Simultaneous Down-Regulation of Intracellular MicroRNA-21 and hTERT mRNA Using AS1411-Functionallized Gold Nanoprobes to Achieve Targeted Anti-Tumor Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparing Au NPs and Au Nanoprobes
2.2. Evaluating the Amount of DNA Duplexes Bound on Each Au Nanoprobe
2.3. Determining the Fluorescence Response of Au Nanoprobes to Target DNA
2.4. Determining the Fluorescence Response of Au Nanoprobes to Intracellular MicroRNA-21 and hTERT mRNA
- (i)
- Cell lysate analysis: Cell lysates were obtained by breaking down MCF-7 cells (1 × 106) using an ultrasonic disruptor. Au nanoprobes (1.5 nM) were incubated with the freshly prepared cell extracts at 37 °C for 4 h. The fluorescence intensity levels of the experimental systems were determined by using the F-7000 spectrofluorometer (Hitachi, Japan) with excitation wavelengths of 530 and 630 nm.
- (ii)
- In situ fluorescence imaging: MCF-7 or HeLa cells (0.4 mL, 1 × 106 mL−1) were, respectively, seeded in a 20 mm glass-bottom confocal dish. After 24 h, Au nanoprobes (1.5 nM) were incubated with cells for 4 h. Then, cells were washed with PBS thrice and observed by LSM880 confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM, Zeiss, Jena, Germany). The fluorescence signals of Cy3 and Cy5 of Au nanoprobes responsive to hTERT mRNA and microRNA-21 were excited with wavelengths of 543 and 633 nm, respectively.
2.5. Quantifying the Uptake of Au Nanoprobes in Cancer Cells
2.6. Analyzing the Intracellular hTERT mRNA and microRNA-21 Level
2.7. Analyzing the Intracellular hTERT Activity
2.8. Determining the Pro-Apoptosis Effect and In Vitro Cytotoxicities of Au Nanoprobes
2.9. In Vivo and Ex Vivo Fluorescence Imaging and Quantifying the Accumulation of Au Nanoprobes in Tumors
2.10. In Vivo Anti-Tumor Study
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
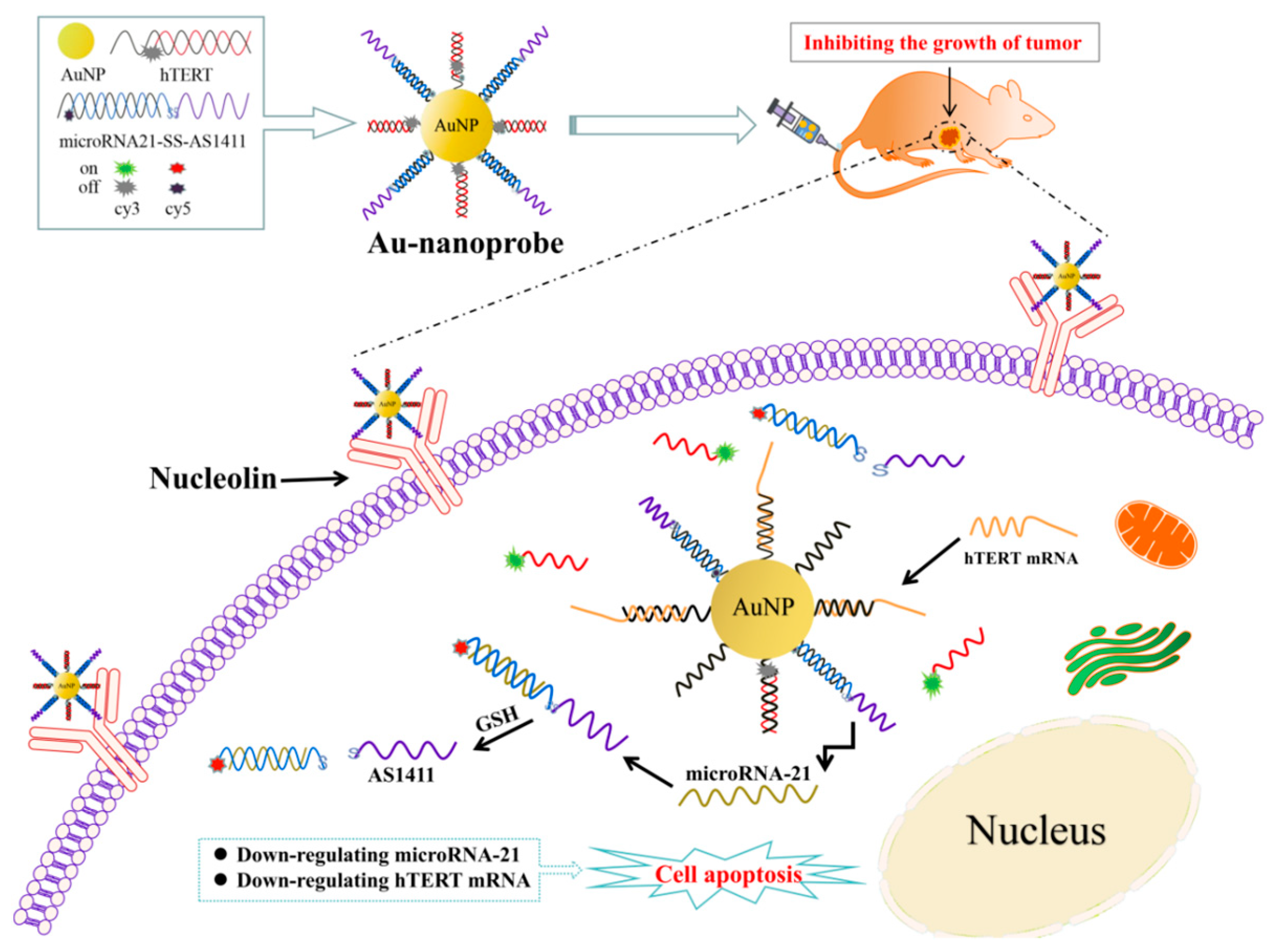
3.1. Design Mechanism of Au Nanoprobes
3.2. Characterization of AuNPs and Au Nanoprobes
3.3. Evaluation of the Amount of DNA Duplexes Bound on Each Au Nanoprobe
3.4. In Vitro Response of Au Nanoprobes to hTERT mRNA and microRNA-21-Related Target DNA
3.5. In Situ Fluorescence Imaging of Intracellular hTERT mRNA and microRNA-21 Using Au Nanoprobes and Evaluating the Intracellular Amount of Au Nanoprobes
3.6. Analysis of the Expression Level of hTERT mRNA and microRNA-21 as Well as hTERT Activity in Cancer Cells Treated with Au Nanoprobes
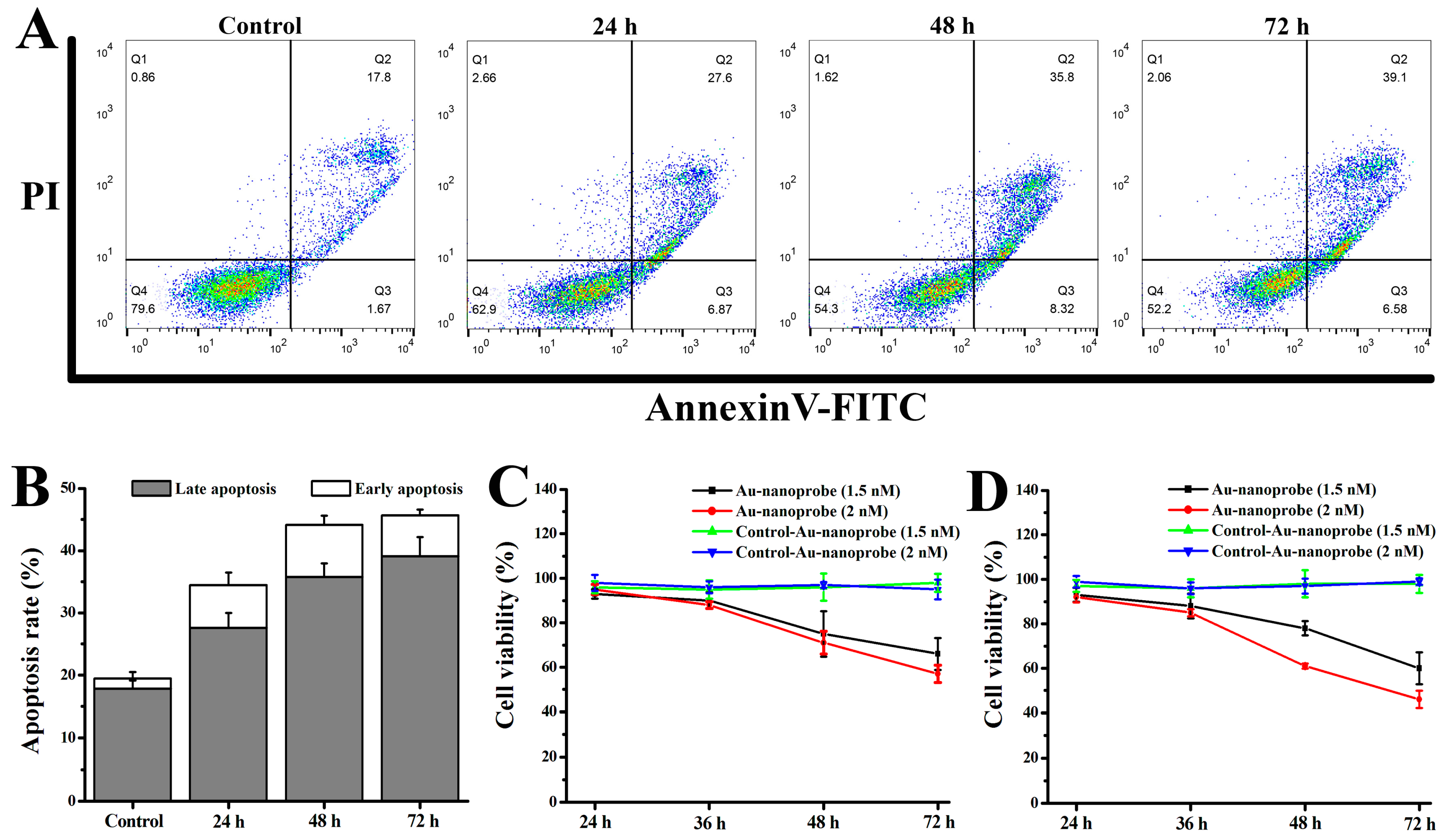
3.7. Studies of the Pro-Apoptosis Effect and In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Au Nanoprobes
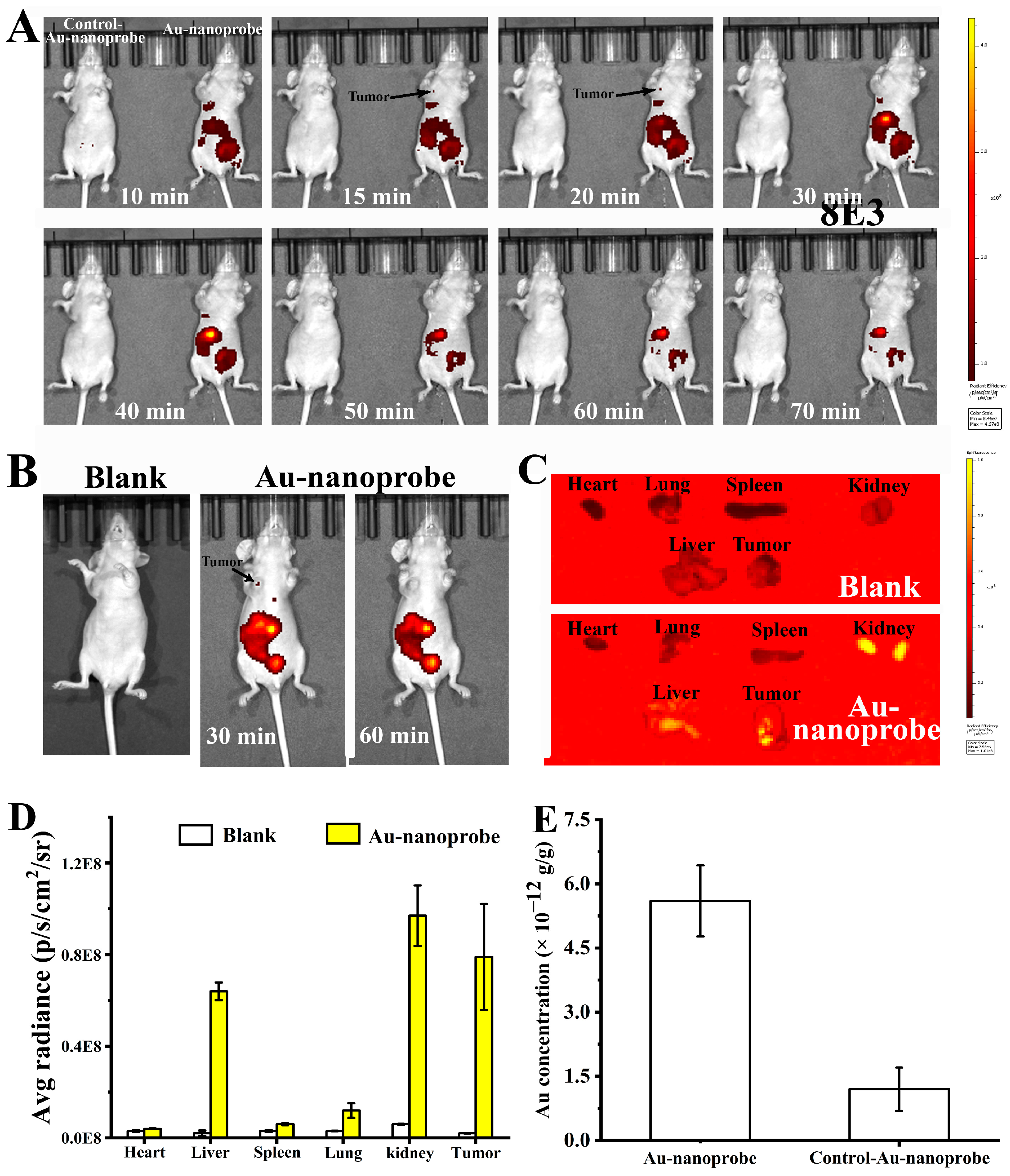
3.8. In Vivo and Ex Vivo Imaging of Au Nanoprobes
3.9. In Vivo Targeted Anti-Tumor Therapy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berei, J.; Eckburg, A.; Miliavski, E.; Anderson, A.D.; Miller, R.J.; Dein, J.; Giuffre, A.M.; Tang, D.; Deb, S.; Racherla, K.S.; et al. Potential telomere-related pharmacological targets. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 458–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrdličková, R.; Nehyba, J.; Bargmann, W.; Bose, H.R. Multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs regulate telomerase and TCF7, an important transcriptional regulator of the Wnt pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86990–e87001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.D.; Tam, J.; Wu, R.A.; Greber, B.J.; Toso, D.; Nogales, E.; Collins, K. Cryo-EM structure of substrate-bound human telomerase holoenzyme. Nature 2018, 557, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, W.; Zeng, Y.X.; Zheng, B.X.; Li, Y.B.; Wang, Y.K.; Chan, K.H.; She, M.T.; Lu, Y.J.; Cao, C.; Wong, W.L. Targeting hTERT Promoter G-Quadruplex DNA Structures with Small-Molecule Ligand to Downregulate hTERT Expression for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 13363–13382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckburg, A.; Dein, J.; Berei, J.; Schrank, Z.; Puri, N. Oligonucleotides and microRNAs targeting telomerase subunits in cancer therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, R.; Hummel, T.R.; Kumar, S.S.; Dorris, K.; Li, S.; Lin, T.; Daryani, V.M.; Stewart, C.F.; Miles, L.; Poussaint, T.Y.; et al. A molecμLar biology and phase II study of imetelstat (GRN163L) in children with recurrent or refractory central nervous system malignancies: A pediatric brain tumor consortium study. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2016, 129, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, T.; Naohiro, S.; Nakayama, Y.; Osaki, M.; Okada, F.; Oshimura, M.; Kugoh, H. MiR-19b regulates hTERT mRNA expression through targeting PITX1 mRNA in melanoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8201–8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Wang, R.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Qi, Y.; Wan, H.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. miR-346 and miR-138 competitively regulate hTERT in GRSF1- and AGO2-dependent manners, respectively. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15793–15808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C. MiR-21: An environmental driver of malignant melanoma? J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.J.; Tao, H.; Jin, W.S. MicroRNA-21 controls hTERT via PTEN in human colorectal cancer cell proliferation. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 71, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Sun, G.; Luo, H.; Wang, X.F.; Lan, F.M.; Yue, X.; Fu, L.S.; Pu, P.Y.; Kang, C.S.; Liu, N.; et al. MiR-21 Modulates hTERT Through a STAT3-Dependent Manner on Glioblastoma Cell Growth. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2012, 18, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrank, Z.; Khan, N.; Osude, C.; Singh, S.; Miller, R.J.; Merrick, C.; Mabel, A.; Kuckovic, A.; Puri, N. Oligonucleotides Targeting Telomeres and Telomerase in Cancer. Molecules 2018, 23, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A.; Ruoslahti, E.; Meng, H. New insights into “Permeability” as in the enhanced permeability and retention effect of cancer nanotherapeutics. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9567–9569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, J.D.; Betancourt, T.; Brannon-Peppas, L. Active targeting schemes for nanoparticle systems in cancer therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llevot, A.; Astruc, D. Applications of vectorized gold nanoparticles to the diagnosis and therapy of cancer. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazi, M.E.; Giust, D.; El-Sagheer, A.H.; Lackie, P.M.; Muskens, O.L.; Brown, T.; Kanaras, A.G. Multiplexed mRNA Sensing and Combinatorial-Targeted Drug Delivery Using DNA-Gold Nanoparticle Dimers. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3333–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyawati, M.I.; Wang, Q.; Ni, N.; Tee, J.K.; Ariga, K.; Ke, P.C.; Ho, H.K.; Wang, Y.; Leong, D.T. Engineering tumoral vascular leakiness with gold nanoparticles. Nat. Comm. 2023, 14, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Hong, M.; Yang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, G.; Yue, Q.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Li, C.Z. Visualizing the down-regulation of hTERT mRNA expression using gold-nanoflare probes and verifying the correlation with cancer cell apoptosis. Analyst 2019, 144, 2994–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Sun, H.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, S.; Yu, S.; Fan, S.; Li, C.; Cui, C.; Tan, W. A microRNA-21-responsive doxorubicin-releasing sticky-flare for synergistic anticancer with silencing of microRNA and chemotherapy. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrnia, S.S.; Hashemi, B.; Mowla, S.J.; Nikkhah, M.; Arbabi, A. Radiosensitization of breast cancer cells using AS1411 aptamer-conjugated gold nanoparticles. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 6, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigodich, A.E.; Seferos, D.S.; Massich, M.D.; Giljohann, D.A.; Lane, B.C.; Mirkin, C.A. Nano-flares for mRNA Regulation and Detection. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, L.M.; Mirkin, C.A.; Mucic, R.C.; Reynolds, R.A.; Leitsinger, R.L.; Viswanadham, G. A fluorescence-based method for determining the surface coverage and hybridization efficiency of thiol-capped oligonucleotides bound to gold thin films and nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 5535–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, K.; Fuessel, S.; Schmidt, U.; Kotzsch, M.; Schwenzer, B.; Wirth, M.P.; Meye, A. Antisense-mediated hTERT Inhibition Specifically Reduces the Growth of Human Bladder Cancer Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 3794–3800. [Google Scholar]
- Ryoo, S.R.; Lee, J.; Yeo, J.; Na, H.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.H.; Han, S.W.; Lee, Y.; Ki, V.N.; et al. Quantitative and Multiplexed MicroRNA Sensing in Living Cells Based on Peptide Nucleic Acid and Nano Graphene Oxide (PANGO). ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5882–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, J.; Mergny, J.L.; Salgado, G.F.; Queiroz, J.A.; Cruz, C. G-quadruplex, friend or foe: The role of the g-quartet in anticancer strategies. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, D.H.M.; Lee, J.H.; Sisco, P.N.; Co, D.T.; Zhang, M.; Wasielewski, M.R.; Odom, T.W. Direct Observation of Nanoparticle Cancer Cell Nucleus Interactions. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3318–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Sun, H.; Xu, L.; Yue, Q.; Shen, G.; Li, M.; Tang, B.; Li, C.Z. In situ monitoring of cytoplasmic precursor and mature microRNA using gold nanoparticle and graphene oxide composite probes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1021, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Li, C.; Bai, W.D.; Su, L.L.; Liu, J.Q.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.H.; Cai, W.X.; Bai, X.Z.; Jia, Y.H.; et al. MicroRNA-21 Regulates hTERT via PTEN in Hypertrophic Scar Fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, G.; Rengan, A.K. Aptamer-Mediated Nanotheranostics for Cancer Treatment: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mat. 2020, 3, 9542–9559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.M.; Gaume, X.; Bouvet, P. The roles of nucleolin subcellular localization in cancer. Biochimie 2015, 113, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.S.; Gonçalves, N.; Fonseca, N.A.; Moreira, J.N. Cancer stem cells and nucleolin as drivers of carcinogenesis. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, N.F.; Amini, R.; Ramezani, M.; Saidijam, M.; Hashemi, S.M.; Najaf, R. AS1411 aptamer-functionalized exosomes in the targeted delivery of doxorubicin in fighting colorectal cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, A.; Posch, C.; Garcimartín, Y.; Celli, A.; Sanlorenzo, M.; Vujic, I.; Ma, J.; Zekhtser, M.; Rappersberger, K.; Ortiz-Urda, S.; et al. DNA and aptamer stabilized gold nanoparticles for targeted delivery of anticancer therapeutics. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7436–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, D. Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Theranostics. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2021, 9, 647905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Dou, J.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, C.; Pan, H.; Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Leong, D.T.; et al. Breaking through the basement membrane barrier to improve nanotherapeutic delivery to tumours. Nat. Nanotech. 2024, 19, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Yung, L.Y.L.; Tan, P.H.; Bay, B.H. Harnessing the Immunogenic Potential of Gold Nanoparticle-Based Platforms as a Therapeutic Strategy in Breast Cancer Immunotherapy: A Mini Review. Front. Immun. 2022, 13, 865554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, Q.; Yang, Q.; Ou, M.; Hong, M. Simultaneous Down-Regulation of Intracellular MicroRNA-21 and hTERT mRNA Using AS1411-Functionallized Gold Nanoprobes to Achieve Targeted Anti-Tumor Therapy. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14231956
Ji Q, Yang Q, Ou M, Hong M. Simultaneous Down-Regulation of Intracellular MicroRNA-21 and hTERT mRNA Using AS1411-Functionallized Gold Nanoprobes to Achieve Targeted Anti-Tumor Therapy. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(23):1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14231956
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Qinghong, Qiangqiang Yang, Mengyao Ou, and Min Hong. 2024. "Simultaneous Down-Regulation of Intracellular MicroRNA-21 and hTERT mRNA Using AS1411-Functionallized Gold Nanoprobes to Achieve Targeted Anti-Tumor Therapy" Nanomaterials 14, no. 23: 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14231956
APA StyleJi, Q., Yang, Q., Ou, M., & Hong, M. (2024). Simultaneous Down-Regulation of Intracellular MicroRNA-21 and hTERT mRNA Using AS1411-Functionallized Gold Nanoprobes to Achieve Targeted Anti-Tumor Therapy. Nanomaterials, 14(23), 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14231956





