4D-Printed Magnetic Responsive Bilayer Hydrogel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
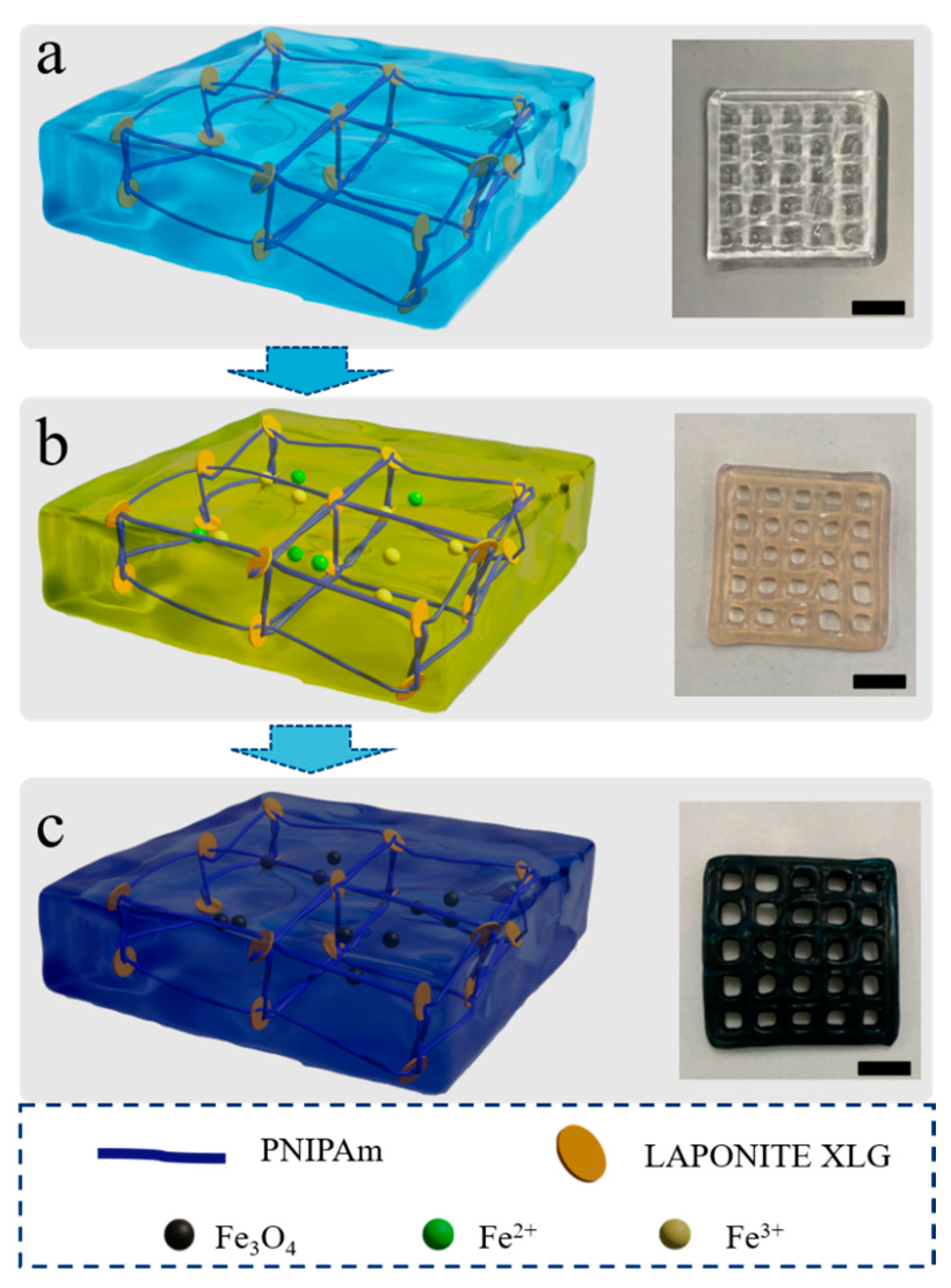
2.2.1. Preparation of the Thermal-Sensitive Hydrogel
2.2.2. Preparation of Magnetic Hydrogel
2.3. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
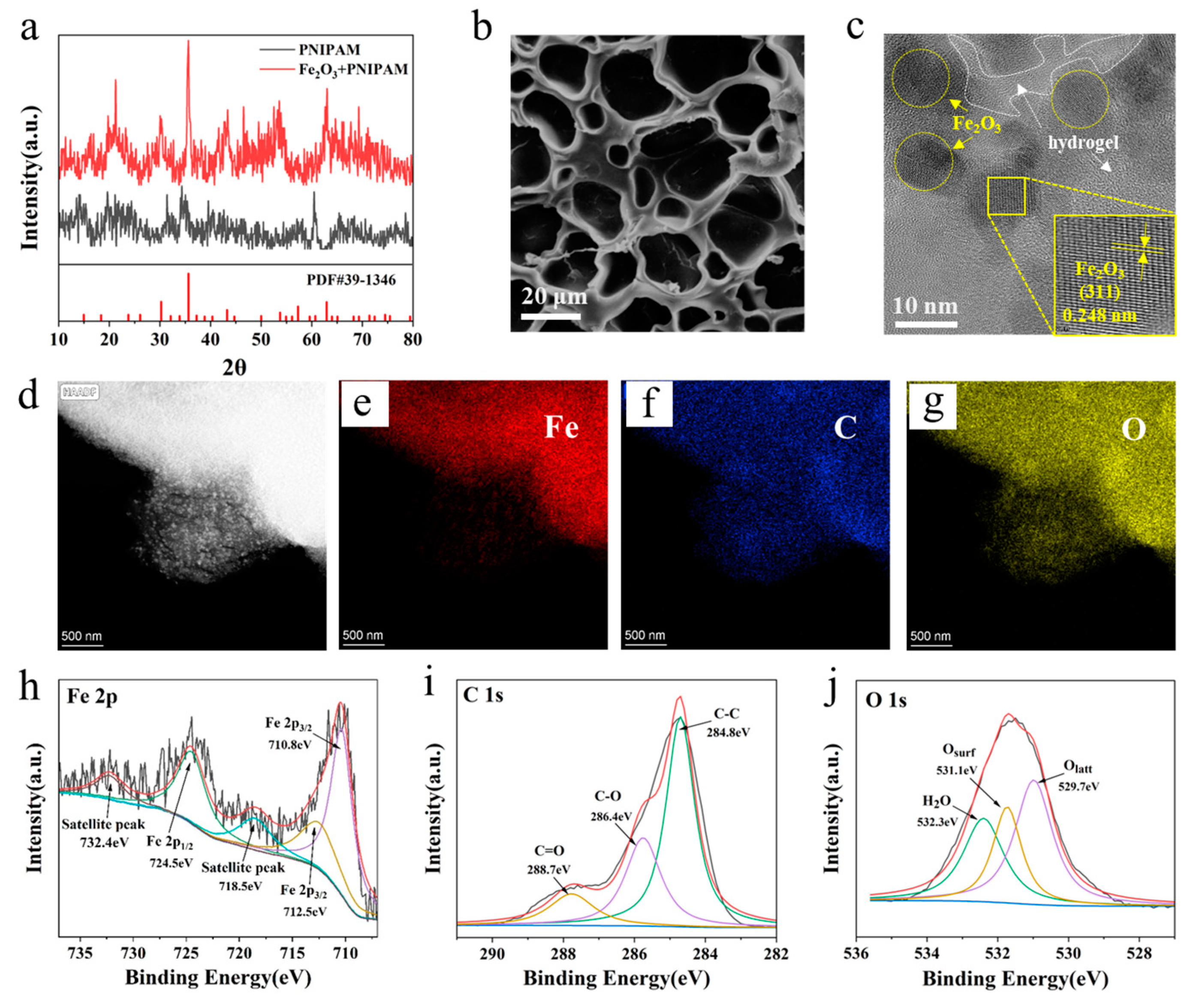
3.1. Morphology Characterization of Magnetic Gel
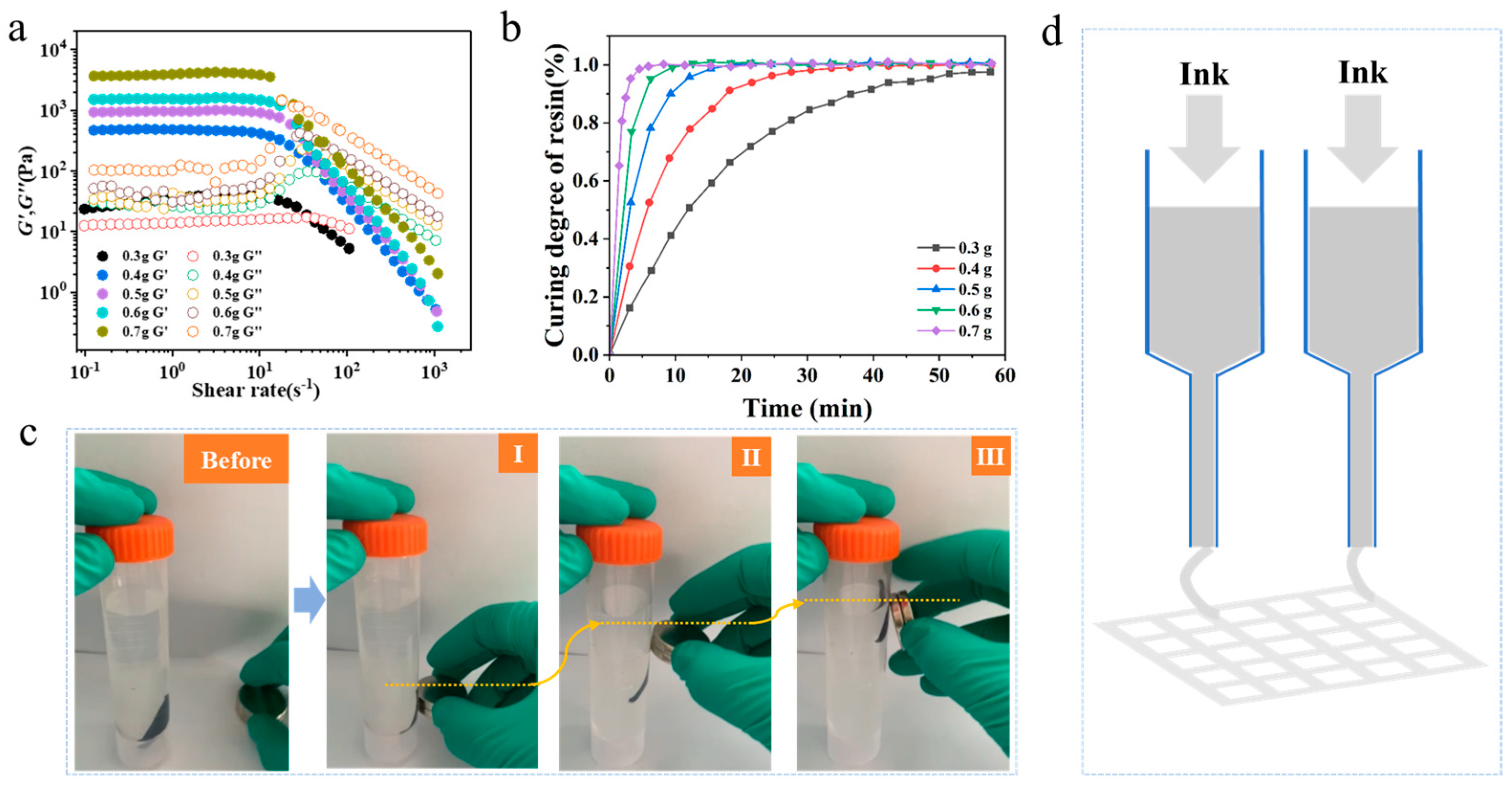
3.2. 3D Printing of Magnetic Gel
3.3. Structural Characterization of Magnetic Gel
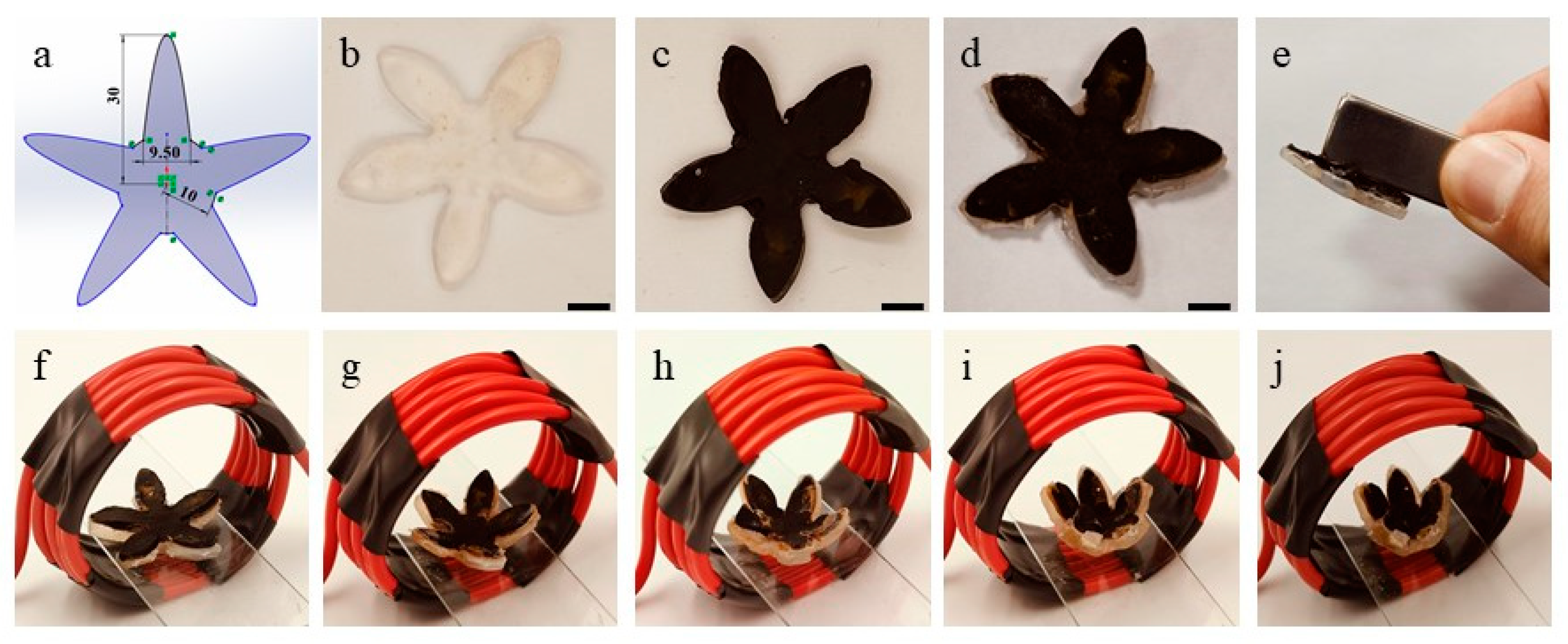
3.4. 4D Deformation of Magnetic Gel
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, M.; Song, Y. Printable smart materials and devices: Strategies and applications. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5144–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Cho, S.M.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, S.J. Thermo- and pH-responsive behaviors of graft copolymer and blend based on chitosan and N-isopropylacrylamide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.Y.; Arif, Z.U.; Noroozi, R.; Hossain, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Umer, R. 3D/4D printing of cellulose nanocrystals-based biomaterials: Additives for sustainable applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, Z.U.; Khalid, M.Y.; Zolfagharian, A.; Bodaghi, M. 4D bioprinting of smart polymers for biomedical applications: Recent progress, challenges, and future perspectives. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 179, 105374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.Y.; Arif, Z.U.; Ahmed, W.; Umer, R.; Zolfagharian, A.; Bodaghi, M. 4D printing: Technological developments in robotics applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 343, 113670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.N.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Z.L. Recent advances in 3D printing of tough hydrogels: A review. Compos. Part B 2022, 238, 109895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Husseiny, H.M.; Mady, E.A.; Hamabe, L.; Abugomaa, A.; Shimada, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yokoi, A.; Elbadawy, M.; Tanaka, R. Smart/stimuli-responsive hydrogels: Cutting-edge platforms for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 13, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, F.; Hassani N., M.M.; Liu, X.; Ni, J. A review of 4D printing. Mater. Design 2017, 122, 42–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Huang, Z.; Tsui, G.C.-P.; Tang, C.-Y.; Deng, Y. Recent advances in 4D printing of hydrogels. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2024, 63, 20240028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farham, B.; Baltazar, L. A review of smart materials in 4D printing for hygrothermal rehabilitation: Innovative insights for sustainable building stock management. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Larrea, N.; Wustoni, S.; Peñas, M.I.; Uribe, J.; Dominguez-Alfaro, A.; Gallastegui, A.; Inal, S.; Mecerreyes, D. PNIPAM/PEDOT:PSS hydrogels for multifunctional organic electrochemical transistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2403708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Fan, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, G.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S. A self-cleaning TiO2 nanosisal-like coating toward disposing nanobiochips of cancer detection. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9284–9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, A.A.; Schillo, S.M.; Demir, K.; Ueda, E.; Nesterov-Mueller, A.; Levkin, P.A. Droplet-array (DA) sandwich chip: A versatile platform for high-throughput cell screening based on superhydrophobic–superhydrophilic micropatterning. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5217–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liang, W.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Biomimetic super-lyophobic and super-lyophilic materials applied for oil/water separation: A new strategy beyond nature. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 336–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil–water separation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Liang, Y.; Dong, R. Physical dynamic double-network hydrogels as dressings to facilitate tissue repair. Nat. Protoc. 2023, 18, 3322–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashikumar, U.; Saraswat, A.; Deshmukh, K.; Hussain, C.M.; Chandra, P.; Tsai, P.-C.; Huang, P.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Ke, L.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; et al. Innovative technologies for the fabrication of 3D/4D smart hydrogels and its biomedical applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 328, 103163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fan, Q.; Yin, Y. Colloidal self-assembly approaches to smart nanostructured materials. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 4976–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champeau, M.; Heinze, D.A.; Viana, T.N.; de Souza, E.R.; Chinellato, A.C.; Titotto, S. 4D printing of hydrogels: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shi, K.; Liu, J.; Yang, P.; Han, R.; Pan, M.; Yuan, L.; Fang, C.; Yu, Y.; Qian, Z. Sustained co-delivery of 5-fluorouracil and cis-platinum via biodegradable thermo-sensitive hydrogel for intraoperative synergistic combination chemotherapy of gastric cancer. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezar, C.A.; Kennedy, S.M.; Mehta, M.; Weaver, J.C.; Gu, L.; Vandenburgh, H.; Mooney, D.J. Biphasic Ferrogels for Triggered Drug and Cell Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmauch, M.M.; Mishra, S.R.; Evans, E.E.; Velev, O.D.; Tracy, J.B. Chained Iron Microparticles for Directionally Controlled Actuation of Soft Robots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11895–11901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, Q. Magnetically controllable colloidal photonic crystals: Unique features and intriguing applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 6013–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezar, C.A.; Roche, E.T.; Vandenburgh, H.H.; Duda, G.N.; Walsh, C.J.; Mooney, D.J. Biologic-free mechanically induced muscle regeneration. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tong, Z.; Xia, Y.; Liu, M.; Lv, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lu, T.; Xie, S.; Pei, Y.; Fang, D.; et al. Super tough magnetic hydrogels for remotely triggered shape morphing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Sahandi Zangabad, P.; Ghasemi, A.; Amiri, M.; Bahrami, M.; Malekzad, H.; Ghahramanzadeh Asl, H.; Mahdieh, Z.; Bozorgomid, M.; Ghasemi, A.; et al. Temperature-Responsive Smart Nanocarriers for Delivery Of Therapeutic Agents: Applications and Recent Advances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21107–21133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.J.; Rajendran, R.R.; Mohanto, S.; Agarwal, U.; Panda, K.; Dhotre, K.; Manne, R.; Deepak, A.; Zafar, A.; Yasir, M.; et al. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Gels 2022, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, K.; Buchner, R.; Sato, T. Microscopic insights into the phase transition of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in aqueous media: Effects of molecular weight and polymer concentration. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 302, 112025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Wang, L. Peculiar porous α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 nanospheres: Facile synthesis and electromagnetic properties. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Wei, M.; Zhou, J.; Mu, L.; Song, S. Modulation of the Phase Transformation of Fe2O3 for Enhanced Water Oxidation under a Magnetic Field. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Liu, C.; Dong, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, C. Reduced Graphene Oxide/MXene/FeCoC Nanocomposite Aerogels Derived from Metal–Organic Frameworks toward Efficient Microwave Absorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Zhang, G.; Xian, G.; Ren, Z.; Wei, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, Z. Tetracycline degradation by persulfate activated with magnetic γ-Fe2O3/CeO2 catalyst: Performance, activation mechanism and degradation pathway. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Luo, P.; Liu, J.; Ma, L.; Gao, G.-L.; Jiang, Z. 4D-Printed Magnetic Responsive Bilayer Hydrogel. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15020134
Li Y, Li Y, Cao J, Luo P, Liu J, Ma L, Gao G-L, Jiang Z. 4D-Printed Magnetic Responsive Bilayer Hydrogel. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(2):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15020134
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yangyang, Yuanyi Li, Jiawei Cao, Peng Luo, Jianpeng Liu, Lina Ma, Guo-Lin Gao, and Zaixing Jiang. 2025. "4D-Printed Magnetic Responsive Bilayer Hydrogel" Nanomaterials 15, no. 2: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15020134
APA StyleLi, Y., Li, Y., Cao, J., Luo, P., Liu, J., Ma, L., Gao, G.-L., & Jiang, Z. (2025). 4D-Printed Magnetic Responsive Bilayer Hydrogel. Nanomaterials, 15(2), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15020134







