Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Hexagonally Ordered Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica as Ni Supports for Ethanol Steam Reforming
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Catalyst Synthesis
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
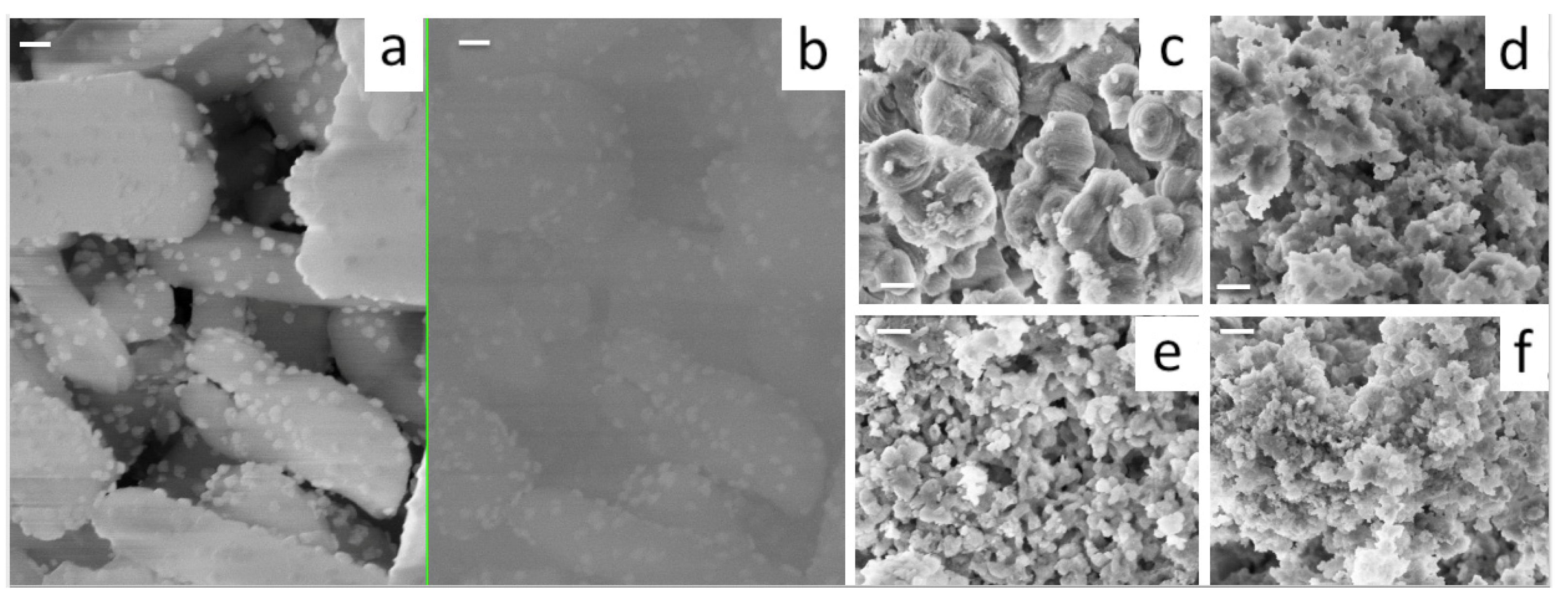
3.1. Effect of Ultrasound and Microwave Irradiation on the Characteristics of Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica
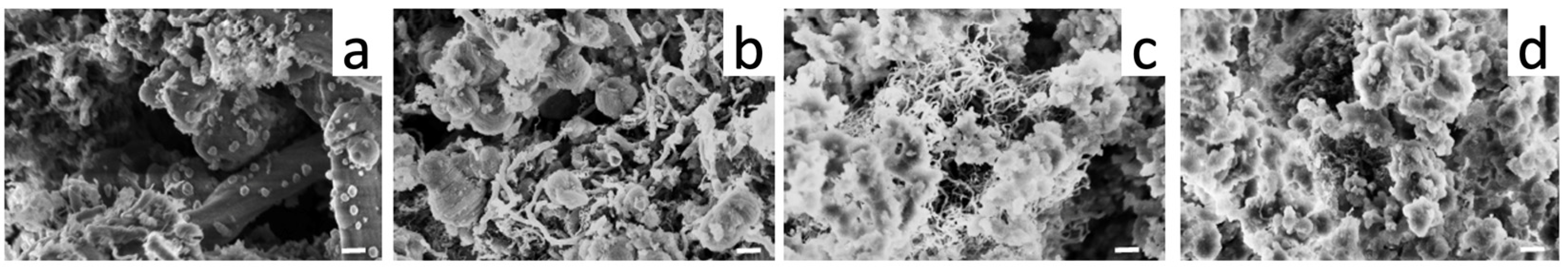
3.2. Ce-Modified Hexagonal Silica as Catalytic Supports for Nickel
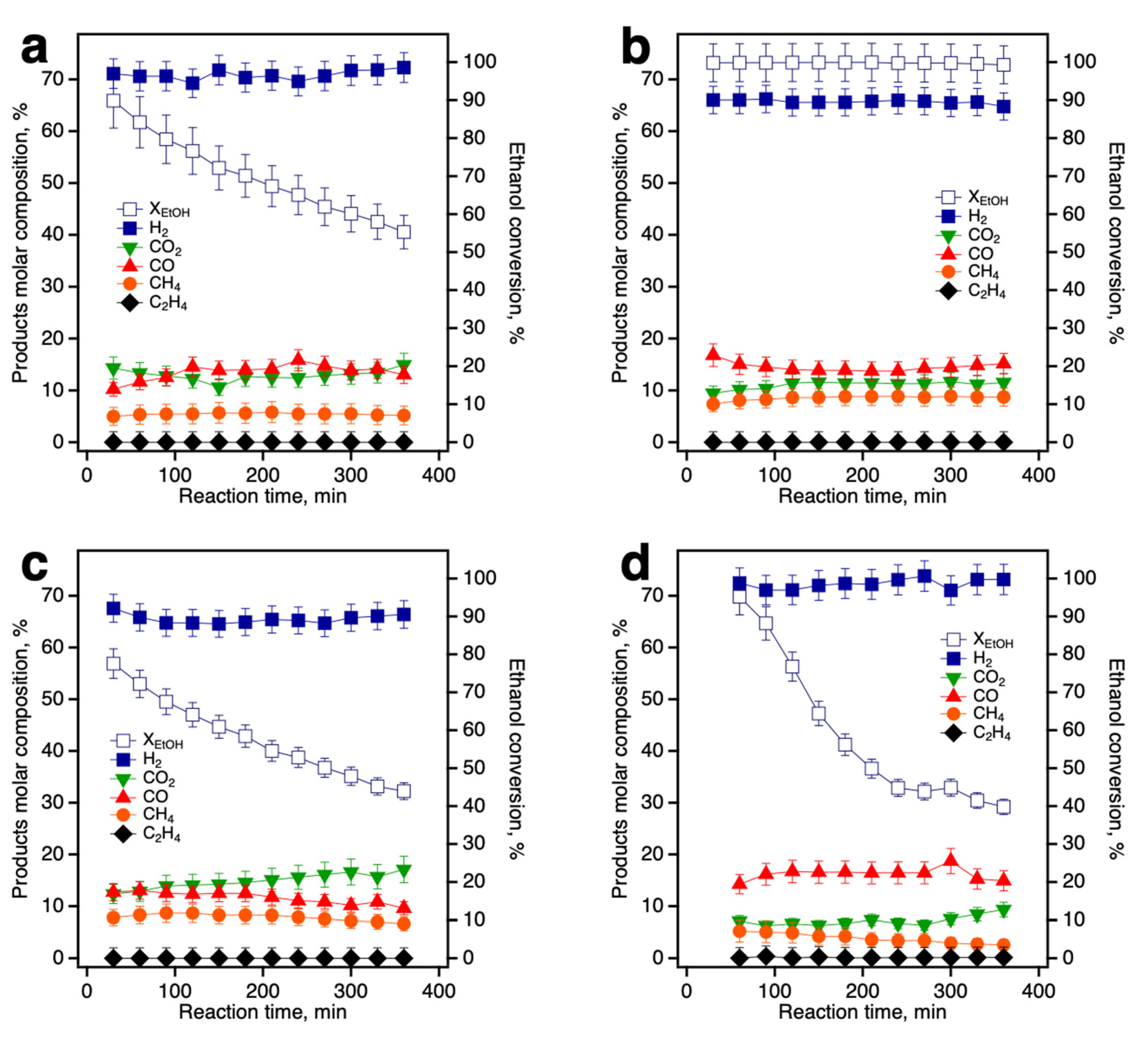
3.3. Catalytic Evaluation of Ni/Ce-Promoted Silica in the Ethanol Steam Reforming Reaction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pal, N.; Cho, E.-B.; Patra, A.K.; Kim, D. Ceria-Containing Ordered Mesoporous Silica: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.S.; Fratini, E.; Baglioni, P.; Chen, J.H.; Liu, Y. Pore Size Effect on Methane Adsorption in Mesoporous Silica Materials Studied by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8849–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, W.S.; Fratini, E.; Baglioni, P.; Georgi, D.; Chen, J.H.; Liu, Y. Methane Adsorption in Model Mesoporous Material, SBA-15, Studied by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 4354–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Dutta, S.; Wu, K.C.W. Integrated, Cascading Enzyme-/Chemocatalytic Cellulose Conversion Using Catalysts Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 3241–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Fuku, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Kamegawa, T.; Mori, K.; Yamashita, H. Design and Functionalization of Photocatalytic Systems within Mesoporous Silica. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresge, C.T.; Roth, W.J. The Discovery of Mesoporous Molecular Sieves from the Twenty Year Perspective. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3663–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Xia, K.; Gan, N.; Lu, X.; Nie, R.; Xia, Q. Construction of Solely Lewis Acidic Sites on Zr-MCM-41 and the Catalytic Activity for the Prins Condensation of β-pinene and Paraformaldehyde to Nopol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 230, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, B.; Pradhan, A.C.; Parida, K. A Comparative Study on Adsorption and Photocatalytic Dye Degradation under Visible Light Irradiation by Mesoporous MnO 2 Modified MCM-41 Nanocomposite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 226, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, O.G.; Heredia, J.D.L.R.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Castellanos, A.M.; Llanos, M. Hydrogen Production over Rh/Ce-MCM-41 catalysts via Ethanol Steam Reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 13914–13925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérardin, C.; Reboul, J.; Bonne, M.; Lebeau, B. Ecodesign of Ordered Mesoporous Silica Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4217–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handbook of Ultrasonics and Sonochemistry; Springer: Singapore, 2016; ISBN 978-981-287-277-7.
- Askari, S.; Alipour, S.M.; Halladj, R.; Farahani, M.H.D.A. Effects of Ultrasound on the Synthesis of Zeolites: A review. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompsett, G.A.; Conner, W.C.; Yngvesson, K.S. Microwave Synthesis of Nanoporous Materials. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 296–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, I.; Ricci, A.S. Chemical Activation Using an Open-End Coaxial Applicator. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2006, 41, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.T.; Peden, C.H.F. Oxygen Vacancies and Catalysis on Ceria Surfaces. Science 2005, 309, 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivier, L.; Duprez, D. Ceria-Based Solid Catalysts for Organic Chemistry. Chemsuschem 2010, 3, 654–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akondi, A.M.; Trivedi, R.; Sreedhar, B.; Kantam, M.L.; Bhargava, S. Cerium-Containing MCM-41 Catalyst for Selective Oxidative Arene Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reactions. Catal. Today 2012, 198, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Chen, Y.; Min, L.; Fang, H.; Yan, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Liquid Oxidation of Cyclohexane to Cyclohexanol over Cerium-Doped MCM-41. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2006, 246, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Valenzuela, M.; Salas, P.; García-Ruiz, A.; Toledo, J.; Cortes-Jácome, M.; Angeles-Chavez, C.; Novaro, O. Ni/Ce-MCM-41 Mesostructured Catalysts for Simultaneous Production of Hydrogen and Nanocarbon via Methane Decomposition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 3509–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zeng, L.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Gong, J. Ceria-promoted Ni/SBA-15 Catalysts for Ethanol Steam Reforming with Enhanced Activity and Resistance to Deactivation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 176, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cai, W.; Yue, B.; He, H. Promotional Effect of Cerium on Nickel-Containing Mesoporous Silica for Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane. Sci. China Chem. 2015, 58, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Castaldo, F.; Ciambelli, P.; Iaquaniello, G. CeO2-supported Pt/Ni Catalyst for the Renewable and Clean H2 Production via Ethanol Steam Reforming. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 145, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, I.A.C.; Montini, T.; Lorenzut, B.; Troiani, H.; Gennari, F.C.; Graziani, M.; Fornasiero, P. Hydrogen Production from Ethanol Steam Reforming on M/CeO2/YSZ (M=Ru, Pd, Ag) Nanocomposites. Catal. Today 2012, 180, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calles, J.; Carrero, A.; Vizcaíno, A. Ce and La Modification of Mesoporous Cu–Ni/SBA-15 Catalysts for Hydrogen Production Through Ethanol Steam Reforming. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 119, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.; Ereña, J.; Montero, C.; Azkoiti, M.J.; Bilbao, J.; Gayubo, A.G. Reaction Pathway for Ethanol Steam Reforming on A Ni/SiO 2 Catalyst Including coke Formation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 18820–18834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rivera, J.; Galindo-Esquivel, I.R.; Onor, M.; Bramanti, E.; Longo, I.; Ferrari, C. Heterogeneous Catalytic Reaction of Microcrystalline Cellulose in Hydrothermal Microwave-Assisted Decomposition: Effect of Modified Zeolite Beta. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, T.N.; Huang, T.C.; Toraya, H.; Hubbard, C.R.; Robie, S.B.; Louër, D.; Göbel, H.E.; Will, G.; Gilles, R.; Raftery, T. JCPDS—International Centre for Diffraction Data Round Robin Study of Silver Behenate. A Possible Low-Angle X-Ray Diffraction Calibration Standard. Powder Diffr. 1995, 10, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A New Family of Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Prepared with Liquid Crystal Templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rivera, J.; Tovar-Rodríguez, J.; Bramanti, E.; Duce, C.; Longo, I.; Fratini, E.; Galindo-Esquivel, I.R.; Ferrari, C. Surfactant Recovery from Mesoporous Metal-modified Materials (Sn–, Y–, Ce–, Si–MCM-41), by Ultrasound Assisted Ion-Exchange Extraction and Its Re-Use for a Microwave in Situ Cheap and Eco-Friendly MCM-41 Synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7020–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, B.; Gómez, V.; Platero-Prats, A.E.; Revés, M.; Echeverría, J.; Cremades, E.; Barragán, F.; Alvarez, S. Covalent Radii Revisited. Dalton Trans. 2008, 21, 2832–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleitz, F.; Schmidt, W.; Schüth, F. Evolution of Mesoporous Materials during the Calcination Process: Structural and Chemical Behavior. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 44, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H. Small Angle Neutron Scattering Studies of the Structure and Interaction in Micellar and Microemulsion Systems. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1986, 37, 351–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Song, B.Y.; Lee, T.G. Effects of Surfactant/Silica and Silica/Cerium Ratios on the Characteristics of Mesoporous Ce-MCM-41. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, T.; Li, C.; Yin, H. Effect of the Si/Ce Molar Ratio on the Textural Properties of Rare Earth Element Cerium Incorporated Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Obtained Room Temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 9425–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Li, C.-S.; Yin, H. Characterization and Synthesis of Ce-Incorporated Mesoporous Molecular Sieves under Microwave Irradiation Condition. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.M.; Zholobenko, V.L.; Thursfield, A.; Plaisted, R.J.; Cundy, C.S.; Dwyer, J. In situ FTIR Study of the Formation of MCM-41. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1998, 94, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, S.; Mukherjee, P.; Sainkar, S.; Kumar, R. Cerium Containing MCM-41-Type Mesoporous Materials and their Acidic and Redox Catalytic Properties. J. Catal. 2002, 207, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gulková, D.; Vít, Z. Silica-Ceria as Support for the Preparation of NiMo(P) Hydrodesulfurization and Hydrodenitrogenation Catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1995, 125, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, Q.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Low-Temperature Water-Gas Shift Reaction over Cu- and Ni-Loaded Cerium Oxide Catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2000, 27, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, N.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Han, C. Nickel Nanoparticles Highly Dispersed with An Ordered Distribution in MCM-41 Matrix as An Efficient Catalyst for Hydrodechlorination of Chlorobenzene. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 185, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L. A Simple Method to Prepare Highly Active and Dispersed Ni/MCM-41 Catalysts by Co-Impregnation. Catal. Commun. 2013, 42, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haryanto, A.; Fernando, S.; Murali, N.; Adhikari, S. Current Status of Hydrogen Production Techniques by Steam Reforming of Ethanol: A Review. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 2098–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlett, C.M.A.; Aydin, A.; Durndell, L.J.; Frattini, L.; Isaacs, M.A.; Lee, A.F.; Liu, X.; Olivi, L.; Trofimovaite, R.; Wilson, K.; et al. Tailored Mesoporous Silica Supports for Ni Catalysed Hydrogen Production from Ethanol Steam Reforming. Catal Commun 2017, 91, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Liu, Z.; Johnston-Peck, A.C.; Senanayake, S.D.; Zhou, G.; Stacchiola, D.; Stach, E.A.; Rodriguez, J.A. Steam Reforming of Ethanol on Ni/CeO2: Reaction Pathway and Interaction between Ni and the CeO2 Support. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankhah, S.; Abatzoglou, N.; Gitzhofer, F.; Blanchard, J.; Oudghiri-Hassani, H. Catalytic Properties of Carbon Nano-Filaments Produced by Iron-Catalysed Reforming of Ethanol. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 139, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
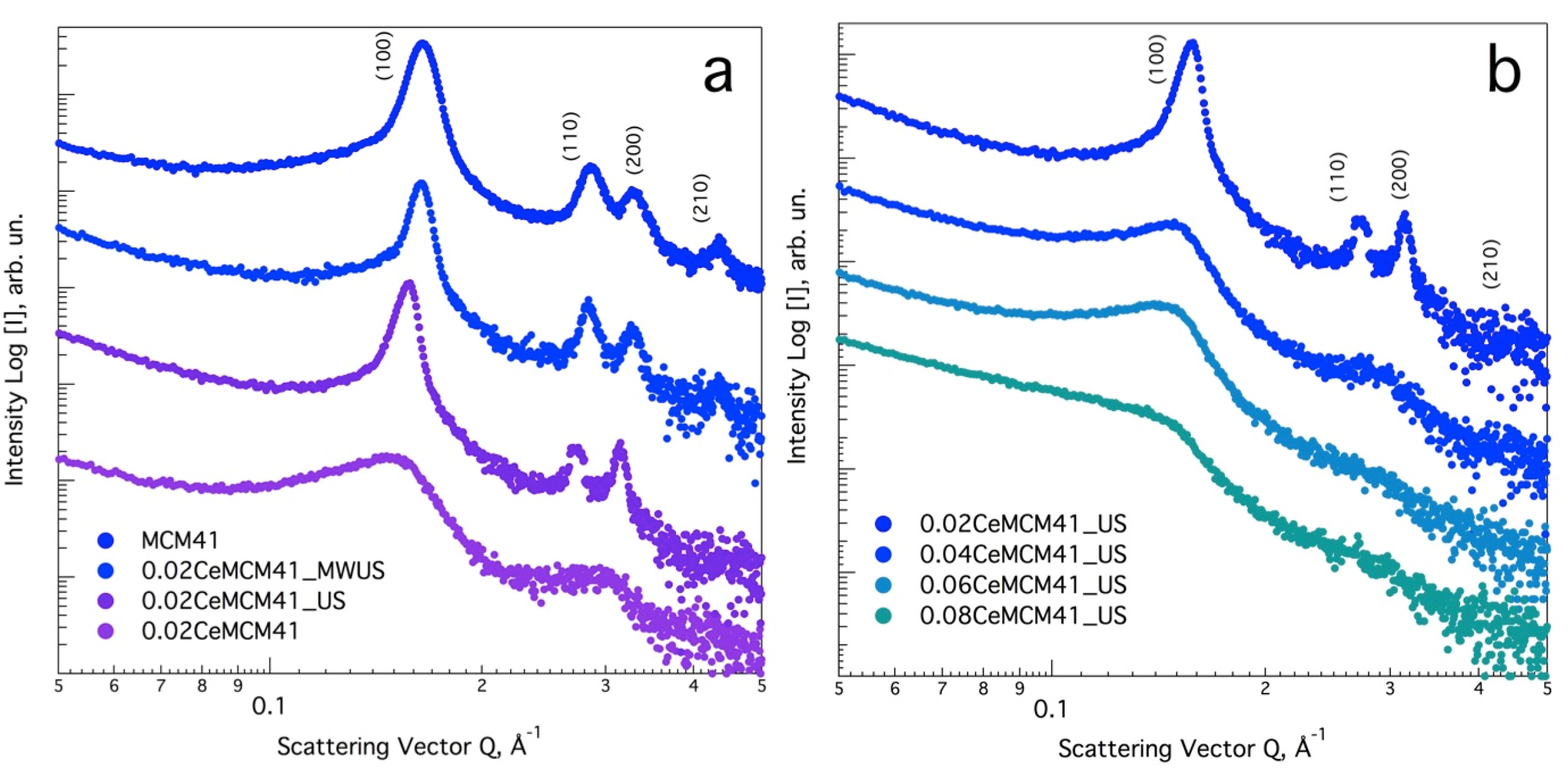
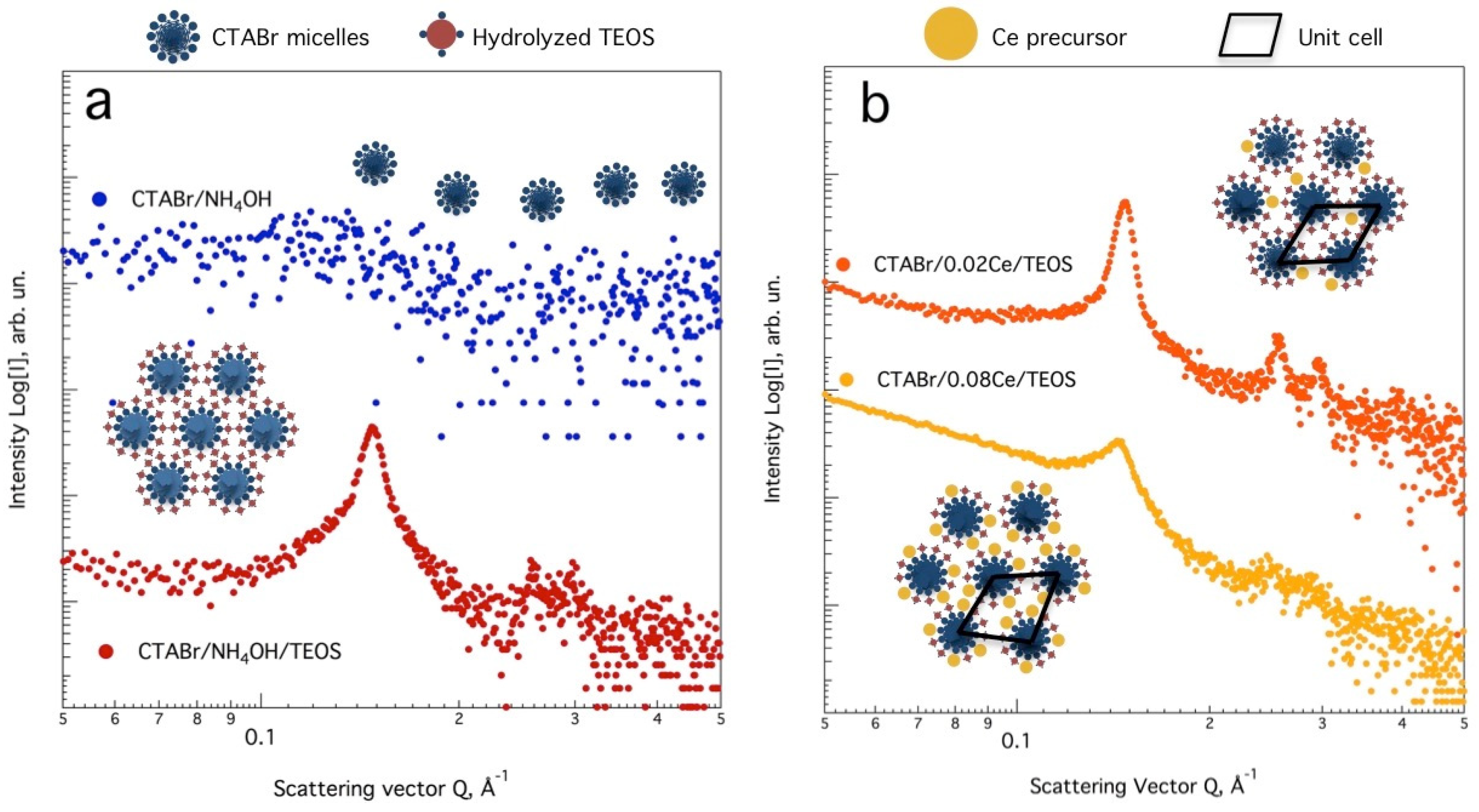

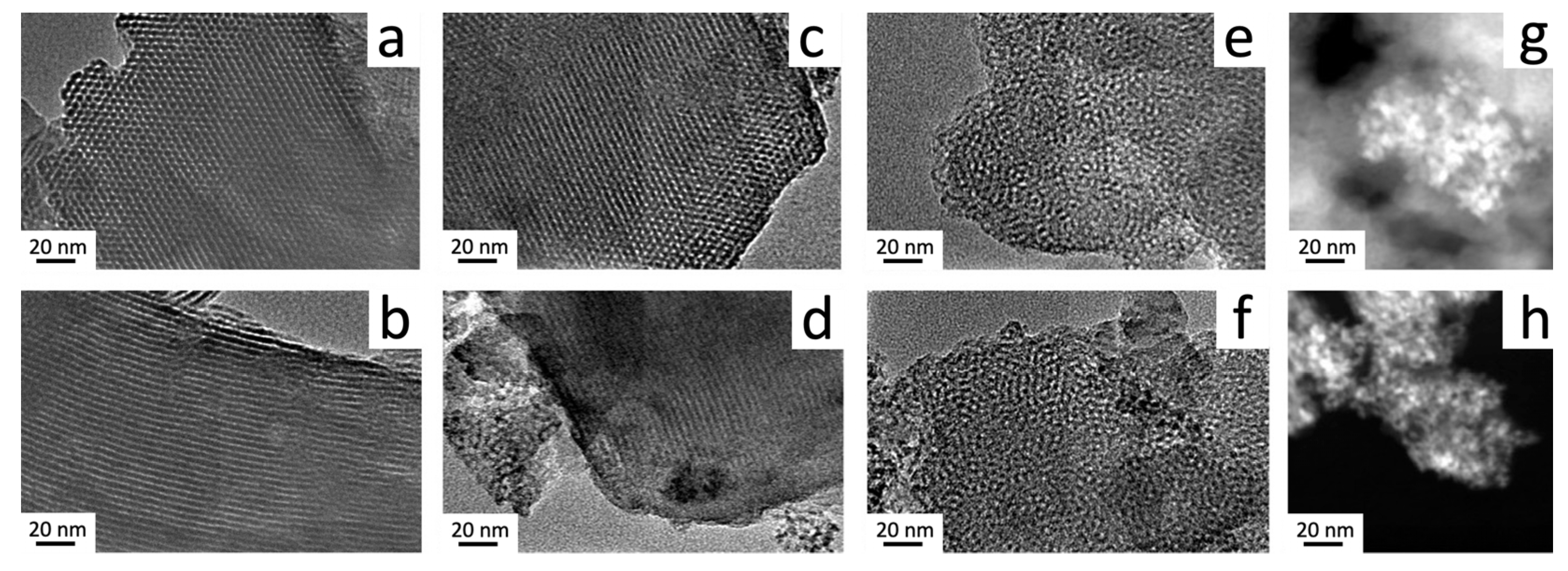
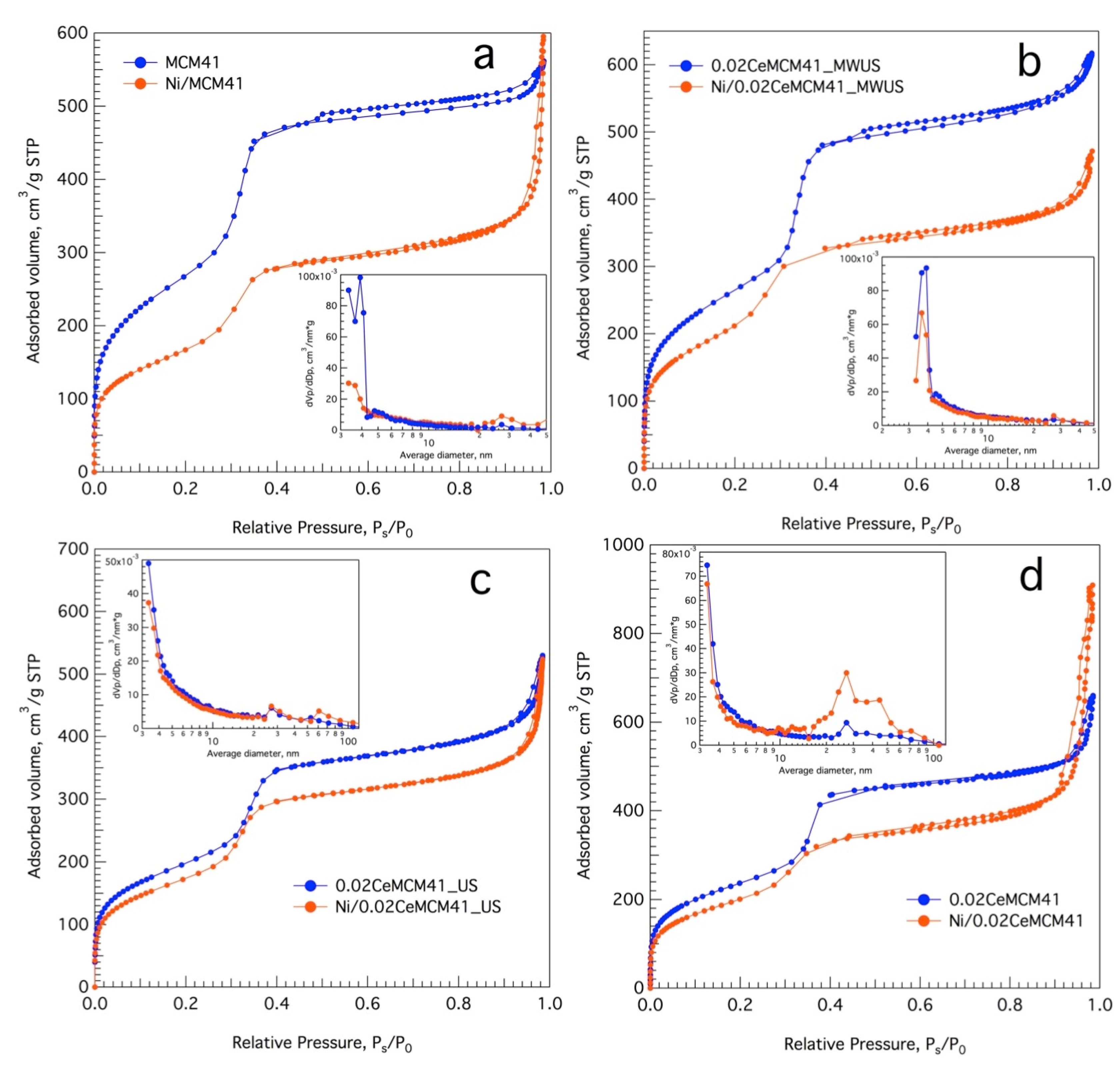

| Sample Name | Ce/Si Ratio | d100, nm [a] | a0, nm [b] |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41 | 0 | 4.42 | 5.10 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41_MWUS [c] | 0.02 | 4.46 | 5.15 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41 [d] | 0.02 | 4.78 | 5.52 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41_US [e] | 0.02 | 4.63 | 5.35 |
| 0.04Ce-MCM-41_US [e] | 0.04 | 4.88 | 5.63 |
| 0.06Ce-MCM-41_US [e] | 0.06 | 4.98 | 5.75 |
| 0.08Ce-MCM-41_US [e] | 0.08 | 5.04 | 5.82 |
| Sample Name | SBET [a], m2g−1 | Vpore [b], cm3g−1 | Vmonolayer [c], cm3g−1 | Dpore [d], nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCM-41 | 980 | 0.86 | 225 | 3.49 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41_MWUS | 967 | 0.94 | 222 | 3.88 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41 | 865 | 0.96 | 199 | 4.45 |
| 0.02Ce-MCM-41_US | 806 | 0.77 | 185 | 3.84 |
| 0.04Ce-MCM-41_US | 711 | 0.68 | 163 | 3.84 |
| 0.06Ce-MCM-41_US | 629 | 0.65 | 145 | 4.14 |
| 0.08Ce-MCM-41_US | 546 | 0.60 | 125 | 4.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tovar-Rodriguez, J.; Fratini, E.; Baglioni, P.; Ferrari, C.; de los Reyes-Heredia, J.A.; Ramírez-Hernández, Y.; Galindo-Esquivel, I.R. Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Hexagonally Ordered Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica as Ni Supports for Ethanol Steam Reforming. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13060997
Tovar-Rodriguez J, Fratini E, Baglioni P, Ferrari C, de los Reyes-Heredia JA, Ramírez-Hernández Y, Galindo-Esquivel IR. Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Hexagonally Ordered Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica as Ni Supports for Ethanol Steam Reforming. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(6):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13060997
Chicago/Turabian StyleTovar-Rodriguez, Jorge, Emiliano Fratini, Piero Baglioni, Carlo Ferrari, José Antonio de los Reyes-Heredia, Yonatan Ramírez-Hernández, and Ignacio René Galindo-Esquivel. 2023. "Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Hexagonally Ordered Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica as Ni Supports for Ethanol Steam Reforming" Nanomaterials 13, no. 6: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13060997
APA StyleTovar-Rodriguez, J., Fratini, E., Baglioni, P., Ferrari, C., de los Reyes-Heredia, J. A., Ramírez-Hernández, Y., & Galindo-Esquivel, I. R. (2023). Ultrasound and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Hexagonally Ordered Ce-Promoted Mesoporous Silica as Ni Supports for Ethanol Steam Reforming. Nanomaterials, 13(6), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13060997








