Influence of Solution Properties and Process Parameters on the Formation and Morphology of YSZ and NiO Ceramic Nanofibers by Electrospinning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Solution Properties
2.2. Process Parameters
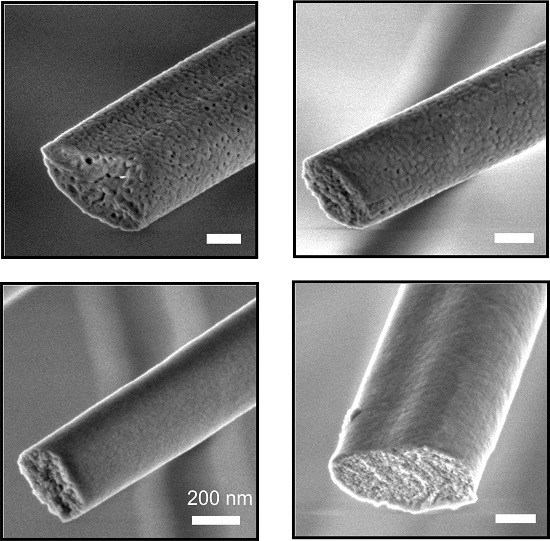
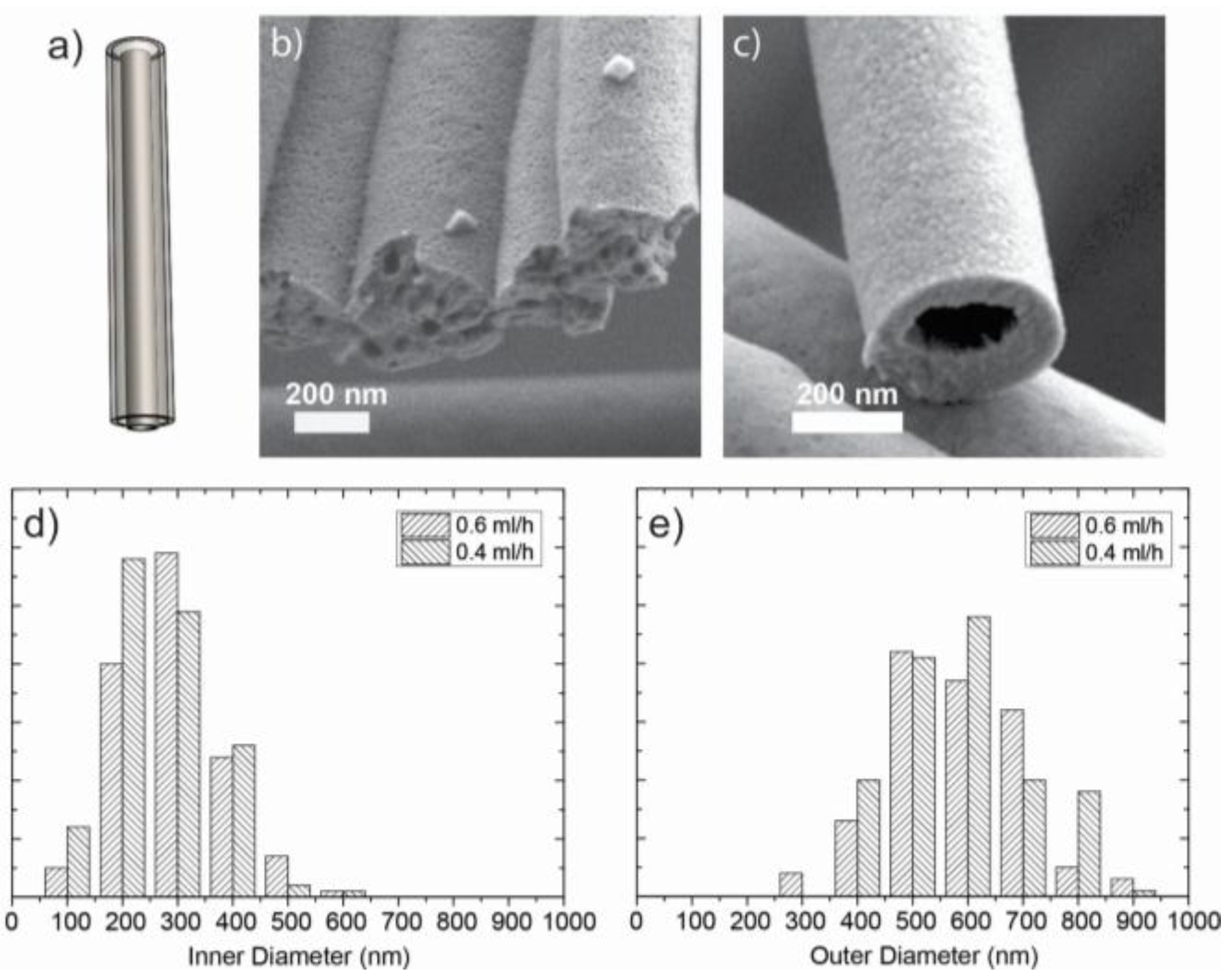
2.3. Hollow Fibers
2.4. Nanofiber Alignment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Electrospinning Solutions
3.3. Fabrication Parameters
3.4. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; McCann, J.T.; Xia, Y.; Marquez, M. Electrospinning: A Simple and Versatile Technique for Producing Ceramic Nanofibers and Nanotubes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Pan, W.; Lin, D.; Li, H. Electrospinning of Ceramic Nanofibers: Fabrication, assembly and applications. J. Adv. Ceram. 2012, 1, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Kim, H.E.; Knowles, J.C. Production and Potential of Bioactive Glass Nanofibers as a Next-Generation Biomaterial. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasita, R.; Katti, D.S. Nanofibers and Their Applications in Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2006, 1, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, V.; Dott, C.; Choonara, Y.E.; Tyagi, C.; Tomar, L.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Ndesendo, V.M.K. A Review of the Effect of Processing Variables on the Fabrication of Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 789289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E.; Xu, H. Electrospinning of Nanofibers from Polymer Solutions and Melts. Adv. Appl. Mech. 2007, 41, 43–346. [Google Scholar]
- Teo, W.E.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Electrospinning Design and Nanofibre Assemblies. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, R89–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, G.; Federici, J.; Imura, Y.; Catalani, L.H. Charge Generation, Charge Transport, and Residual Charge in the Electrospinning of Polymers: A Review of Issues and Complications. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 044701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Polymer Nanofibers by Electrospinning and Their Applications in Nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Functional Materials by Electrospinning of Polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 963–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L.; Fong, H.; Koombhongse, S. Bending Instability of Electrically Charged Liquid Jets of Polymer Solutions in Electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4531–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Koombhongse, S.; Reneker, D.H. Taylor Cone and Jetting from Liquid Droplets in Electrospinning of Nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 4836–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lihua, L.; Yuris, A.D. Analysis of the Effects of the Residual Charge and Gap Size on Electrospun Nanofiber Alignment in a Gap Method. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 355307. [Google Scholar]
- Kalayci, V.E.; Patra, P.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Ugbolue, S.C.; Warner, S.B. Charge Consequences in Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Nanofibers. Polymer 2005, 46, 7191–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Polymeric and Ceramic Nanofibers as Uniaxially Aligned Arrays. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaseshan, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Jose, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanostructured Ceramics by Electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, W.; Formo, E.; Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Ceramic Nanofibers Fabricated by Electrospinning and Their Applications in Catalysis, Environmental Science, and Energy Technology. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, V.; Anandjiwala, R.D.; Maaza, M. The Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Structural Morphology and Diameter of Electrospun Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Systematic Parameter Study for Ultra-Fine Fiber Fabrication via Electrospinning Process. Polymer 2005, 46, 6128–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelofsky, A.H. Surface Tension-Viscosity Relation for Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1966, 11, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonhorn, H. Surface Tension-Viscosity Relationship for Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1967, 12, 524–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.-H.; Yu, J.-Y.; Zeng, H.-M. Controlling Numbers and Sizes of Beads in Electrospun Nanofibers. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.J. The Stretching of an Electrified Non-Newtonian Jet: A Model for Electrospinning. Phys. Fluids 2002, 14, 3912–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohman, M.M.; Shin, M.; Rutledge, G.; Brenner, M.P. Electrospinning and Electrically Forced Jets. I. Stability Theory. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 2201–2220. [Google Scholar]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, K.; Magder, J.; Vukasovich, M.S.; Lockhart, R.J. Ferroelectrics of Ultrafine Particle Size: I, Synthesis of Titanate Powders of Ultrafine Particle Size. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1966, 49, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawski, T.M.; Veldhuis, S.A.; Göbel, O.F.; ten Elshof, J.E.; Blank, D.H.A. Effects of Reaction Medium on the Phase Synthesis and Particle Size Evolution of BaTiO3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 3443–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.; Tejedor, J.; Rodríguez, L.J. Encapsulation of Nabumetone by Means of -Drug: (β-Cyclodextrin)2:Polyvinylpyrrolidone Ternary Complex Formation. J. Lumin. 2007, 126, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, S.A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Experimental Investigation of the Governing Parameters in the Electrospinning of Polymer Solutions. Polymer 2004, 45, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.L.; Bates, W.D.; Frisch, H.L.; Wnek, G.E. Role of Chain Entanglements on Fiber Formation during Electrospinning of Polymer Solutions: Good Solvent, Non-Specific Polymer–Polymer Interaction Limit. Polymer 2005, 46, 3372–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, T.J.; Xu, J.; Elmas, S.; Mange, Y.J.; Skinner, W.M.; Xu, H.; Nann, T. NiO Nanofibers as a Candidate for a Nanophotocathode. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ercolano, G.; Farina, F.; Cavaliere, S.; Jones, D.J.; Rozière, J. Nickel Based Electrospun Materials with Tuned Morphology and Composition. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.J.; Chase, G.G.; Yarin, A.L.; Reneker, D.H. Effects of Parameters on Nanofiber Diameter Determined from Electrospinning Model. Polymer 2007, 48, 6913–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrikh, S.; Yu, J.; Brenner, M.; Rutledge, G. Controlling the Fiber Diameter during Electrospinning. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 144502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappe, C.O.; Dallinger, D.; Murphree, S.S. Practical Microwave Synthesis for Organic Chemists: Strategies, Instruments, and Protocols; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–299. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Binner, J.; Vaidhyanathan, B.; Joomun, N.; Kilner, J.; Dimitrakis, G.; Cross, T.E. Evidence for the Microwave Effect during Hybrid Sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y. Microwave Processing and Properties of Ceramics with Different Dielectric Loss. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 19, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, A.; Chang, T.H.; Chang, H.Y.; Cheng, S.Y. Low-Temperature Crystallization of Sol–Gel-Derived Lead Zirconate Titanate Thin Films Using 2.45 GHz Microwaves. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaresan, S.; Rao, M.; Tian, Y.; Schreifels, J.; Wood, M.; Jones, K.; Davydov, A. Comparison of Solid-State Microwave Annealing with Conventional Furnace Annealing of Ion-Implanted SiC. J. Electron. Mater. 2007, 36, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaresan, S.G.; Rao, M.V.; Tian, Y.-L.; Ridgway, M.C.; Schreifels, J.A.; Kopanski, J.J. Ultrahigh-Temperature Microwave Annealing of Al+- And P+-Implanted 4H-SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 073708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Travitzky, N.; Singurindy, A.; Kravchik, M. Direct Microwave Sintering of Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia At 2.45 GHz. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 19, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuis, S.A.; Brinks, P.; ten Elshof, J.E. Rapid densification of sol–gel derived yttria-stabilized zirconia thin films. Thin Solid Films 2015, 589, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroe, R.; Rowley, A.T. Evidence for a Non-Thermal Microwave Effect in The Sintering of Partially Stabilized Zirconia. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadafalch Gazquez, G.; Lei, S.; George, A.; Gullapalli, H.; Boukamp, B.A.; Ajayan, P.M.; ten Elshof, J.E. Low-Cost, Large-Area, Facile, and Rapid Fabrication of Aligned ZnO Nanowire Device Arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13466–13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurey, V.; Chiang, P.-C.; Polanco, C.; Su, Y.-H.; Chou, C.-F.; Swami, N.S. Interplay of Electrical Forces for Alignment of Sub-100 nm Electrospun Nanofibers on Insulator Gap Collectors. Langmuir 2010, 26, 19022–19026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.C.; Koch, W.F.; Arvay, E.; Feng, D.; Holland, L.A.; Juhasz, E. A DC Method for the Absolute Determination of Conductivities of the Primary Standard KCl Solutions from 0 °C to 50 °C. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 1994, 99, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Koch, W.F.; Pratt, K.W. Proposed New Electrolytic Conductivity Primary Standards for KCl Solutions. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 1991, 96, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, K.W.; Koch, W.F.; Wu, Y.C.; Berezansky, P.A. Molality-Based Primary Standards of Electrolytic Conductivity. Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nature Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






| 3YSZ | NiO | |
|---|---|---|
| η (mPa·s) | 46 ± 0.15 | 325 ± 2 |
| σ (μS/cm) | 58 ± 0.07 | 397 ± 5 |
| γ (mN/m) | 9.45 ± 0.07 | 9.58 ± 0.05 |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cadafalch Gazquez, G.; Smulders, V.; Veldhuis, S.A.; Wieringa, P.; Moroni, L.; Boukamp, B.A.; Ten Elshof, J.E. Influence of Solution Properties and Process Parameters on the Formation and Morphology of YSZ and NiO Ceramic Nanofibers by Electrospinning. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7010016
Cadafalch Gazquez G, Smulders V, Veldhuis SA, Wieringa P, Moroni L, Boukamp BA, Ten Elshof JE. Influence of Solution Properties and Process Parameters on the Formation and Morphology of YSZ and NiO Ceramic Nanofibers by Electrospinning. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleCadafalch Gazquez, Gerard, Vera Smulders, Sjoerd A. Veldhuis, Paul Wieringa, Lorenzo Moroni, Bernard A. Boukamp, and Johan E. Ten Elshof. 2017. "Influence of Solution Properties and Process Parameters on the Formation and Morphology of YSZ and NiO Ceramic Nanofibers by Electrospinning" Nanomaterials 7, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7010016
APA StyleCadafalch Gazquez, G., Smulders, V., Veldhuis, S. A., Wieringa, P., Moroni, L., Boukamp, B. A., & Ten Elshof, J. E. (2017). Influence of Solution Properties and Process Parameters on the Formation and Morphology of YSZ and NiO Ceramic Nanofibers by Electrospinning. Nanomaterials, 7(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7010016