators for harvesting energy from a moving object or human motion in contact and non-contact modes. Adv Mater 2014, 26, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. A robust rolling-mode direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator arising from electrostatic breakdown effect. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 106014. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Xu, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Zhou, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Breeze-Wind-Energy-Powered Autonomous Wireless Anemometer Based on Rolling Contact-Electrification. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 2343–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Feng, Y.; Chen, P.; Liang, X.; Pang, H.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Wind-Driven Soft-Contact Rotary Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Rabbit Fur with High Performance and Durability for Smart Farming. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2108580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Yi, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J. Hexadecane-containing sandwich structure based triboelectric nanogenerator with remarkable performance enhancement. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Simultaneously Enhancing Power Density and Durability of Sliding-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator via Interface Liquid Lubrication. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2002920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xi, Y.; Shi, Y. Toward wear-resistive, highly durable and high performance triboelectric nanogenerator through interface liquid lubrication. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.H.; Lee, S.S.; Choi, G.J.; Park, I.K. Churros-like Polyvinylidene Fluoride Nanofibers for Enhancing Output Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 17824–17832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Wan, H.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G. High β phase content in PVDF/CoFe2O4 nanocomposites induced by DC magnetic fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 102904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.D.; Hemalatha, J. Enhanced dielectric and ferroelectric properties of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) fiber embedded polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) multiferroic composite films. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 094007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, X.; Zhu, S.; Bai, J.; Zhu, X.; Dai, J.; Yin, L.; Song, W.; Sun, Y. Magnetic field induced formation of ferroelectric β phase of poly (vinylidene fluoride). Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 126–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.L.; Ahn, K.K. Triboelectric Enhancement of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane Using Magnetic Nanoparticle for Water-Based Energy Harvesting. Polymers 2022, 14, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.R.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Electronics. Adv Mater 2016, 28, 4283–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
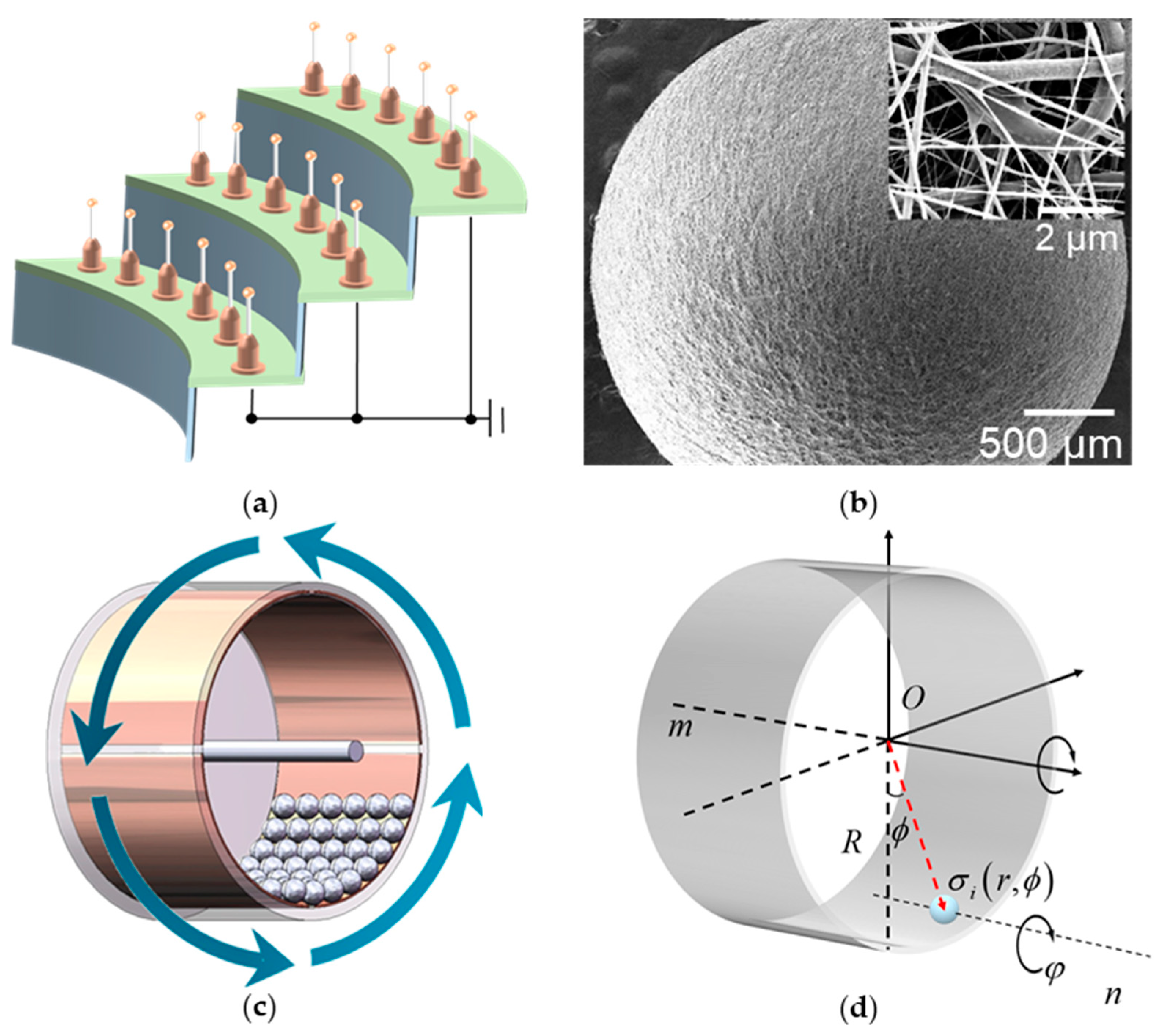


| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| R | Radius of the drum |
| r | Radius of the ball |
| Iim | Moment of inertia about the m-axis |
| Iin | Moment of inertia about the n-axis |
| Mim | Rotational torque about m-axis |
| Min | Rotational torque about n-axis |
| ϕ | Rotation angle of the drum |
| φ | Rotation angle of the ball |
| Gi | Gravity of the ball |
| Fe,im | Electrostatic force about m-axis |
| Fe,in | Electrostatic force about n-axis |
| Fc,i | Contact force |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Q.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. Ball-Mill-Inspired Durable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Collecting and Speed Monitoring. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050939
Qin Q, Cao X, Wang N. Ball-Mill-Inspired Durable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Collecting and Speed Monitoring. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(5):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050939
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Qinghao, Xia Cao, and Ning Wang. 2023. "Ball-Mill-Inspired Durable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Collecting and Speed Monitoring" Nanomaterials 13, no. 5: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050939
APA StyleQin, Q., Cao, X., & Wang, N. (2023). Ball-Mill-Inspired Durable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Collecting and Speed Monitoring. Nanomaterials, 13(5), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050939







