Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Uric Acid Using a Poly(l-lysine)/Graphene Oxide Modified Electrode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fabrication and Characterization of Poly(l-lysine)/Graphene Oxide Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode (PLL/GO/GCE)
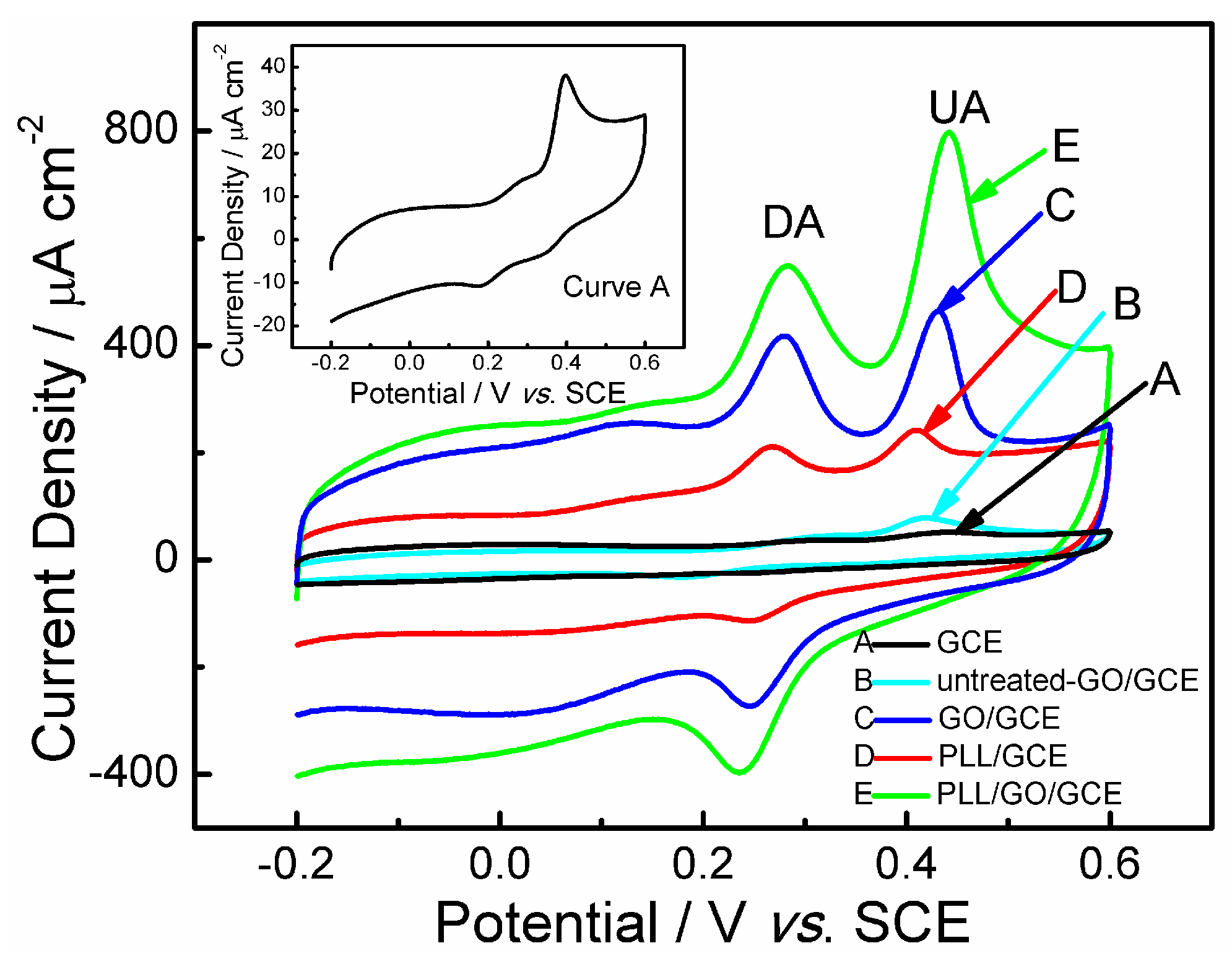
2.2. Electrochemical Behaviors of Uric Acid and Dopamine at Various Electrodes
2.3. Effective Surface Area of the PLL/GO/GCE
2.4. Influence of Scan Rate
2.5. Influence of pH
2.6. Optimization of Preparation Conditions of PLL/GO/GCE Sensor
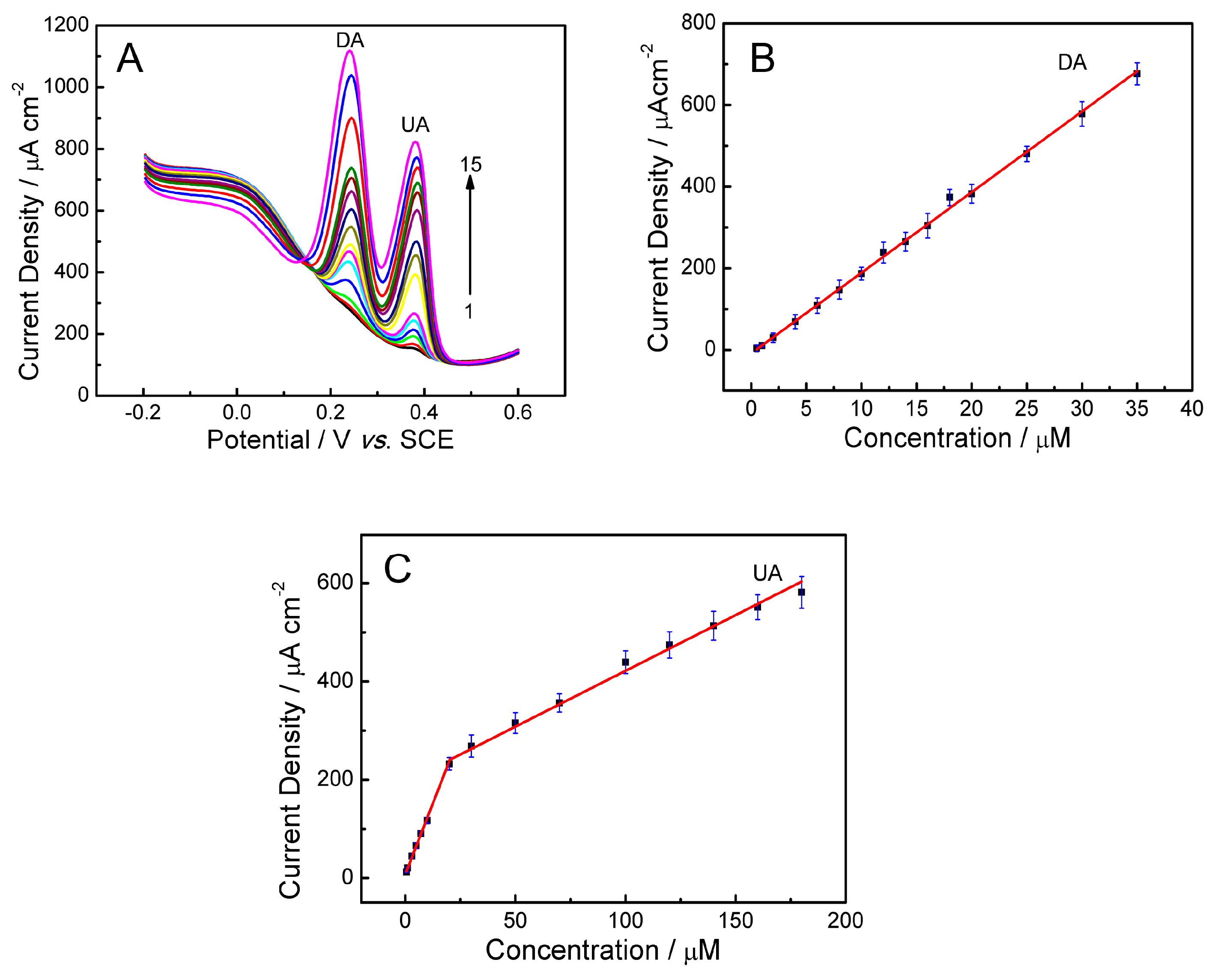
2.7. Detection of UA and DA
2.7.1. Selective Detection
2.7.2. Simultaneous Detection
2.8. Reproducibility, Stability and Interferences
2.9. Analysis of Practical Samples
2.9.1. Determination of UA in Real Biological Samples
2.9.2. Determination of DA in Dopamine Hydrochloride Injection
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Preparation of the Modified Electrodes
3.4. Experimental Methods
3.5. Sample Preparation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopin, I. Catecholamine metabolism: Basic aspects and clinical significance. Pharmacol. Rev. 1985, 37, 333–364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wightman, R.M.; May, L.J.; Michael, A.C. Detection of dopamine dynamics in the brain. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 769A–793A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, M.R.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.; Shahbazikhah, P. Chemometric-assisted kinetic-spectrophotometric method for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, uric acid, and dopamine. Anal. Chem. 2011, 410, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Chen, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, W. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence behavior of peptide nanovesicle and its application in sensing dopamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Song, H.; Hao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Lv, Y. Luminescent zno quantum dots for sensitive and selective detection of dopamine. Talanta 2013, 107, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Qiu, P.; Yang, L.; Cao, X.; Jin, L. Determination of dopamine in rat striatum by microdialysis and high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection on a functionalized multi-wall carbon nanotube electrode. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 384, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Feng, L.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Electrochemical detection of dopamine using porphyrin-functionalized graphene. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xing, X.; Yu, J.; Lian, W.; Li, J.; Cui, M.; Huang, J. A novel label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on graphene-polyaniline composite film for dopamine determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.R.; Ma, Y.; Parajuli, R.R.; Balogun, Y.; Lai, W.Y.-C.; He, H. A nonoxidative sensor based on a self-doped polyaniline/carbon nanotube composite for sensitive and selective detection of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 2583–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venton, B.J.; Wightman, R.M. Psychoanalytical electrochemistry: Dopamine and behavior. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 414A–421A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutt, V.E.; Mottola, H. Determination of uric acid at the microgram level by a kinetic procedure based on a pseudo-induction period. Anal. Chem. 1974, 46, 1777–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lin, P.; Yan, X.; Kang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lei, Y.; Li, C.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y. Enzyme-coated single zno nanowire fet biosensor for detection of uric acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.H.; Zheng, X.Q.; Xu, J.Y.; Bao, W.J.; Wang, F.B.; Xia, X.H. Electrochemical sensor based on nitrogen doped graphene: Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.-W.; Li, J.; Lin, J.-M.; Li, H.-F. Determination of gouty arthritis’ biomarkers in human urine using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Anal. 2014, 4, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ying, Y. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid using high-performance screen-printed graphene electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; You, T. Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid at electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Du, J.; Wang, H.; Zou, C.E.; Jiang, F.; Yang, P.; Du, Y. A facile electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide and au nanoplates modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Zhou, L.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Hrapovic, S.; Liu, Y.; Moynihan, H.A.; Glennon, J.D.; Luong, J.H. Selective nanomolar detection of dopamine using a boron-doped diamond electrode modified with an electropolymerized sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin-doped poly(n-acetyltyramine) and polypyrrole composite film. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4089–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Hou, H.; You, T. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine, uric acid and ascorbic acid using palladium nanoparticle-loaded carbon nanofibers modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-C.; Tsai, T.-H.; Chen, S.-M. Performing enzyme-free h 2 o 2 biosensor and simultaneous determination for aa, da, and ua by mwcnt–pedot film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-X.; Zheng, J.-N.; Wang, A.-J.; Wu, L.-J.; Chen, J.-R.; Feng, J.-J. Facile synthesis of porous bimetallic alloyed pdag nanoflowers supported on reduced graphene oxide for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Analyst 2015, 140, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhou, X.; Ji, X.; Lin, R.; Lin, W. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid using poly(4-aminobutyric acid) modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 178, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Honma, I.; Zhou, H. Simultaneous voltammetric detection of dopamine and uric acid at their physiological level in the presence of ascorbic acid using poly(acrylic acid)-multiwalled carbon-nanotube composite-covered glassy-carbon electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, X. Simultaneous electroanalysis of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid by poly (vinyl alcohol) covalently modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 115, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Taei, M.; Khayamian, T.; Arabzadeh, A. Highly selective determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid by differential pulse voltammetry using poly(sulfonazo iii) modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 147, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Cai, X.; Shi, Q.; Liu, L.; Wan, D.; Tan, S. Poly-l-lysine-modified reduced graphene oxide stabilizes the copper nanoparticles with higher water-solubility and long-term additively antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 107, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, R. Glucose sensor based on an electrochemical reduced graphene oxide-poly(l-lysine) composite film modified gc electrode. Analyst 2012, 137, 5716–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, C.; Yang, H.; Han, D.; Zhang, Q.; Ivaska, A.; Niu, L. Water-soluble graphene covalently functionalized by biocompatible poly-l-lysine. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12030–12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, F.-X.; Wang, K.; Wang, F.-B.; Xia, X.-H. Synthesis of a hydrophilic poly-l-lysine/graphene hybrid through multiple non-covalent interactions for biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhan, Y.; He, L. Graphene oxide/poly-l-lysine assembled layer for adhesion and electrochemical impedance detection of leukemia k562 cancercells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, X.; Li, G.; Gao, H.; Sun, Z. Electrochemical deoxyribonucleic acid biosensor based on carboxyl functionalized graphene oxide and poly-l-lysine modified electrode for the detection of tlh gene sequence related to vibrio parahaemolyticus. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 752, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, A.; Gasnier, A.; Pedano, M.L.; Gonzalez-Dominguez, J.M.; Ansón-Casaos, A.; Hernández-Ferrer, J.; Galicia, L.; Rubianes, M.D.; Martínez, M.T.; Rivas, G.A. Electrochemical sensor for the quantification of dopamine using glassy carbon electrodes modified with single-wall carbon nanotubes covalently functionalized with polylysine. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Huang, G.-Q.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Xu, X.-F. Graphene oxide-ag/poly-l-lysine modified glassy carbon electrode as an electrochemical sensor for the determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 759, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Han, Z.; Lei, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, M.; Hao, Q. Fast electrochemical determination of imidacloprid at an activated glassy carbon electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, B9–B13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, M.A.; John, S.A. Simultaneous determination of uric acid, xanthine, hypoxanthine and caffeine in human blood serum and urine samples using electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 771, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anson, F. Application of potentiostatic current integration to the study of the adsorption of cobalt (iii)-(ethylenedinitrilo (tetraacetate) on mercury electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.N. Electrochemistry at Solid Electrodes; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1969; p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, X. Electrochemical behavior of a covalently modified glassy carbon electrode with aspartic acid and its use for voltammetric differentiation of dopamine and ascorbic acid. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, L.-L. Electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of uric acid, xanthine and hypoxanthine based on poly(bromocresol purple) modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.P.; Lima, A.W.O.; Serrano, S.H. Simultaneous voltammetric detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid using a pyrolytic graphite electrode modified into dopamine solution. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 612, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y. Glassy carbon electrode modified with poly(dibromofluorescein) for the selective determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid. Microchim. Acta 2012, 178, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hao, Q.; Yang, X.; Lu, L.; Wang, X. Effect of graphene oxide on the properties of its composite with polyaniline. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Electrode | Analyte | Linear Range (μM) | Detection Limit (μM) | Sensitivity (μA·cm−2·μM−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen doped graphene/GCE | DA | 0.5–170 | 0.28 | 0.45 | [13] |
| UA | 0.1–20 | 0.045 | 20.61 | ||
| ERGOa/GCE | DA | 0.5–60 | 0.5 | 7.11 | [16] |
| UA | 0.5–60 | 0.5 | 7.97 | ||
| Poly(Vinyl alcohol) | DA | 2–70 | 1.4 | 13.52 | [24] |
| UA | 2–50 | 0.6 | 43.82 | ||
| Au/Reduced graphene oxide/GCE | DA | 6.8–41 | 1.4 | 14.08 | [17] |
| UA | 8.8–53 | 1.8 | 7.04 | ||
| PLL/GO/GCE | DA | 0.5–35 | 0.021 | 19.72 | This work |
| UA | 0.5–20 20–200 | 0.074 | 11.50 |
| Sample | Found (μM) | Added (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%) | R.S.D (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum 1 | 48.26 | 10 | 58.4 | 101.4 | 2.4 |
| Serum 2 | 56.57 | 20 | 75.87 | 96.5 | 3.1 |
| Urine 1 | 45.17 | 20 | 64.30 | 95.65 | 1.4 |
| Urine 2 | 40.46 | 15 | 56.05 | 103.9 | 1.8 |
| DA Specified (μM) | Added (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%) | R.S.D (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.5 | 0 | 10.25 | - | 1.86 |
| 10.5 | 5 | 15.63 | 102.6 | 1.07 |
| 10.5 | 10 | 20.45 | 99.5 | 0.83 |
| 10.5 | 15 | 25.67 | 101.1 | 1.21 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Lei, W.; Xu, Y.; Xia, X.; Hao, Q. Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Uric Acid Using a Poly(l-lysine)/Graphene Oxide Modified Electrode. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6100178
Zhang Y, Lei W, Xu Y, Xia X, Hao Q. Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Uric Acid Using a Poly(l-lysine)/Graphene Oxide Modified Electrode. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(10):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6100178
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuehua, Wu Lei, Yujuan Xu, Xifeng Xia, and Qingli Hao. 2016. "Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Uric Acid Using a Poly(l-lysine)/Graphene Oxide Modified Electrode" Nanomaterials 6, no. 10: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6100178
APA StyleZhang, Y., Lei, W., Xu, Y., Xia, X., & Hao, Q. (2016). Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Uric Acid Using a Poly(l-lysine)/Graphene Oxide Modified Electrode. Nanomaterials, 6(10), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6100178






