Cytotoxic Potencies of Zinc Oxide Nanoforms in A549 and J774 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ZnO Nanoforms
2.2. Physicochemical Characteristics
2.3. Nanoparticle Solutions for Dosing Cells
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Exposure of Cells to ZnO NPs
2.6. Cytotoxicity Analysis
2.7. Oxidative Stress Analysis
2.8. Multiplexed Protein Array Analysis
2.9. Endotoxin Analysis
2.10. Statistical and Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of the ZNO NPs
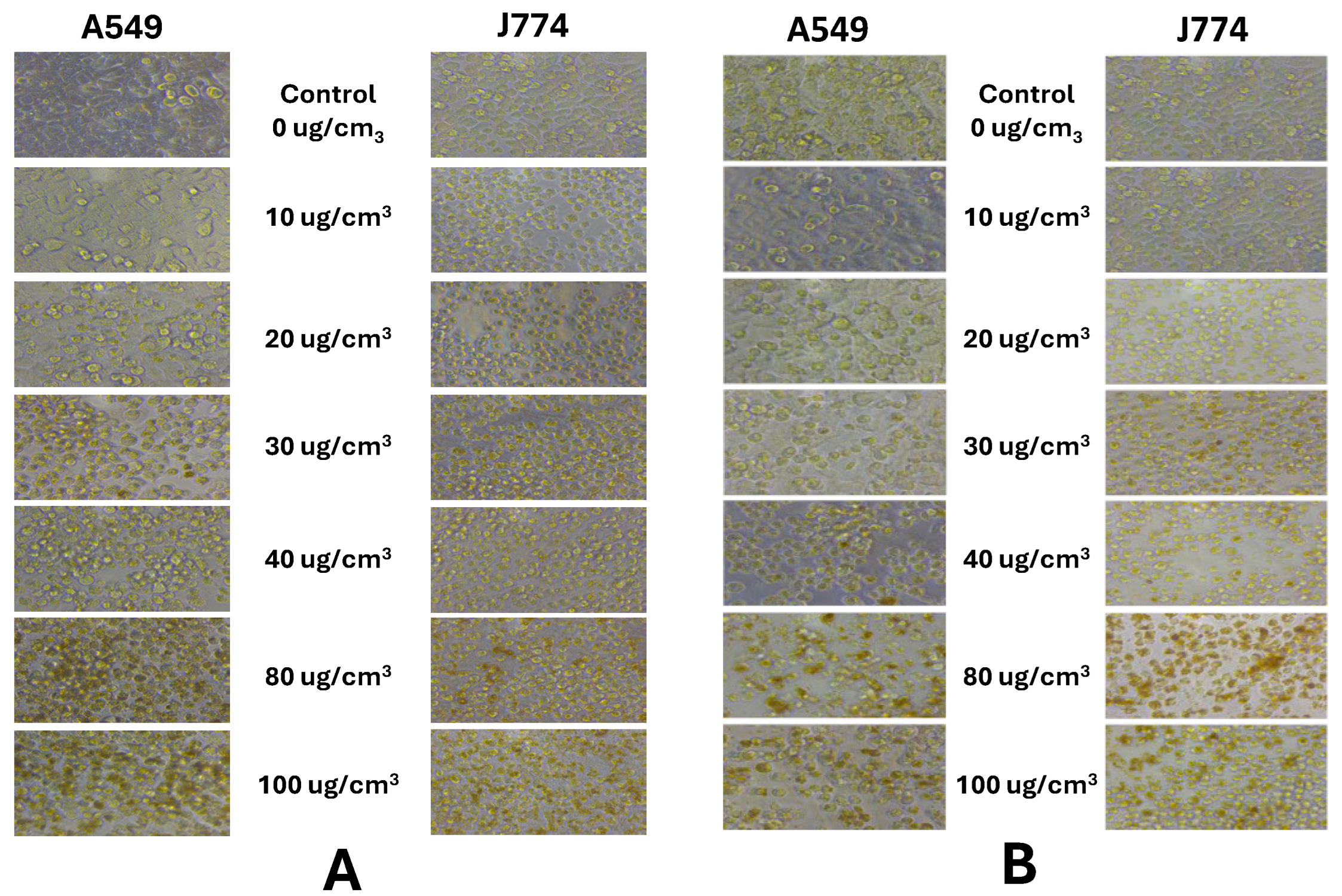
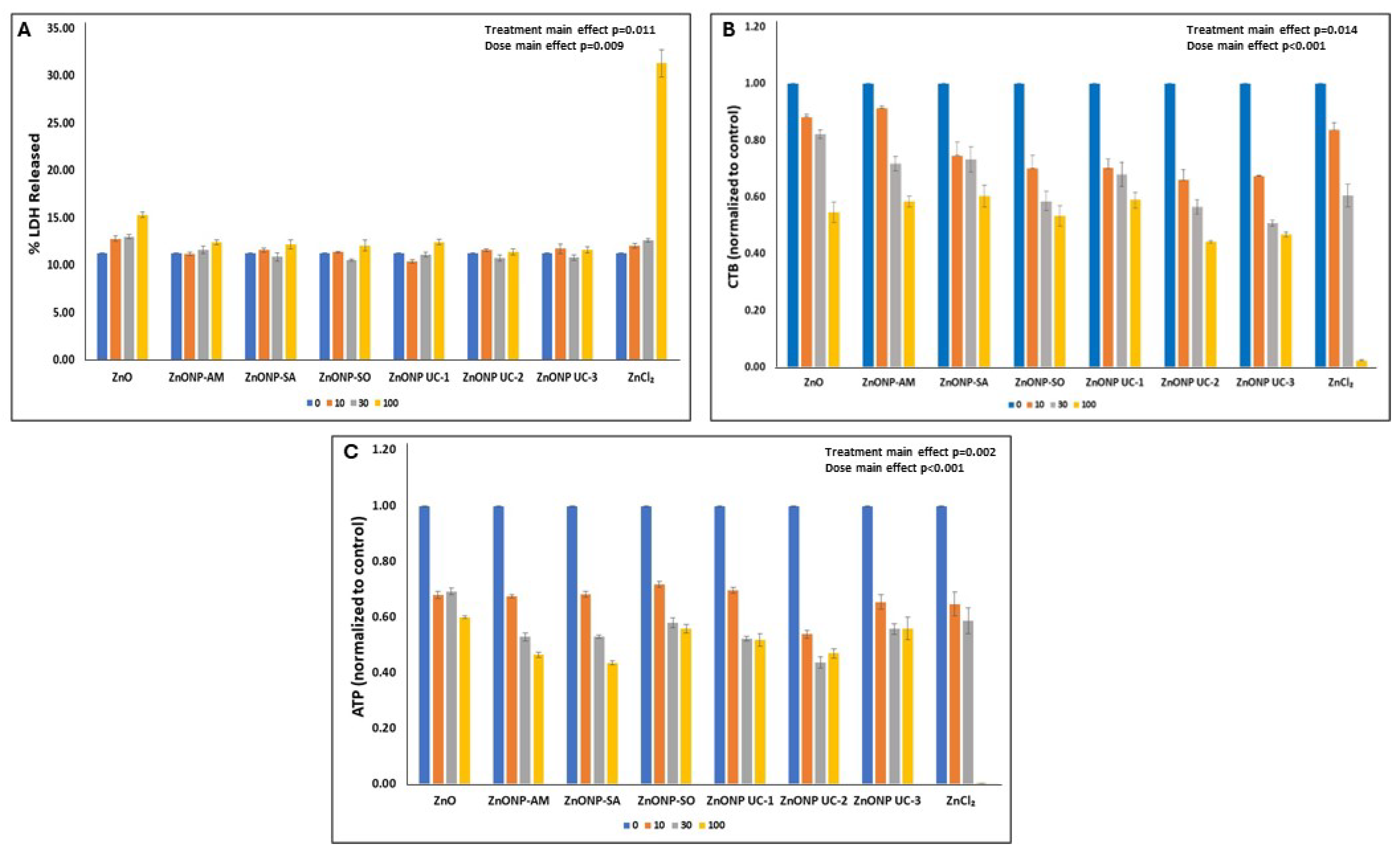
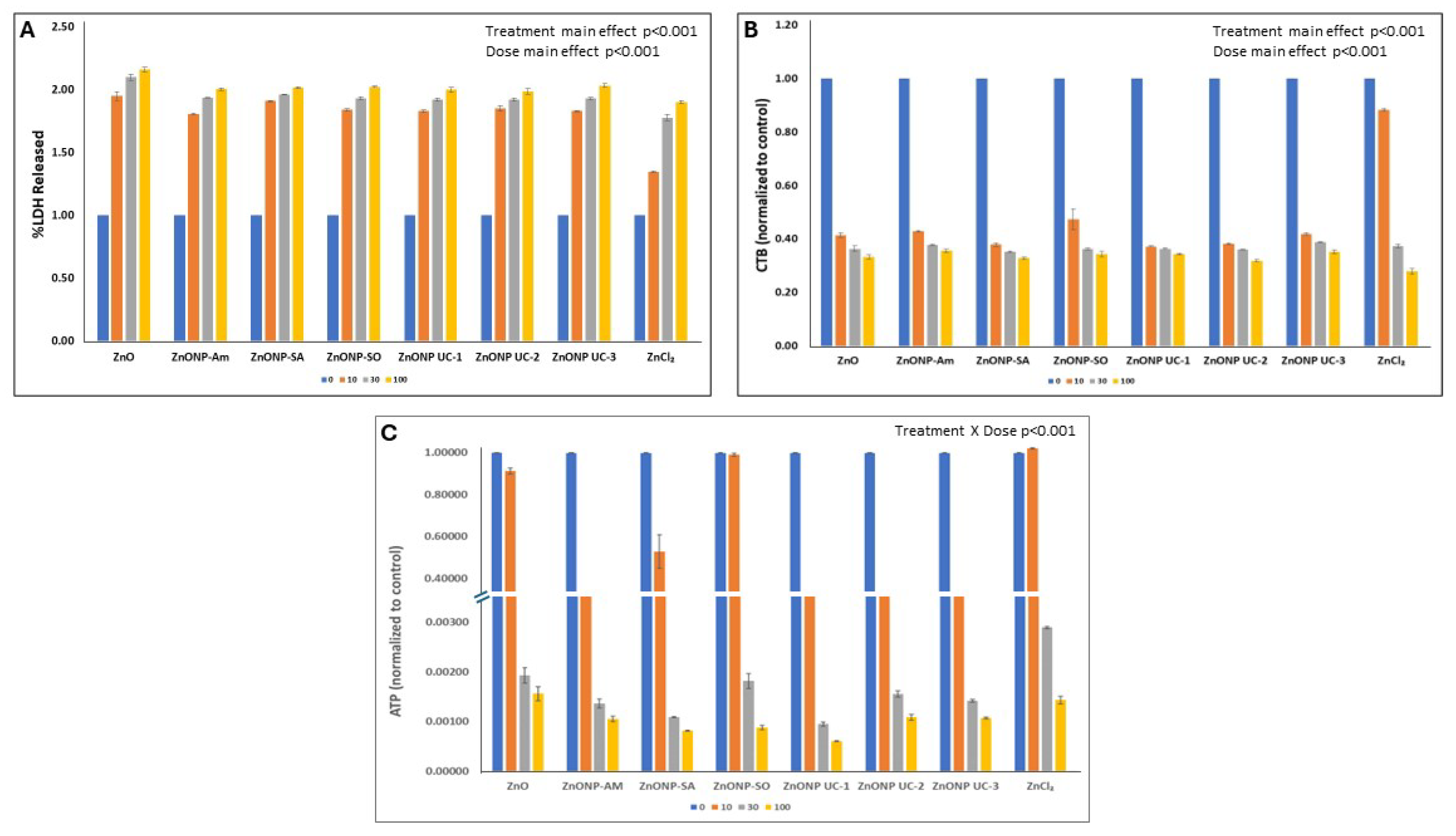
3.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Particles
3.3. Correlation Results for Physicochemical Properties of NPs vs. Corresponding Potency Estimates
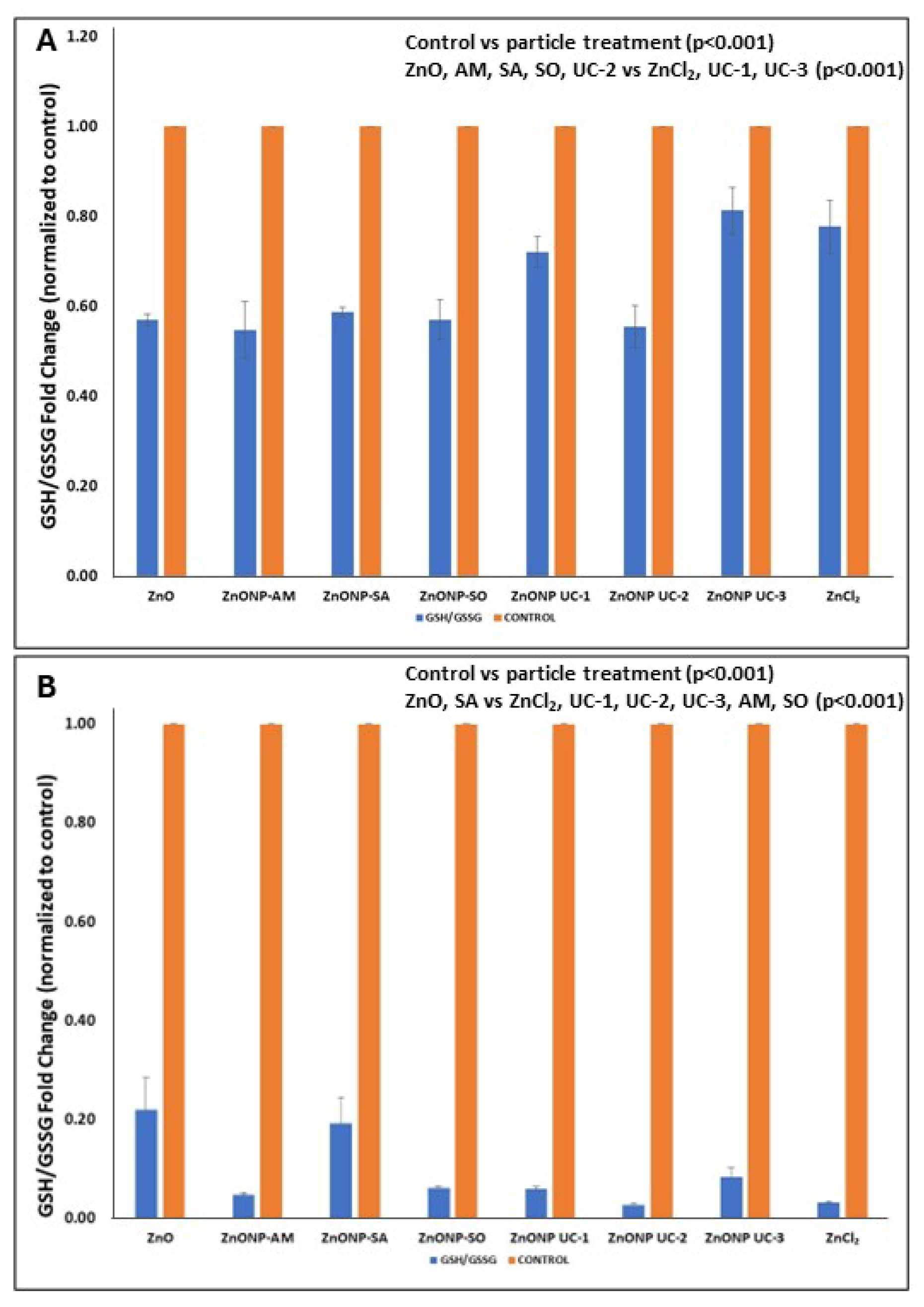
3.4. Cellular Oxidative Stress
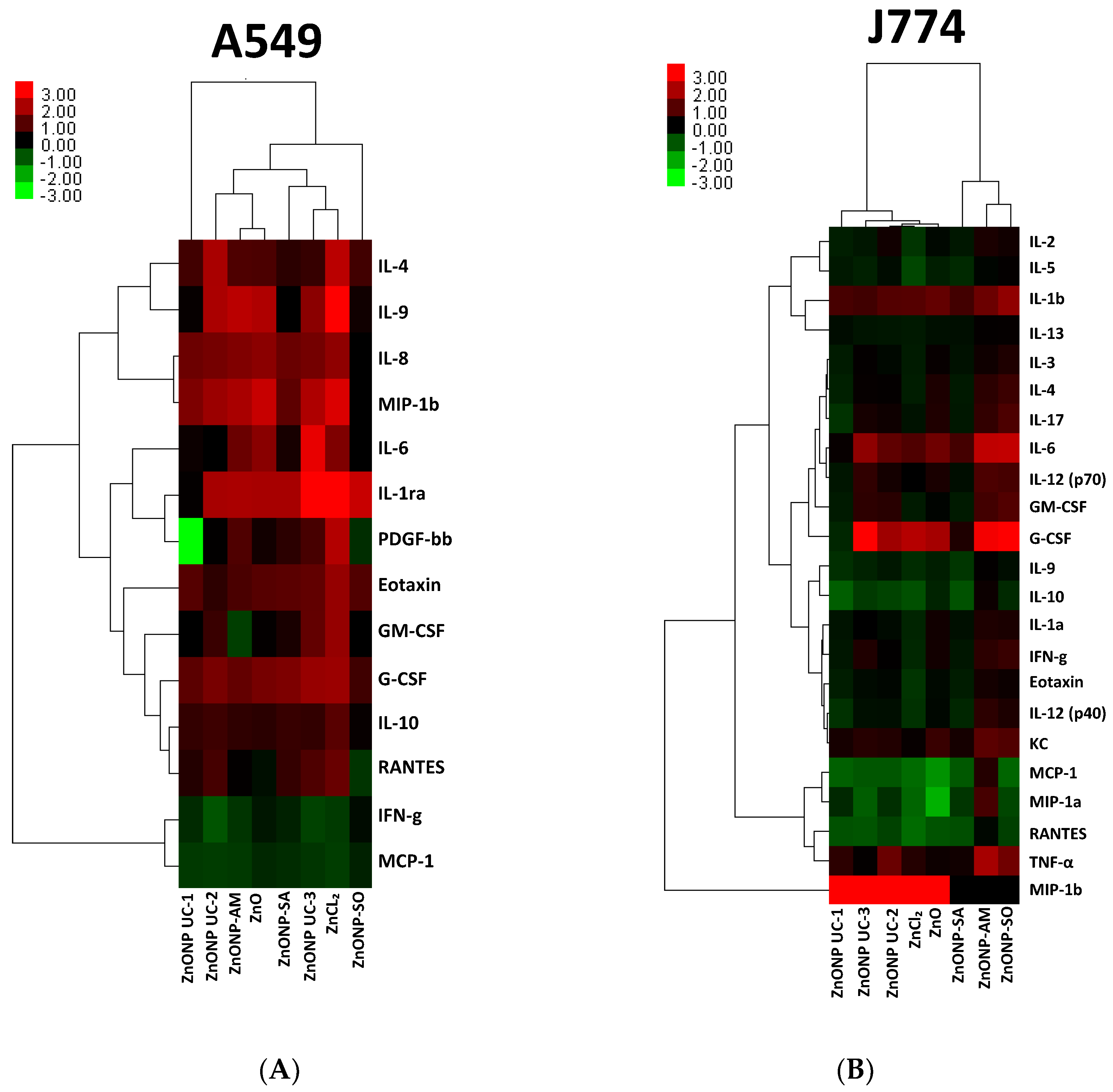
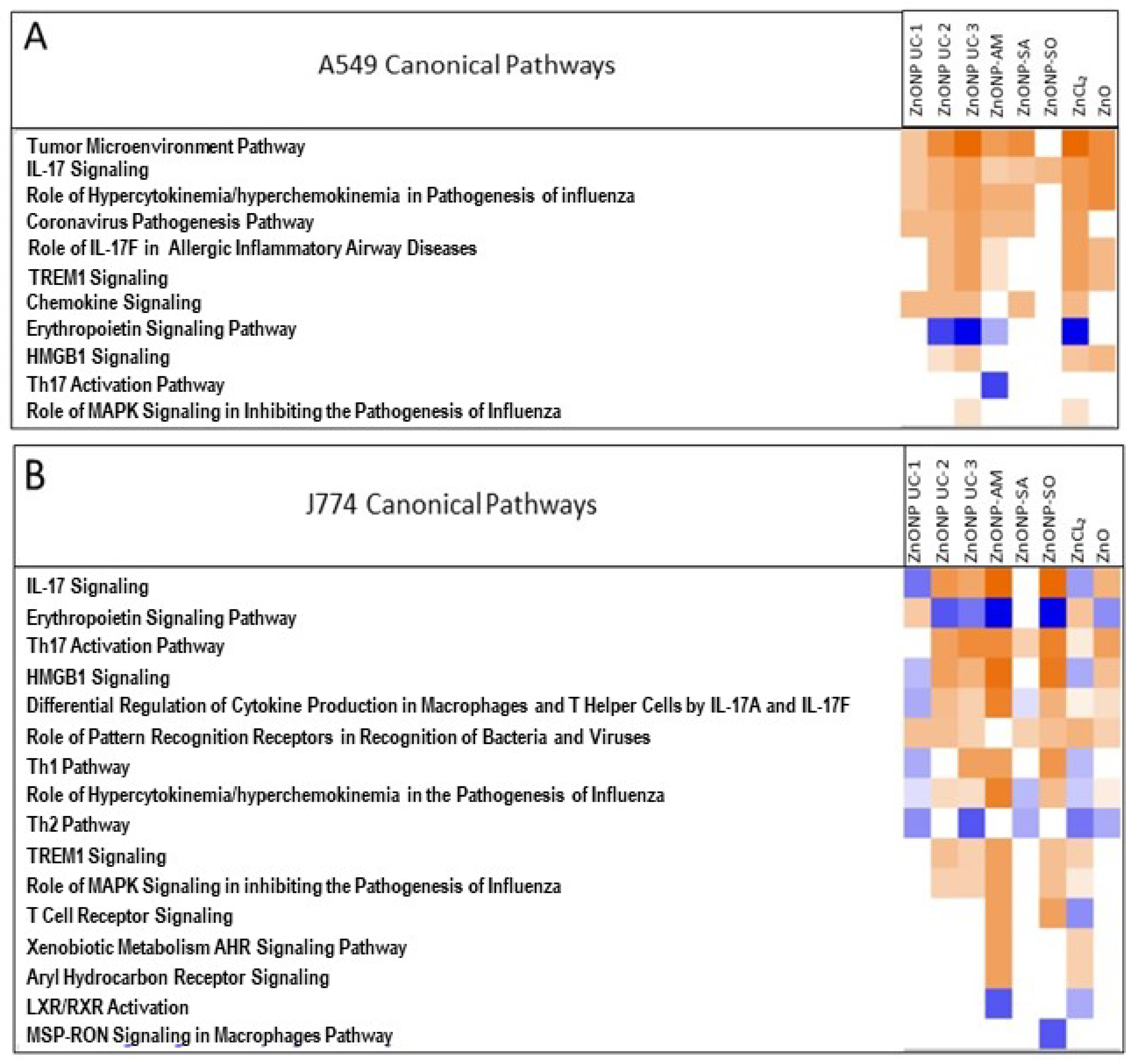
3.5. NP Exposure-Related Protein-Level Changes and Impacts on Mechanistic Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhattacharya, P.; Mukherjee, D.; Deb, N.; Swarnakar, S.; Banerjee, S. Application of Green Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticle Coated Ceramic Ultrafiltration Membrane for Remediation of Pharmaceutical Components from Synthetic Water: Reusability Assay of Treated Water on Seed Germination. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.J.B.; Bouwmeester, H.; Gottardo, S.; Amenta, V.; Arena, M.; Brandhoff, P.; Marvin, H.J.P.; Mech, A.; Moniz, F.B.; Pesudo, L.Q.; et al. Nanomaterials for Products and Application in Agriculture, Feed and Food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Functional Oxide Nanobelts: Materials, Properties and Potential Applications in Nanosystems and Biotechnology. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2004, 55, 159–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Pi, J.; Cai, J. The Advancing of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 1062562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederickson, C.J.; Koh, J.-Y.; Bush, A.I. The Neurobiology of Zinc in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espitia, P.J.P.; Soares, N. de F.F.; Coimbra, J.S. dos R.; de Andrade, N.J.; Cruz, R.S.; Medeiros, E.A.A. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Antimicrobial Activity and Food Packaging Applications. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 1447–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer-Jungemann, A.; Feliu, N.; Bakaimi, I.; Hamaly, M.; Alkilany, A.; Chakraborty, I.; Masood, A.; Casula, M.F.; Kostopoulou, A.; Oh, E.; et al. The Role of Ligands in the Chemical Synthesis and Applications of Inorganic Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4819–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, P.S.; Rao, S.B.N.; Rajendran, D.; Dominic, G.; Selvaraju, S. Nano Zinc, an Alternative to Conventional Zinc as Animal Feed Supplement: A Review. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 2, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Takeda, T.-A.; Takagishi, T.; Fukue, K.; Kambe, T.; Fukada, T. Physiological Roles of Zinc Transporters: Molecular and Genetic Importance in Zinc Homeostasis. J. Physiol. Sci. 2017, 67, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smijs, T.G.M.; Bouwstra, J.A. Focus on Skin as a Possible Port of Entry for Solid Nanoparticles and the Toxicological Impact. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Wei, L.; Chen, L.; Song, B.; Shao, L. The Toxicology of Ion-Shedding Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 46, 348–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Garg, R.; Kumari, A. A Review on Biogenic Synthesis, Applications and Toxicity Aspects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 1325–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Bu, X.; Lu, F.; Qu, D.; Yao, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J. The Effect of Fe2O3 and ZnO Nanoparticles on Cytotoxicity and Glucose Metabolism in Lung Epithelial Cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsen, P.H.; Cao, Y.; Roursgaard, M.; Møller, P.; Loft, S. Endothelial Cell Activation, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Induced by a Panel of Metal-Based Nanomaterials. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-H.; Chen, Y.; Zha, H.-X.; Song, L.-J.; Li, C.-Y.; Li, J.-Q.; Xia, X.-H. Determination, Characterization and Cytotoxicity on HELF Cells of ZnO Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.; Seo, G.; Kwon, J.-T.; Lee, M.; cheun Lee, B.; Eom, I.; Kim, P.; Choi, K. Exposure to Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Affects Reproductive Development and Biodistribution in Offspring Rats. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 38, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-S.; Park, M.-K.; Kim, M.-S.; Lim, J.-H.; Park, G.-J.; Maeng, E.-H.; Shin, J.-H.; Kim, M.-K.; Jeong, J.; Park, J.-A.; et al. Prenatal Development Toxicity Study of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liang, H.; Chen, A.; Lai, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Kang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shao, L. Neuroinflammation Is Induced by Tongue-Instilled ZnO Nanoparticles via the Ca2+-Dependent NF-κB and MAPK Pathways. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Costa, C.; Kiliç, G.; Costa, S.; Pásaro, E.; Laffon, B.; Teixeira, J.P. Neuronal Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity Induced by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Environ. Int. 2013, 55, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohynek, G.J.; Lademann, J.; Ribaud, C.; Roberts, M.S. Grey Goo on the Skin? Nanotechnology, Cosmetic and Sunscreen Safety. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2007, 37, 251–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.-K.; Tripathy, N.; Son, H.-J.; Ha, K.-T.; Jeong, H.-S.; Hahn, Y.-B. A Comprehensive in Vitro and in Vivo Study of ZnO Nanoparticles Toxicity. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2985–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titma, T.; Shimmo, R.; Siigur, J.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of Antimony, Copper, Cobalt, Manganese, Titanium and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for the Alveolar and Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Cells in Vitro. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 2363–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, K.-J.; Chuang, K.-J.; Ma, C.-M.; Chang, T.-Y.; Chuang, H.-C. Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells with an EGFR Mutation Are Sensitive to Non-Autophagic Cell Death Induced by Zinc Oxide and Aluminium-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 42, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, B.; Xu, G.; Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Ju, X.; Bose, D.D.; Qiu, F.; et al. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Harness Autophagy to Induce Cell Death in Lung Epithelial Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmi, V.; Fischer, U.; Weighardt, H.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Nickel, C.; Stahlmecke, B.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Scherbart, A.M.; Esser, C.; Schins, R.P.F.; et al. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Necrosis and Apoptosis in Macrophages in a P47phox- and Nrf2-Independent Manner. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canta, M.; Cauda, V. The Investigation of the Parameters Affecting the ZnO Nanoparticle Cytotoxicity Behaviour: A Tutorial Review. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 6157–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kad, A.; Pundir, A.; Arya, S.K.; Puri, S.; Khatri, M. Meta-Analysis of in-Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation Studies of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Paving Way for Safer Innovations. Toxicol. Vitr. 2022, 83, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, H.M.; Abd El-Daim, T.M.; Ali, O.A.; Hassan, A.A.; Mohammed, F.F.; Fathy, M.M. Surface Modifications Affect Iron Oxide Nanoparticles’ Biodistribution after Multiple-Dose Administration in Rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canada, E. Canadian Environmental Protection Act Registry. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/canadian-environmental-protection-act-registry.html (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Breznan, D.; Nazemof, N.; Kunc, F.; Hill, M.; Vladisavljevic, D.; Gomes, J.; Johnston, L.J.; Vincent, R.; Kumarathasan, P. Acellular Oxidative Potential Assay for Screening of Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles. Analyst 2020, 145, 4867–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunc, F.; Kodra, O.; Brinkmann, A.; Lopinski, G.P.; Johnston, L.J. A Multi-Method Approach for Quantification of Surface Coatings on Commercial Zinc Oxide Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breznan, D.; Das, D.D.; O’Brien, J.S.; MacKinnon-Roy, C.; Nimesh, S.; Vuong, N.Q.; Bernatchez, S.; DeSilva, N.; Hill, M.; Kumarathasan, P.; et al. Differential Cytotoxic and Inflammatory Potency of Amorphous Silicon Dioxide Nanoparticles of Similar Size in Multiple Cell Lines. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarathasan, P.; Vincent, R.; Blais, E.; Bielecki, A.; Guénette, J.; Filiatreault, A.; Brion, O.; Cakmak, S.; Thomson, E.M.; Shutt, R.; et al. Cardiovascular and Inflammatory Mechanisms in Healthy Humans Exposed to Air Pollution in the Vicinity of a Steel Mill. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, R.; Goegan, P.; Johnson, G.; Brook, J.R.; Kumarathasan, P.; Bouthillier, L.; Burnett, R.T. Regulation of Promoter-CAT Stress Genes in HepG2 Cells by Suspensions of Particles from Ambient Air. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1997, 39, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, Y.-M.; Lai, B.-H.; Chien, H.-J.; Ho, M.; Cheng, T.-J.; Lai, C.-C. Changes in Protein Expression in Rat Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid after Exposure to Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: An iTRAQ Proteomic Approach. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Stebounova, L.V.; Kim, J.S.; Vorrink, S.U.; Ault, A.P.; O’Shaughnessy, P.T.; Grassian, V.H.; Thorne, P.S. Toxicity Assessment of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Sub-Acute and Sub-Chronic Murine Inhalation Models. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, H.; Nounou, H.; Shalaby, M. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induced Oxidative DNA Damage, Inflammation and Apoptosis in Rat’s Brain after Oral Exposure. Toxics 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, A.M.; Varun, S.; Karumuthil, S.C.; Varghese, S.; Mural, P.K.S. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Coated with (3-Aminopropyl)Triethoxysilane as Additives for Boosting the Dielectric, Ferroelectric, and Piezoelectric Properties of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Films for Energy Harvesting. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yang, L.; Yan, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xiong, L.; Shi, R.; Sun, Q. ZnO Nanoparticles Coated and Stearic Acid Modified Superhydrophobic Chitosan Film for Self-Cleaning and Oil–Water Separation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 231, 123293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, A.I.; Moriana, R.; Hillborg, H.; Strömberg, E. Super-Hydrophobic Zinc Oxide/Silicone Rubber Nanocomposite Surfaces. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 14, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solorio-Rodriguez, S.A.; Wu, D.; Boyadzhiev, A.; Christ, C.; Williams, A.; Halappanavar, S. A Systematic Genotoxicity Assessment of a Suite of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles Reveals Their DNA Damaging and Clastogenic Potential. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramescu, M.-L.; Rasmussen, P.E.; Chénier, M.; Gardner, H.D. Influence of pH, Particle Size and Crystal Form on Dissolution Behaviour of Engineered Nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avramescu, M.-L.; Chénier, M.; Beauchemin, S.; Rasmussen, P. Dissolution Behaviour of Metal-Oxide Nanomaterials in Various Biological Media. Nanomaterials 2022, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.P.; Mintern, J.D.; Gleeson, P.A. Macropinocytosis in Different Cell Types: Similarities and Differences. Membranes 2020, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, D.A.; Vanhecke, D.; Michen, B.; Blank, F.; Gehr, P.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Different Endocytotic Uptake Mechanisms for Nanoparticles in Epithelial Cells and Macrophages. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.; Park, J.-H. Endocytosis and Exocytosis of Nanoparticles in Mammalian Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9 (Suppl. 1), 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivask, A.; Mitchell, A.J.; Hope, C.M.; Barry, S.C.; Lombi, E.; Voelcker, N.H. Single Cell Level Quantification of Nanoparticle-Cell Interactions Using Mass Cytometry. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8228–8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquet, J.; Chevalier, Y.; Couval, E.; Bouvier, D.; Noizet, G.; Morlière, C.; Bolzinger, M.-A. Antimicrobial Activity of Zinc Oxide Particles on Five Micro-Organisms of the Challenge Tests Related to Their Physicochemical Properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 460, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prach, M.; Stone, V.; Proudfoot, L. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Monocytes: Impact of Size, Charge and Solubility on Activation Status. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 266, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerki-Thurnherr, T.; Xiao, L.; Diener, L.; Arslan, O.; Hirsch, C.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Grieder, K.; Wampfler, B.; Mathur, S.; Wick, P.; et al. In Vitro Mechanistic Study towards a Better Understanding of ZnO Nanoparticle Toxicity. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, K.C.; Lefebvre, D.E.; Shwed, P.S.; Crosthwait, J.; Bondy, G.S.; Tayabali, A.F. Critical Experimental Parameters Related to the Cytotoxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Mädler, L.; Gilbert, B.; Shi, H.; Yeh, J.I.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Comparison of the Mechanism of Toxicity of Zinc Oxide and Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Based on Dissolution and Oxidative Stress Properties. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2121–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rashaideh, T.; Metwali, N.; Perry, S.S.; Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Thorne, P.S. Cerium Oxide Enhances the Toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Lung Epithelial Cell Cultures. Toxics 2022, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, R.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Saquib, Q.; Dwivedi, S.; Ahmad, J.; Musarrat, J.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Shin, H.-S. ZnO Nanoparticles Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 Cancer Cells and Their Antibacterial Activity. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, D.; Ding, W. ZnO Nanoparticle-Induced Oxidative Stress Triggers Apoptosis by Activating JNK Signaling Pathway in Cultured Primary Astrocytes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saptarshi, S.R.; Feltis, B.N.; Wright, P.F.; Lopata, A.L. Investigating the Immunomodulatory Nature of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles at Sub-Cytotoxic Levels in Vitro and after Intranasal Instillation in Vivo. J. Nanobiotechnology 2015, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, V.A.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, G.S.; Pandey, A.K.; Dhawan, A. ZnO Nanoparticles Induced Inflammatory Response and Genotoxicity in Human Blood Cells: A Mechanistic Approach. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 85, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, I.Y.; Prieditis, H.; Hedgecock, C.; Vincent, R. Zinc Is the Toxic Factor in the Lung Response to an Atmospheric Particulate Sample. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2000, 166, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, R.; Kumarathasan, P.; Goegan, P.; Bjarnason, S.G.; Guénette, J.; Karthikeyan, S.; Thomson, E.M.; Adamson, I.Y.; Watkinson, W.P.; Battistini, B.; et al. Acute Cardiovascular Effects of Inhaled Ambient Particulate Matter: Chemical Composition-Related Oxidative Stress, Endothelin-1, Blood Pressure, and ST-Segment Changes in Wistar Rats. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrup, N.; Knudsen, K.B.; Berthing, T.; Wolff, H.; Bengtson, S.; Kofoed, C.; Espersen, R.; Højgaard, C.; Winther, J.R.; Willemoës, M.; et al. Pulmonary Effects of Nanofibrillated Celluloses in Mice Suggest That Carboxylation Lowers the Inflammatory and Acute Phase Responses. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 66, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Parashar, V.; Chauhan, L.K.S.; Shanker, R.; Das, M.; Tripathi, A.; Dwivedi, P.D. Mechanism of Uptake of ZnO Nanoparticles and Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages Require PI3K Mediated MAPKs Signaling. Toxicol Vitr. 2014, 28, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomela, S.; Autio, R.; Buerki-Thurnherr, T.; Arslan, O.; Kunzmann, A.; Andersson-Willman, B.; Wick, P.; Mathur, S.; Scheynius, A.; Krug, H.F.; et al. Gene Expression Profiling of Immune-Competent Human Cells Exposed to Engineered Zinc Oxide or Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, D.; Kannan, G.M.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Size-Dependent Effect of Zinc Oxide on Toxicity and Inflammatory Potential of Human Monocytes. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2014, 77, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandebriel, R.J.; De Jong, W.H. A Review of Mammalian Toxicity of ZnO Nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2012, 5, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Yadav, S.S.; Mishra, S.; Yadav, S.K.; Parmar, D.; Yadav, S. A Combined microRNA and Proteome Profiling to Investigate the Effect of ZnO Nanoparticles on Neuronal Cells. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Ji, S. Proteomics and Metabolomics Analysis Reveals the Toxicity of ZnO Quantum Dots on Human SMMC-7721 Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Mao, W.; Liu, T.; Sun, M.; Wu, Y. TREM1: A Positive Regulator for Inflammatory Response via NF-κB Pathway in A549 Cells Infected with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Broadening Horizons: The Role of Ferroptosis in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRedmond, R.; Singhera, G.K.; Dorscheid, D.R. Erythropoietin Inhibits Respiratory Epithelial Cell Apoptosis in a Model of Acute Lung Injury. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, F.J.; Sherr, D.H. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Control of Adaptive Immunity. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniyi, O.E.; Adebayo, O.A.; Akinloye, O.; Adaramoye, O.A. Combined Cerium and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induced Hepato-Renal Damage in Rats through Oxidative Stress Mediated Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Elements (ppm) | ZnO | ZnONP AM | ZnONP SA | ZnONP SO | ZnONP UC-1 | ZnONP UC-2 | ZnONP UC-3 | ZnCl₂ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.03 | <0.01 |
| Al | 2.15 | 75.47 | 104.51 | 41.28 | 79.88 | 50.67 | 20.05 | 1.20 |
| Ba | 0.27 | 3.60 | 1.95 | 1.22 | 2.28 | 14.67 | 0.29 | 0.06 |
| Bi | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.23 |
| Ca | 17.92 | 347.11 | 876.69 | 1067.04 | 641.47 | 1835.73 | 20.43 | 16.67 |
| Cd | 11.86 | 0.42 | 0.71 | 0.12 | 1.09 | 0.62 | 3.44 | 2.22 |
| Ce | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.28 | 1.11 | 0.41 |
| Co | <0.01 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.26 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Cr | 0.36 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 4.21 | 0.10 | 0.33 |
| Cs | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Cu | 0.75 | 3.24 | 5.24 | 2.50 | 3.89 | 1.63 | 10.39 | 0.38 |
| Dy | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.04 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Er | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Eu | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Fe | 3.35 | 287.07 | 19.36 | 22.20 | 18.24 | 167.89 | 10.18 | 2.90 |
| Gd | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.12 | 0.01 | <0.01 |
| Hf | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Ho | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| K | 8.19 | 14.44 | 13.80 | 18.56 | 11.25 | 20.21 | 10.59 | 7.02 |
| La | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 10.67 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Lu | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Mg | 1.21 | 112.06 | 173.98 | 220.07 | 119.84 | 538.70 | 2.47 | 1.01 |
| Mn | 0.17 | 1.54 | 4.40 | 3.65 | 1.01 | 64.47 | 0.13 | 0.09 |
| Mo | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Na | 7.94 | 780.06 | 363.74 | 1724.20 | 949.48 | 217.37 | 11.68 | 3.74 |
| Nb | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Nd | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 1.20 | <0.01 | 0.01 |
| Ni | 0.07 | 0.63 | 1.24 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 21.68 | 0.09 | 0.19 |
| Pr | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.42 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Rb | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Sb | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Sc | <0.01 | 0.03 | <0.01 | 0.06 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Si | 10.46 | 1173.68 | 46.21 | 2718.81 | 24.77 | 36.37 | 27.72 | 9.04 |
| Sm | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Sr | 0.02 | 1.80 | 5.33 | 4.32 | 3.50 | 13.56 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| Ta | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Tb | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Th | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 |
| Ti | 0.97 | 320.69 | 382.85 | 489.93 | 228.36 | 1.54 | 1.32 | 0.66 |
| Tm | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| U | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.13 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| V | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Yb | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Zn | 770,268 | 763,278 | 715,683 | 721,911 | 760,799 | 718,568 | 753,952 | 616,834 |
| Zr | 0.05 | 0.30 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Nano Particle | TEM (nm) | BETSA (m2/g) | DLS (nm) | PDI | ZP (mV) | Transition Metals (ppm)a | TGA µmol/g (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnONP AM | 30 (20,200) | 16.3 | 212 | 0.12 | 19.3 | 613.8 | 119 (0.69%) |
| ZnONP SA | 10–30(20, 50–100) | 29 | 420 | 0.13 | nd | 413. 7 | 165 (4.69%) |
| ZnONP SO | 30 (15, 100) | 14.1 | na | na | nd | 519.1 | (4.21%) |
| ZnONP UC-1 | 30 (<100) | 21.6 | 223 | 0.19 | 23.2 | 252.7 | |
| ZnONP UC-2 | 35–45 (20–40) | 34.5 | 278 | 0.39 | 23 | 261.8 | |
| ZnONP UC-3 | 53 ± 23 (20–30, >100) | 11.9 | 232 | 0.14 | 30.5 | 22.2 |
| Nano Particle | A549 | J774 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATP (β) | LDH (β) | CTB (β) | Consensus Average β | Rank | ATP (β) | LDH (β) | CTB (β) | Consensus Average β | Rank | |
| ZnO | 0.120 | 0.058 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 8 | 0.348 | 0.189 | 0.295 | 0.277 | 7 |
| ZnONP AM | 0.173 | 0.014 | 0.093 | 0.093 | 7 | 1.600 | 0.170 | 0.280 | 0.683 | 1 |
| ZnONP SA | 0.177 | 0.008 | 0.106 | 0.097 | 4 | 0.493 | 0.174 | 0.311 | 0.326 | 6 |
| ZnONP SO | 0.140 | 0.003 | 0.146 | 0.096 | 5 | 0.328 | 0.172 | 0.277 | 0.259 | 8 |
| ZnONP UC-1 | 0.160 | 0.007 | 0.121 | 0.096 | 6 | 1.233 | 0.170 | 0.305 | 0.569 | 4 |
| ZnONP UC-2 | 0.213 | 0.001 | 0.173 | 0.129 | 2 | 1.381 | 0.170 | 0.310 | 0.620 | 2 |
| ZnONP UC-3 | 0.152 | 0.003 | 0.176 | 0.110 | 3 | 1.258 | 0.172 | 0.282 | 0.571 | 3 |
| ZnCl2 | 0.265 | 0.172 | 0.220 | 0.219 | 1 | 1.258 | 0.145 | 0.205 | 0.536 | 5 |
| Cell Type | Predictor(s) |
|---|---|
| A549 | βATP: BETSA (p = 0.023) |
| βLDH: TEM (p = 0.049), BETSA (p = 0.046) | |
| βCTB: TEM (p = 0.039), Total Metals (p = 0.032) | |
| J774 | βATP: DLS (p = 0.029) |
| βLDH: BETSA (p = 0.054), DLS (p = 0.028) | |
| βCTB: BESTA (p = 0.041) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazemof, N.; Breznan, D.; Dirieh, Y.; Blais, E.; Johnston, L.J.; Tayabali, A.F.; Gomes, J.; Kumarathasan, P. Cytotoxic Potencies of Zinc Oxide Nanoforms in A549 and J774 Cells. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14191601
Nazemof N, Breznan D, Dirieh Y, Blais E, Johnston LJ, Tayabali AF, Gomes J, Kumarathasan P. Cytotoxic Potencies of Zinc Oxide Nanoforms in A549 and J774 Cells. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(19):1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14191601
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazemof, Nazila, Dalibor Breznan, Yasmine Dirieh, Erica Blais, Linda J. Johnston, Azam F. Tayabali, James Gomes, and Premkumari Kumarathasan. 2024. "Cytotoxic Potencies of Zinc Oxide Nanoforms in A549 and J774 Cells" Nanomaterials 14, no. 19: 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14191601
APA StyleNazemof, N., Breznan, D., Dirieh, Y., Blais, E., Johnston, L. J., Tayabali, A. F., Gomes, J., & Kumarathasan, P. (2024). Cytotoxic Potencies of Zinc Oxide Nanoforms in A549 and J774 Cells. Nanomaterials, 14(19), 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14191601






