Revealing the Role of Interfacial Charge Transfer in Mechanoluminescence
Abstract
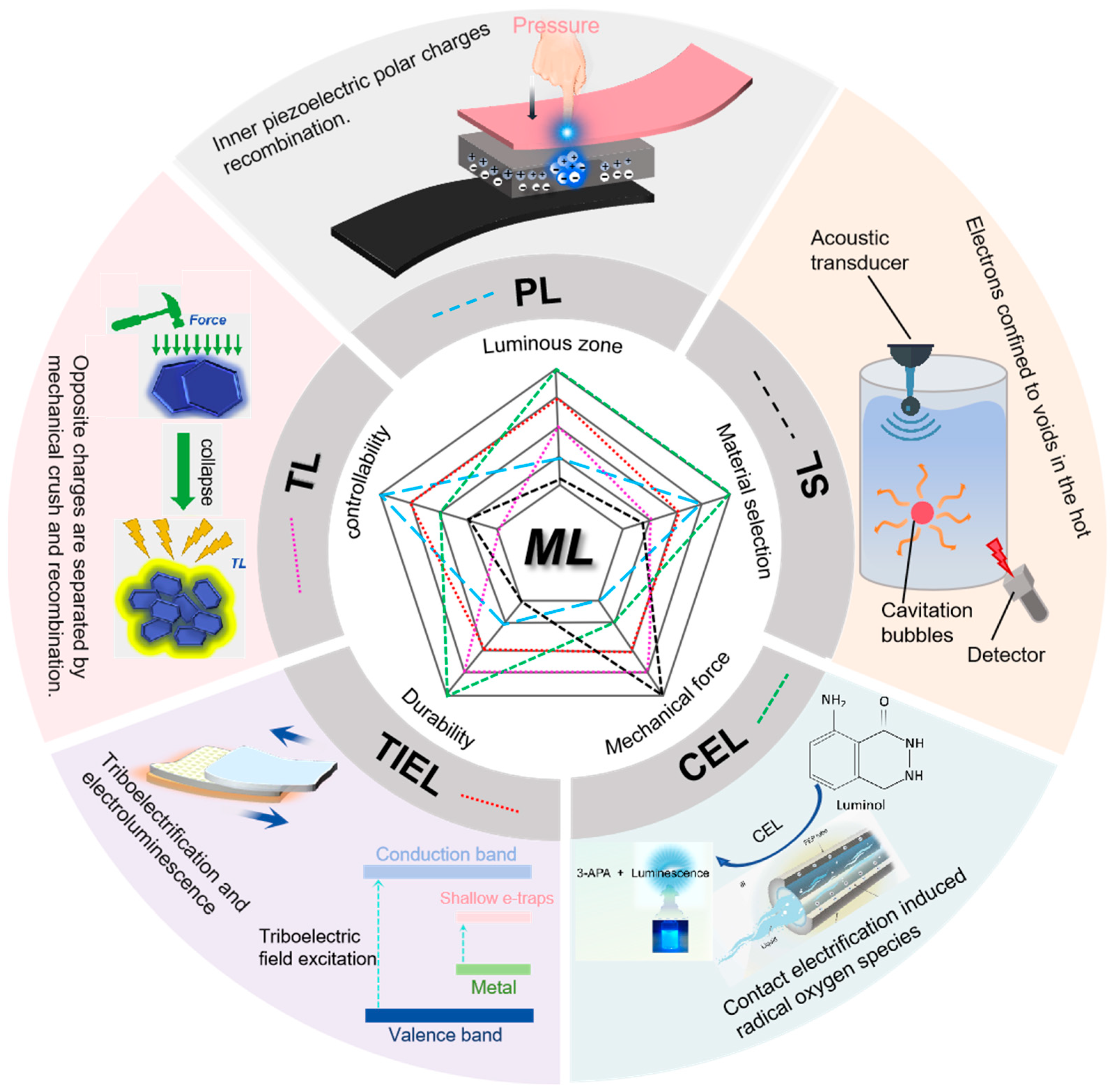
1. Introduction
2. Chemical Reaction Initiated by Triboelectric Charge from CE
2.1. Contact-Electro-Chemistry (CE-Chemistry)
2.2. CEL

3. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Hu, H.; Peng, D.; Dong, L.; Zhu, D. Soft devices empowered by mechanoluminescent materials. Soft Sci. 2023, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Runowski, M.; Martín, I.R.; Soler-Carracedo, K.; Peng, L.; Skwierczyńska, M.; Sójka, M.; Barzowska, J.; Mahlik, S.; Peng, D.; et al. Mechanoluminescence and Photoluminescence Heterojunction for Superior Multimode Sensing Platform of Friction, Force, Pressure, and Temperature in Fibers and 3D-Printed Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2304140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, B.; Ren, B.; Tu, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Ren, Z.; et al. Smart Mechanoluminescent Phosphors: A Review of Strontium-Aluminate-Based Materials, Properties, and Their Advanced Application Technologies. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2204925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, B.P.; Rathore, A.S. Classification of Mechanoluminescence. Cryst. Res. Technol. 1995, 30, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo-Liu, W.; Zhao, H.-B.; Wang, Y.-Z. Advanced Flame-Retardant Methods for Polymeric Materials. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zheng, W.; Gong, Z.; You, W.; Wei, J.; Chen, X. Rare earth ion– and transition metal ion–doped inorganic luminescent nanocrystals: From fundamentals to biodetection. Mater. Today Nano 2019, 5, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuba, K.C.; Buccino, A.P.; Bartram, J.; Gaub, B.M.; Fauser, F.J.; Ronchi, S.; Kumar, S.S.; Geissler, S.; Nava, M.M.; Hierlemann, A.; et al. Mechanical stimulation and electrophysiological monitoring at subcellular resolution reveals differential mechanosensation of neurons within networks. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-C.; Wang, X.; Marriott, G.; Xu, C.-N. Trap-controlled mechanoluminescent materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 678–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, B.-H.; Chen, Y.-L. Recent progress in organic mechanoluminescent materials. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Zhang, K.; Peng, D.; Deng, Y.; Shan, C.-X.; Dong, L. Mechanoluminescent functional devices: Developments, applications and prospects. Nano Energy 2024, 122, 109325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.J. Interfacial Ion-Transfer Mechanism for the Intense Luminescence Observed When Opening Self-Seal Envelopes. Langmuir 2012, 28, 13294–13299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, D. Mechanoluminescence and Its Recent Applications. Curr. Mater. Sci. 2023, 17, 352–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Niu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Bu, Y.; Zou, H.; Wang, X. Principles, properties, and sensing applications of mechanoluminescence materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 14968–15000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Willatzen, M.; Lin Wang, Z.; Wei, D. Contact-electro-luminescence triggered by triboelectric charge. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 501, 157754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, H.; Schultes, H. Luminescenz im ultraschallbeschickten Wasser. Z. Für Phys. Chemie 1934, 27B, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, S.-I.; Mitome, H.; Yasui, K.; Hayashi, S. Single-Bubble Sonochemiluminescence in Aqueous Luminol Solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 10250–10251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, M.P.; Hilgenfeldt, S.; Lohse, D. Single-bubble sonoluminescence. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 426–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, L.S.; Zakin, M.R. Confined Electron Model for Single-Bubble Sonoluminescence. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 14619–14627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yao, K.; Cui, K.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Y.; Wang, W.; Jin, X.; Zhou, J. Contact Electrification Induced Multicolor Self-Recoverable Mechanoluminescent Elastomer for Wearable Smart Light-Emitting Devices. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2203112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, F.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z.; Luo, H.; Jin, L.; Xie, R.J. Visualizing Dynamic Mechanical Actions with High Sensitivity and High Resolution by Near-Distance Mechanoluminescence Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2202864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atari, N.A.; Ramani, R. Piezoluminescence and thermoluminescence spectral shifts in γ-irradiated KBr and KCl crystals. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 1986, 97, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.T. Room-Temperature Deformation Luminescence in Alkali Halides. Phys. Rev. 1965, 141, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyas, M.; Chandra, B.P.; Kathuria, S.P. Spectroscopy of luminescence produced during the application and release of pressure from coloured alkali halide crystals. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 1981, 66, K21–K24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, R.; Dong, L.; Peng, D.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.L. Dynamic Pressure Mapping of Personalized Handwriting by a Flexible Sensor Matrix Based on the Mechanoluminescence Process. Adv. Mater 2015, 27, 2324–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Luo, J.; Peng, D.; Peng, L.; Woźny, P.; Barzowska, J.; Kamiński, M.; Mahlik, S.; Moszczyński, J.; Soler-Carracedo, K.; et al. Persistent Photoluminescence and Mechanoluminescence of a Highly Sensitive Pressure and Temperature Gauge in Combination with a 3D-Printable Optical Coding Platform. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2408686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atari, N.A. Piezoluminescence phenomenon. Phys. Lett. A 1982, 90, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, D.; Huang, B.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.L. Piezophotonic effect based on mechanoluminescent materials for advanced flexible optoelectronic applications. Nano Energy 2018, 55, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z. Triboluminescence: Recalling Interest and New Aspects. Chem 2018, 4, 943–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, J.I.; Hardy, G.E.; Sutton, J.E. Triboluminescence of sugars. J. Phys. Chem. 1976, 80, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawale, D.O.; Okoli, O.O.I.; Fontenot, R.S.; Division, C.; Hollerman, W.A. Triboluminescence: Theory, Synthesis, and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, H.; Xu, C.-N.; Akiyama, M.; Watanabe, T. Strong Mechanoluminescence from UV-Irradiated Spinels of ZnGa2O4:Mn and MgGa2O4:Mn. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 39, 6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Xu, C.-N.; Tateyama, H. Stress-stimulated luminescence from ZnAl2O4:Mn. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 1068–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Xun, X.; Gao, F.; Xu, L.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Self-powered user-interactive electronic skin for programmable touch operation platform. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Wei, D. Contact-electro-chemistry induced by flow electrification in dielectric tubes. Nano Energy 2025, 134, 110526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Li, S.; Sun, B.; Wang, Z.L.; Wei, D. Recent Progress of Chemical Reactions Induced by Contact Electrification. Molecules 2025, 30, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.; Wollmann, A.; Weers, M.; Benker, B.; Weber, A.P. Triboelectric charging and separation of fine powder mixtures. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2020, 43, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, P.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Wei, D. A green approach to induce and steer chemical reactions using inert solid dielectrics. Nano Energy 2024, 122, 109286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Bard, A.J. Electrons on dielectrics and contact electrification. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2009, 480, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z.L. Electrostatic Charges Regulate Chemiluminescence by Electron Transfer at the Liquid–Solid Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 2754–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Berbille, A.; Feng, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Contact-electro-catalysis for the degradation of organic pollutants using pristine dielectric powders. Nat Commun. 2022, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, S.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, J.; Willatzen, M.; Wang, Z.L.; Wei, D. Nonaqueous Contact-Electro-Chemistry via Triboelectric Charge. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 31574–31584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, X.; Li, S.; Sun, B.; Wang, Z.; Wei, D. Revealing the Role of Interfacial Charge Transfer in Mechanoluminescence. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090656
Huo X, Li S, Sun B, Wang Z, Wei D. Revealing the Role of Interfacial Charge Transfer in Mechanoluminescence. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(9):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090656
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Xinyi, Shaoxin Li, Bing Sun, Zhonglin Wang, and Di Wei. 2025. "Revealing the Role of Interfacial Charge Transfer in Mechanoluminescence" Nanomaterials 15, no. 9: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090656
APA StyleHuo, X., Li, S., Sun, B., Wang, Z., & Wei, D. (2025). Revealing the Role of Interfacial Charge Transfer in Mechanoluminescence. Nanomaterials, 15(9), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15090656









