Self-Assembly of Silver Nanowire Films for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
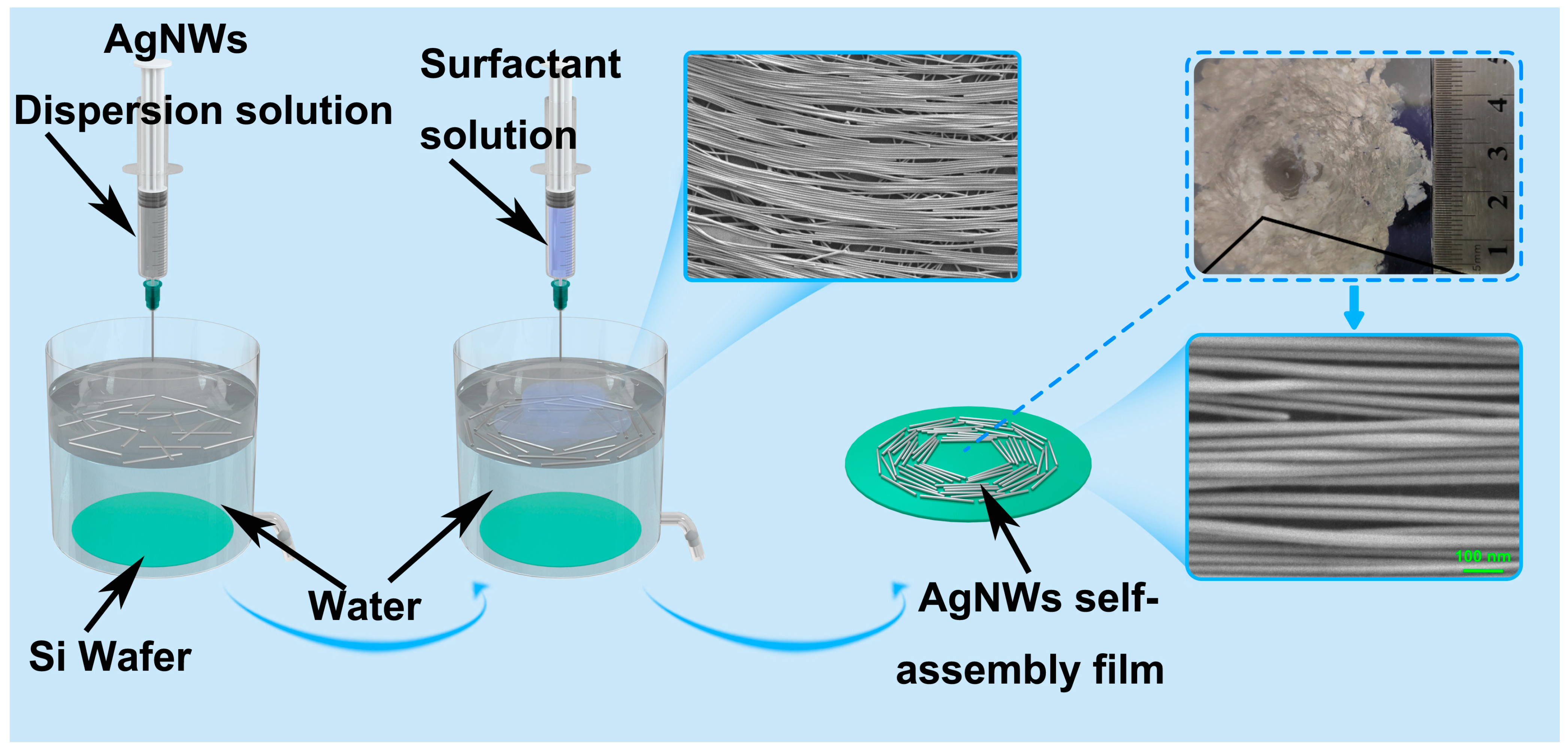
2.1. Self-Assembly of AgNWs Films
2.2. Morphology Characterization
2.3. Raman Spectroscopy Measurement
2.4. Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
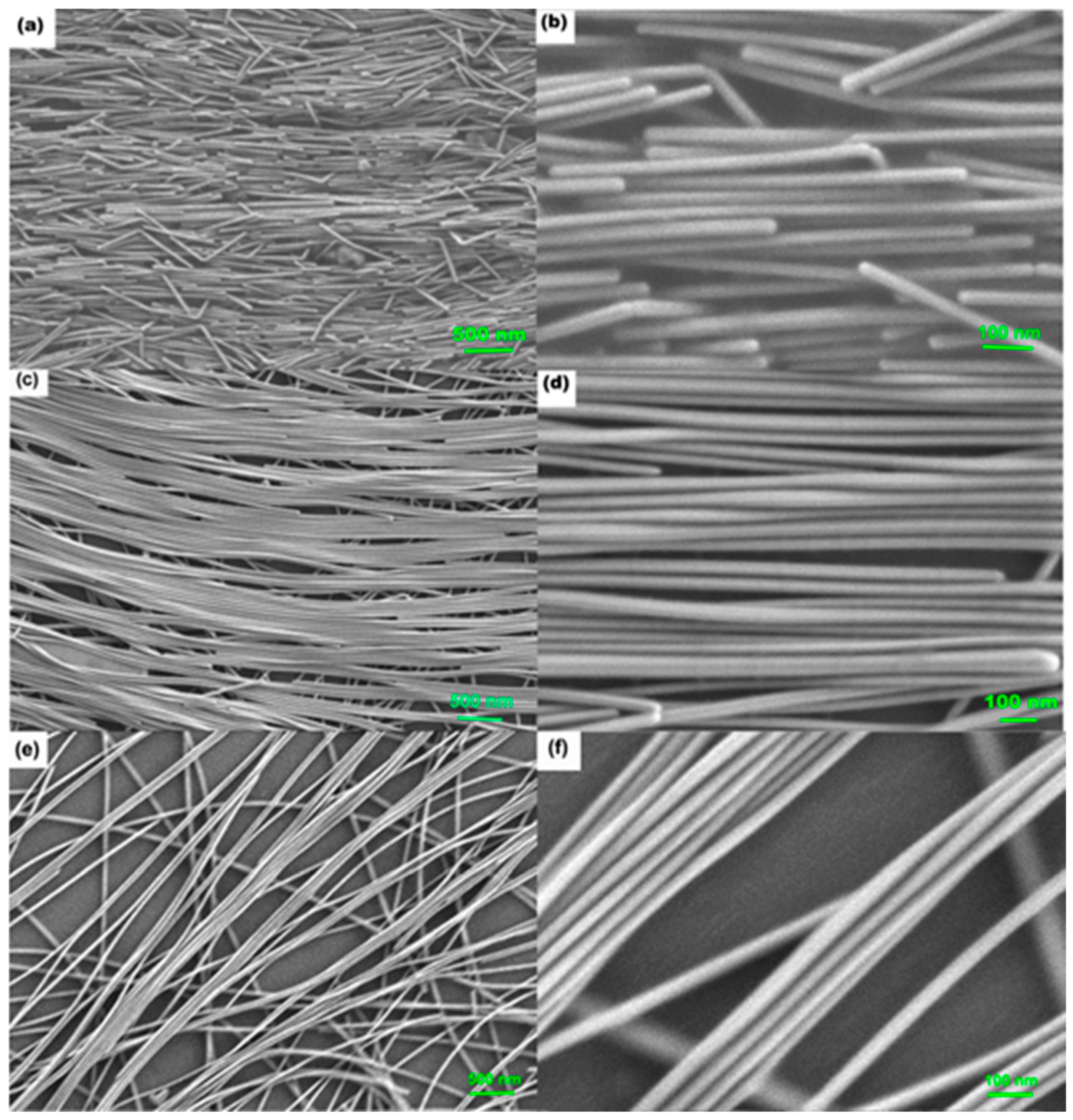
3.1. The Optimal AgNW Concentration to Obtain Aligned AgNW Self-Assembly Films
3.2. Determining the Reproducibility of Prepared Substrates
3.3. Hot-Spot Characterization and Enhancement Mechanism of AgNW Substrate
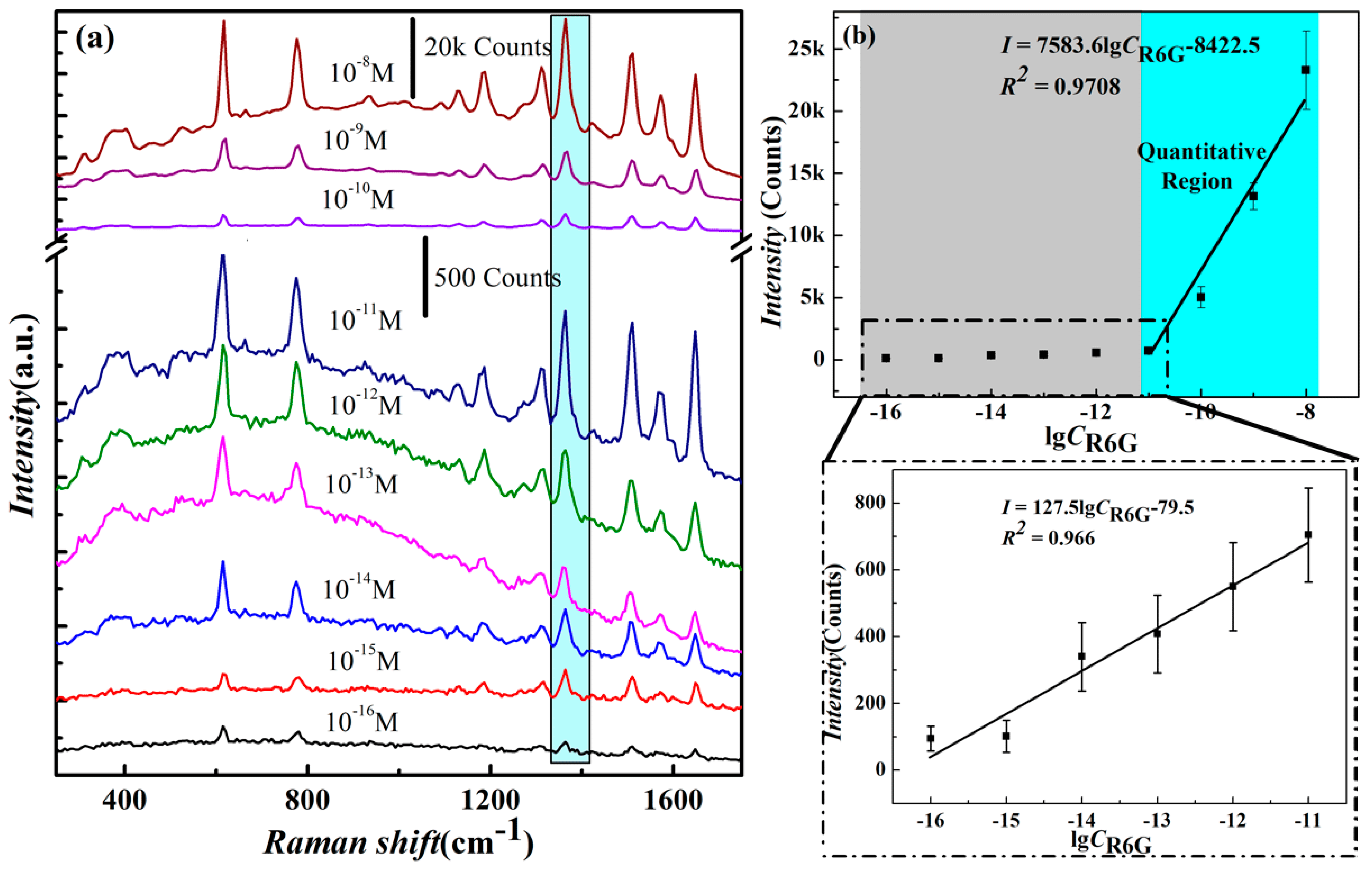
3.4. Determining Detection Limit and Linear Detection Range
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, W.; Xia, L.; Hu, Y.; Li, G. Recent progress on three-dimensional substrates for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic analysis. Microchem. J. 2022, 172, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Thomas, M.R.; Bergholt, M.S.; Pence, I.J.; Seong, H.; Charchar, P.; Todorova, N.; Nagelkerke, A.; Belessiotis-Richards, A.; Payne, D.J. Surface enhanced Raman scattering artificial nose for high dimensionality fingerprinting. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granger, J.H.; Schlotter, N.E.; Crawford, A.C.; Porter, M.D. Prospects for point-of-care pathogen diagnostics using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3865–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.S.; Jones, S.; Pramanik, A.; Ray, P.C. Nanoarchitecture based SERS for biomolecular fingerprinting and label-free disease markers diagnosis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2725–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhou, R.; Takei, K.; Hong, M. Toward flexible surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) sensors for point-of-care diagnostics. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. In Situ SERS monitoring of the plasmon-driven catalytic reaction by using single Ag@ Au nanowires as substrates. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 11736–11744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Yang, J.; Su, R.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, G. Recent progress in fast sample preparation techniques. Anal. Chem. 2019, 92, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneipp, K.; Moskovits, M.; Kneipp, H. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering: Physics and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 103. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, J.; Jimenez de Aberasturi, D.; Aizpurua, J.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Auguié, B.; Baumberg, J.J.; Bazan, G.C.; Bell, S.E.; Boisen, A.; Brolo, A.G. Present and future of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Acs. Nano. 2019, 14, 28–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nam, J.-M.; Oh, J.-W.; Lee, H.; Suh, Y.D. Plasmonic Nanogap-Enhanced Raman Scattering with Nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, J.E.; Afonso, M.A.; Dos Santos, D.P.; Mercadal, P.A.; Coronado, E.A.; Poppi, R.J. Colloidal gold clusters formation and chemometrics for direct SERS determination of bioanalytes in complex media. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 224, 117380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strehle, K.R.; Cialla, D.; Rösch, P.; Henkel, T.; Köhler, M.; Popp, J. A reproducible surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy approach. Online SERS measurements in a segmented microfluidic system. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1542–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zou, Y.; Song, Z.; Jin, S. Highly reproducible SERS sensor based on self-assembled Au nanocubic monolayer film for sensitive and quantitative detection of glutathione. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 540, 148381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, L.; Xiao, D.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Cao, D.; Shi, Z.; Cui, Z.; Lu, N. A silver nanoislands on silica spheres platform: Enriching trace amounts of analytes for ultrasensitive and reproducible SERS detection. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 16749–16754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Wang, J.; Du, L. Highly sensitive and reproducible SERS substrates based on ordered micropyramid array and silver nanoparticles. Acs. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 29222–29229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippa, M.; Sagnelli, D.; Vestri, A.; Marchesano, V.; Munari, B.; Carnicelli, D.; Varrone, E.; Brigotti, M.; Tozzoli, R.; Montalbano, M. Plasmonic Metasurfaces for Specific SERS Detection of Shiga Toxins. Acs. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2022, 14, 4969–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Hu, H.; Chen, P.; Dong, F.; Huang, H.; Xu, L.; Yan, L.; Song, Z.; Xu, T.; Chu, W. Dielectric Walls/Layers Modulated 3D Periodically Structured SERS Chips: Design, Batch Fabrication, and Applications. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charconnet, M.; Korsa, M.T.; Petersen, S.; Plou, J.; Hanske, C.; Adam, J.; Seifert, A. Generalization of Self-Assembly Toward Differently Shaped Colloidal Nanoparticles for Plasmonic Superlattices. Small Methods 2023, 2201546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Meng, D.; Su, G.; Hu, P.; Song, B.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Yang, H.; Yuan, T.; Chen, B. Ultrafast Early Warning of Heart Attacks through Plasmon-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy using Collapsible Nanofingers and Machine Learning. Small 2023, 19, 2204719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggio, D.; Mirabile, A.; Lazzari, M. Sensing soluble molecules through SERS substrates in one-step procedure: Unrevealing the Meiji woodblock printing materials. Talanta 2023, 254, 124177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Mejia, E.; Nam, W.; Nie, M.; Wang, W.; Vikesland, P.; Zhou, W. Microporous Multiresonant Plasmonic Meshes by Hierarchical Micro–Nanoimprinting for Bio-Interfaced SERS Imaging and Nonlinear Nano-Optics. Small 2022, 18, 2106887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Xu, Y.; Bell, S.E. Self-assembly of colloidal nanoparticles into 2D arrays at water–Oil interfaces: Rational construction of stable SERS substrates with accessible enhancing surfaces and tailored plasmonic response. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 5937–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Gerislioglu, B.; Ahmadivand, A.; Kaushik, A.; Cheng, G.J.; Ouyang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yadav, V.S.; Mishra, Y.K.; Wu, Y. Controlled self-assembly of plasmon-based photonic nanocrystals for high performance photonic technologies. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Shin, K.; Jang, A.-R.; Seo, M.-K.; Hong, W.-K.; Sohn, J.I. Highly sensitive multiplex-detection of surface-enhanced Raman scattering via self-assembly arrays of porous AuAg nanoparticles with built-in nanogaps. J. Alloy Compd. 2021, 888, 161504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Managò, S.; Quero, G.; Zito, G.; Tullii, G.; Galeotti, F.; Pisco, M.; De Luca, A.C.; Cusano, A. Tailoring lab-on-fiber SERS optrodes towards biological targets of different sizes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 339, 129321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisco, M.; Galeotti, F.; Grisci, G.; Quero, G.; Cusano, A. Self-assembled periodic patterns on the optical fiber tip by microsphere arrays. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Optical Fibre Sensors, Curitiba, Brazil, 28 September 2015; Volume 9634, pp. 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Zheng, C.; Yin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Luo, D.; Liu, Y.J. Hierarchically ordered silicon metastructures from improved self-assembly-based nanosphere lithography. Acs. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 12345–12352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Jin, X.; Zhou, M.; Ma, K.; Duan, P.; Yu, Z.-Q. Amplifying the excited state chirality through self-assembly and subsequent enhancement via plasmonic silver nanowires. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 19760–19767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Ahn, H.S.; Ha, D.H.; Yi, S.N. Enhancing SERS Intensity by Coupling PSPR and LSPR in a Crater Structure with Ag Nanowires. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Tian, D.; Ke, P.; Yang, X.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Hu, C.; Ji, H. Assembly of long silver nanowires into highly aligned structure to achieve uniform “Hot Spots” for Surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 273, 121030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wei, Q.; Lieber, C.M. Directed assembly of one-dimensional nanostructures into functional networks. Science 2001, 291, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Ge, D.; Calderon-Ortiz, G.A.; Exarhos, A.L.; Bretz, C.; Alsayed, A.; Kurz, D.; Kikkawa, J.; Dreyfus, R.; Yang, S. Highly conductive and transparent coatings from flow-aligned silver nanowires with large electrical and optical anisotropy. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 6438–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Duan, S.; Zhao, H. Advances in constructing silver nanowire-based conductive pathways for flexible and stretchable electronics. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 11484–11511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, S.; Pullithadathil, B. Unidirectional Langmuir–Blodgett-mediated alignment of polyaniline-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes for NH3 gas sensor applications. Langmuir 2020, 36, 11618–11628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Jr, O.N.; Caseli, L.; Ariga, K. The past and the future of Langmuir and Langmuir–Blodgett films. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 6459–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Fan, Z.; Pan, L. MOF-derived AuNS/LDH with high adsorption ability for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1224, 340201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.-Q.; Zheng, Y.; Qu, W.-G.; Yu, H.-Q.; Xu, A.-W. Hydrophobic Teflon films as concentrators for single-molecule SERS detection. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20986–20990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamplecoskie, K.G.; Scaiano, J.C.; Tiwari, V.S.; Anis, H. Optimal size of silver nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, Z.; Ye, Q.; He, J.; Nie, X.; He, G.; Song, C.; Shang, W.; Wu, J.; Tao, P.; et al. Substrateless Welding of Self-Assembled Silver Nanowires at Air/Water Interface. Acs Appl Mater Inter 2016, 8, 20483–20490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; You, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, H.; Shi, D.; Chen, H.; Shen, Z. Individual Ag nanowire dimer for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Plasmonics 2011, 6, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hao, J.; Zhu, L.; Yao, Y.; Meng, X.; Weimer, W.; Wang, Q.K. Direct two-phase interfacial self-assembly of aligned silver nanowire films for surface enhanced Raman scattering applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 13496–13501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-W.; Wang, J.-L.; Huang, W.-R.; Yu, L.; Ren, X.-F.; Wen, W.-C.; Yu, S.-H. Ordering Ag nanowire arrays by a glass capillary: A portable, reusable and durable SERS substrate. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Su, Q.; Yin, X.; Huang, Z.; Lin, X.; Lin, W.; Yi, G. Au-Nanoparticle-Array/Aligned-Ag-Nanowire-Based Flexible Dual Plasmonic Substrate for Sensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Detection. Part Part Syst. Char. 2021, 38, 2100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Lv, K.-P.; Huang, H.-T.; Cong, H.-P.; Yu, S.-H. Co-assembly of Au nanorods with Ag nanowires within polymer nanofiber matrix for enhanced SERS property by electrospinning. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5348–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| SERS Substrate Structure | Detection Limit | EF | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ordered AgNWs | 5 × 10−6 M R6G | 6.6 × 105 | [41] |
| Ordered AgNWs | 5 × 10−9 MR6G | [42] | |
| Aligned AgNWs | 10−10 M MG 1 | 4 × 103 | [43] |
| Aligned AgNWs | 10−10 M R6G | 104 | [30] |
| AuNR–AgNW nanocomposite 2 | 10−4 M DTTCI 3 | [44] | |
| Aligned AgNWs | 10−16 M R6G | 6 × 1011 | Our work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, Y.; Jin, M. Self-Assembly of Silver Nanowire Films for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13081358
Pang Y, Jin M. Self-Assembly of Silver Nanowire Films for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Applications. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(8):1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13081358
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Yanzhao, and Mingliang Jin. 2023. "Self-Assembly of Silver Nanowire Films for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Applications" Nanomaterials 13, no. 8: 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13081358
APA StylePang, Y., & Jin, M. (2023). Self-Assembly of Silver Nanowire Films for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Applications. Nanomaterials, 13(8), 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13081358




