Investigating the ROS Formation and Particle Behavior of Food-Grade Titanium Dioxide (E171) in the TIM-1 Dynamic Gastrointestinal Digestion Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Determination of a Physiologically Relevant E171 Dose
2.2. E171-aq and E171-yog Sample Preparation
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization of E171-aq and E171-yog
2.4. Measurement of ROS Formation via Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Spectroscopy of E171-aq and E171-yog
2.5. TIM-1 Model
2.6. Preparation of TIM-1 Samples
2.7. Physicochemical Characterization of TIM-1 Samples
2.8. Measurement of ROS Formation via ESR Spectroscopy of TIM-1 Samples
2.9. Analysis of Protein Corona Formation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Particle Characterization in E171-aq and E171-yog
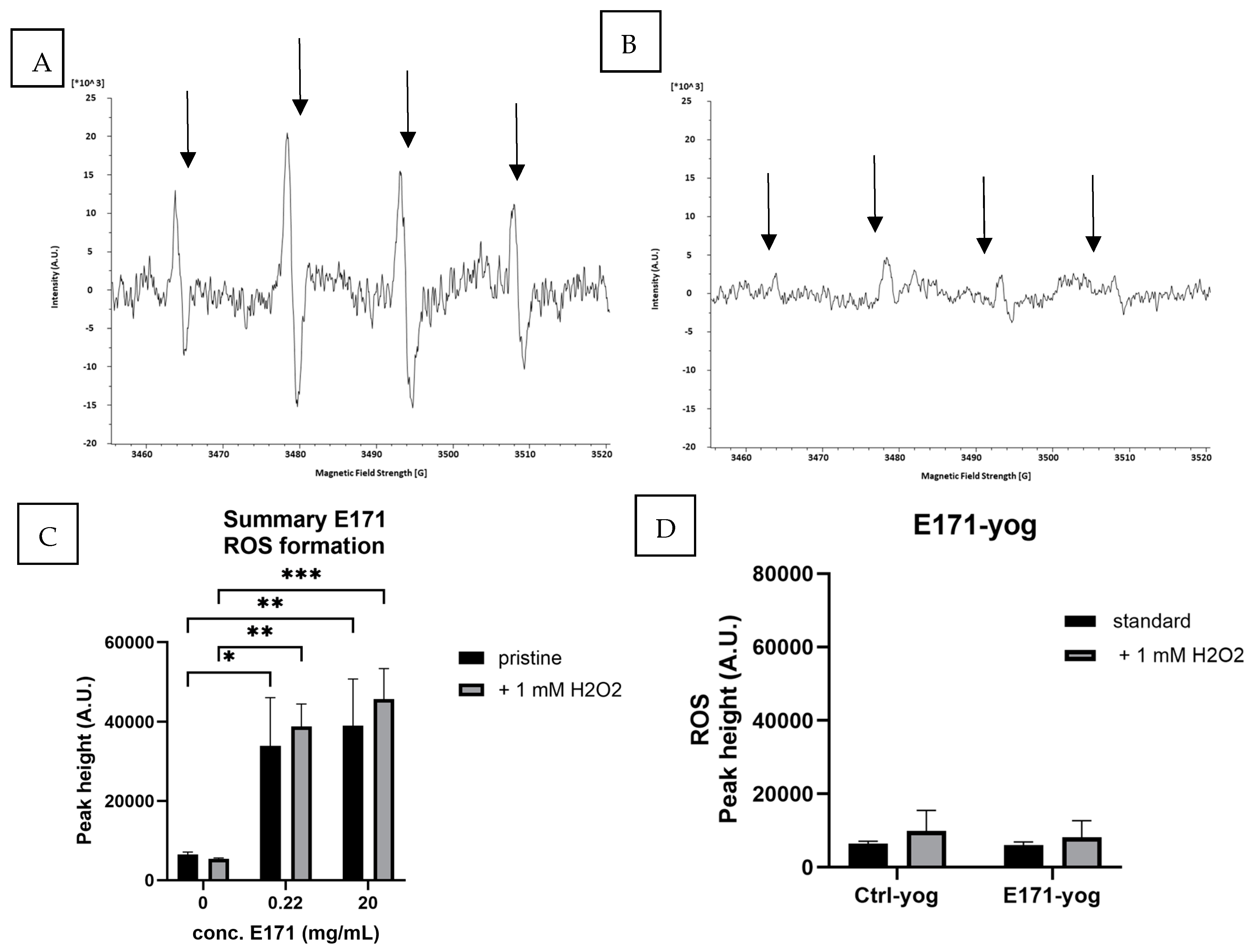
3.2. ROS Formation in E171-aq and E171-yog
3.3. Particle Characterization of TIM-1 Digested E171-aq and Digested E171-yog
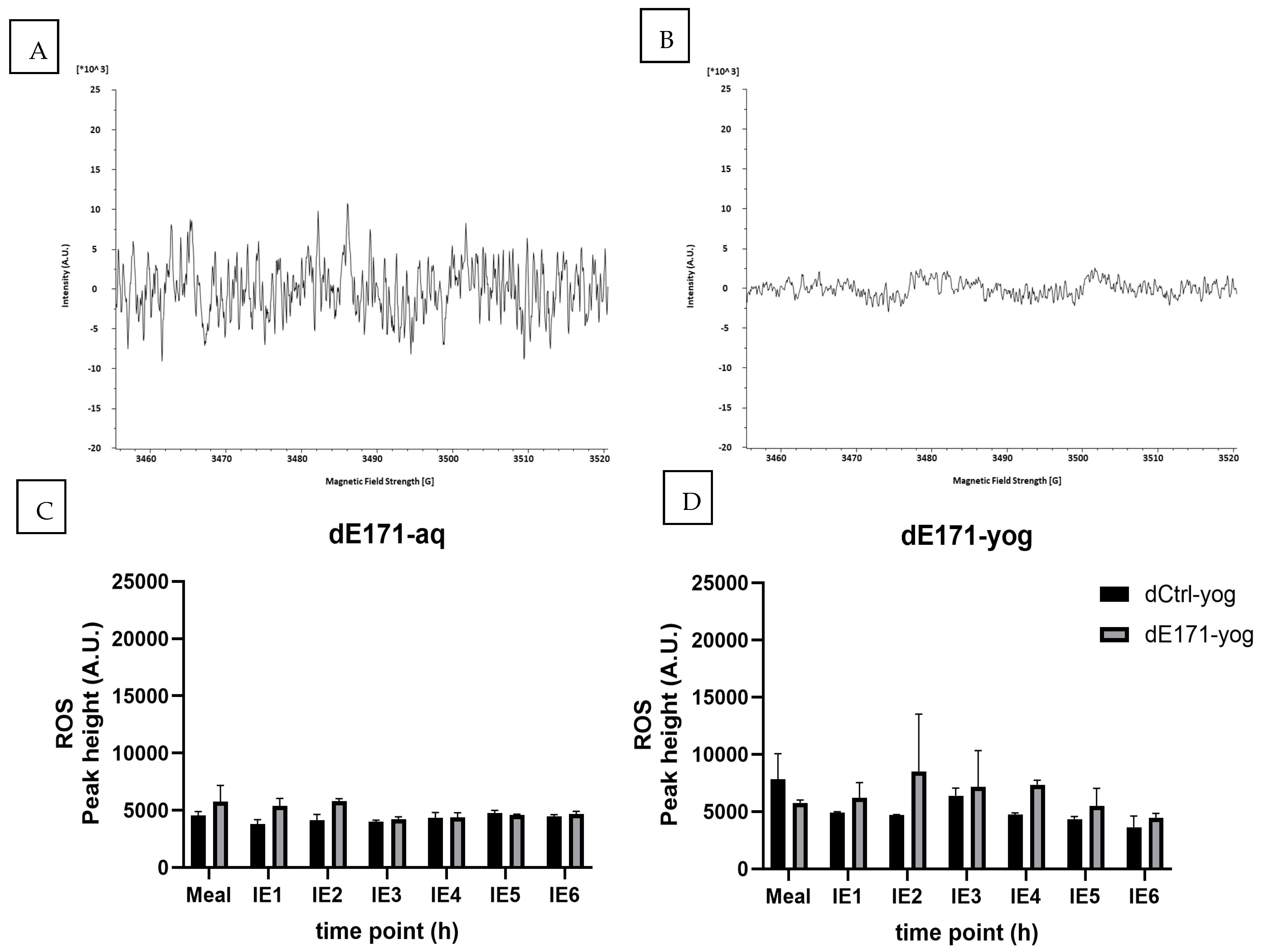
3.4. ROS Formation Digested E171-aq and Digested E171-yog
4. Protein Corona
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOM | Azoxymethane |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| Ctrl-aq | Control aqueous dispersion |
| Ctrl-yog | Control yogurt dispersion |
| dCtrl-aq | Digested control aqueous dispersion |
| dCtrl-yog | Digested control yogurt dispersion |
| dE171-aq | Digested E171 in aqueous dispersion |
| dE171-yog | Digested E171 in yogurt dispersion |
| DF | Dilution factor |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| DMPO | 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide |
| DSS | Dextran sodium sulfate |
| E171-aq | E171 in aqueous dispersion |
| E171-yog | E171 in yogurt dispersion |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| EM | Electron microscopy |
| ESR | Electron spin resonance |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| GES | Gastric enzymatic solution |
| HD | Hydrodynamic diameter |
| IE | Ileal efflux |
| JCR | Joint Research Centre |
| LDS | Lithium dodecyl sulfate |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffer saline |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| spICP-MS | Single-particle-induced coupled mass spectrometry |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| TIM | TNO gastrointestinal model |
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| TNO | Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research |
References
- Bischoff, N.S.; de Kok, T.M.; Sijm, D.; van Breda, S.G.; Briedé, J.J.; Castenmiller, J.J.M.; Opperhuizen, A.; Chirino, Y.I.; Dirven, H.; Gott, D.; et al. Possible Adverse Effects of Food Additive E171 (Titanium Dioxide) Related to Particle Specific Human Toxicity, Including the Immune System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, A.; Westerhoff, P.; Fabricius, L.; Hristovski, K.; von Goetz, N. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Food and Personal Care Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Flavourings (FAF); Younes, M.; Aquilina, G.; Castle, L.; Engel, K.-H.; Fowler, P.; Fernandez, M.J.F.; Fürst, P.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Gürtler, R.; et al. Safety Assessment of Titanium Dioxide (E171) as a Food Additive. Efsa J. 2021, 19, e06585. [Google Scholar]
- Lamas, B.; Evariste, L.; Houdeau, E. Dysregulation Along the Gut Microbiota—Immune System Axis After Oral Exposure to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: A Possible Environmental Factor Promoting Obesity—Related Metabolic Disorders*. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Der Leyen, U. Commission Regulation (EU) 2022/63 of 14 January 2022 Amending Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards the Food Additive Titanium Dioxide (E 171) (Text with EEA relevance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2022, L11/1. [Google Scholar]
- Bettini, S.; Boutet-Robinet, E.; Cartier, C.; Coméra, C.; Gaultier, E.; Dupuy, J.; Naud, N.; Taché, S.; Grysan, P.; Reguer, S.; et al. Food-grade TiO2 Impairs Intestinal and Systemic Immune Homeostasis, Initiates Preneoplastic Lesions and Promotes Aberrant Crypt Development in the Rat Colon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia-Ortega, I.M.; Garduño-Balderas, L.G.; Delgado-Buenrostro, N.L.; Freyre-Fonseca, V.; Flores-Flores, J.O.; González-Robles, A.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Hernández-Pando, R.; Rodríguez-Sosa, M.; León-Cabrera, S.; et al. Food-Grade Titanium Dioxide Exposure Exacerbates Tumor Formation in Colitis Associated Cancer Model. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 93, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Proquin, H.; Jetten, M.J.; Jonkhout, M.C.; Garduño-Balderas, L.G.; Briedé, J.J.; de Kok, T.M.; Chirino, Y.I.; van Loveren, H. Gene Expression Profiling in Colon of Mice Exposed to Food Additive Titanium Dioxide (E171). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proquin, H.; Jetten, M.J.; Jonkhout, M.C.M.; Garduño-Balderas, L.G.; Briedé, J.J.; de Kok, T.M.; van Loveren, H.; Chirino, Y.I. Transcriptomics Analysis Reveals New Insights in E171—Induced Molecular Alterations in a Mouse Model of Colon Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9738. [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff, N.S.; Proquin, H.; Jetten, M.J.; Schrooders, Y.; Jonkhout, M.C.M.; Briedé, J.J.; van Breda, S.G.; Jennen, D.G.J.; Medina-Reyes, E.I.; Delgado-Buenrostro, N.L.; et al. The Effects of the Food Additive Titanium Dioxide (E171) on Tumor Formation and Gene Expression in the Colon of a Transgenic Mouse Model for Colorectal Cancer. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proquin, H.; Rodriguez-Ibarra, C.; Moonen, C.G.; Urrutia-Ortega, I.M.; Briede, J.J.; de Kok, T.M.; van Loveren, H.; Chirino, Y.I. Titanium Dioxide Food Additive (E171) Induces ROS Formation and Genotoxicity: Contribution of Micro and Nano-Sized Fractions. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 139–149, Erratum in Mutagenesis 2018, 33, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, C.; Bello, D.; Kelleher, S.L.; Tucker, K.L.; Mangano, K.M. Stool Titanium Dioxide is Positively Associated with Stool Alpha-1 Antitrypsin and Calprotectin in Young Healthy Adults. NanoImpact 2024, 33, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Administration USFaD. Titanium Dioxide as a Color Additive in Foods; USFaD: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Health Canada’s Food Directorate. Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) as a Food Additive: Current Science Report; Health Canada’s Food Directorate: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Blevins, L.K.; Crawford, R.B.; Bach, A.; Rizzo, M.D.; Zhou, J.; Henriquez, J.E.; Khan, D.M.I.O.; Sermet, S.; Arnold, L.L.; Pennington, K.L.; et al. Evaluation of immunologic and intestinal effects in rats administered an E 171-containing diet, a food grade titanium dioxide (TiO2). Food Chem Toxicol. 2019, 133, 110793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, F.; Raggi, A.; Ponti, J.; Mehn, D.; Gilliland, D.; Savini, S.; Iacoponi, F.; Aureli, F.; Aureli, L.; Cubadda, F. Agglomeration Behavior and Fate of Food-Grade Titanium Dioxide in Human Gastrointestinal Digestion and in the Lysosomal Environment. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudefoi, W.; Rabesona, H.; Rivard, C.; Mercier-Bonin, M.; Humbert, B.; Terrisse, H.; Ropers, M.-H. In vitro digestion of food grade TiO2(E171) and TiO2 nanoparticles: Physicochemical characterization and impact on the activity of digestive enzymes. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5975–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska-Wojcik, E.; Szwajgier, D.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A. A review of research on the impact of E171/TiO2 NPs on the digestive tract. J. Trace Elem. Med. Bio. 2022, 72, 126988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoz, N.; Canga, E.M.; Yildirim-Elikoglu, S.; Oz, H.; Dudak, F.C. Effect of real food matrix on the behavior and toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2022, 24, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, A.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Gramacho, A.C.; Vieira, A.; Rolo, D.; Martins, C.; Assunção, R.; Alvito, P.; Silva, M.J.; Louro, H. Analysis of the Characteristics and Cytotoxicity of Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials Following Simulated In Vitro Digestion. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.; Vital, N.; Rolo, D.; Roque, R.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Bettencourt, A.; Silva, M.J.; Louro, H. Investigation of the genotoxicity of digested titanium dioxide nanomaterials in human intestinal cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 161, 112841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleysen, E.; Waegeneers, N.; Brassinne, F.; De Vos, S.; Jimenez, I.O.; Mathioudaki, S.; Mast, J. Physicochemical Characterization of the Pristine E171 Food Additive by Standardized and Validated Methods. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M. The TNO Gastro-Intestinal Model (TIM). In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Verhoeckx, K., Cotter, P., Lopez-Exposito, I., Kleiveland, C., Lea, T., Mackie, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) related to L-Carnitine-L-tartrate for use in foods for particular nutritional purposes. EFSA J. 2003, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hjartåker, A.; Lagiou, A.; Slimani, N.; Lund, E.; Chirlaque, M.D.; Vasilopoulou, E.; Zavitsanos, X.; Berrino, F.; Sacerdote, C.; Ocké, M.; et al. Consumption of dairy products in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort: Data from 35955 24-hour dietary recalls in 10 European countries. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Action, N.J. NANOGENOTOX Final report. In Facilitating the Safety Evaluation of Manufactured Nanomaterials by Characterising Their Potential Genotoxic Hazard; French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety (ANSES): Maisons-Alfort, France, 2013; Available online: https://www.anses.fr/en/system/files/ANSES-Ft-Nanogenotox_FinalReport.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Mech, A.; Babick, F.; Hodoroaba, V.D.; Ghane, A.M.; Wohlleben, W.; Marvin, H.; Löschner, K.; Brüngel, R.; Friedrich, C.M. The NanoDefine Methods Manual. Part 3: Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs); JRC117501; DTU Library: Lyngby, Denmark, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.W.; Liu, Y.T.; Wamer, W.G.; Yin, J.J. Electron spin resonance spectroscopy for the study of nanomaterial-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagov, A.V.; Summerhill, V.I.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Zhigmitova, E.B.; Postnov, A.Y.; Orekhov, A.N. Potential use of antioxidants for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1378335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havenaar, R.; Bellmann, S. Results from a Validated in vitro Gastrointestinal Model (TIM) used as input Data for in silico Modeling Give Highly Predictive Information for the Human Situation. Med. Res. Arch. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, H.; Porbahaie, M.; Boeren, S.; Busch, M.; Bouwmeester, H. The in vitro gastrointestinal digestion-associated protein corona of polystyrene nano- and microplastics increases their uptake by human THP-1-derived macrophages. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.; Kembouche, Y.; Christiansen, E.; Jacobsen, N.; Wallin, H.; Guiot, C.; Spalla, O.; Witscher, O. The Generic NANOGENOTOX Dispersion Protocol—Standard Operation Procedure (SOP). NANOGENOTOX Deliverable Report 3. June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen, N.P.; Caffaro, M.M.; Aravamudhan, S.; Beeravalli, L.; Prattipati, S.; Snyder, R.W.; Watson, S.L.; Patel, P.R.; Weber, F.X.; Montgomery, S.A.; et al. Simulated Gastric Digestion and In Vivo Intestinal Uptake of Orally Administered CuO Nanoparticles and TiO2 E171 in Male and Female Rat Pups. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marucco, A.; Prono, M.; Beal, D.; Alasonati, E.; Fisicaro, P.; Bergamaschi, E.; Carriere, M.; Fenoglio, I. Biotransformation of Food-Grade and Nanometric TiO2 in the Oral-Gastro-Intestinal Tract: Driving Forces and Effect on the Toxicity toward Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.S.; Susnik, E.; Drasler, B.; Taladriz-Blanco, P.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Understanding nanoparticle endocytosis to improve targeting strategies in nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5397–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreau, F.; Tisseyre, C.; Ménard, S.; Ferrand, A.; Carriere, M. Titanium dioxide particles from the diet: Involvement in the genesis of inflammatory bowel diseases and colorectal cancer. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, K.; Schrader, K.; Klempt, M. Cellular Response to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Intestinal Epithelial Caco-2 Cells is Dependent on Endocytosis-Associated Structures and Mediated by EGFR. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, H.C.; Notter, T.; Meyer, U.; Naegeli, H. Critical review of the safety assessment of titanium dioxide additives in food. J. Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saptarshi, S.R.; Duschl, A.; Lopata, A.L. Interaction of nanoparticles with proteins: Relation to bio-reactivity of the nanoparticle. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Han, Y.; Li, F.; Li, Z.; McClements, D.J.; He, L.; Decker, E.A.; Xing, B.; Xiao, H. Impact of protein-nanoparticle interactions on gastrointestinal fate of ingested nanoparticles: Not just simple protein corona effects. Nanoimpact 2019, 13, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
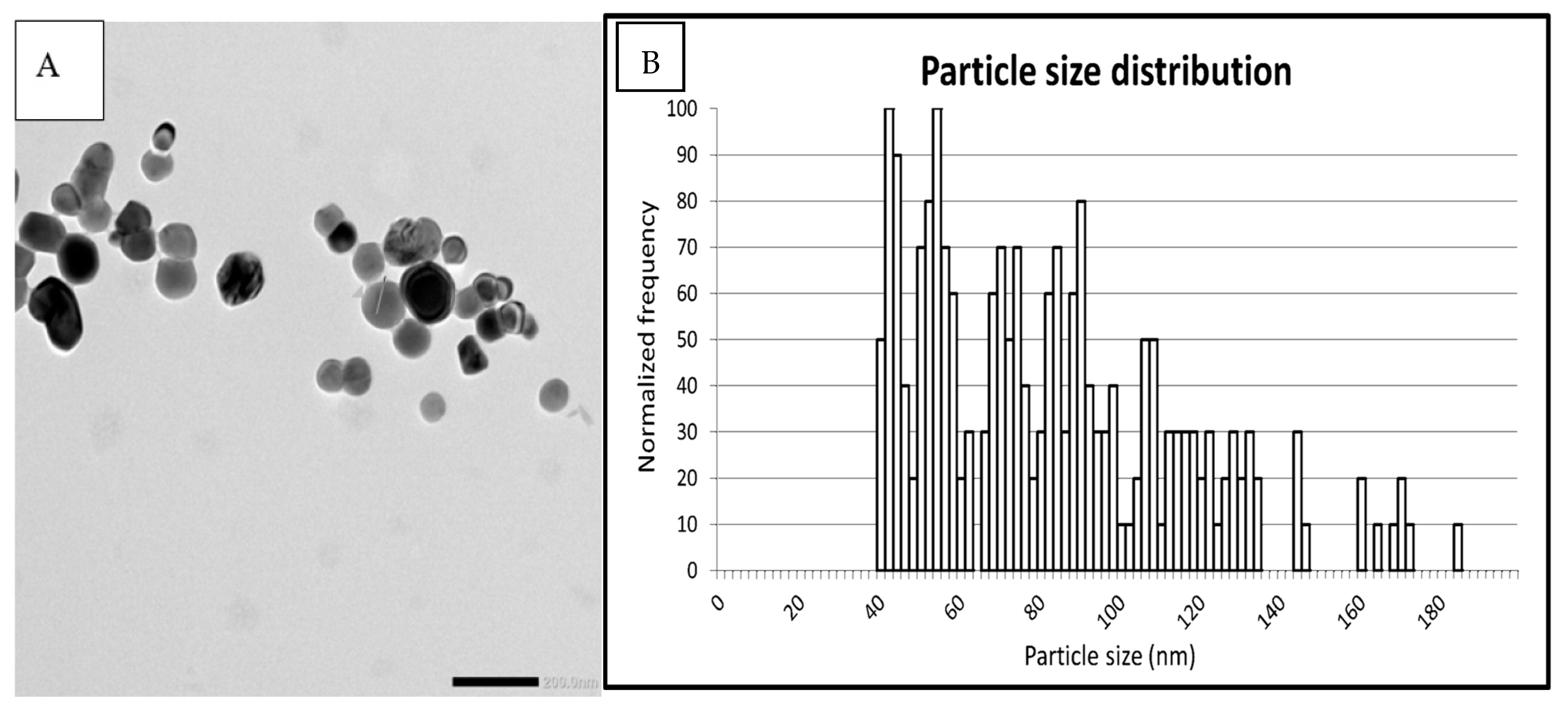
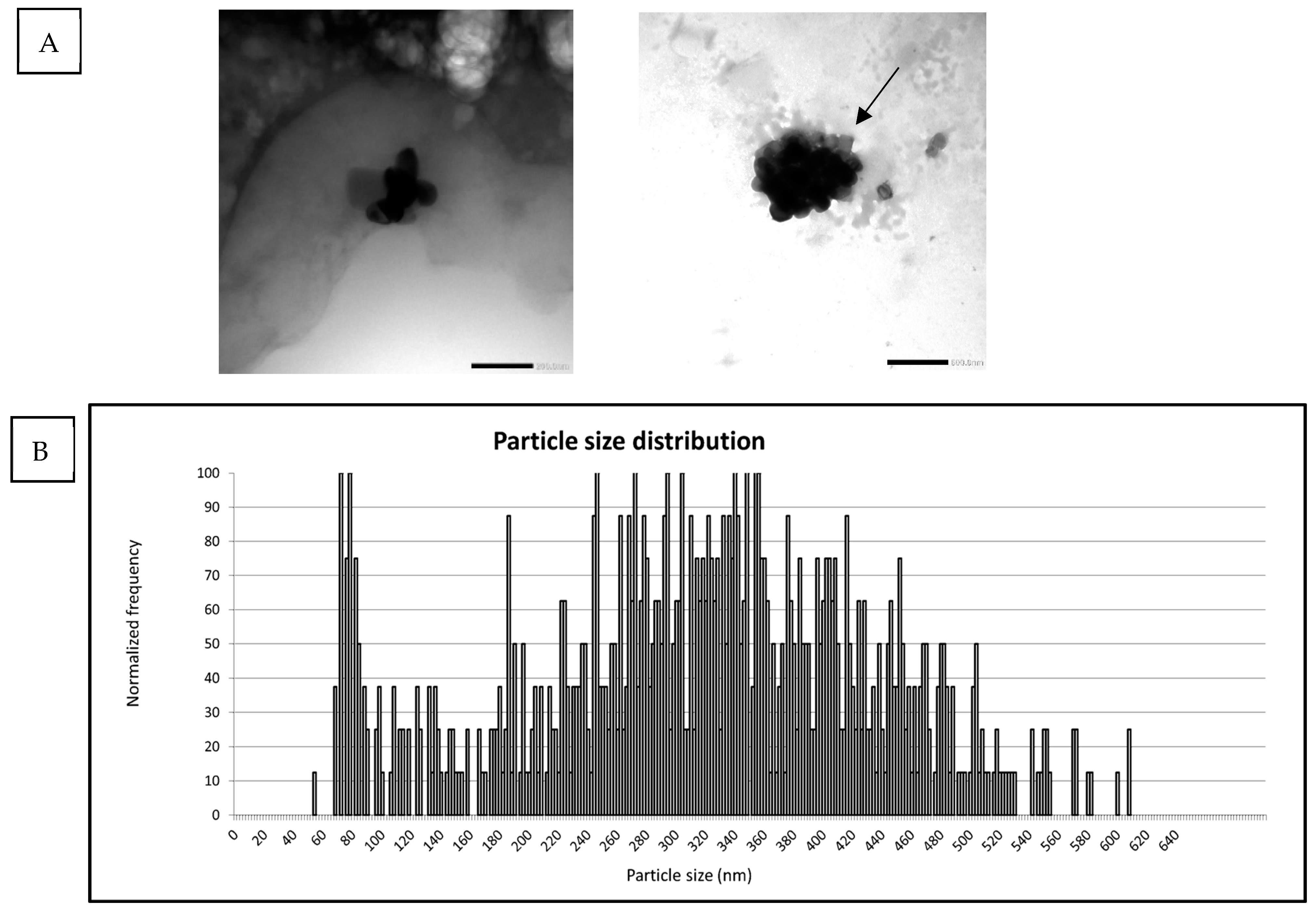


| Sample | Technique | Median Size (nm) | % of Particles < 100 nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine E171 | spICP-MS | 78 | 75 |
| Pristine E171 | TEM | 79 | 73 |
| E171-yog | spICP-MS | 282 | 15 |
| E171-yog | TEM | N/A | N/A |
| Sample | Meal | IE1 | IE2 | IE3 | IE4 | IE5 | IE6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dilution factor | N/A | N/A | 2.5 | 1.9 | 1.0 | 1.7 | 2.8 | 4.7 |
| Volume (mL) | N/A | 310 | 102 | 124 | 63.6 | 87.8 | 98.1 | 100.7 |
| E171 (mg) | N/A | 140 | 56.0 | 29.5 | 29.5 | 17.3 | 6.2 | 1.3 |
| dE171-aq (mg/mL) | 20 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 0.46 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| dE171-yog (mg/mL) | 0.9 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 0.46 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bischoff, N.S.; Undas, A.K.; van Bemmel, G.; Briedé, J.J.; van Breda, S.G.; Verhoeven, J.; Verbruggen, S.; Venema, K.; Sijm, D.T.H.M.; de Kok, T.M. Investigating the ROS Formation and Particle Behavior of Food-Grade Titanium Dioxide (E171) in the TIM-1 Dynamic Gastrointestinal Digestion Model. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010008
Bischoff NS, Undas AK, van Bemmel G, Briedé JJ, van Breda SG, Verhoeven J, Verbruggen S, Venema K, Sijm DTHM, de Kok TM. Investigating the ROS Formation and Particle Behavior of Food-Grade Titanium Dioxide (E171) in the TIM-1 Dynamic Gastrointestinal Digestion Model. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleBischoff, Nicolaj S., Anna K. Undas, Greet van Bemmel, Jacco J. Briedé, Simone G. van Breda, Jessica Verhoeven, Sanne Verbruggen, Koen Venema, Dick T. H. M. Sijm, and Theo M. de Kok. 2025. "Investigating the ROS Formation and Particle Behavior of Food-Grade Titanium Dioxide (E171) in the TIM-1 Dynamic Gastrointestinal Digestion Model" Nanomaterials 15, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010008
APA StyleBischoff, N. S., Undas, A. K., van Bemmel, G., Briedé, J. J., van Breda, S. G., Verhoeven, J., Verbruggen, S., Venema, K., Sijm, D. T. H. M., & de Kok, T. M. (2025). Investigating the ROS Formation and Particle Behavior of Food-Grade Titanium Dioxide (E171) in the TIM-1 Dynamic Gastrointestinal Digestion Model. Nanomaterials, 15(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15010008







