Preparation of Molybdenum Disulfide with Different Nanostructures and Its Adsorption Performance for Copper (Ⅱ) Ion in Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Instruments and Equipment
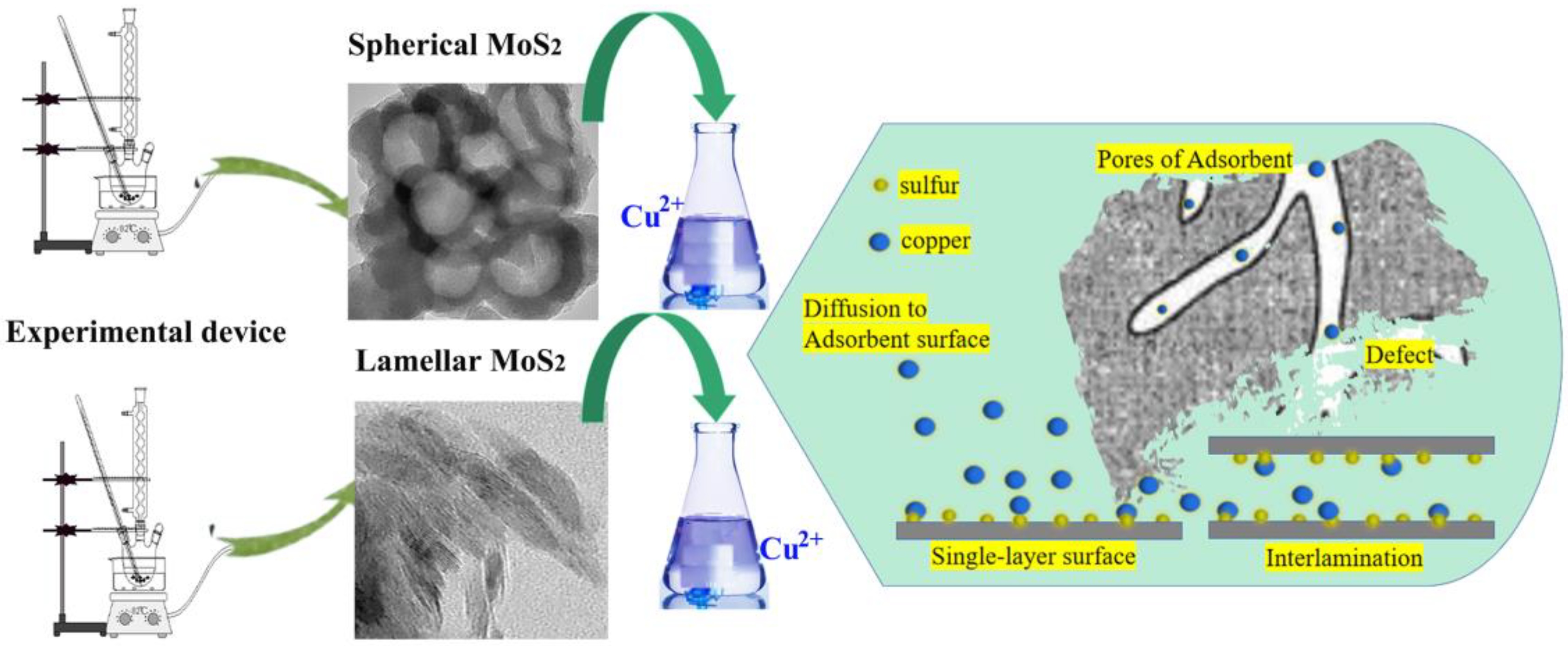
2.3. Preparation of MoS2 with Different Micromorphologies
2.4. Measurements and Analysis Approach of Cu2+ Removal Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Factors Affecting Adsorption Performance
3.2.1. Effect of Initial pH Values
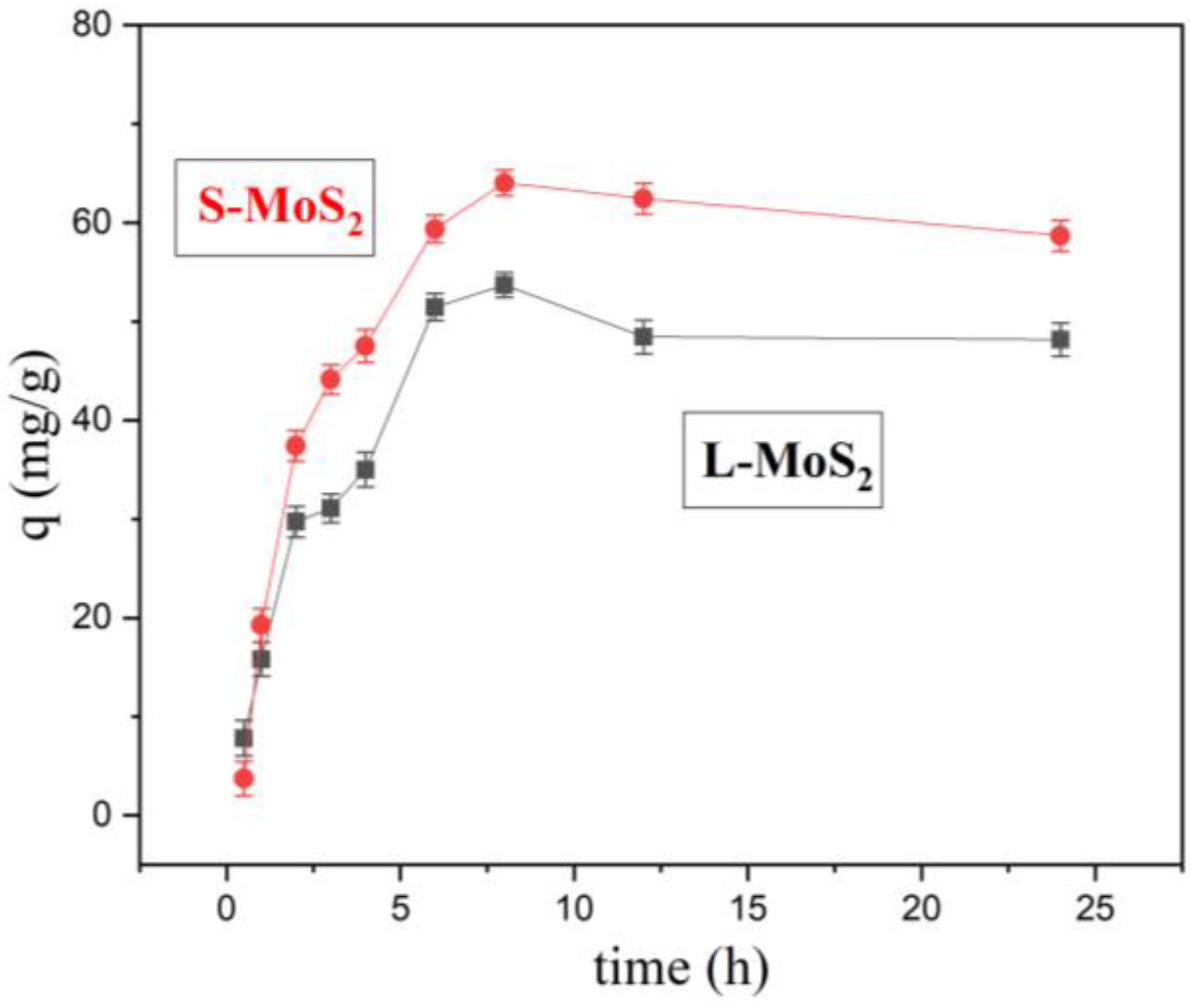
3.2.2. Effect of Adsorption Duration
3.2.3. Effect of Initial Concentration
3.2.4. Effect of Different Temperatures
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm
3.3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
3.3.2. Adsorption Isotherm
3.3.3. Thermodynamic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mak, K.; Shan, J. Photonics and optoelectronics of 2D semiconductor transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Dutta, H.; Gogoi, S.; Devi, R.; Khan, R. Nanostructured MoS2-based advanced biosensors: A review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2017, 1, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais Antunes, F.P.; Vaiss, V.S.; Tavares, S.R.; Capaz, R.B.; Leitão, A.A. Van der Waals interactions and the properties of graphite and 2H-, 3R- and 1T-MoS2: A comparative study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2018, 152, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Meng, H.; Sheng, B.; Liu, J. Preparation and photocatalytic properties of nanofilm molybdenum disulfide. New Chem. Mater. 2017, 45, 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, M.; Yu, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, M.; Du, M. Synthesis and Hydrogen Evolution Performance of Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheets/Carbon Nanofibers Hybrid Materials. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 33, 595–600. [Google Scholar]
- Escalera-Lopez, D.; Lou, Z.; Rees, N. Benchmarking the activity, stability, and inherent electrochemistry of amorphous molybdenum sulfide for hydrogen production. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1802614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Raj, C.; Nagaraju, G.; Pyo, M.; Kim, B. Selective design of binder-free hierarchical nickel molybdenum sulfide as a novel battery-type material for hybrid supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 25467–25480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, R. Study on ultrasound-assisted liquid-phase exfoliation for preparing graphene-like molybdenum disulfide nanosheets. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2020, 63, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Wu, A.; Zhou, S.; Huang, H.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, H. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of MoS2 thin film anode material. J. Funct. Mater. 2020, 51, 8105–8110. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, D.; Jiang, C.; Xiao, G.; Wang, D.; Guo, X.; Xu, Y. Synthesis of MoS2/Ni Foam Composite by One-step Hydrothermal Method and Its Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performance. J. Ludong Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 35, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Branimir, R.; Andras, K. Mobility engineering and a metal-insulator transition in monolayer MoS2. Nat. Mater. 2013, 9, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H. Design, Synthesis and Application of New Magnetic Nanomaterials and Mesoporous Silica Materials; Fudan University: Shanghai, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Ai, X.; Han, S. Preparation and photocatalytic properties of petal-shaped MoS2. J. Jilin Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 39, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, F. Design and optimization of H2O2 sensor based on nano MoS2 material. Chem. Sens. 2019, 39, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Shi, B.; Hu, E.; Hu, K.; Hu, X. Reuse of spent bleaching clay for supporting MoS2 nanoparticles as a lubricating filler in ABS plastics. Tribol. Int. 2019, 131, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Jhung, S. Adsorptive removal and separation of chemicals with metal-organic frameworks: Contribution of p-complexation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Khan, A.; Wen, T.; Hu, B.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. Two-dimensional MAX-derived titanate nanostructures for efficient removal of Pb(II). Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, F.; Liu, C.; Yang, B.; Zhang, X.; Yi, H.; Ni, J.; Song, S. Thermal modification of the molybdenum disulfide surface for tremendous improvement of Hg2+ adsorption from aqueous solution. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9065–9073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Jang, J.; Lim, S.; Lee, D. Unique selectivity and rapid uptake of molybdenum-disulfide-functionalized MXene nanocomposite for mercury adsorption. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, W.; Yang, P.; Li, Z.; Xia, B.; Li, M.; Xue, C.; Liu, D. One-pot synthesis of N-doped carbon intercalated molybdenum disulfide nanohybrid for enhanced adsorption of tetracycline from aqueous solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wen, T.; Bai, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, J.; Yang, L.; Xia, L.; Song, S. Adsorption toward Cu(II) and inhibitory effect on bacterial growth occurring on molybdenum disulfide montmorillonite hydrogel surface. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Park, C.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; An, B.; Yun, S.; Lee, S.; Choi, J. Removal of copper, nickel and chromium mixtures from metal plating wastewater by adsorption with modified carbon foam. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Wen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, H.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, Q. Antibacterial activity of the sediment of copper removal from wastewater by using mechanically activated calcium carbonate. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, D.; Soomro, R.; Fu, F.; Qiao, N.; Yu, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, B. Ceramic supported attapulgite-graphene oxide composite membrane for effificient removal of heavy metal contamination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, T.; Hsu, P.C.; Xie, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, K.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Tang, J.; Ye, Z.; et al. Direct/alternating current electrochemical method for removing and recovering heavy metal from water using graphene oxide electrode. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6431–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dou, Y.; Gao, C.; He, C.; Gao, J.; Zhao, S.; Deng, L. Removal of Cd(II) by modifified maifanite coated with Mg-layered double hydroxides in constructed rapid infifiltration systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.; Lin, S.; Nizeyimana, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X. Removal of copper ions from wastewater via adsorption on modified hematite (α-Fe2O3) iron oxide coated sand. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ji, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhan, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y. Preparation of PAMAM modified PVDF membrane and its adsorption performance for copper ions. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, Q.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L. Facile and low-cost fabrication of composite hydrogels to improve adsorption of copper ions. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, R.; Chang, J.; Juang, S.; Lee, D. Manganese ferrite modified agricultural waste-derived biochars for copper ions adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 367, 128303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KashifUddin, M. A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 438–462. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, G.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Zhong, W.; Wan, S. High-efficiency adsorption removal for Cu(II) and Ni(II) using a novel acylamino dihydroxamic acid chelating resin. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 160984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Hu, X. Formation, exfoliation and restacking of MoS2 nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 25, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, K.; Han, C. Morphological influence of molybdenum disulfide on the tribological properties of rapeseed oil. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 49, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, Y.; Yin, P.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; et al. Construction of a novel double network polymer composite and evaluation of its highly efficient adsorption properties for copper ions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 53007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, A.; Hamid, A.; Ghauri, M.; Nasrullah, A.; Iqbal, J.; Shah, N.; Rafiq, S.; Irfan, M.; Muhammad, N. Lignin/alginate/hydroxyapatite composite beads for the efficient removal of copper and nickel ions from aqueous solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 184, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Ruan, J.; Li, Q.; Tian, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Synthesis of polyacrylamide immobilized molybdenum disulfide (MoS2@PDA@PAM) composites via mussel-inspired chemistry and surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization for removal of copper (II) ions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 86, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, J. A coupling technology of capacitive deionization and MoS2/nitrogen-doped carbon spheres with abundant active sites for efficiently and selectively adsorbing low-concentration copper ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 564, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, E.; He, F.; Shi, C.; He, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, N. 2D sandwich-like carboncoated ultrathin TiO2@defect-rich MoS2 hybrid nanosheets: Synergistic-effectpromoted electrochemical performance for lithium ion batteries. Nano Energy 2016, 26, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Hu, X.; Sun, X. Morphological effect of MoS2 nanoparticles on catalytic oxidation and vacuum lubrication. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 2517–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, G.; Jia, J.; Zhan, H.; Wen, Z. Three-dimensional network architecture with hybrid nanocarbon composites supporting few-layer MoS2 for lithium and sodium storage. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1592–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Hamadi, A.; Foroutan, R.; Peighambardoust, S.; Ramavandi, B. Decontamination of Cd2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solution using a magnetic nanocomposite of eggshell/starch/Fe3O4. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 48, 102911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, J.; Castillo, X.; Jara, S.; Ortiz, C.; Navarro, P.; Cid, H.; Rioseco, H.; Barros, D.; Belzile, N. Adsorption of Cu2+ on coal fly ash modified with functionalized mesoporous silica. Fuel 2015, 156, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah-Hagan, E.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Arteca, G.A.; Pizarro, J.; Mercier, L.; Wei, O.; Belzile, N. Simple and energy-saving modifications of coal fly ash to remove simultaneously six toxic metal cations from mine effluents. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 6, 5498–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.; Rostom, M.; Farghaly, F.; Abdel Khalek, M. Bio-sorption for tannery efuent treatment using eggshell wastes; kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic study. Egypt. J. Pet. 2020, 29, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykova, Y.; Strömvall, A.; Steenari, B. Adsorption of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn on Sphagnum peat from solutions with low metal concentrations. J. Hazard Mater. 2008, 152, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, M.; Lee, T.; Lin, Y.; Hsu, S.; Wang, M.; Li, P.; Huang, P.; Lu, W.; Ho, J. On the removal efciency of copper ions in wastewater using calcined waste eggshells as natural adsorbents. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Shao, T.; Zhao, X.; Peng, H.; Gong, Y.; Wan, H. Enhanced copper adsorption by DTPA-chitosan/alginate composite beads: Mechanism and application in simulated electroplating wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, J.; Su, Z.; Huang, Y.; Dong, X. Highly effective removal of Cu(II) by a novel 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane functionalized polyethyleneimine/sodium alginate porous membrane adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; You, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Lv, Y. Fabrication of ultrathin MoS2 nanosheets and application on adsorption of organic pollutants and heavy metals. Processes 2020, 8, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yu, Z.; Islam, S.; Shi, K.; Cheng, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zhao, J.; Sun, G.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; et al. Remarkable Acid Stability of Polypyrrole-MoS4: A Highly Selective and Efficient Scavenger of Heavy Metals Over a Wide pH Range. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.; Bikiaris, D.; Seredych, M.; Bandosz, T.; Deliyanni, E. Removal of dorzolamide from biomedical wastewaters with adsorption onto graphite oxide/poly (acrylic acid) grafted chitosan nanocomposite. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthik, R.; Meenakshi, S. Synthesis, characterization and Cr (VI) uptake study of polyaniline coated chitin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Lou, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, X. A review of functionalized carbon nanotubes and graphene for heavy metal adsorption from water: Preparation, application, and mechanism. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm Model | Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoS2 | K (L/mg) | Qm (mg/g) | R2 | n | KF | R2 |
| S-MoS2 | 0.0913 | 136.98 | 0.9842 | 1.99 | 14.39 | 0.9100 |
| L-MoS2 | 0.0442 | 136.79 | 0.9695 | 1.93 | 12.11 | 0.9307 |
| Adsorbent | Qm (mg/g) | Experimental Conditions | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Temperature (°C) | |||
| MoS2 nanosheets | 169.5 | 6 | 25 | [51] |
| MoS2@2DMMT | 65.75 | 5 | 30 | [21] |
| Polypyrrole-MoS4 | 111 | 3 | room temperature | [52] |
| MoS2@PDA@PAM | 50.57 | 7 | 25 | [38] |
| Spherical MoS2 | 136.98 | 5 | 25 | This work |
| Lamellar MoS2 | 136.79 | 5 | 25 | This work |
| MoS2 | T (°C) | ΔG (kJ/mol) | ΔS (J·K/mol) | ΔH (kJ/mol) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-MoS2 | 20 | −1.01 | 96.592 | 27.529 | 0.881 |
| - | 40 | −2.24 | - | - | - |
| - | 60 | −4.148 | - | - | - |
| - | 80 | −8.248 | - | - | - |
| - | 100 | −7.601 | - | - | - |
| S-MoS2 | 20 | −2.605 | 90.041 | 24.203 | 0.884 |
| - | 40 | −3.155 | - | - | - |
| - | 60 | −5.561 | - | - | - |
| - | 80 | −8.900 | - | - | - |
| - | 100 | −8.742 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.-Z.; Shi, Y.-J.; Hu, K.-H. Preparation of Molybdenum Disulfide with Different Nanostructures and Its Adsorption Performance for Copper (Ⅱ) Ion in Water. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071194
Yao Y-Z, Shi Y-J, Hu K-H. Preparation of Molybdenum Disulfide with Different Nanostructures and Its Adsorption Performance for Copper (Ⅱ) Ion in Water. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(7):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071194
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, You-Zhi, Yong-Jie Shi, and Kun-Hong Hu. 2023. "Preparation of Molybdenum Disulfide with Different Nanostructures and Its Adsorption Performance for Copper (Ⅱ) Ion in Water" Nanomaterials 13, no. 7: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071194
APA StyleYao, Y. -Z., Shi, Y. -J., & Hu, K. -H. (2023). Preparation of Molybdenum Disulfide with Different Nanostructures and Its Adsorption Performance for Copper (Ⅱ) Ion in Water. Nanomaterials, 13(7), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071194







