Micro-Nano Bubbles: A New Field of Eco-Friendly Cleaning
Abstract
1. Introduction
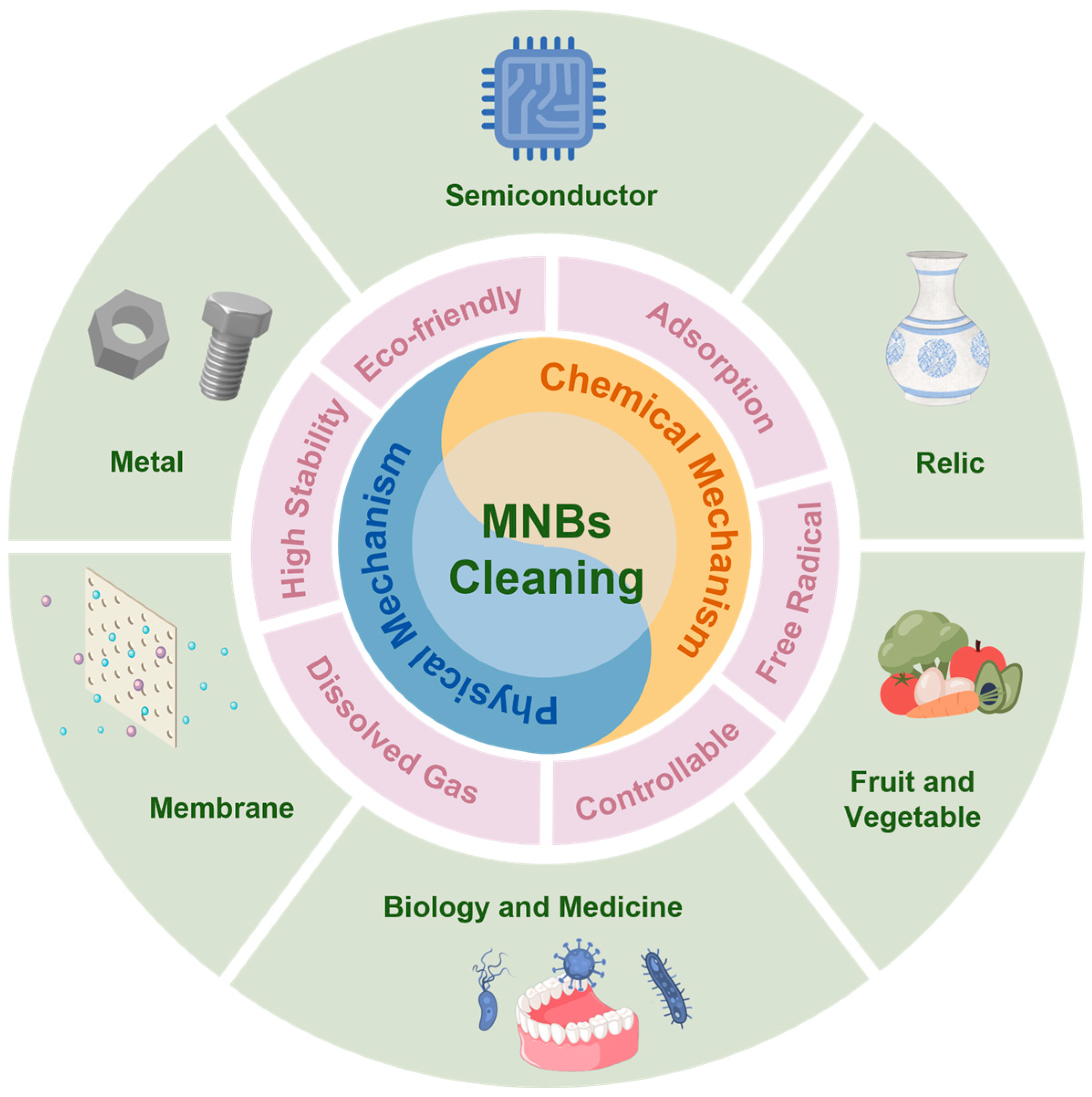
2. Properties in Cleaning
2.1. High Stability
2.2. High Mass Transfer Efficiency
2.3. Adjustability
2.4. Adsorb Contaminant Easily
2.5. Generate Free Radicals
2.6. Environment-Friendly
3. Influencing Factors
3.1. Gas Types
3.2. Bubble Sizes
3.3. Cleaning Methods
4. Cleaning Mechanisms
4.1. Physical Mechanisms
4.2. Chemical Mechanisms
5. Application of MNBs in Cleaning
5.1. Semiconductor Cleaning
5.2. Membrane Cleaning
5.3. Metal Cleaning
5.4. Biological and Medicine Cleaning or Sterilization
5.5. Fruit and Vegetable Cleaning
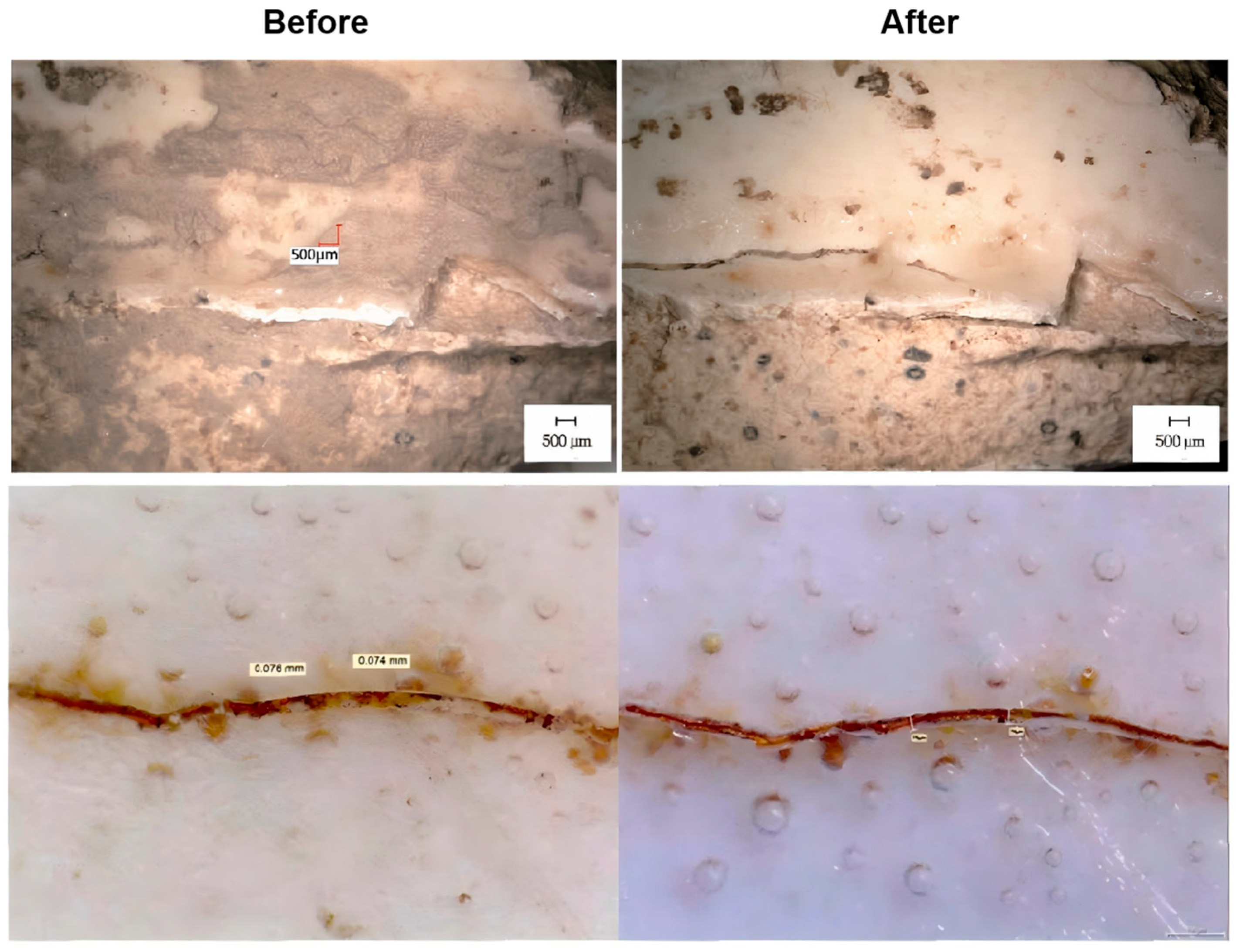
5.6. Cultural Relic Cleaning
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suryadevara, B. Advances in Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP); Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. The Fundamental Mechanisms of Laser Cleaning Technology and Its Typical Applications in Industry. Processes 2023, 11, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumi, M.R.; Abdellatif, A.K. Effect of surface finish on fatigue strength. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1995, 51, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, N.J. Digital technologies to unlock safe and sustainable opportunities for medical device and healthcare sectors with a focus on the combined use of digital twin and extended reality applications: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, N.J.; Kremer, T.; McDonnell, G. A review of Spaulding’s classification system for effective cleaning, disinfection and sterilization of reusable medical devices: Viewed through a modern-day lens that will inform and enable future sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 162976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, D.; Killington, A.; Fouhy, K.; Loh, M.; Malakar, P. The CDC biofilm bioreactor is a suitable method to grow biofilms, and test their sanitiser susceptibilities, in the dairy context. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 126, 105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.W.; Yang, Y.S.; Lee, Y.-U.; Han, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, J.P.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, D.; Song, N. Pesticide residues and risk assessment from monitoring programs in the largest production area of leafy vegetables in South Korea: A 15-year study. Foods 2021, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisco, E.; Najarro, M.; Burns, A. Quantifying the effectiveness of cleaning agents at removing drugs from laboratory benches and floor tiles. Forensic Chem. 2019, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, L.; Zha, F.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Pan, X. Research on heavy metal level and co-occurrence network in typical ecological fragile area. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.W.; Kang, D.H.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, K.; Koh, Y.S. Comparisons of Various Physical Cleaning. Solid State Phenom. 2012, 187, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedialkov, N.N.; Imamova, S.E.; Atanasov, P.A. Ablation of metals by ultrashort laser pulses. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2004, 37, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, H.; Sato, K.; Osaka, T.; Kuniyasu, H.; Hattori, T. Damage-Free Ultradiluted HF ∕ Nitrogen Jet Spray Cleaning for Particle Removal with Minimal Silicon and Oxide Loss. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2006, 9, G62. [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez, S.; Griffiths, W.; Dietz, L.; Horve, P.; Nunez, S.; Hu, J.; Shen, J.; Fretz, M.; Bi, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. From one species to another: A review on the interaction between chemistry and microbiology in relation to cleaning in the built environment. Indoor Air 2019, 29, 880–894. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, W. Chapter 1—Overview and Evolution of Silicon Wafer Cleaning Technology∗. In Handbook of Silicon Wafer Cleaning Technology, 3rd ed.; Reinhardt, K.A., Kern, W., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 3–85. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, B.; Liang, X.; Du, A. Inversion of surface damage and residual stress in ground silicon wafers by laser surface acoustic wave technology. Ultrasonics 2021, 113, 106367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, A.N.; House, R.; Lipszyc, J.C.; Liss, G.M.; Holness, D.L.; Tarlo, S.M. Cleaning agent usage in healthcare professionals and relationship to lung and skin symptoms. J. Asthma 2022, 59, 673–681. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, N.; Cai, H.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y. Water strategies and practices for sustainable development in the semiconductor industry. Water Cycle 2023, 4, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaka, K.; Himuro, S.; Ando, K.; Hata, T. Introduction to Fine Bubble Science and Technology; The Union of Fine Bubble Scientists and Engineers, Ed.; Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun, Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alheshibri, M.; Qian, J.; Jehannin, M.; Craig, V.S.J. A History of Nanobubbles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11086–11100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Ishikawa, H.; Asano, T.; Horibe, H. Effect of Microbubbles on Ozonized Water for Photoresist Removal. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 12578–12583. [Google Scholar]
- Sueishi, N.; Ohshima, T.; Oikawa, T.; Takemura, H.; Kasai, M.; Kitano, K.; Maeda, N.; Nakamura, Y. Plaque-removal effect of ultrafine bubble water: Oral application in patients undergoing orthodontic treatment. Dent. Mater. J. 2021, 40, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafeeq, S.; Ovissipour, R. The effect ultrasound and surfactants on nanobubbles efficacy against Listeria innocua and Escherichia coli O157: H7, in cell suspension and on fresh produce surfaces. Foods 2021, 10, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, P.S.; Plesset, M.S. On the stability of gas bubbles in liquid-gas solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1950, 18, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discher, B.M.; Bermudez, H.; Hammer, D.A.; Discher, D.E.; Won, Y.-Y.; Bates, F.S. Cross-linked Polymersome Membranes: Vesicles with Broadly Adjustable Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 2848–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, V.S.J. Very small bubbles at surfaces—The nanobubble puzzle. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, D.; Zhang, X. Surface nanobubbles and nanodroplets. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 981–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qin, Z.; Duan, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, B.; Weng, H. Effects of micro-nano bubble water addition on maturation degree and microbial community during aerobic composting. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, S.; Qiu, X.; Klammler, H.; Mohamed, M.M.A. The use of micro-nano bubbles in groundwater remediation: A comprehensive review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M. Surface Tension and Stability of a Nanobubble in Water: Molecular Simulation. J. Fluid Sci. Technol. 2008, 3, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulatowski, K.; Sobieszuk, P. Gas nanobubble dispersions as the important agent in environmental processes—Generation methods review. Water Environ. J. 2020, 34, 772–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temesgen, T.; Bui, T.T.; Han, M.; Kim, T.-i.; Park, H. Micro and nanobubble technologies as a new horizon for water-treatment techniques: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 246, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.N.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, H.-T.; Ando, K.; Kim, T.-G.; Kang, B.-K.; Klipp, A.; Yerriboina, N.P.; Park, J.-G. Chemically controlled megasonic cleaning of patterned structures using solutions with dissolved gas and surfactant. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 82, 105859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Ando, K. Low-intensity ultrasound induced cavitation and streaming in oxygen-supersaturated water: Role of cavitation bubbles as physical cleaning agents. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 52, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Xia, Z. Application of ozone micro-nano-bubbles to groundwater remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi Phan, K.K.; Truong, T.; Wang, Y.; Bhandari, B. Nanobubbles: Fundamental characteristics and applications in food processing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 118–130. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, C.-R.; Wang, J.; Fang, Z.; Zhou, L.-M.; Zhang, L.-J.; Hu, J. Formation and stability of ultrasonic generated bulk nanobubbles. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 118104. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, K.; Matsushima, H.; Asakura, Y. Generation and reduction of bulk nanobubbles by ultrasonic irradiation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 195, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Ohuchi, S.; Terasaka, K.; Fujioka, S. Destabilization of ultrafine bubbles in water using indirect ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 71, 105366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.; Etchepare, R.; Calgaroto, S.; Rubio, J. Aqueous dispersions of nanobubbles: Generation, properties and features. Miner. Eng. 2016, 94, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Zou, Z.; Tai, R.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J. Formation and Stability of Surface/Bulk Nanobubbles Produced by Decompression at Lower Gas Concentration. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 22418–22423. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.K.A.; Sun, C.; Hua, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Marhaba, T. Generation of nanobubbles by ceramic membrane filters: The dependence of bubble size and zeta potential on surface coating, pore size and injected gas pressure. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmalkar, N.; Pacek, A.W.; Barigou, M. On the Existence and Stability of Bulk Nanobubbles. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10964–10973. [Google Scholar]
- Ushikubo, F.Y.; Furukawa, T.; Nakagawa, R.; Enari, M.; Makino, Y.; Kawagoe, Y.; Shiina, T.; Oshita, S. Evidence of the existence and the stability of nano-bubbles in water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 361, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, A.; Takahashi, O.; Ishii, Y.; Sekimoto, Y.; Kurata, Y. Water Purification Using the Adsorption Characteristics of Microbubbles. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 6574. [Google Scholar]
- Abel, B. Hydrated Interfacial Ions and Electrons. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2013, 64, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Chiba, K.; Li, P. Formation of Hydroxyl Radicals by Collapsing Ozone Microbubbles under Strongly Acidic Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 11443–11446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, K.; Maruyama, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sato, G.; Atsumi, R.; Murakami, Y. Influence of microbubbles on free radical generation by ultrasound in aqueous solution: Implication of the important roles of nanobubbles. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2022, 48, 1045–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Yijia, S. Study of New Deep Cleaning Processing Technology of Fruits and Vegetables. J. Food Sci. Technol.—Mysore 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; An, W.-g.; Huo, M.-x.; Yang, W.; Zhu, S.-y.; Lin, S.-s. Solubilization and stabilization for prolonged reactivity of ozone using micro-nano bubbles and ozone-saturated solvent: A promising enhancement for ozonation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116484. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Duan, Y.; Fan, W.; Guo, T.; Huo, M.; Yang, W.; Zhu, S.; An, W. Intensifying ozonation treatment of municipal secondary effluent using a combination of microbubbles and ultraviolet irradiation. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 21915–21924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Choi, J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S. Ultrasonic-assisted removal of inorganic scales in high-salinity wastewater treatment using membrane distillation. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 157, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Lin, T.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Y. Cleaning efficiency and mechanism of ozone micro-nano-bubbles on ceramic membrane fouling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 331, 125698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.-K.; Kim, M.-S.; Park, J.-G. Effect of dissolved gases in water on acoustic cavitation and bubble growth rate in 0.83MHz megasonic of interest to wafer cleaning. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2014, 21, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Tikekar, R.V. Air microbubble assisted washing of fresh produce: Effect on microbial detachment and inactivation. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 181, 111687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.-T.; Ouyang, Z.-Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.-J.; Hu, J.; Li, M.-Q.; Yang, F.-J. Nanobubbles on solid surface imaged by atomic force microscopy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2000, 18, 2573–2575. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B.; Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Tai, R.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L. Interfacial Nanobubbles on Atomically Flat Substrates with Different Hydrophobicities. ChemPhysChem 2015, 16, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, W.; Wang, S.; Guo, W.; Tang, Y.; Dong, Y. Study on Nanobubble Generation: Saline Solution/Water Exchange Method. ChemPhysChem 2013, 14, 2589–2593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guan, N.; Wang, Y.; Wen, B.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. The regulation of surface nanobubble generation via solvent exchange on different substrates. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 676, 132290. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, E.; Kumar, A.; Lo, S.-L. Advancing nanobubble technology for carbon-neutral water treatment and enhanced environmental sustainability. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118980. [Google Scholar]
- Gevari, M.T.; Abbasiasl, T.; Niazi, S.; Ghorbani, M.; Koşar, A. Direct and indirect thermal applications of hydrodynamic and acoustic cavitation: A review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 171, 115065. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, X.; Alheshibri, M. The effect of ultrasound on bulk and surface nanobubbles: A review of the current status. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 76, 105629. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, K.; Ioka, A.; Oku, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Saihara, Y.; Ogumi, Z. Concentration determination of oxygen nanobubbles in electrolyzed water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 329, 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, A.J.; Barigou, M. Electrochemically Induced Bulk Nanobubbles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 17999–18006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotto, P.; Miano, D.; Celebi, A.T.; Valtiner, M. Removal of Nanoparticles by Surface Nanobubbles Generated via Solvent–Water Exchange: A Critical Perspective. Langmuir 2024, 40, 27127–27136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Duisterwinkel, A. Removal of Nanoparticles from Plain and Patterned Surfaces Using Nanobubbles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11430–11435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Onzuka, A.; Nishijima, W.; Yamazaki, M.; Aoki, M.; Sao, T. Effect of fine bubbles for washing of monolith type porous ceramic membranes treating oil-in-water emulsions. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayarathne, H.N.P.; Choi, J.; Jang, A. Enhancement of cleaning-in-place (CIP) of a reverse osmosis desalination process with air micro-nano bubbles. Desalination 2017, 422, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, H.; Kiuchi, S.; Kakuda, T.; Hafuka, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Matsui, Y.; Kimura, K. Fouling mitigation in membrane bioreactors by nanobubble-assisted backwashing. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broumand, M.; Birouk, M. Effect of nozzle-exit conditions on the near-field characteristics of a transverse liquid jet in a subsonic uniform cross airflow. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 113303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, T.; Nishiuchi, Y.; Minagawa, H. Development of New Agriculture and Aquaculture Technology Using Fine Bubbles. Int. J. Plasma Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 12, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, K.; Huang, Z.; Lin, H.; Shen, L.; Gao, C.; Zhou, G.; Hu, J.; Yang, H.; Xu, F. Effects of micro-/nanobubble on membrane antifouling performance and the mechanism insights. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotchie, A.; Grieser, F.; Ashokkumar, M. Effect of Power and Frequency on Bubble-Size Distributions in Acoustic Cavitation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 084302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Jeon, M.J.; Kim, H.-S. The effect of aeration types on foulant removal in ex-situ chemical cleaning in place (CIP) with membranes fouled by secondary effluents. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkin, P.R.; Offin, D.G.; Vian, C.J.B.; Leighton, T.G. Electrochemical ‘bubble swarm’ enhancement of ultrasonic surface cleaning. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 21709–21715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, K.; Ogawa, S.; Kasaki, S.; Koyama, K.; Kodama, M.; Yanase, S. Cleaning polymer ink from a glass substrate using microbubbles generated by a hydrogen bubble method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 142, 242–250. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, H.H.W.B.; Ouyang, L.; Cha, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Tan, B.H.; Vashi, A.; Nguyen, N.-T.; An, H. Surface Cleaning of Oil Contaminants Using Bulk Nanobubbles. ChemSusChem 2024, 17, e202400802. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
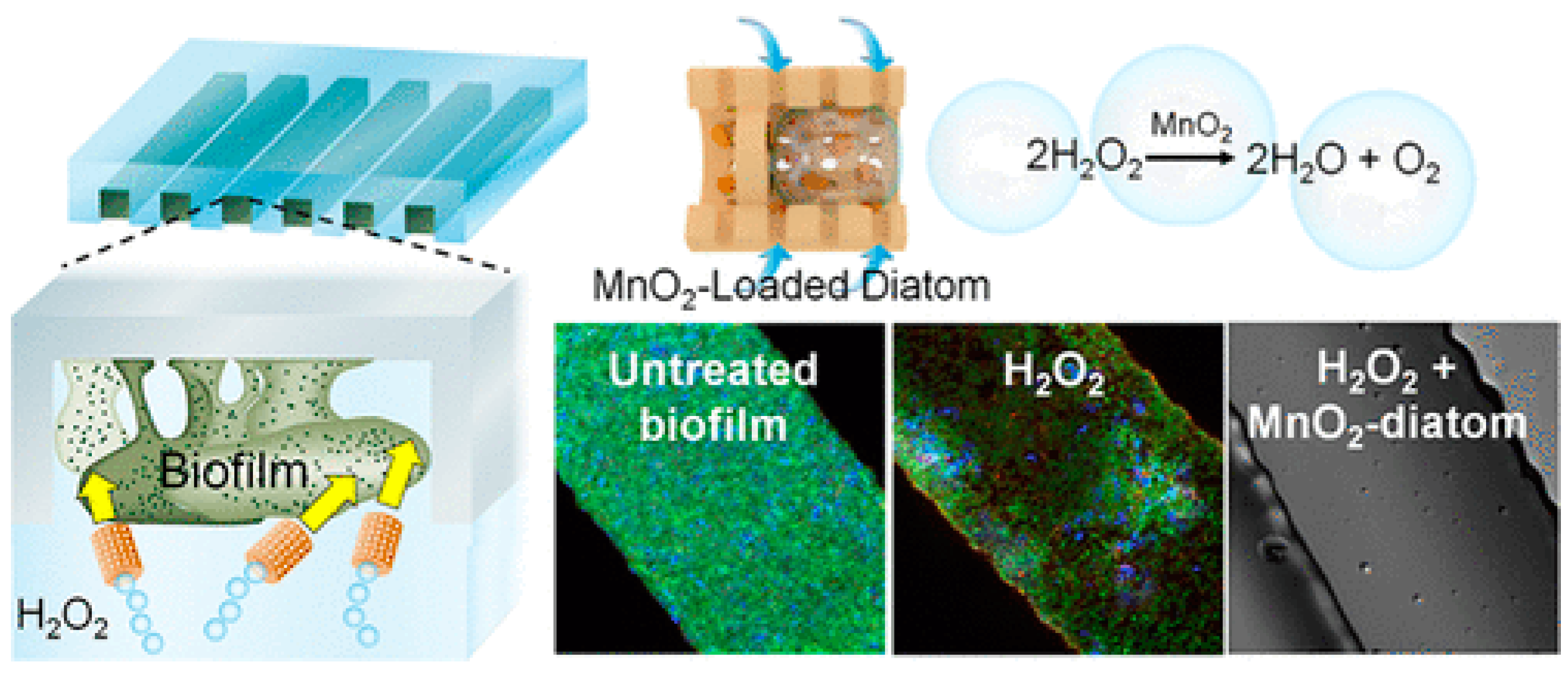
- Seo, Y.; Leong, J.; Park, J.D.; Hong, Y.-T.; Chu, S.-H.; Park, C.; Kim, D.H.; Deng, Y.-H.; Dushnov, V.; Soh, J.; et al. Diatom Microbubbler for Active Biofilm Removal in Confined Spaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 35685–35692. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeura, H.; Kobayashi, F.; Tamaki, M. Removal of residual pesticide, fenitrothion, in vegetables by using ozone microbubbles generated by different methods. J. Food Eng. 2011, 103, 345–349. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Wang, J.; Liao, Z.; Ueda, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Zhang, G. Microbubbles for Effective Cleaning of Metal Surfaces Without Chemical Agents. Langmuir 2022, 38, 769–776. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.-J. The Application Method of Nanobubble Conveyor on the Effect of Preventive Oral Hygiene. J. Healthc. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8871849. [Google Scholar]
- Mwanga, N.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Xia, S.; Yin, D.; Rui, M.; Ye, Y. Effect of micro and nanobubble size and concentration on membrane fouling: Strategies for energy-saving and ultrafiltration efficiency enhancement. Desalination 2024, 587, 117929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ali, J.; Wang, Z.; Oladoja, N.A.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, C.; Mailhot, G.; Pan, G. Oxygen nanobubbles enhanced photodegradation of oxytetracycline under visible light: Synergistic effect and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124227. [Google Scholar]
- Ushida, A.; Koyama, T.; Nakamoto, Y.; Narumi, T.; Sato, T.; Hasegawa, T. Antimicrobial effectiveness of ultra-fine ozone-rich bubble mixtures for fresh vegetables using an alternating flow. J. Food Eng. 2017, 206, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuziuti, T. Influence of sonication conditions on the efficiency of ultrasonic cleaning with flowing micrometer-sized air bubbles. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2016, 29, 604–611. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, R.M. Efficacy of Microscale/Nanoscale Aqueous Ozone on the Removal of Bacillus spp. Biofilms from Polyethersulfone Membranes in the Dairy Industry. Master’s Thesis, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shawli, H.; Iohara, K.; Tarrosh, M.; Huang, G.T.-J.; Nakashima, M.; Azim, A.A. Nanobubble-enhanced antimicrobial agents: A promising approach for regenerative endodontics. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, H.; Kiuchi, S.; Kakuda, T.; Hafuka, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Matsui, Y.; Kimura, K. Synergistic effects of nanobubbles and chemicals on backwashing for submerged MBRs treating municipal wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105541. [Google Scholar]
- Ushida, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Takahashi, N.; Nakajima, T.; Murao, S.; Narumi, T.; Uchiyama, H. Effect of mixed nanobubble and microbubble liquids on the washing rate of cloth in an alternating flow. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2012, 15, 695–702. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Gu, J.; Luo, C.; Tong, Y.; Ren, X. Experimental and numerical investigation of bubble oscillation and jet impact near a solid boundary. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 138, 106606. [Google Scholar]
- Ohl, C.-D.; Arora, M.; Dijkink, R.; Janve, V.; Lohse, D. Surface cleaning from laser-induced cavitation bubbles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 074102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Cheng, H.; Runge, K. A comprehensive review on aeration methods used in flotation machines: Classification, mechanisms and technical perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Shafaei, S.Z.; Shahbazi, B.; Chehreh Chelgani, S. Study relationships between flotation variables and recovery of coarse particles in the absence and presence of nanobubble. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 559, 284–288. [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Morita, T.; Nishiuchi, Y.; Tada, K.; Nagahara, J.; Hata, T. Cleaning Effect by Fine Bubbles Generated with Gas–Liquid Share Method. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2018, 51, 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, J. Nanobubbles influence on BSA adsorption on mica surface. Surf. Interface Anal. 2006, 38, 990–995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Oshita, S.; Kawabata, S.; Makino, Y.; Yoshimoto, T. Identification of ROS Produced by Nanobubbles and Their Positive and Negative Effects on Vegetable Seed Germination. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11295–11302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Oshita, S.; Makino, Y.; Wang, Q.; Kawagoe, Y.; Uchida, T. Oxidative Capacity of Nanobubbles and Its Effect on Seed Germination. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.-J.; Chu, K.-C.; Sheng, Y.-J.; Tsao, H.-K. Sliding Dynamic Behavior of a Nanobubble on a Surface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 17932–17940. [Google Scholar]
- Matafonova, G.; Batoev, V. Review on low- and high-frequency sonolytic, sonophotolytic and sonophotochemical processes for inactivating pathogenic microorganisms in aqueous media. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115085. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, F.; Xie, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, H. Magnetothermally Triggered Free-Radical Generation for Deep-Seated Tumor Treatment. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2926–2931. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; An, W.; Huo, M.; Xiao, D.; Lyu, T.; Cui, J. An integrated approach using ozone nanobubble and cyclodextrin inclusion complexation to enhance the removal of micropollutants. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117039. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takenouchi, T. Behavior of hydrogen nanobubbles in alkaline electrolyzed water and its rinse effect for sulfate ion remained on nickel-plated surface. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 849–854. [Google Scholar]
- Dayarathne, H.N.P.; Jeong, S.; Jang, A. Chemical-free scale inhibition method for seawater reverse osmosis membrane process: Air micro-nano bubbles. Desalination 2019, 461, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dockar, D.; Gibelli, L.; Borg, M.K. Shock-induced collapse of surface nanobubbles. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 6884–6898. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Nam, Y.; Jeon, S.; Kim, C.; Kim, E.; Choi, S.; Lee, S.; Park, S.-H.; Hong, S.; Kim, T. Environmentally friendly buff cleaning of ceria nanoparticles using bubbles in gas-dissolved water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 671, 131558. [Google Scholar]
- Yabe, A.; Morimatsu, T. Cleaning Effect of Small Particle Contaminated Plate by Utilizing Nano-bubbles Contained Water. J. Heat Transfar Soc. Jpn. 2004, 43, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.K.; Lee, S.H. Fabrication of Ozone Bubble Cleaning System and its Application to Clean Silicon Wafers of a Solar Cell. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2015, 10, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.B.; Zhang, Z. Ceramic membrane technology for water and wastewater treatment: A critical review of performance, full-scale applications, membrane fouling and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129481. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Pei, H.; Zou, Y.; Ding, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hui, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Gumbi, N.N.; et al. Dissecting the impacts of nanobubbles and heat generated in polymerization on polyamide nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 699, 122646. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, Q.; He, B.; Gao, M.; Ji, Y.; Cui, Z.; Yan, F.; Ma, X.; Younas, M.; Li, J. Preparation of Small-Pore Ultrafiltration Membranes with High Surface Porosity by In Situ CO2 Nanobubble-Assisted NIPS. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 8633–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.S.; Amamcharla, J.K. Effect of bulk nanobubbles on ultrafiltration membrane performance: Physiochemical, rheological, and microstructural properties of the resulting skim milk concentrate dispersions. J. Food Eng. 2023, 337, 111238. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Jang, A. Influence of microbubble in physical cleaning of MF membrane process for wastewater reuse. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8451–8459. [Google Scholar]
- Gwenaelle, M.P.O.; Jung, J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S. Effect of microbubbles on microfiltration pretreatment for seawater reverse osmosis membrane. Desalination 2017, 403, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, A.; Saghravani, S.F.; Ghasemipanah, K.; Dahrazma, B.; Rasekh, B. Evaluation of the performance of air micro-nano bubbles for cleaning in place to reduce the reverse osmosis membrane clogging. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, H.-S. Effect of different physical conditions on fouling control in in-situ chemical cleaning in place (CIP) for flat sheet membranes fouled by secondary effluents. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, E.-T.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.S.S.; Hong, S.; Fortner, J.D. Harnessing the potential of in-situ, electrically generated microbubbles via nickel foam for enhanced, low energy membrane fouling control. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MINAGAWA, H.; SUGIMOTO, K.; KURIMOTO, R.; YASUDA, T. Basic Study on Immersion Cleaning Using Microbubble Water. J. Jpn. Soc. Exp. Mech. 2018, 17, 298–303. [Google Scholar]
- Ulatowski, K.; Szczygielski, P.; Sobieszuk, P. Impact of Water Purity and Oxygen Content in Gas Phase on Effectiveness of Surface Cleaning with Microbubbles. Materials 2024, 17, 6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.A.; Mohan, Y.; Liew, K.J.; Chong, S.H.; Poh, P.E. Development of an effective cleaning method for metallic parts using microbubbles. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bers, A.V.; Wahl, M. The Influence of Natural Surface Microtopographies on Fouling. Biofouling 2004, 20, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, H.; Dong, Y.; Mao, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Craig, V.S.J.; Hu, J. Cleaning using nanobubbles: Defouling by electrochemical generation of bubbles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagara, K.; Kataoka, S.; Yoshida, A.; Ansai, T. The effects of exposure to O2- and HOCl-nanobubble water on human salivary microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-J.; Chuang, M.-C.; Chang, S.-C. Research on the Cleaning Efficacy of Micro-bubbles on Dental Plaque. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 3, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tanaka, Y.; Xiao, L.; Miwa, N. Hydrogen-rich bath with nano-sized bubbles improves antioxidant capacity based on oxygen radical absorbing and inflammation levels in human serum. Med. Gas Res. 2022, 12, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, P.; Radigan, H.; Aziz, Y. Harlequin Ichthyosis Nanobubble Hydrotherapy: A Breakthrough in Treatment. Cureus 2024, 16, e68581. [Google Scholar]
- Khadre, M.A.; Yousef, A.E.; Kim, J.G. Microbiological Aspects of Ozone Applications in Food: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malahlela, H.K.; Belay, Z.A.; Mphahlele, R.R.; Caleb, O.J. Micro-nano bubble water technology: Sustainable solution for the postharvest quality and safety management of fresh fruits and vegetables—A review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 94, 103665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-L.; Arcega, R.D.; Liao, P.-Y.; Hou, C.-Y.; Liu, W.-C.; Chen, Y.-R.; Wu, J.-S.; Wang, W.-R.; Lin, C.-M. Reduction of pesticides and bacteria on Napa cabbage by ozone microbubble water. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 204, 112444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, Q.; Wu, L. Safety evaluation of micronano bubble cleaning for underwater porcelain from Nanhai I shipwreck. Sci. Conserv. Archaeol. 2017, 29, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, l.; Yang, Q. Research on micro-nano bubble cleaning for unearthed porcelain from Qinglong Town, Shanghai. Sci. Conserv. Archaeol. 2020, 32, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, X.; Wu, X.; Li, P. Eco-friendly textile cleaning: Micro-nano bubbles technology for enhanced efficiency and sustainability. J. Text. Inst. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Ling, X.; Su, Z.; Cao, X.; Guo, J.; Wan, Z.; Liu, K.; Pan, W. Development of suitable washing methods for textile relics adsorbing composite organic/inorganic stains. J. Text. Inst. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirwa, W.; Li, P.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Application of fine bubble technology toward sustainable agriculture and fisheries. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Kioka, A.; Maurya, S.; Doong, R.-A. Innovative nanobubble technology: Fuelling the future of bioenergy and carbon mitigation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 209, 115118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Xu, G. Mass transfer of nanobubble aeration and its effect on biofilm growth: Microbial activity and structural properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, M.; Benetti, D.; Yan, C.; Rosei, F. Confining nitrogen nanobubbles within plasma etched voids to promote reactant supply for enhanced electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction under ambient conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145830. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, R.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Snyder, S.A.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Togbah, C.F.; Gao, N. Micro and nanobubbles-assisted advanced oxidation processes for water decontamination: The importance of interface reactions. Water Res. 2024, 265, 122295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| MNBs Generation Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages | Size (μm) | Detections | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent exchange | Good repeatability In situ observation Low energy consumption | Difficult to mass produce | 0.02–200 (Air) | AFM | [64,65] |
| Pressurized dissolved gas | Mature technology Straightforward processes High flexibility | Low efficiency High energy consumption | 1–60 (O3) | PCS | [20] |
| 14–56 (Air) | OM | [66] | |||
| 0.15–0.25 (Air) | DLS | [67] | |||
| 0.02–0.4 (Air) | NTA | [68] | |||
| Hydrodynamic cavitation | Enables mass preparation Low energy consumption | Limited uniformity of size Clogged and corroded | 10–100 (Air) | HSC | [69] |
| 0.02–2 (Air) | DLS | [70] | |||
| 0.2–0.9 (Air) | NTA | [71] | |||
| Ultrasonic cavitation | Controllable bubble size | Low density of bubbles results in limited scalability | 100–300 (O2) | HSC | [33] |
| 1–4.5 (Air) | SCL | [72] | |||
| 0.05–0.15 (Air) | NTA | [37] | |||
| Porous-membrane | Controllable bubble size | Producing porous microstructures faces challenges | 10–200 (Air) | HSC | [73] |
| Electrolysis | Controllable bubble size High gas purity | High consumption Low bubble yield Singular gas species | 20–200 (H2, O2) | HSC | [74] |
| 10–100 (H2, O2) | OM | [75] | |||
| 0.02–0.2 (H2, O2) | NTA | [76] | |||
| Chemical reaction | High efficiency Low energy consumption | Bubble size control difficult | 12 (O2) | OM | [77] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, N.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. Micro-Nano Bubbles: A New Field of Eco-Friendly Cleaning. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070480
Guan N, Wang Y, Hu J, Zhang L. Micro-Nano Bubbles: A New Field of Eco-Friendly Cleaning. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(7):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070480
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Nan, Yao Wang, Jun Hu, and Lijuan Zhang. 2025. "Micro-Nano Bubbles: A New Field of Eco-Friendly Cleaning" Nanomaterials 15, no. 7: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070480
APA StyleGuan, N., Wang, Y., Hu, J., & Zhang, L. (2025). Micro-Nano Bubbles: A New Field of Eco-Friendly Cleaning. Nanomaterials, 15(7), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070480





