Ku-Band Mixers Based on Random-Oriented Carbon Nanotube Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Randomly Oriented Carbon Nanotube Films
2.1.1. Preparation of the CNT Films
2.1.2. Pretreatment of the CNT Films before Transistor Fabrication
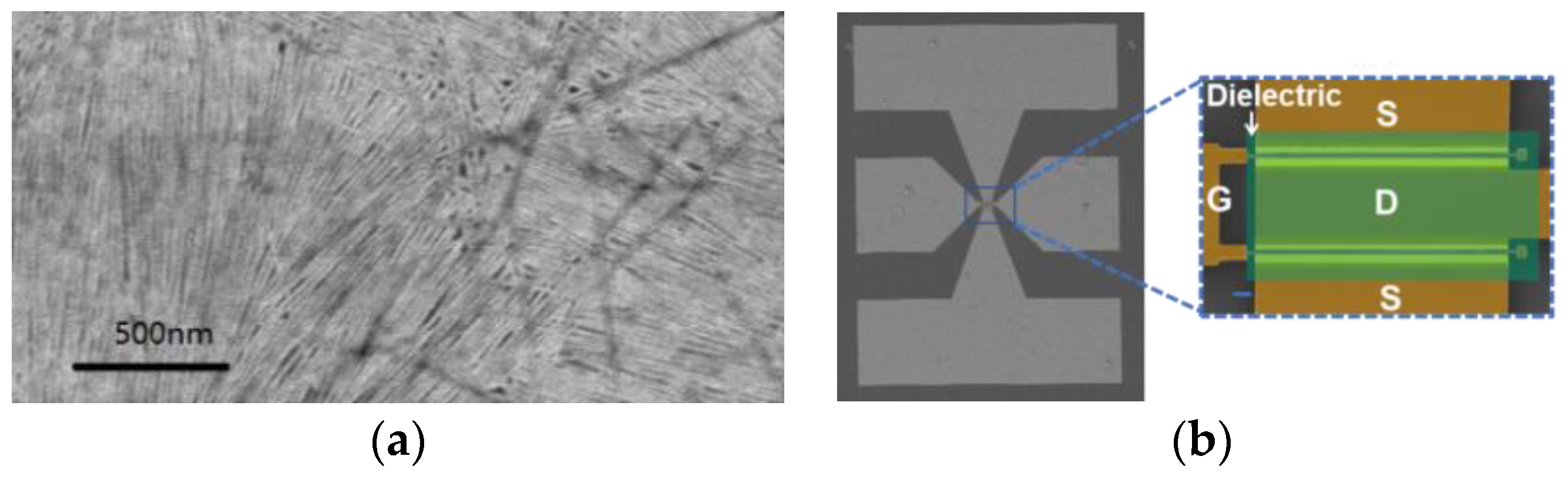
2.1.3. Characterization of the CNT Films
2.2. Fabrication of Carbon Nanotube RF Transistors
2.3. Measurement of S Parameter
2.4. Measurement of Mixer
2.4.1. Mixing Performance Measurement of the Mixer
2.4.2. Linearity Measurement of Mixer
3. Results and Discussion
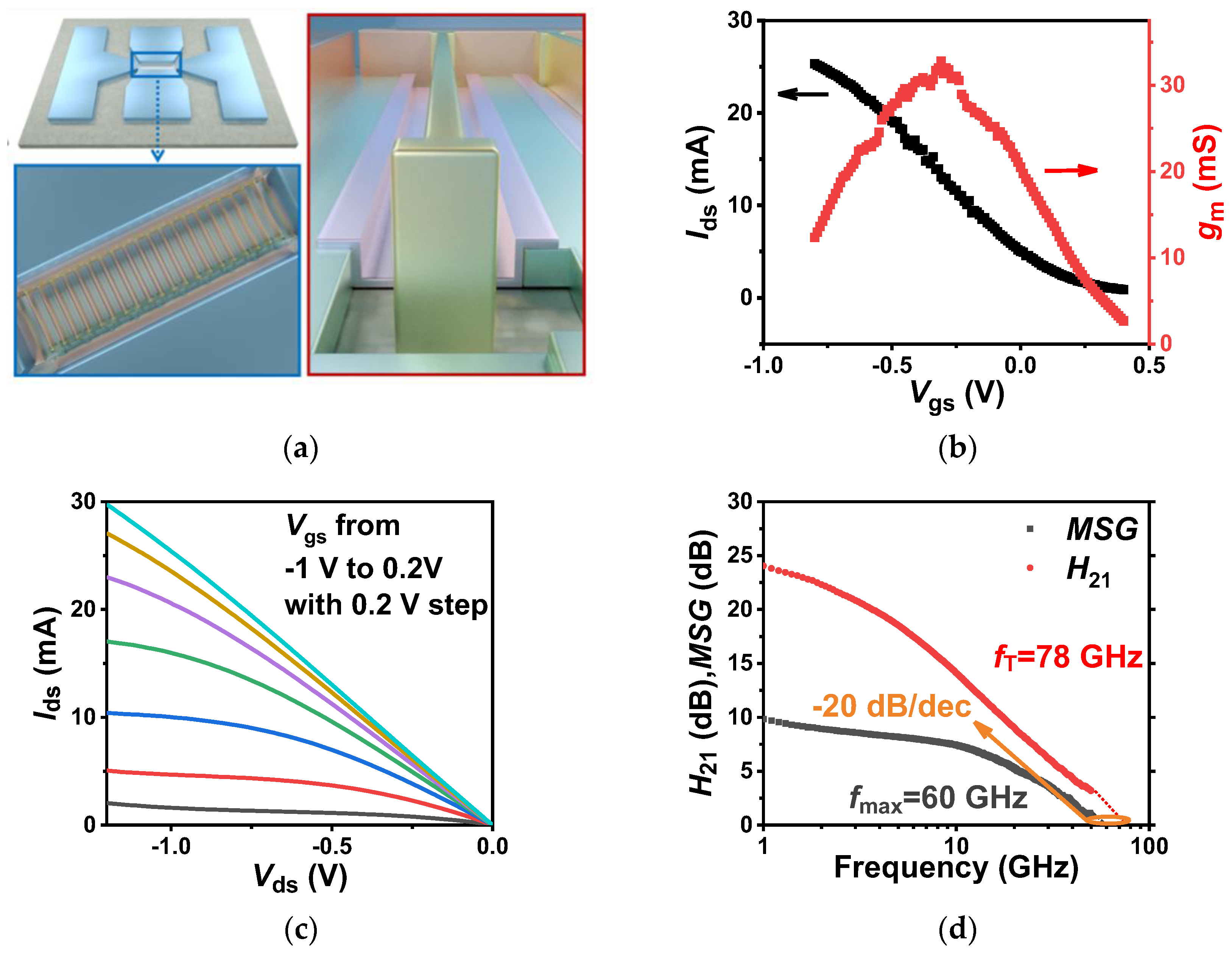
3.1. Electrical Characterization of RF Transistors
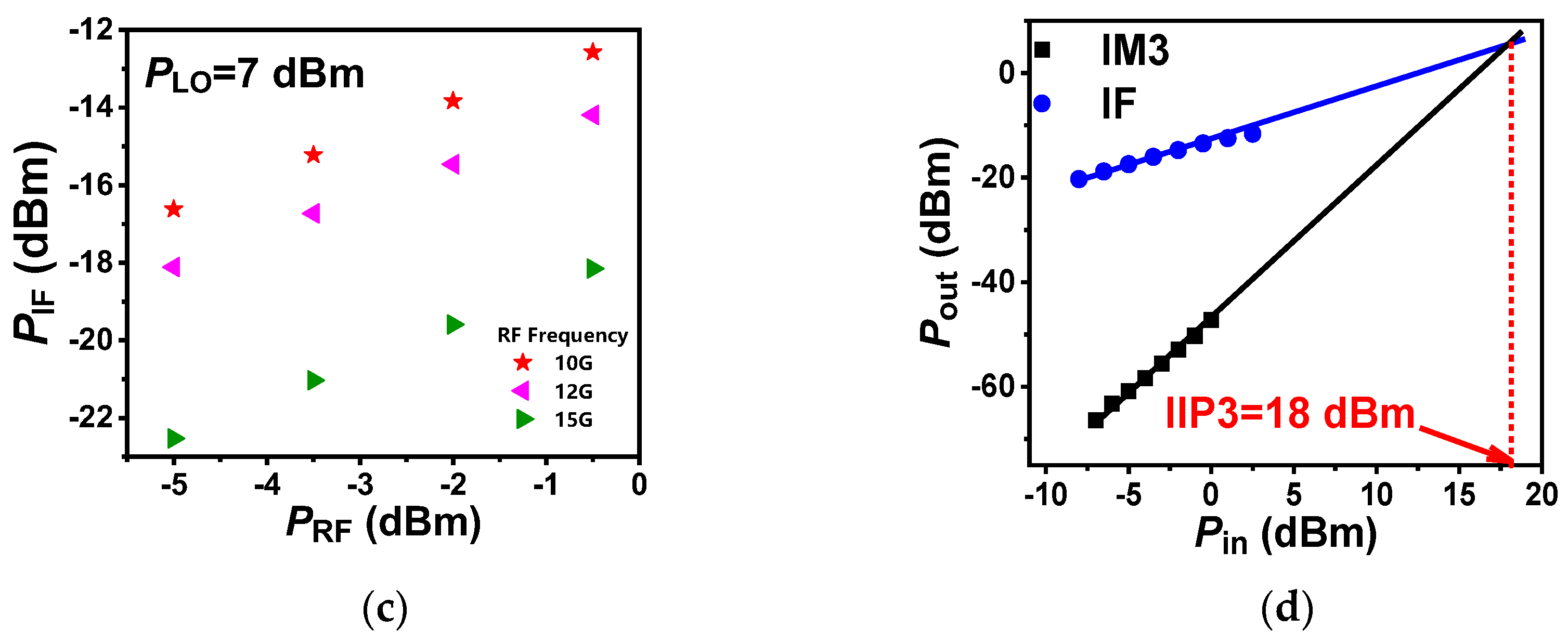
3.2. Mixing Performance Characterization of Mixer
3.3. Benchmarking of Mixers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iijima, S. Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Park, J.-Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, J.; McEuen, P.L. Band Structure, Phonon Scattering, and the Performance Limit of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Transistors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 146805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherglen, C.; Jain, D.; Burke, P. Nanotube Electronics for Radiofrequency Applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avouris, P.; Chen, Z.; Perebeinos, V. Carbon-Based Electronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, A.D. Electronics: The Road to Carbon Nanotube Transistors. Nature 2013, 498, 443–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.-M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. Carbon Nanotube Electronics: Recent Advances. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.J. Application of the Johnson Criteria to Graphene Transistors. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2013, 28, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Ago, H.; Takahashi, K.; Ikuta, T.; Abe, H.; Shimizu, T. Measuring the Thermal Conductivity of a Single Carbon Nanotube. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 065502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paydavosi, N.; Alam, A.U.; Ahmed, S.; Holland, K.D.; Rebstock, J.P.; Vaidyanathan, M. RF Performance Potential of Array-Based Carbon-Nanotube Transistors—Part I: Intrinsic Results. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2011, 58, 1928–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paydavosi, N.; Rebstock, J.P.; Holland, K.D.; Ahmed, S.; Alam, A.U.; Vaidyanathan, M. RF Performance Potential of Array-Based Carbon-Nanotube Transistors—Part II: Extrinsic Results. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2011, 58, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Shi, H.; Ding, L.; Zhao, C.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, L.-M. Carbon Nanotube Film-Based Radio Frequency Transistors with Maximum Oscillation Frequency above 100 GHz. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 42496–42503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Brady, G.J.; Gui, H.; Rutherglen, C.; Arnold, M.S.; Zhou, C. Radio Frequency Transistors Using Aligned Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes with Current-Gain Cutoff Frequency and Maximum Oscillation Frequency Simultaneously Greater than 70 GHz. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6782–6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geier, M.L.; McMorrow, J.J.; Xu, W.; Zhu, J.; Kim, C.H.; Marks, T.J.; Hersam, M.C. Solution-Processed Carbon Nanotube Thin-Film Complementary Static Random Access Memory. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chien, J.-C.; Takei, K.; Takahashi, T.; Nah, J.; Niknejad, A.M.; Javey, A. Extremely Bendable, High-Performance Integrated Circuits Using Semiconducting Carbon Nanotube Networks for Digital, Analog, and Radio-Frequency Applications. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, P.; Ding, L.; Han, J.; Qiu, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, L.-M. Highly Uniform Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistors and Medium Scale Integrated Circuits. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5120–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, L.-M. High-Performance Complementary Transistors and Medium-Scale Integrated Circuits Based on Carbon Nanotube Thin Films. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4124–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherglen, C.; Kane, A.A.; Marsh, P.F.; Cain, T.A.; Hassan, B.I.; AlShareef, M.R.; Zhou, C.; Galatsis, K. Wafer-Scalable, Aligned Carbon Nanotube Transistors Operating at Frequencies of over 100 GHz. Nat. Electron. 2019, 2, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Ding, L.; Zhong, D.; Han, J.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Sun, P.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Fang, L.; et al. Radiofrequency Transistors Based on Aligned Carbon Nanotube Arrays. Nat. Electron. 2021, 4, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ren, L.; Li, H.; Cheng, X.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, L.; Peng, L.-M. Carbon Nanotube Radiofrequency Transistors with fT/fMAX of 376/318 GHz. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2023, 44, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, L.; Han, J.; Xiao, M.; Si, J.; Xu, L.; Qiu, C.; Peng, L.-M. Gigahertz Integrated Circuits Based on Carbon Nanotube Films. Nat. Electron. 2017, 1, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, L.; Shi, H.; Zhu, M.; Cheng, X.; Ren, L.; Ding, L.; Peng, L.-M.; Zhang, Z. Carbon Nanotube Based Radio Frequency Transistors for K-Band Amplifiers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 37475–37482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.; Saeed, M.; Negra, R. Graphene-Based Frequency-Conversion Mixers for High-Frequency Applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Technol. 2020, 68, 2090–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y. Improvement of Conversion Loss of Resistive Mixers Using Bernal-Stacked Bilayer Graphene. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2019, 40, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.S.; Seo, H.-C.; Antcliffe, M.; Le, D.; McGuire, C.; Schmitz, A.; Nyakiti, L.O.; Gaskill, D.K.; Campbell, P.M.; Lee, K.-M.; et al. Graphene FETs for Zero-Bias Linear Resistive FET Mixers. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2013, 34, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Ma, T.; Niu, J.; Ren, W.; et al. Double-Balanced Graphene Integrated Mixer with Outstanding Linearity. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6677–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-M.; Valdes-Garcia, A.; Han, S.-J.; Farmer, D.B.; Meric, I.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dimitrakopoulos, C.; Grill, A.; Avouris, P.; et al. Wafer-Scale Graphene Integrated Circuit. Science 2011, 332, 1294–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Kim, P.; Zhou, C. T-Gate Aligned Nanotube Radio Frequency Transistors and Circuits with Superior Performance. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4343–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhong, D.; Han, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, L. Exploring the Performance Limit of Carbon Nanotube Network Film Field-Effect Transistors for Digital Integrated Circuit Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Han, J.; Liu, D.; Yu, X.; Kang, L.; Qiu, S.; Jin, H.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J. Solution-Processable High-Purity Semiconducting SWCNTs for Large-Area Fabrication of High-Performance Thin-Film Transistors. Small 2016, 12, 4993–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Han, J.; Yao, S.; Wang, S.; Peng, L.-M. Improving the Performance and Uniformity of Carbon-Nanotube-Network-Based Photodiodes via Yttrium Oxide Coating and Decoating. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11736–11742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, Z. Terahertz Transistors Based on Aligned Carbon Nanotube Arrays. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2022, 65, 117301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, D. Modern Microwave Transistors—Theory, Design and Performance. (The Book End). Microw. J. 2003, 46, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Koster, N.H.L. C/NL2 for Windows: Linear and Nonlinear Microwave Circuit Analysis and Optimization, by Stephen A. Maas and Arthur Nichols, Nonlinear Consulting, P.O. Box 7284, Long Beach, CA 90807, USA. Tel/Fax: 310-426-1639. Int. J. Microw. Millim.-Wave Comput.-Aided Eng. 1994, 4, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Y. Scalable High Performance Radio Frequency Electronics Based on Large Domain Bilayer MoS2. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-D.; Lin, Z.-M. 2.4 GHz High IIP3 and Low-Noise Down-Conversion Mixer. In Proceedings of the APCCAS 2006—2006 IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems, Singapore, 4–7 December 2006; IEEE: Singapore, 2006; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- HMC220B Datasheet: GaAs, MMIC, Fundamental Mixer, Analog Devices. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/hmc220b.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2023).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, M.; Qian, J.; Li, Z.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Cao, J.; Ding, L. Ku-Band Mixers Based on Random-Oriented Carbon Nanotube Films. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14050450
Chang M, Qian J, Li Z, Cheng X, Wang Y, Fan L, Cao J, Ding L. Ku-Band Mixers Based on Random-Oriented Carbon Nanotube Films. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(5):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14050450
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Mengnan, Jiale Qian, Zhaohui Li, Xiaohan Cheng, Ying Wang, Ling Fan, Juexian Cao, and Li Ding. 2024. "Ku-Band Mixers Based on Random-Oriented Carbon Nanotube Films" Nanomaterials 14, no. 5: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14050450
APA StyleChang, M., Qian, J., Li, Z., Cheng, X., Wang, Y., Fan, L., Cao, J., & Ding, L. (2024). Ku-Band Mixers Based on Random-Oriented Carbon Nanotube Films. Nanomaterials, 14(5), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14050450






