Size- and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
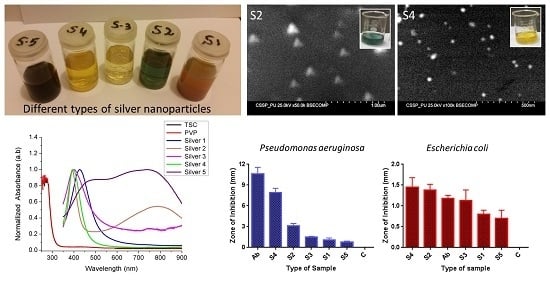
2.1. Silver Nanoparticles Production
2.2. UV-VIS Spectroscopy Investigations
2.3. Scanning Electron Micrscopy Analysis
2.4. X-Ray Diffraction Pattern
2.5. Antibacterial Activity Study
3. Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization Analysis
3.2. Effect of Shape and Size on Antibacterial Activity
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles
4.2.1. Sample 1 (S1)
4.2.2. Sample 2 (S2)
4.2.3. Sample 3 (S3)
4.2.4. Sample 4 (S4)
4.2.5. Sample 5 (S5)
4.3. Characterization of Prepared Silver Nanoparticle Samples
4.4. Antibacterial Activity Tests
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| TSC | Tri-sodium citrate |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| ZOI | Zone of Inhibition |
| FCC | Face Centered Cubic |
References
- Takeshima, T.; Tada, Y.; Sakaguchi, N.; Watari, F.; Fugetsu, B. DNA/Ag nanoparticles as antibacterial agents against gram-negative bacteria. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Size-dependent catalytic activity of silver nanoparticles for the oxidation of styrene. Chem. Asian J. 2006, 1, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles. Science 2002, 298, 2176–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pileni, M.-P. Magnetic Fluids: Fabrication, Magnetic Properties, and Organization of Nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2001, 11, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.W. History of the medical use of silver. Surg. Infect. 2009, 10, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastus, N.G.; Merkoci, F.; Piella, J.; Puntes, V. Synthesis of highly monodisperse citrate-stabilized silver nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: Kinetic control and catalytic properties. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2836–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panacek, A.; Kolar, M.; Vecerova, R.; Prucek, R.; Soukupova, J.; Krystof, V.; Hamal, P.; Zboril, R.; Kvitek, L. Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles against Candida spp. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6333–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdiero, S.; Falanga, A.; Vitiello, M.; Cantisani, M.; Marra, V.; Galdiero, M. Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antiviral Agents. Molecules 2011, 16, 8894–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernousova, S.; Epple, M. Silver as antibacterial agent: Ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Deng, K.K.; Kim, N.J.; Ross, L.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Hu, Z.Q. The inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles, silver ions, and silver chloride colloids on microbial growth. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3066–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, N.; Marcato, P.D.; De Souza, G.I.H.; Alves, O.L.; Esposito, E. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles produced by fungal process on textile fabrics and their effluent treatment. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2007, 3, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Depend on the Shape of the Nanoparticle? A Study of the Gram-Negative Bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodrow Wilson Database. An Inventory of Nanotechnology based Consumer Products Currently on the Market. 2011. Available online: http://www.nanotechproject.org/inventories/consumer/analysis_draft/ (accessed on 25 December 2015).
- Asghari, S.; Johari, S.A.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Jeon, Y.B.; Choi, H.J.; Moon, M.C.; Yu, I.J. Toxicity of various silver nanoparticles compared to silver ions in Daphnia magna. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Castanon, G.A.; Nino-Martinez, N.; Martinez-Gutierrez, F.; Martinez-Mendoza, J.R.; Ruiz, F. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles with different sizes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.V.; Ha, C.H.; Binh, L.T.; Kasbohm, J. Chemical synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel-shaped silver nanoparticles. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kruis, F.; Fissan, H.; Rellinghaus, B. Sintering and evaporation characteristics of gas-phase synthesis of size-selected PbS nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2000, 69, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafune, F.; Kohno, J.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Sawabe, H. Structure and stability of silver nanoparticles in aqueous solution produced by laser ablation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 8333–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, J.P.; Wark, A.W.; Brevet, P.F.; Girault, H.H. Preparation of silver nanoparticles in solution from a silver salt by laser irradiation. Chem. Commun. 2002, 7, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swathy, B. A Review on Metallic Silver Nanoparticles. IOSR J. Pharm. 2014, 4, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanpuria, P.; Rana, N.K.; Yadav, S.K. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles: Technological concepts and future applications. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, B.; Garmaroudi, F.S.; Hashemi, M.; Nezhad, H.R.; Nasrollahi, A.; Ardalan, S.; Ardalan, S. Comparison of the anti-bacterial activity on the nanosilver shapes: Nanoparticles, nanorods and nanoplates. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramirez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, L.A.; Gmez-Quintero, T.J.R.; Padron, G.H.; Santana, F.B.; Hernandez, J.F.; Castano, V.M. Silver nanoprisms and nanospheres for prosthetic biomaterials, IADR/AADR/CADR General Session and Exhibition 2013; 03/2013. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266784565_Silver_nanoprisms_and_nanospheres_for_prosthetic_biomaterials (accessed on 25 December 2015).
- El-Kheshen, A.A.; El-Rab, S.F.G. Effect of reducing and protecting agents on size of silver nanoparticles and their anti-bacterial activity. Pharma Chem. 2012, 4, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Albanese, A.; Tang, P.S.; Chan, W.C.W. The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, B.; Sun, Y.; Mayers, B.; Xi, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanostructures: The case of silver. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, G.; Singh, D.; Yadawa, P.K. Study of Copper/Palladium Nanoclusters Using Acoustic Particle Sizer. Platin. Met. Rev. 2013, 57, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Lu, Z.Z.; Velayudham, M.; Lu, K.L.; Rajagopal, S. Alumina supported nanoruthenium as efficient heterogeneous catalyst for the selective H2O2 oxidation of aliphatic and aromatic sulfides to sulfoxides. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2010, 332, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agasti, N.; Kaushik, N.K. One pot synthesis of crystalline silver nanoparticles. Am. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, R.; Bashir, M.; Raza, M.A.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Effect of calcination on structural and magnetic properties of Co doped ZnO nanostructures. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Lee, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Høiby, N.; Song, Z. Effects of ginseng on Pseudomonas aeruginosa motility and biofilm formation. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloning & Expression of sMMO. Available online: http://2014.igem.org/Team:Braunschweig/Results-content (accessed on 16 February 2016).
- Registery of Standard Bilogical Parts. Available online: http://parts.igem.org/File:2014SDUGrowth_curve_%28WT,_OneProt, _Empty_vector%29.png (accessed on 16 February 2016).
- Li, D.; Kaner, R.B. Shape and Aggregation Control of Nanoparticles: Not Shaken, Not Stirred. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Cao, Y.W.; Mirkin, C.A.; Kelly, K.L.; Schatz, G.C.; Zheng, J.G. Photoinduced Conversion of Silver Nanospheres to Nanoprisms. Science 2001, 294, 1901–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragg, P.D.; Rainnie, D.J. The effect of silver ions on the respiratory chains of Escherichia coli. Can. J. Microbiol. 1974, 20, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Puppala, H.L.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Negligible Particle-Specific Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4271–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, Y.K.; Pal, S.; Naoghare, P.K.; Rangasamy, S.; Song, J.M. Shape-dependent skin penetration of silver nanoparticles: Does it really matter. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Sample | Precursor | Reducing Agent | Stabilizing Agent | Oxidizing Agent | Reaction Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | AgNO3 (1 mM, 50 mL) | Na3C6H5O7 (1%, 5 mL), added dropwise | TSC | - | At boiling temp, vigorous continuous stirring, finally cooled at room temp |
| S2 | AgNO3 (5 mM, 1 mL) | NaBH4 (50 mM, 0.5 mL), Na3C6H5O7 (30 mM, 3 mL) | PVP (0.5 mL, 1 mM), TSC | H2O2 (0.2 mL) | At room temp, continuous stirring (400 rpm) through the experiment |
| S3 | AgNO3 (1 mM, 2 mL), Added dropwise | NaBH4 (2 mM, 50 mL) | - | - | At ice cooling, stirring (400 rpm) until all AgNO3 was added |
| S4 | AgNO3 (5 mM, 1 mL) | NaBH4 (50 mM, 0.5 mL), Na3C6H5O7 (30 mM, 0.5 mL) | PVP (0.5 mL, 1 mM), TSC | - | At room temp, NaBH4 was added quickly, Stirring (400 rpm) was stopped before adding NaBH4 |
| S5 | AgNO3 (5 mM, 1 mL) | NaBH4 (50 mM, 0.5 mL), Na3C6H5O7 (30 mM, 3 mL) | PVP (0.5 mL, 1 mM), TSC | H2O2 (0.2 mL) | At room temp, in dark, stirring (400 rpm) was stopped before adding NaBH4 |
| Sample | Peaks | FWHM | Color | Shape | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 426 nm | 107 nm | Greenish yellow | Spherical | 30–80 nm |
| S2 | 392 nm | 53 nm | Dark green | Triangular | Edge-length 150 nm |
| 789 nm | |||||
| S3 | 403 nm | 152 nm | Light yellow | spherical | 25–70 nm |
| S4 | 397 nm | 73 nm | Bright yellow | spherical | 15–50 nm |
| S5 | 504 nm | 544 nm | Dark blue | spherical | 30–200 nm |
| 678 nm | |||||
| 735 nm |
| Sample | P. aeruginosa | E. coli |
|---|---|---|
| C | 0 | 0 |
| Ab | 11.3 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.1 |
| S1 | 1 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.15 |
| S2 | 3 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.2 |
| S3 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.35 |
| S4 | 8 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.3 |
| S5 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.3 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size- and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6040074
Raza MA, Kanwal Z, Rauf A, Sabri AN, Riaz S, Naseem S. Size- and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(4):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6040074
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaza, Muhammad Akram, Zakia Kanwal, Anum Rauf, Anjum Nasim Sabri, Saira Riaz, and Shahzad Naseem. 2016. "Size- and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes" Nanomaterials 6, no. 4: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6040074
APA StyleRaza, M. A., Kanwal, Z., Rauf, A., Sabri, A. N., Riaz, S., & Naseem, S. (2016). Size- and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes. Nanomaterials, 6(4), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6040074