Toxicity of Silver–Chitosan Nanocomposites to Aquatic Microcrustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus and Naturally Luminescent Bacteria Vibrio fischeri
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Ag-Chitosan Nanocomposites
2.2. Hydrodynamic Size, ξ-Potential and Stability Measurements
2.3. Solubility/Dissolution
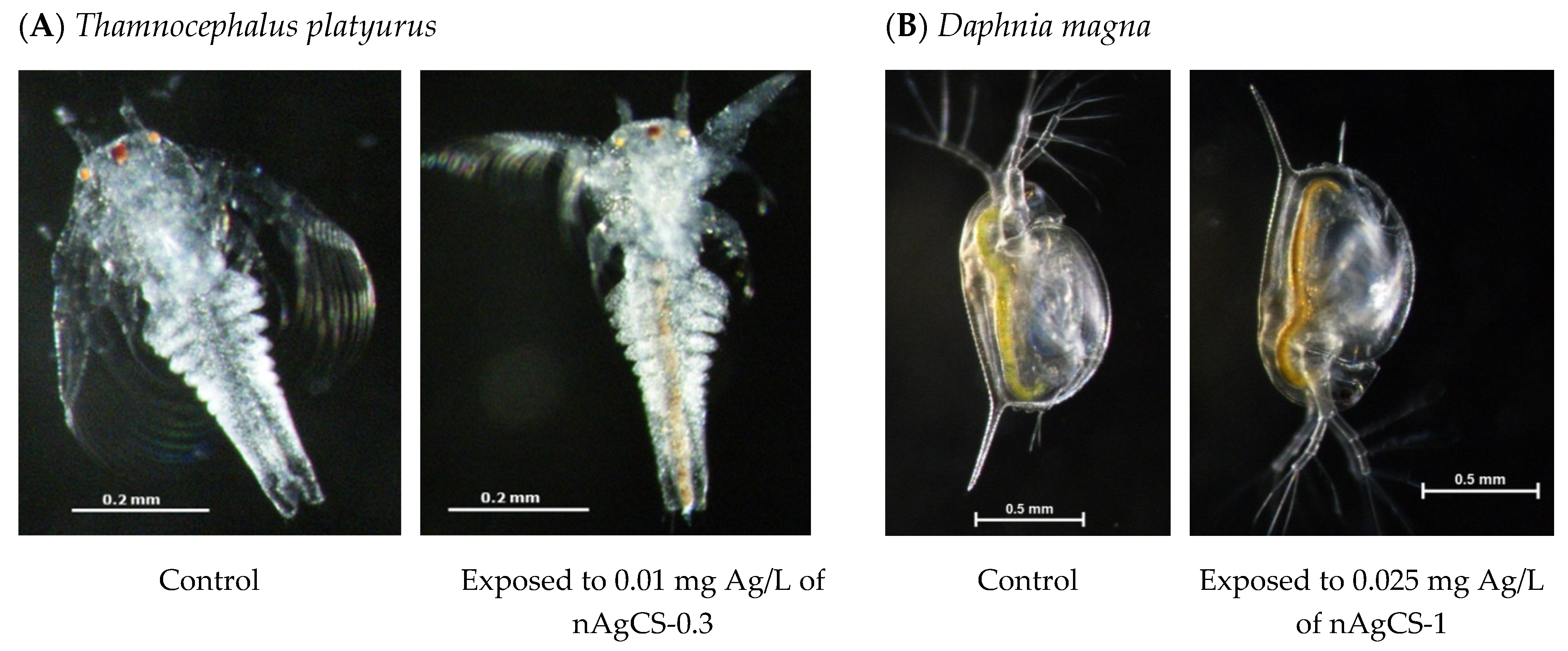
2.4. Toxicity Tests with Aquatic Microcrustaceans
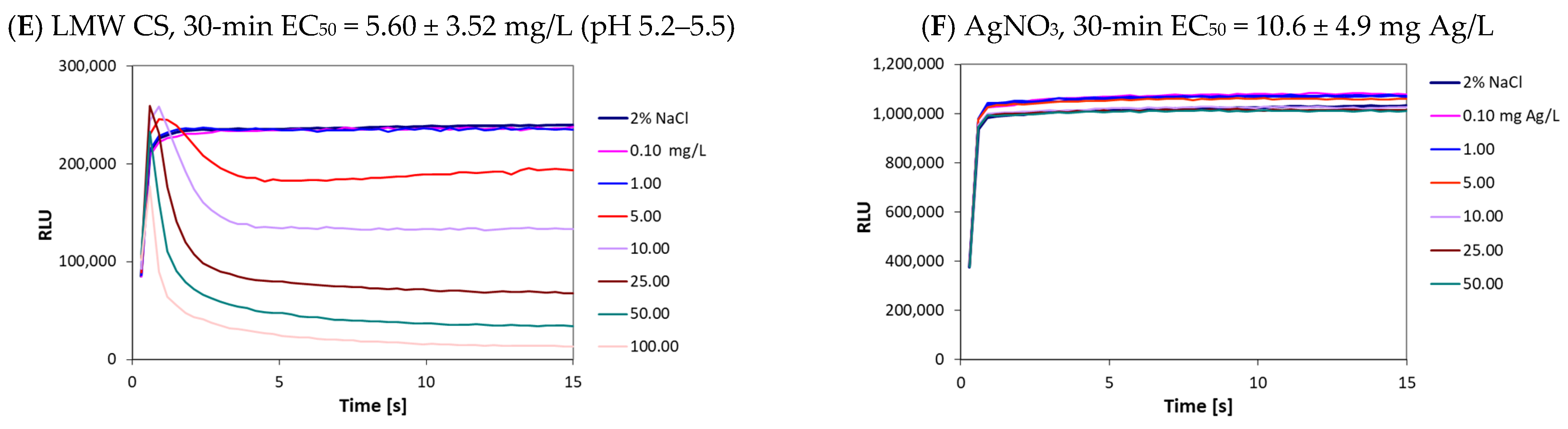
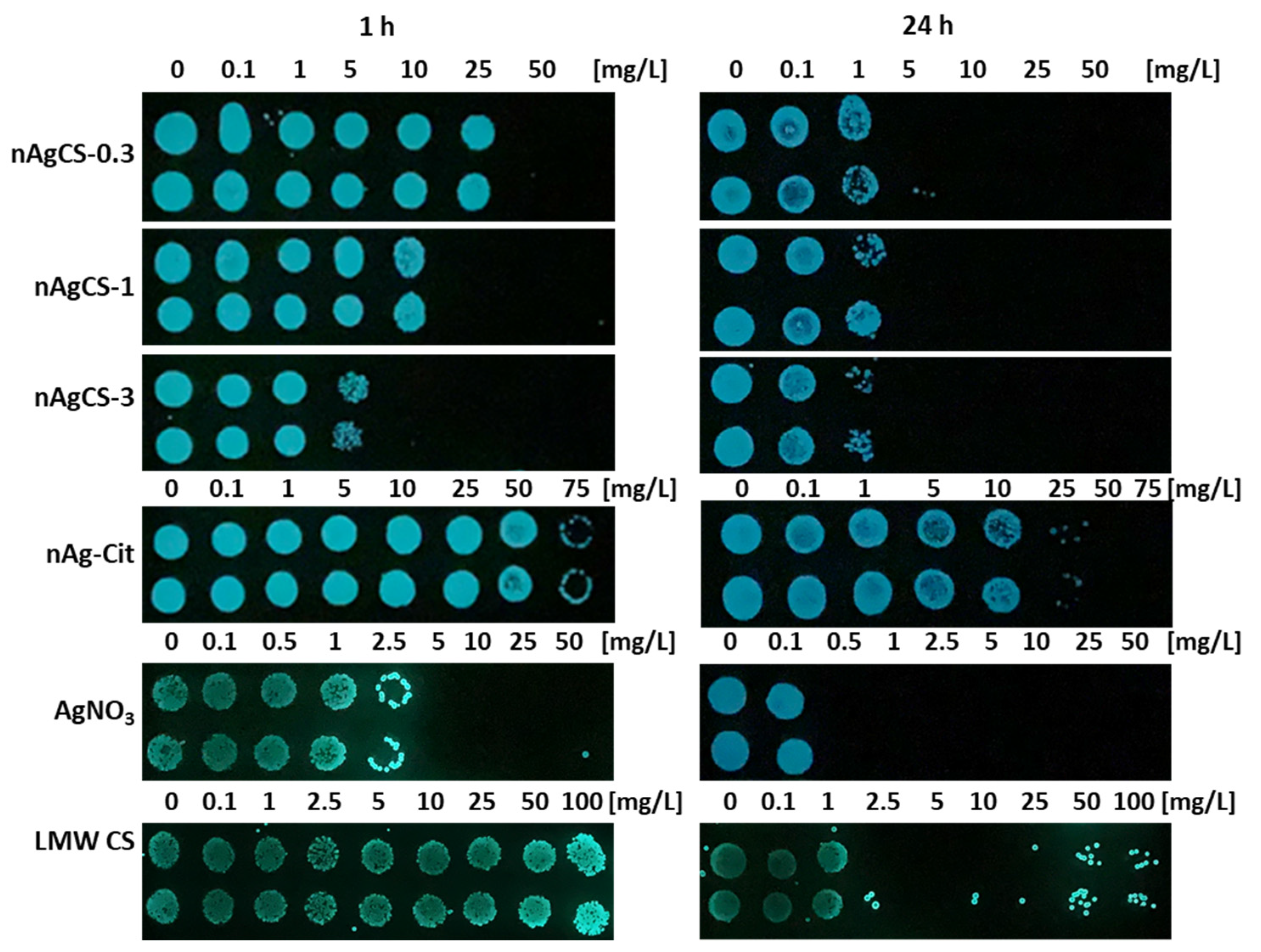
2.5. Bioluminescent Inhibition Tests with Bacteria Vibrio fischeri
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Studied Nanomaterials
3.2. Toxicity of Studied Compounds to Bacteria Vibrio fischeri
3.3. Ecotoxicity Evaluation of Studied Compounds to Aquatic Microcrustaceans
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Juganson, K.; Ivask, A.; Blinova, I.; Mortimer, M.; Kahru, A. NanoE-Tox: New and in-Depth Database Concerning Ecotoxicity of Nanomaterials. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1788–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarenko, O.; Juganson, K.; Ivask, A.; Kasemets, K.; Mortimer, M.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of Ag, CuO and ZnO Nanoparticles to Selected Environmentally Relevant Test Organisms and Mammalian Cells in Vitro: A Critical Review. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1181–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. EC Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 Concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH), Establishing a European Chemicals Agency, Amending Directive 1999/45/EC and Repealing Council Regulation (EEC) No 793/93 and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 as Well as Council Directive 76/769/EEC and Commission Directives 91/155/EEC, 93/67/EEC, 93/105/EC and 2000/21/EC.; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ECHA CHEM European Chemicals Agency Chemicals Database. 2024. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.028.301 (accessed on 6 May 2024).
- Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V.M.; Zoroddu, M.A. Medical Uses of Silver: History, Myths, and Scientific Evidence. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5923–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Gao, M.; Yun, Y.; Malmsten, M.; Rotello, V.M.; Zboril, R.; Akhavan, O.; Kraskouski, A.; Amalraj, J.; Cai, X.; et al. Antibacterial Nanomaterials: Mechanisms, Impacts on Antimicrobial Resistance and Design Principles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202217345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver Nanoparticles as a New Generation of Antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danish Nanodatabase. The Nanodatabase, Developed by the DTU Environment, the Danish Ecological Council and Danish Consumer Council. 2024. Available online: https://nanodb.dk/en/ (accessed on 6 May 2024).
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. A Functional Chitosan-Based Hydrogel as a Wound Dressing and Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of Wound Healing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7533–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abourehab, M.A.S.; Pramanik, S.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Abualsoud, B.M.; Kadi, A.; Ansari, M.J.; Deepak, A. Recent Advances of Chitosan Formulations in Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thambiliyagodage, C.; Jayanetti, M.; Mendis, A.; Ekanayake, G.; Liyanaarachchi, H.; Vigneswaran, S. Recent Advances in Chitosan-Based Applications—A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Chitosan-Based Materials: Preparation, Modification and Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14380:2011; Water Quality—Determination of the Acute Toxicity to Thamnocephalus Platyurus (Crustacea, Anostraca). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- OECD. Test No. 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test. Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development; OECD: Paris, France, 2004; ISBN 9789264069947. [Google Scholar]
- MicroBioTests. Crustacean Toxicity Screening Test for Freshwater. Thamnotoxkit F—Thamnocephalus Toxicity Test; MicroBioTests: Gent, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 21338:2010; Water Quality—Kinetic Determination of the Inhibitory Effects of Sediment, Other Solids and Coloured Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio Fischeri (Kinetic Luminescent Bacteria Test). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Suppi, S.; Kasemets, K.; Ivask, A.; Künnis-Beres, K.; Sihtmäe, M.; Kurvet, I.; Aruoja, V.; Kahru, A. A Novel Method for Comparison of Biocidal Properties of Nanomaterials to Bacteria, Yeasts and Algae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindimian, E. REGTOX Macro Excel. Ver. 2020; Microsoft: Redmond, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sihtmäe, M.; Laanoja, J.; Otsus, M.; Vija, H.; Kahru, A.; Kasemets, K. Do Silver-Chitosan Nanocomposites Promote Bacterial Resistance to Silver or Common Antibiotics? bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Marambio-Jones, C.; Peng, F.; Huang, X.; Damoiseaux, R.; Hoek, E.M.V. High-Throughput Screening of Silver Nanoparticle Stability and Bacterial Inactivation in Aquatic Media: Influence of Specific Ions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7321–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvern Instruments Limited. Zeta Potential—An Introduction in 30 Minutes. Technical Note. 2015. Available online: https://www.research.colostate.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/ZetaPotential-Introduction-in-30min-Malvern.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2024).
- Müller, R.H.; Jacobs, C. Buparvaquone Mucoadhesive Nanosuspension: Preparation, Optimisation and Long-Term Stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 237, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvamani, V. Stability Studies on Nanomaterials Used in Drugs. In Characterization and Biology of Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 425–444. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanczyk, H.; Ast, J.C.; Higgins, M.J.; Carson, J.; Dunlap, P.V. Reclassification of Vibrio fischeri, Vibrio logei, Vibrio salmonicida and Vibrio wodanis as Aliivibrio fischeri Gen. Nov., Comb. Nov., Aliivibrio logei Comb. Nov., Aliivibrio salmonicida Comb. Nov. and Aliivibrio wodanis Comb. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2823–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.L.E.; Devillers, J. (Eds.) Ecotoxicity of Chemicals to Photobacterium Phosphoreum; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 1994; ISBN 9781315094694. [Google Scholar]
- Bulich, A.A. A Practical and Reliable Method for Monitoring the Toxicity of Aquatic Samples. Process Biochem. 1982, 17, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Parvez, S.; Venkataraman, C.; Mukherji, S. A Review on Advantages of Implementing Luminescence Inhibition Test (Vibrio fischeri) for Acute Toxicity Prediction of Chemicals. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, M.T.D.; Schultz, T.W. Validation of Vibrio fisheri Acute Toxicity Data: Mechanism of Action-Based QSARs for Non-Polar Narcotics and Polar Narcotic Phenols. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 204, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, M.; Kasemets, K.; Heinlaan, M.; Kurvet, I.; Kahru, A. High Throughput Kinetic Vibrio fischeri Bioluminescence Inhibition Assay for Study of Toxic Effects of Nanoparticles. Toxicol. In Vitro 2008, 22, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domard, A. PH and c.d. Measurements on a Fully Deacetylated Chitosan: Application to CuII—Polymer Interactions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1987, 9, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-M.; Mi, F.-L.; Horng, J.-L.; Lin, L.-Y.; Tsai, M.-L.; Liu, C.-L.; Lu, K.-Y.; Chu, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Lee, Y.-L.A.; et al. Characterization and Toxicology Evaluation of Low Molecular Weight Chitosan on Zebrafish. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-Y.; Tsai, M.-H.; Ryan, D.K.; Pancorbo, O.C. Toxicity of the 13 Priority Pollutant Metals to Vibrio fisheri in the Microtox® Chronic Toxicity Test. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 320, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinova, I.; Niskanen, J.; Kajankari, P.; Kanarbik, L.; Käkinen, A.; Tenhu, H.; Penttinen, O.-P.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of Two Types of Silver Nanoparticles to Aquatic Crustaceans Daphnia Magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 3456–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. ECOTOXicology Knowledgebase; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2024.
- Erickson, R.J.; Brooke, L.T.; Kahl, M.D.; Venter, F.V.; Harting, S.L.; Markee, T.P.; Spehar, R.L. Effects of Laboratory Test Conditions on the Toxicity of Silver to Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, N.R.; Shaw, J.; Glover, C.; Hogstrand, C. Derivation of a Toxicity-Based Model to Predict How Water Chemistry Influences Silver Toxicity to Invertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 133, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karen, D.J.; Ownby, D.R.; Forsythe, B.L.; Bills, T.P.; La Point, T.W.; Cobb, G.B.; Klaine, S.J. Influence of Water Quality on Silver Toxicity to Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), Fathead Minnows (Pimephales promelas), and Water Fleas (Daphnia magna). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D. Ecology, Epidemiology, and Evolution of Parasitism in Daphnia; National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2005; ISBN 1932811060.
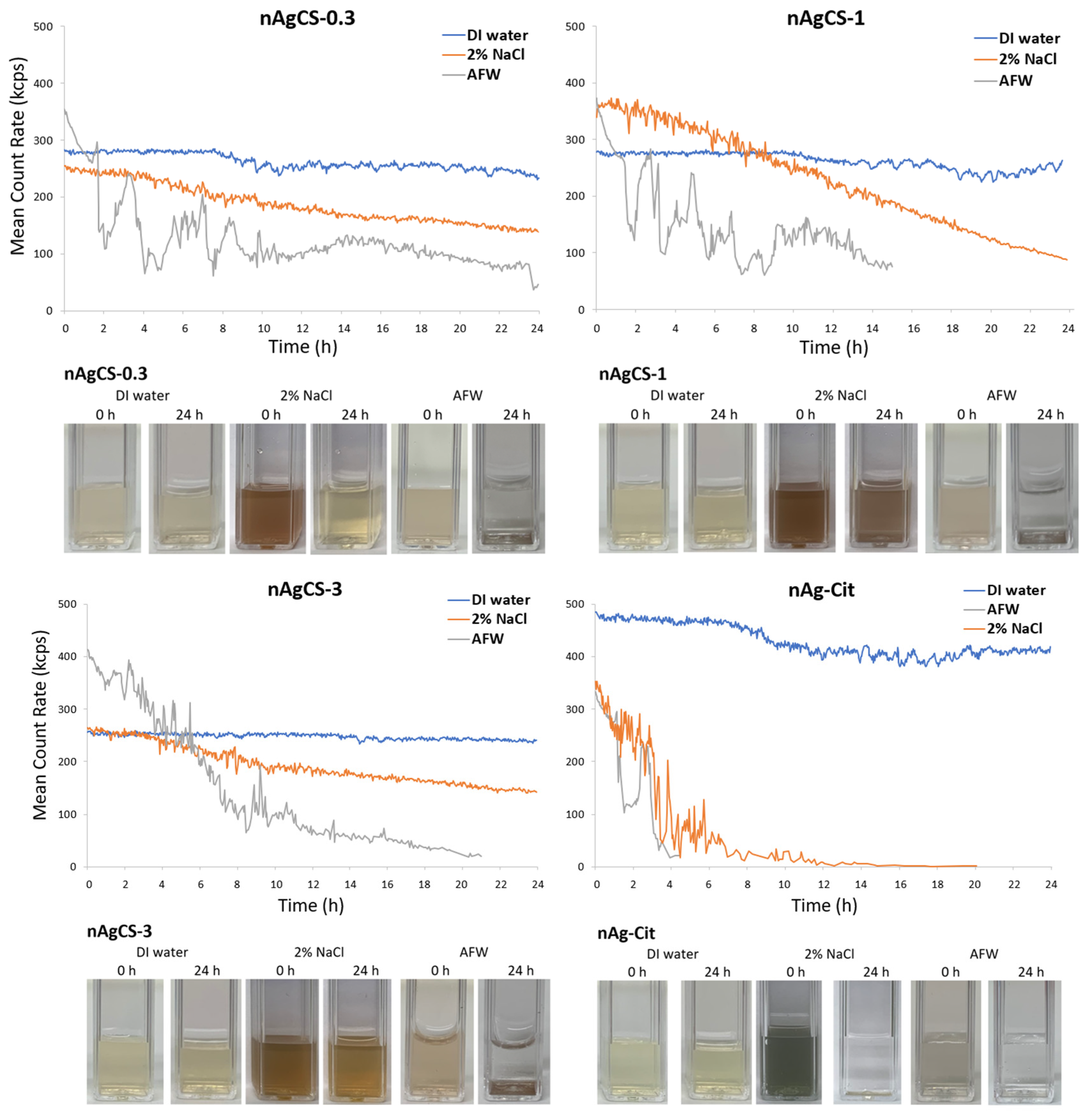

| Tested Compounds | Ag:CS Weight Ratio | Primary Size a [nm] | ζ-Potential [mV] | Hydrodynamic Diameter Dhyd b [nm] and (PDI) c | Solubility d, µg Ag/L (%) e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DI water | 2% NaCl | AFW | 1-h 2% NaCl | 24-h AFW | 48-h AFW | ||||
| nAgCS-0.3 | 1:0.3 | ~50 | +15.8 | 102 ± 8 (0.22) | 113 ± 1 (0.29) | >1000 | 32.4 ± 6.6 (3.2%) | 10.1 ± 1.0 (1.0%) | 8.9 ± 1.5 (0.9%) |
| nAgCS-1 | 1:1 | ~50 | +21.8 | 91.8 ± 9.6 (0.32) | 92.2 ± 1.2 (0.27) | >1000 | 16.0 ± 2.9 (1.6%) | 5.6 ± 0.3 (0.6%) | 4.9 ± 0.5 (0.5%) |
| nAgCS-3 | 1:3 | ~50 | +26.4 | 78.8 ± 7.3 (0.45) | 110 ± 1 (0.29) | >1000 | 35.5 ± 13.7 (3.6%) | 5.6 ± 0.4 (0.6%) | 5.5 ± 0.3 (0.6%) |
| nAg-Cit | 1:0 | ~50 | −36.1 | 36.9 ± 3.9 (0.48) | 248 ± 20 (0.30) | >1000 | 20.3 ± 3.7 (2.0%) | 16.7 ± 0.5 (1.7%) | 15.5 ± 0.3 (1.6%) |
| Aquatic Microcrustaceans | Bacteria | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Species: | Daphnia magna | Thamnocephalus platyurus | Vibrio fischeri | ||
| Tested Compounds | 48-h EC50 | 24-h LC50 | 30-min EC50 | 1-h MBC | 24-h MBC |
| nAgCS-0.3 | 0.050 ± 0.01 (0.065) | 0.191 ± 0.02 (0.248) | 25.6 ± 13.19 (33.3) | 50 (65) | 5 (6.5) |
| nAgCS-1 | 0.055 ± 0.02 (0.110) | 0.224 ± 0.02 (0.448) | 9.00 ± 4.62 (18.0) | 25 (50) | 5 (10) |
| nAgCS-3 | 0.058 ± 0.01 (0.232) | 0.261 ± 0.02 (1.044) | 3.20 ± 2.00 (12.8) | 10 (40) | 5 (20) |
| nAg-Cit | 0.118 ± 0.02 (0.568) | 0.112 ± 0.01 (0.539) | >75 (>360) | >75 (360) | 50 (240) |
| AgNO3 | 0.001 ± 0.0005 (0.002) | 0.003 ± 0.0007 (0.005) | 10.6 ± 4.9 (16.8) | 5 (7.94) | 0.5 (0.79) |
| LMW CS | ~12 * | ~12 ** | 5.60 ± 3.52 | >100 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sihtmäe, M.; Laanoja, J.; Blinova, I.; Kahru, A.; Kasemets, K. Toxicity of Silver–Chitosan Nanocomposites to Aquatic Microcrustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus and Naturally Luminescent Bacteria Vibrio fischeri. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141193
Sihtmäe M, Laanoja J, Blinova I, Kahru A, Kasemets K. Toxicity of Silver–Chitosan Nanocomposites to Aquatic Microcrustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus and Naturally Luminescent Bacteria Vibrio fischeri. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(14):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141193
Chicago/Turabian StyleSihtmäe, Mariliis, Jüri Laanoja, Irina Blinova, Anne Kahru, and Kaja Kasemets. 2024. "Toxicity of Silver–Chitosan Nanocomposites to Aquatic Microcrustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus and Naturally Luminescent Bacteria Vibrio fischeri" Nanomaterials 14, no. 14: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141193
APA StyleSihtmäe, M., Laanoja, J., Blinova, I., Kahru, A., & Kasemets, K. (2024). Toxicity of Silver–Chitosan Nanocomposites to Aquatic Microcrustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus and Naturally Luminescent Bacteria Vibrio fischeri. Nanomaterials, 14(14), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141193








