Effects of Top and Bottom Electrodes Materials and Operating Ambiance on the Characteristics of MgFx Based Bipolar RRAMs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
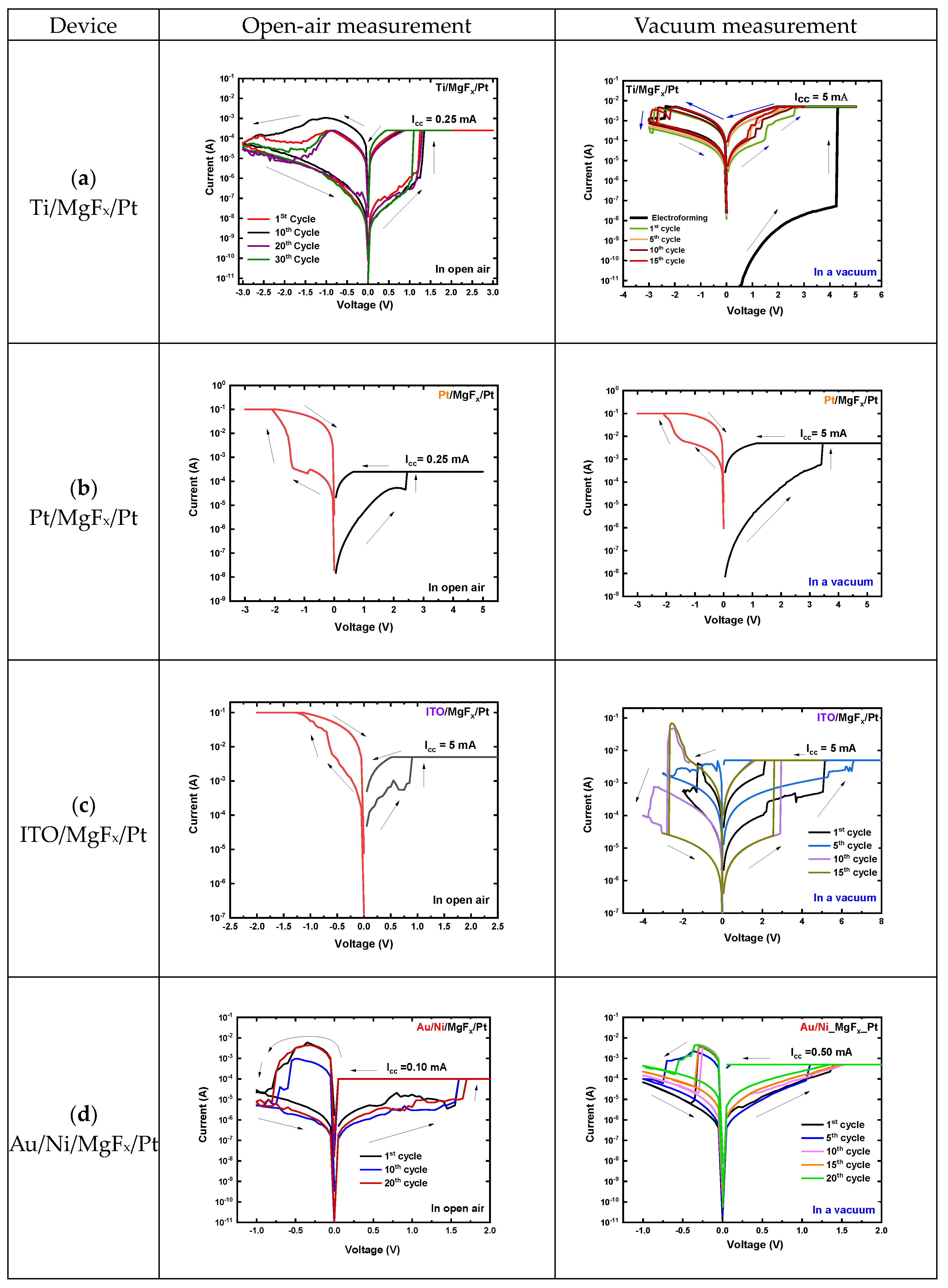
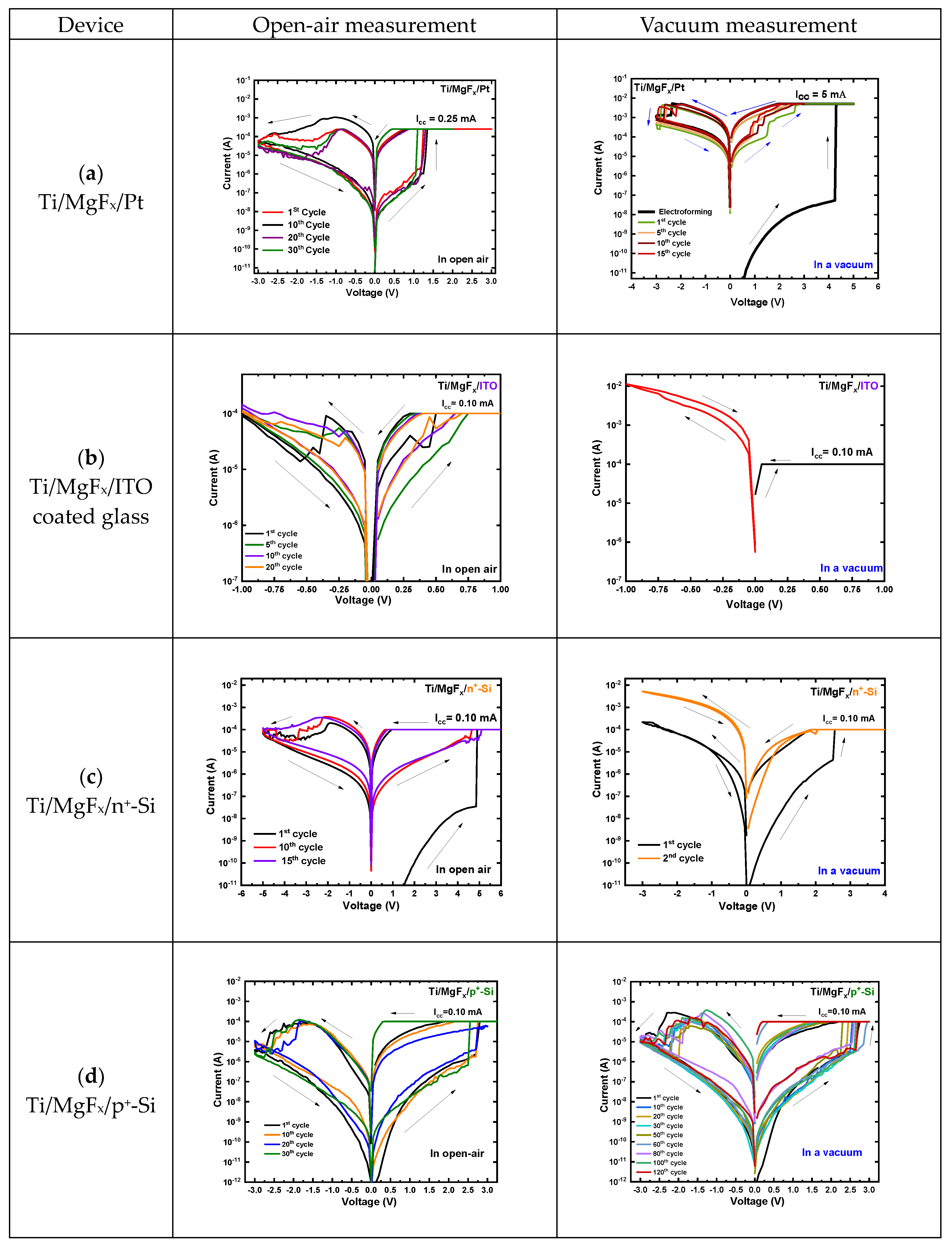
3.1. Effect of Top Electrodes and Operating Environment
3.2. Effect of Bottom Electrodes and Operating Environment
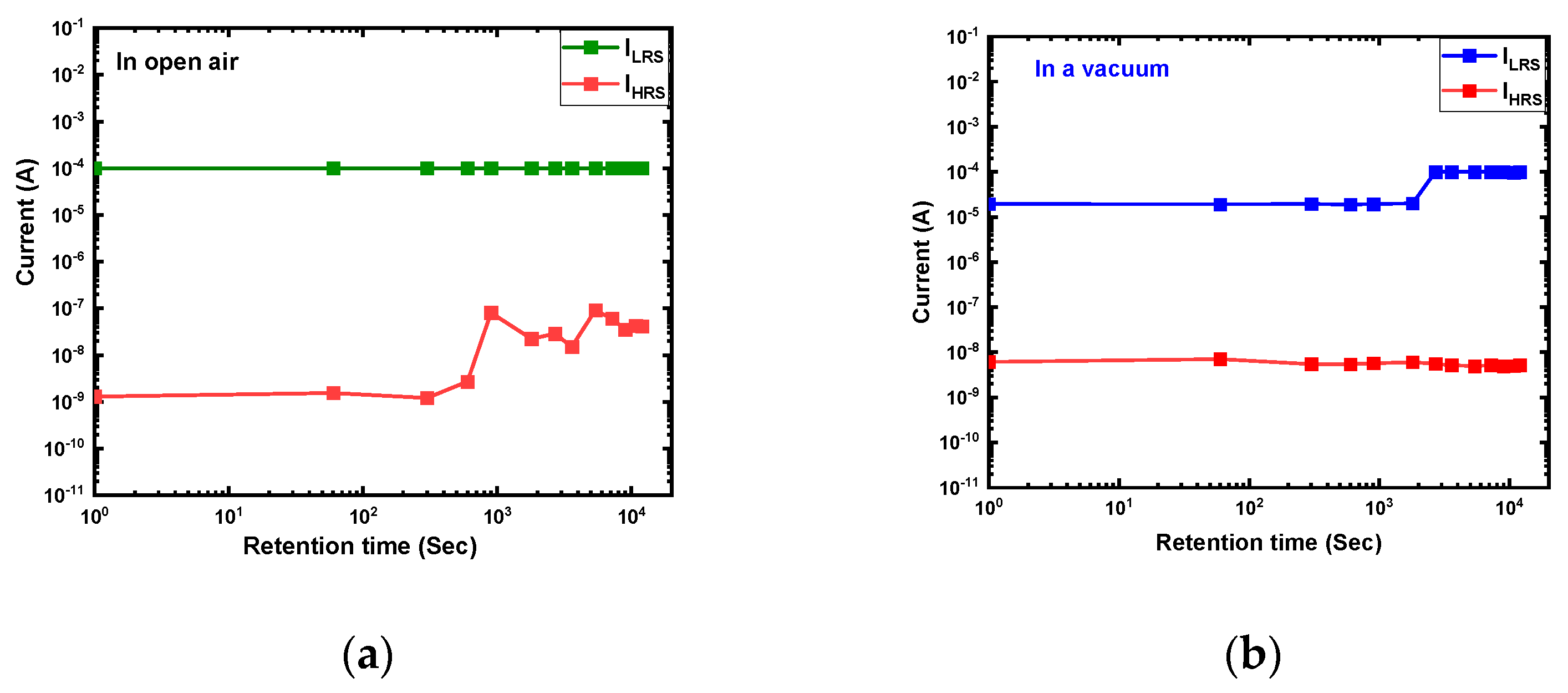
3.3. Factors to Determine the Effect of Electrodes and Operating Environment
3.4. Conduction and RS Mechanism of Ti/MgFx/p+-Si Devices
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Ning, X.; Hao, A.; Chen, R. Metal nanoparticles layer boosted resistive switching property in NiFe2O4-based memory devices. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 908, 164569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Mahata, C.; Kim, S. Tailoring the electrical homogeneity, large memory window, and multilevel switching properties of HfO2-based memory through interface engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 581, 152427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Lee, G.H.; Mahata, C.; Ismail, M.; Kim, H.; Kim, S. Bipolar and complementary resistive switching characteristics and neuromorphic system simulation in a Pt/ZnO/TiN synaptic device. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, N.K.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Asapu, S.; Xia, Q.; Joshua Yang, J. Emerging Memory Devices for Neuromorphic Computing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C. Advances of RRAM devices: Resistive switching mechanisms, materials and bionic synaptic application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Long, S.B.; Liu, Q.; Lü, H.B.; Liu, S.; Liu, M. An overview of resistive random access memory devices. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 3072–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, S.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, D.C.; Ahn, S.E.; Park, B.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Yoo, I.K.; Byun, I.S.; Hwang, I.R.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Electrode dependence of resistance switching in polycrystalline NiO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 263507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, U.; Cagli, C.; Spiga, S.; Cianci, E.; Ielmini, D. Impact of electrode materials on resistive-switching memory programming. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2009, 30, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.B.; Kang, B.S.; Benayad, A.; Lee, M.J.; Ahn, S.E.; Kim, K.H.; Stefanovich, G.; Park, Y.; Yoo, I.K. Effects of metal electrodes on the resistive memory switching property of NiO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 042115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cho, S.; Park, B.G. Effect of bottom electrode on resistive switching voltages in ag-based electrochemical metallization memory device. J. Semicond. Technol. Sci. 2016, 16, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Y.; Rhee, S.W. Effect of electrode material on the resistance switching of Cu2O film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Praveen, P.; Rose, T.P.; Saji, K.J. Top electrode dependent resistive switching in M/ZnO/ITO memristors, M = Al, ITO, Cu, and Au. Microelectron. J. 2022, 121, 105388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, K.; Yanagida, T.; Oka, K.; Kanai, M.; Klamchuen, A.; Rahong, S.; Meng, G.; Horprathum, M.; Xu, B.; Zhuge, F.; et al. Prominent thermodynamical interaction with surroundings on nanoscale memristive switching of metal oxides. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5684–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Robertson, J. Materials selection for oxide-based resistive random access memories. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 223516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molina, J.; Valderrama, R.; Zuniga, C.; Rosales, P.; Calleja, W.; Torres, A.; Dela Hidalga, J.; Gutierrez, E. Influence of the surface roughness of the bottom electrode on the resistive-switching characteristics of Al/Al2O3/Al and Al/Al2O3/W structures fabricated on glass at 300 °C. Microelectron. Reliab. 2014, 54, 2747–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundale, S.S.; Patil, A.P.; Patil, S.L.; Patil, P.B.; Kamat, R.K.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, T.G.; Dongale, T.D. Effects of switching layer morphology on resistive switching behavior: A case study of electrochemically synthesized mixed-phase copper oxide memristive devices. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 27, 101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Toyama, M.; Kita, K.; Kyuno, K.; Toriumi, A. Moisture-absorption-induced permittivity deterioration and surface roughness enhancement of lanthanum oxide films on silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuruoka, T.; Terabe, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Valov, I.; Waser, R.; Aono, M. Effects of moisture on the switching characteristics of oxide-based, gapless-type atomic switches. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valov, I.; Tsuruoka, T. Effects of moisture and redox reactions in VCM and ECM resistive switching memories. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 413001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappertzhofen, S.; Hempel, M.; Valov, I.; Waser, R. Proton mobility in SiO2 thin films and impact of hydrogen and humidity on the resistive switching effect. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2011, 1330, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappertzhofen, S.; Valov, I.; Tsuruoka, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Waser, R.; Aono, M. Generic relevance of counter charges for cation-based nanoscale resistive switching memories. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6396–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lübben, M.; Wiefels, S.; Waser, R.; Valov, I. Processes and Effects of Oxygen and Moisture in Resistively Switching TaOx and HfOx. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1700458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.C.; Kim, M.; Rani, J.R.; Hong, S.-M.; Jang, J.-H. Electroforming-Free Bipolar Resistive Switching Memory Based on Magnesium Fluoride. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.C.; Kim, M.; Rani, J.R.; Hong, S.-M.; Jang, J.-H. Nanoscale Low-temperature characteristics of magnesium fl uoride based bipolar RRAM devices. Low-temperature characteristics of magnesium fluoride based bipolar RRAM devices. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 3738–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.C.; Kim, M.; Kwak, D.U.; Rani, J.R.; Hong, S.M.; Jang, J.H. Effects of the Operating Ambiance and Active Layer Treatments on the Performance of Magnesium Fluoride Based Bipolar RRAM. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubouchi, K.; Ohkubo, I.; Kumigashira, H.; Oshima, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Itaka, K.; Ohnishi, T.; Lippmaa, M.; Koinuma, H. High-throughput characterization of metal electrode performance for electric-field-induced resistance switching in metal/Pr0.7Ca 0.3MnO3/metal structures. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1711–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Chuang, P.Y.; Chen, Y.T. Resistive Switching Characteristic of Low-Temperature Top-Electrode-Free Tin-Oxide Memristor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 64, 3951–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Lee, K.H.; Yang, D.Y.; You, B.H.; Song, I.H. Micro-accelerometer Based on Vertically Movable Gate Field Effect Transistor. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagdzevicius, S.; Maas, K.; Boudard, M.; Burriel, M. Interface-type resistive switching in perovskite materials. J. Electroceram. 2017, 39, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Lei, D.; He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; En, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F. Effect of Moisture Stress on the Resistance of HfO2/TaOx-Based 8-Layer 3D Vertical Resistive Random Access Memory. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2020, 41, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.C.; Oh, S.I.; Rani, J.R.; Hong, S.M.; Jang, J.H. Multilevel bipolar electroforming-free resistive switching memory based on silicon oxynitride. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.C.; Kim, M.; Hong, S.M.; Jang, J.H. Vacuum and Low-Temperature Characteristics of Silicon Oxynitride-Based Bipolar RRAM. Micromachines 2022, 13, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, F.C. A review on conduction mechanisms in dielectric films. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 578168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, E.W.; Ismail, R. Conduction mechanism of valence change resistive switching memory: A survey. Electronics 2015, 4, 586–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, F.C.; Chou, H.W.; Lee, J.Y.M. Electrical conduction mechanisms of metal La2O3Si structure. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 103503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traore, B.; Blaise, P.; Sklenard, B.; Vianello, E.; Magyari-Kope, B.; Nishi, Y. HfO2/Ti Interface Mediated Conductive Filament Formation in RRAM: An Ab Initio Study. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2018, 65, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tsang, M.; Chen, I.W. Biodegradable resistive switching memory based on magnesium difluoride. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15048–15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.C.; Tang, J.L.; Zeng, H.Z.; Wei, X.H. Abnormal coexistence of unipolar, bipolar, and threshold resistive switching in an Al/NiO/ITO structure. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Tseng, T.Y.; Hu, C. Modified resistive switching behavior of ZrO2 memory films based on the interface layer formed by using Ti top electrode. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 094101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Song, B.; Li, N.; Li, Q.; Liu, S. Transition from rectification to resistive-switching in Ti/MgF2/Pt memory. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Z.; Yu, H.Y.; Li, X.; Singh, N.; Lo, G.Q.; Kwong, D.L. HfOx/TiOx/HfOx/TiOx multilayer-based forming-free RRAM devices with excellent uniformity. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2011, 32, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Darling, R.B.; Majumdar, A.; Anantram, M.P. A forming-free bipolar resistive switching behavior based on ITO/V2O5/ITO structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, H.S.P.; Lee, H.Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, P.S.; Lee, B.; Chen, F.T.; Tsai, M.J. Metal-oxide RRAM. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 1951–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Electrode Materials | Ti | Pt | ITO | Au | Ni | n+-Si | p+-Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Work functions (eV) | 4.33 | 5.12 | 4.5 | 5.1 | 5.01 | 4.58 | 5.03 |
| Device | Ti MgFx Pt | Pt MgFx Pt | ITO MgFx Pt | Au/Ni MgFx Pt | Ti MgFx ITO | Ti MgFx n+-Si | Ti MgFx p+-Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Work function difference (eV) | 0.79 | 0 | 0.62 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.70 |
| Substrate and BE | SiO2 | Pt | p+-Si | n+-Si | ITO Coated Glass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roughness, RMS (nm) | 0.928 | 1.701 | 0.250 | 0.197 | 4.050 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, N.C.; Kim, Y.-P.; Hong, S.-M.; Jang, J.-H. Effects of Top and Bottom Electrodes Materials and Operating Ambiance on the Characteristics of MgFx Based Bipolar RRAMs. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13061127
Das NC, Kim Y-P, Hong S-M, Jang J-H. Effects of Top and Bottom Electrodes Materials and Operating Ambiance on the Characteristics of MgFx Based Bipolar RRAMs. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(6):1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13061127
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Nayan C., Yong-Pyo Kim, Sung-Min Hong, and Jae-Hyung Jang. 2023. "Effects of Top and Bottom Electrodes Materials and Operating Ambiance on the Characteristics of MgFx Based Bipolar RRAMs" Nanomaterials 13, no. 6: 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13061127
APA StyleDas, N. C., Kim, Y.-P., Hong, S.-M., & Jang, J.-H. (2023). Effects of Top and Bottom Electrodes Materials and Operating Ambiance on the Characteristics of MgFx Based Bipolar RRAMs. Nanomaterials, 13(6), 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13061127









