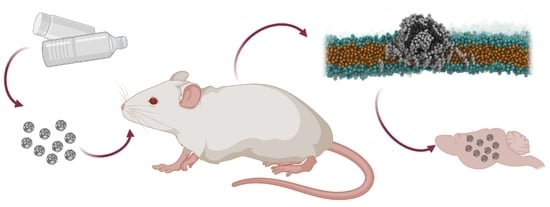
Micro- and Nanoplastics Breach the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB): Biomolecular Corona’s Role Revealed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Material Characterization and Stability
2.3. In Vivo Experiments
2.4. Fluorescent Microscopy Analysis
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Kooi, M.; Diepens, N.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Lifetime Accumulation of Microplastic in Children and Adults. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5084–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and Quantification of Plastic Particle Pollution in Human Blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First Evidence of Microplastics in Human Placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, E.S.; Stadlbauer, V.; Pichler, V.; Resch-Fauster, K.; Todorovic, A.; Meisel, T.C.; Trawoeger, S.; Hollóczki, O.; Turner, S.D.; Wadsak, W.; et al. To Waste or Not to Waste: Questioning Potential Health Risks of Micro- and Nanoplastics with a Focus on Their Ingestion and Potential Carcinogenicity. Expo. Health 2023, 15, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigault, J.; ter Halle, A.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current Opinion: What Is a Nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.; Belz, S.; Hoeveler, A.; Hugas, M.; Okuda, H.; Patri, A.; Rauscher, H.; Silva, P.; Slikker, W.; Sokull-Kluettgen, B.; et al. Regulatory Landscape of Nanotechnology and Nanoplastics from a Global Perspective. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 122, 104885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, J.; Taladriz-Blanco, P.; Lehner, R.; Lubskyy, A.; Ortuso, R.D.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Petri-Fink, A. The Micro-, Submicron-, and Nanoplastic Hunt: A Review of Detection Methods for Plastic Particles. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vethaak, A.D.; Legler, J. Microplastics and Human Health. Science 2021, 371, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, S.; Dass, M.; Musyanovych, A.; Landfester, K.; Mailänder, V. Polymeric Nanoparticles of Different Sizes Overcome the Cell Membrane Barrier. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foged, C.; Brodin, B.; Frokjaer, S.; Sundblad, A. Particle size and surface charge affect particle uptake by human dendritic cells in an in vitro model. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 298, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga, L.S.; Bertini, F.; Stahl, P.D. Fusion of Newly Formed Phagosomes with Endosomes in Intact Cells and in a Cell-Free System. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 6511–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, S.; Tian, F.; Stoeger, T.; Kreyling, W.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Grazú, V.; Borm, P.; Estrada, G.; Ntziachristos, V.; Razansky, D. Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Diagnostics, Drug Delivery and Targeted Treatment across Blood-Brain Barrier: Perspectives on Tracking and Neuroimaging. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuenauer, R.; Müller, S.K.; Römer, W. Pathways of Protein and Lipid Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis in Drug Delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler-Behnke, M.; Kreyling, W.G.; Lipka, J.; Fertsch, S.; Wenk, A.; Takenaka, S.; Schmid, G.; Brandau, W. Biodistribution of 1.4- and 18-Nm Gold Particles in Rats. Small 2008, 4, 2108–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinotti, C.; Ruiz-Perez, L.; Deplazes, E.; Mancera, R.L. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Small Molecules Interacting with Biological Membranes. ChemPhysChem 2020, 21, 1486–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Monticelli, L. Modeling the Effect of Nano-Sized Polymer Particles on the Properties of Lipid Membranes. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 503101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochicchio, D.; Panizon, E.; Monticelli, L.; Rossi, G. Interaction of Hydrophobic Polymers with Model Lipid Bilayers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollóczki, O.; Gehrke, S. Can Nanoplastics Alter Cell Membranes? ChemPhysChem 2020, 21, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Barnoud, J.; Monticelli, L. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Perturb Lipid Membranes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, J.B.; Baulin, V.A. Microplastics Destabilize Lipid Membranes by Mechanical Stretching. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2104610118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thake, T.H.F.; Webb, J.R.; Nash, A.; Rappoport, J.Z.; Notman, R. Permeation of Polystyrene Nanoparticles across Model Lipid Bilayer Membranes. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 10265–10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, S.; Ghosh, S.; McDougall, D.R.; Whitten, A.E.; Mata, J.P.; Köper, I.; McGillivray, D.J. Structure of Soft and Hard Protein Corona around Polystyrene Nanoplastics—Particle Size and Protein Types. Biointerphases 2020, 15, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczyk, D.; Bombelli, F.B.; Monopoli, M.P.; Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. What the Cell “Sees” in Bionanoscience. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5761–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Du, Q.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, Y.; Peng, J. Protein-Coated Microplastics Corona Complex: An Underestimated Risk of Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 157948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Yu, X.; Shao, S.; Li, T.; Xu, S.; Wu, L. Aging of Nanoplastics Significantly Affects Protein Corona Composition Thus Enhancing Macrophage Uptake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 3206–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.; Martins, M.; Costa, M.H.; Costa, P.M. Development of a Method for the Detection of Polystyrene Microplastics in Paraffin-Embedded Histological Sections. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 149, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, T.S.; Kirshner, D.A.; Lau, E.Y.; Wong, S.E.; Nilmeier, J.P.; Lightstone, F.C. A Method to Predict Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability of Drug-Like Compounds Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollóczki, O. Evidence for Protein Misfolding in the Presence of Nanoplastics. Int. J. Quantum. Chem. 2021, 121, e26372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.; Andrade, R.; Birgin, E.G.; Martínez, J.M. PACKMOL: A Package for Building Initial Configurations for Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.M.; Martínez, L. Packing Optimization for Automated Generation of Complex System’s Initial Configurations for Molecular Dynamics and Docking. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrink, S.J.; Risselada, H.J.; Yefimov, S.; Tieleman, D.P.; de Vries, A.H. The MARTINI Force Field: Coarse Grained Model for Biomolecular Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 7812–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatkulov, S.; Fyta, M.; Netz, R.R. Force Fields for Divalent Cations Based on Single-Ion and Ion-Pair Properties. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 024505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; van der Spoel, D. GROMACS 3.0: A Package for Molecular Simulation and Trajectory Analysis. J. Mol. Model. 2001, 7, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, Flexible, and Free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, S.; Páll, S.; Schulz, R.; Larsson, P.; Bjelkmar, P.; Apostolov, R.; Shirts, M.R.; Smith, J.C.; Kasson, P.M.; van der Spoel, D.; et al. GROMACS 4.5: A High-Throughput and Highly Parallel Open Source Molecular Simulation Toolkit. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindah, E. Gromacs: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kästner, J. Umbrella Sampling. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2011, 1, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souaille, M.; Roux, B. Extension to the Weighted Histogram Analysis Method: Combining Umbrella Sampling with Free Energy Calculations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2001, 135, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, P.M.; Saranya, V.; Vijayakumar, S.; Mythili Meera, M.; Ruprekha, S.; Kunal, R.; Pranay, A.; Thomas, J.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Assessment on Interactive Prospectives of Nanoplastics with Plasma Proteins and the Toxicological Impacts of Virgin, Coronated and Environmentally Released-Nanoplastics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollóczki, O.; Gehrke, S. Nanoplastics Can Change the Secondary Structure of Proteins. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, T.; Würth, C.; Laux, E.M.; Hoffmann, K.; Resch-Genger, U. Simple Strategies towards Bright Polymer Particles via One-Step Staining Procedures. Dye. Pigment. 2012, 94, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Acedo, A.; García-Recio, E.; Illescas-Montes, R.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J. Evidence from in Vitro and in Vivo Studies on the Potential Health Repercussions of Micro- and Nanoplastics. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüst, M.; Meijer, J.; Westerink, R.H.S. The Plastic Brain: Neurotoxicity of Micro- and Nanoplastics. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, S.; Baun, A.; Hartmann, N.B. Ingestion of Micro- and Nanoplastics in Daphnia Magna—Quantification of Body Burdens and Assessment of Feeding Rates and Reproduction. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, T.; Zhao, X. Polystyrene Nanoplastics Penetrate across the Blood-Brain Barrier and Induce Activation of Microglia in the Brain of Mice. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sökmen, T.Ö.; Sulukan, E.; Türkoğlu, M.; Baran, A.; Özkaraca, M.; Ceyhun, S.B. Polystyrene Nanoplastics (20 Nm) Are Able to Bioaccumulate and Cause Oxidative DNA Damages in the Brain Tissue of Zebrafish Embryo (Danio Rerio). Neurotoxicology 2020, 77, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Particles | ζ-Potential (mV) | Average Size (nm) | PDI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.14 ± 0.03 µm | H2O (0.55 µS) | −67.81 | 1206 | 0.01031 |
| PBS | −45.89 | 1259 | 0.07191 | |
| RPMI-1640 (fs) | −14.03 | 1419 | 0.05526 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopatz, V.; Wen, K.; Kovács, T.; Keimowitz, A.S.; Pichler, V.; Widder, J.; Vethaak, A.D.; Hollóczki, O.; Kenner, L. Micro- and Nanoplastics Breach the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB): Biomolecular Corona’s Role Revealed. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13081404
Kopatz V, Wen K, Kovács T, Keimowitz AS, Pichler V, Widder J, Vethaak AD, Hollóczki O, Kenner L. Micro- and Nanoplastics Breach the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB): Biomolecular Corona’s Role Revealed. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(8):1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13081404
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopatz, Verena, Kevin Wen, Tibor Kovács, Alison S. Keimowitz, Verena Pichler, Joachim Widder, A. Dick Vethaak, Oldamur Hollóczki, and Lukas Kenner. 2023. "Micro- and Nanoplastics Breach the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB): Biomolecular Corona’s Role Revealed" Nanomaterials 13, no. 8: 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13081404
APA StyleKopatz, V., Wen, K., Kovács, T., Keimowitz, A. S., Pichler, V., Widder, J., Vethaak, A. D., Hollóczki, O., & Kenner, L. (2023). Micro- and Nanoplastics Breach the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB): Biomolecular Corona’s Role Revealed. Nanomaterials, 13(8), 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13081404