Directed Evolution of Near-Infrared Serotonin Nanosensors with Machine Learning-Based Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of ssDNA-SWCNT Nanosensor
2.3. Fluorescence Imaging of ssDNA-SWCNT Nanosensors Immobilized on a Glass Substrate
2.4. Fluorescence Measurement
2.5. Directed Evolution with Machine Learning Screening
3. Results
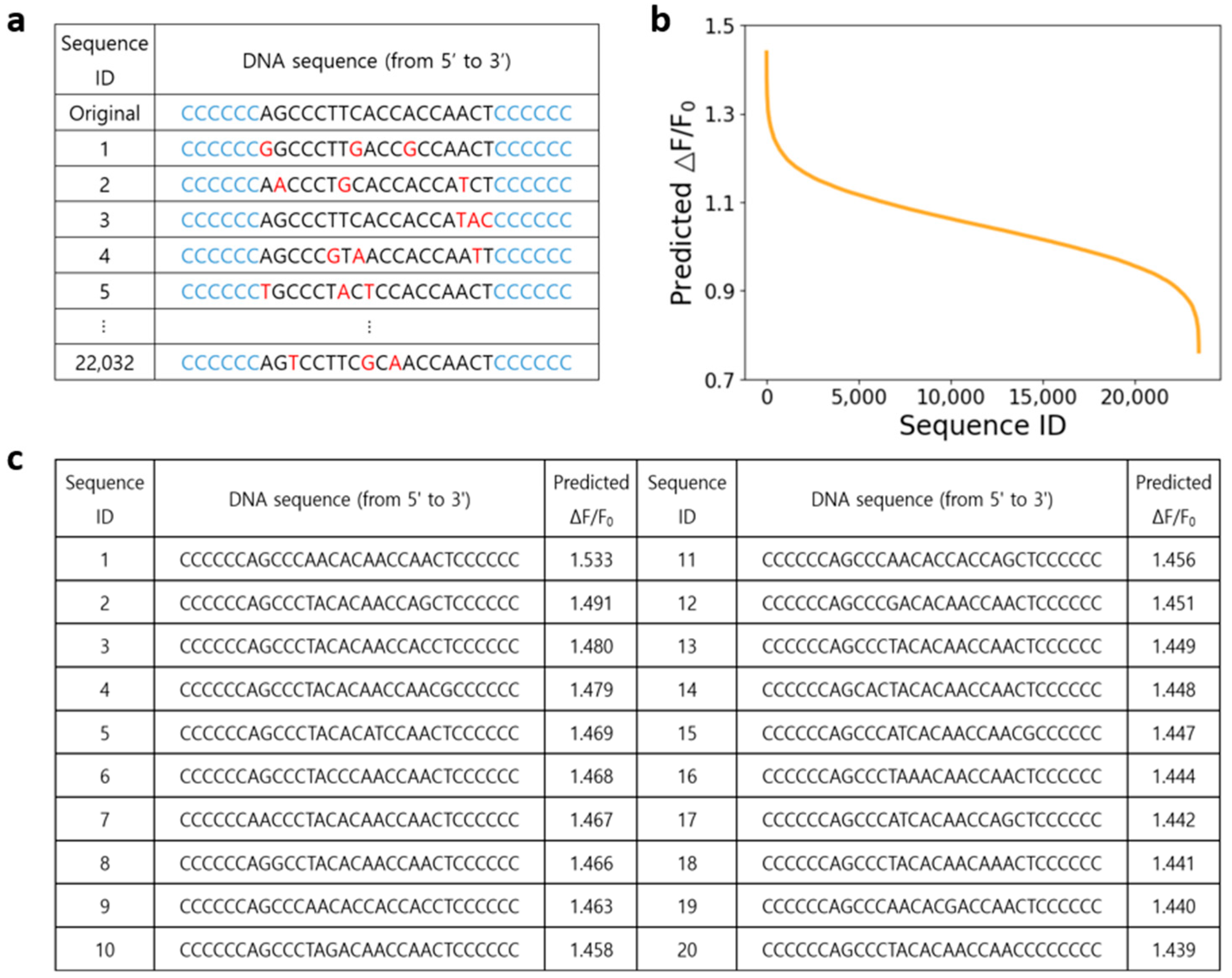
3.1. Directed Evolution with Machine Learning Prediction
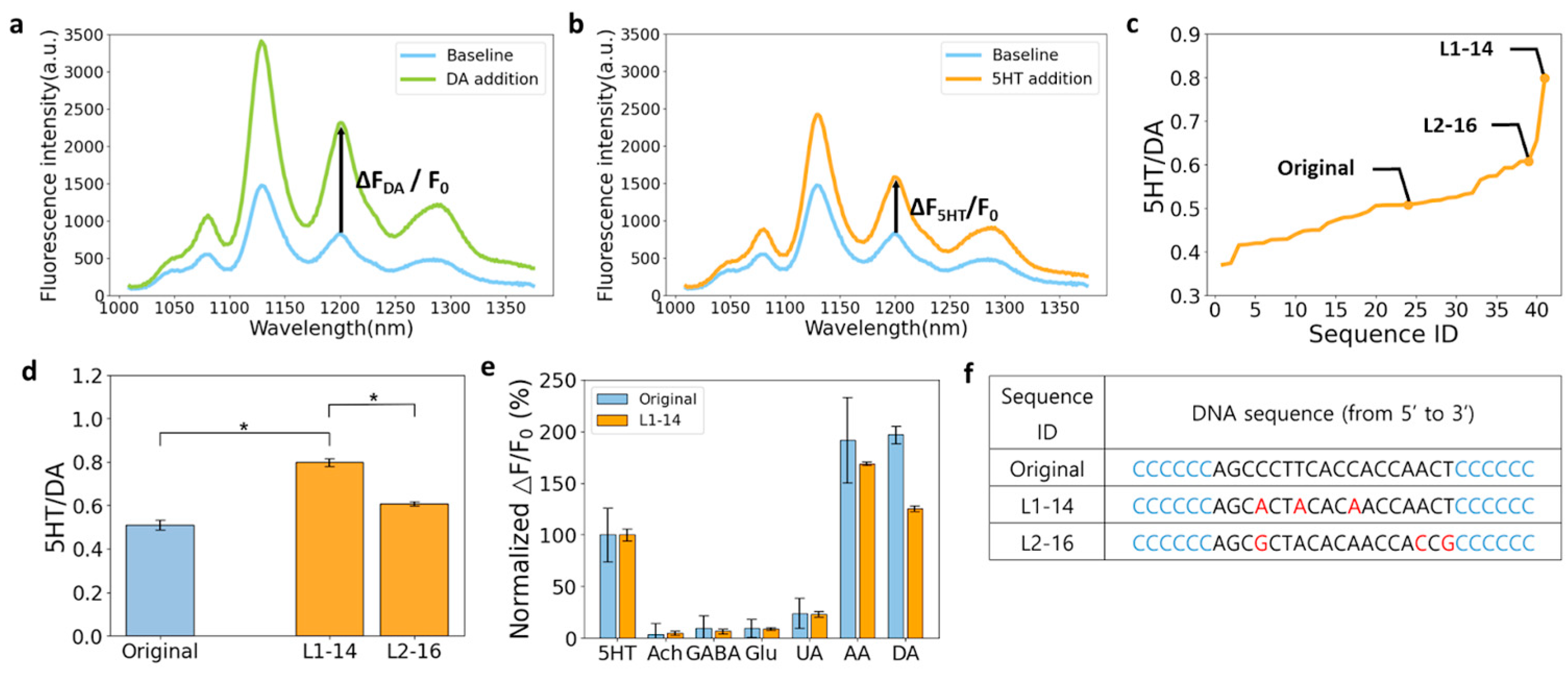
3.2. Towards 5HT Nanosensors with Higher Sensitivity
3.3. Towards 5HT Nanosensors with Higher Selectivity
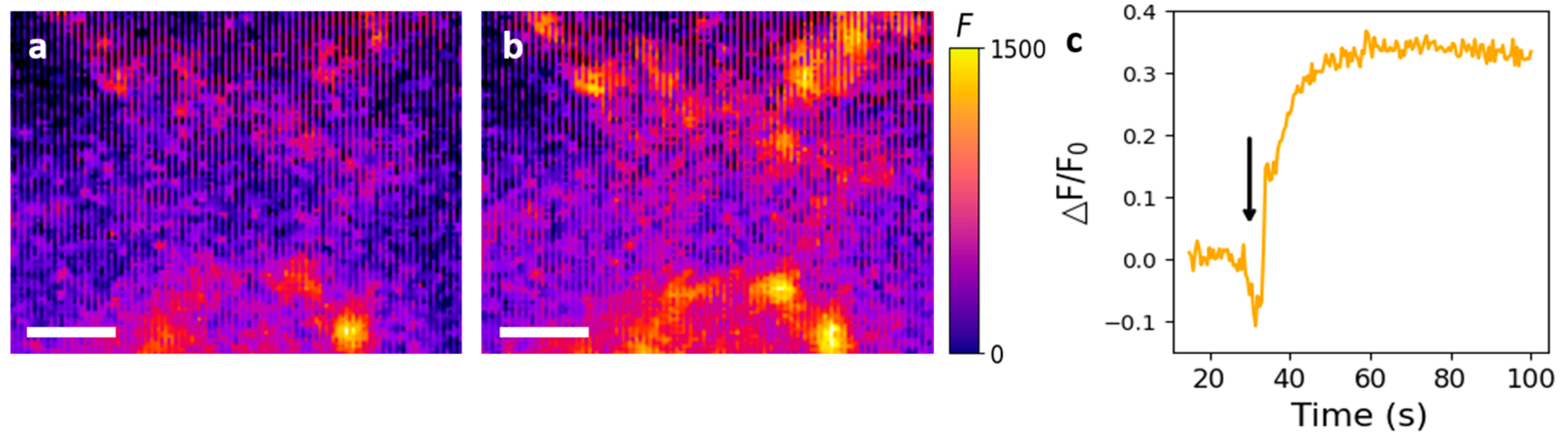
3.4. Fluorescence Image Analysis of Surface-Immobilized Nanosensors after 5HT Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, P. Surface Plasmon Resonance: A Boon for Viral Diagnostics; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-809633-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ligler, F.S. Perspective on optical biosensors and integrated sensor systems. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J. Optical biosensors: An exhaustive and comprehensive review. Analyst 2020, 145, 1605–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruss, S.; Hilmer, A.J.; Zhang, J.; Reuel, N.F.; Mu, B.; Strano, M.S. Carbon nanotubes as optical biomedical sensors. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1933–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, R.; Dutta, D.; Sarkar, A.; Chattopadhyay, P. Functionalized carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, properties and applications in water purification, drug delivery, and material and biomedical sciences. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 5722–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Simón, B.; Bandaru, N.M.; Saint, C.; Voelcker, N.H. Tailored carbon nanotube immunosensors for the detection of microbial contamination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, J.; Metternich, J.T.; Herbertz, S.; Kruss, S. Biosensing with fluorescent carbon nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boghossian, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Barone, P.W.; Reuel, N.F.; Kim, J.-H.; Heller, D.A.; Ahn, J.H.; Hilmer, A.J.; Rwei, A.; Arkalgud, J.R.; et al. Near-Infrared Fluorescent Sensors based on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Life Sciences Applications. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 848–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendler-Neumark, A.; Bisker, G. Fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotubes for protein detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Zadeh, L.F.; Moses, L.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.M. Serotonin: A review. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 31, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhong, M.; Dong, J.; Chen, M.; Shang, J.; Yue, Y. 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) positively regulates pigmentation via inducing melanoblast specification and melanin synthesis in zebrafish embryos. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeff, F.G.; Guimarães, F.S.; De Andrade, T.G.; Deakin, J.F. Role of 5-HT in stress, anxiety, and depression. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1996, 54, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Yang, D.; Beyene, A.G.; Bonis-O’Donnell, J.T.D.; Gest, A.M.M.; Navarro, N.; Sun, X.; Landry, M.P. High-throughput evolution of near-infrared serotonin nanosensors. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaay3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarvand, M.; Neubert, E.; Meyer, D.; Selvaggio, G.; Mann, F.A.; Erpenbeck, L.; Kruss, S. Near-infrared imaging of serotonin release from cells with fluorescent nanosensors. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 6604–6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.K.; Wu, Z.; Arnold, F.H. Machine-learning-guided directed evolution for protein engineering. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, F.H. Design by directed evolution. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.S.; Liu, D.R. Methods for the directed evolution of proteins. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, B.; Gillen, A.J.; Schuergers, N.; Wu, S.; Boghossian, A.A. Directed evolution of the optoelectronic properties of synthetic nanomaterials. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 3239–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelich, P.; Jeong, S.; Navarro, N.; Adams, J.; Sun, X.; Zhao, H.; Landry, M.P.; Vuković, L. Discovery of DNA–Carbon nanotube sensors for serotonin with machine learning and near-infrared fluorescence spectroscopy. ACS Nano 2021, 16, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hie, B.L.; Shanker, V.R.; Xu, D.; Bruun, T.U.J.; Weidenbacher, P.A.; Tang, S.; Wu, W.; Pak, J.E.; Kim, P.S. Efficient evolution of human antibodies from general protein language models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhöfer, T.G.; Mutschke, H.; Popp, J. Employing Theories Far beyond Their Limits—The Case of the (Boguer-) Beer–Lambert Law. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruss, S.; Landry, M.P.; Ende, E.V.; Lima, B.M.; Reuel, N.F.; Zhang, J.; Nelson, J.; Mu, B.; Hilmer, A.; Strano, M. Neurotransmitter Detection Using Corona Phase Molecular Recognition on Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo, E.; Kruss, S. Impact of Redox-Active Molecules on the Fluorescence of Polymer-Wrapped Carbon Nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 3061–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillen, A.J.; Kupis-Rozmyslowicz, J.; Gigli, C.; Schuergers, N.; Boghossian, A.A. Xeno Nucleic Acid Nanosensors for Enhanced Stability Against Ion-Induced Perturbations. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 4336–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, N.; Heard, K.J.; Faillétaz, A.; Momotenko, D.; Vörös, J.; Gage, F.H.; Vadodaria, K.C. Sensing serotonin secreted from human serotonergic neurons using aptamer-modified nanopipettes. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, S.; Suh, Y.; Kelich, P.; Lee, D.; Vukovic, L.; Jeong, S. Directed Evolution of Near-Infrared Serotonin Nanosensors with Machine Learning-Based Screening. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030247
An S, Suh Y, Kelich P, Lee D, Vukovic L, Jeong S. Directed Evolution of Near-Infrared Serotonin Nanosensors with Machine Learning-Based Screening. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(3):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030247
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Seonghyeon, Yeongjoo Suh, Payam Kelich, Dakyeon Lee, Lela Vukovic, and Sanghwa Jeong. 2024. "Directed Evolution of Near-Infrared Serotonin Nanosensors with Machine Learning-Based Screening" Nanomaterials 14, no. 3: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030247





