New Three-Dimensional Porous Electrode Concept: Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes Directly Grown on Embroidered Copper Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
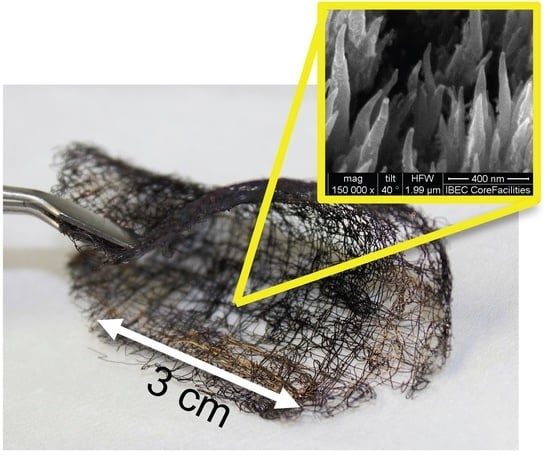
2.1. Morphological Characteristics of the Anodes
2.2. Electrochemical Performance of the Anodes
3. Discussion
- (1)
- A better performance of short CNTs (200 nm) compared to longer CNTs (5 µm) as described in [5]. They reached values of about 600 mAh·g−1 at 25 mA·g−1, which are still lower than our specific capacities. However, those samples were not VA-CNTs.
- (2)
- A higher Li ion diffusion and intercalation on the CNTs. That was already observed in VA-CNTs, but the cylindrical geometry of the embroidered Cu current collectors might have helped to increase the Li+ diffusion and intercalation, and enhance the performance of as-grown VA-CNTs.
- (3)
- Other factors not considered, such as the role of the metal particles on the VA-CNTs, which could also react with the Li+. However that effect was not observed on the voltage profiles, where larger voltages should have been observed during lithiation and delithiation.
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mazouzi, D.; Reyter, D.; Gauthier, M.; Moreau, P.; Guyomard, D.; Roué, L.; Lestriez, B. Very high surface capacity observed using Si negative electrodes embedded in copper foam as 3D current collectors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiló-Aguayo, N.; Espiñeira, P.P.; Manian, A.P.; Bechtold, T. Three-dimensional embroidered current collectors for ultra-thick electrodes in batteries. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 69685–69690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, B.J.; Ganter, M.J.; Cress, C.D.; DiLeo, R.A.; Raffaelle, R.P. Carbon nanotubes for lithium ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 638–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Patel, M.; Rangasamy, B.; Jung, K. Three-dimensional carbon nanotubes for high capacity lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 299, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Wang, J.N.; Chang, H.; Zhang, Y.F. Preparation of short carbon nanotubes and application as an electrode material in Li-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3613–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Yun, Y.; Jin, H.-J. Applications of Carbon Nanotubes for Lithium Ion Battery Anodes. Materials 2013, 6, 1138–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.Y.; Hong, S.; Yu, A.; Jung, S.M.; Jeoung, S.K.; Jung, Y.J. Efficient lithium storage from modified vertically aligned carbon nanotubes with open-ends. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 68875–68880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Sohn, H.-J. Li-alloy based anode materials for Li secondary batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3115–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, N.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhong, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q. Fe2O3 nanoparticles wrapped in multi-walled carbon nanotubes with enhanced lithium storage capability. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goriparti, S.; Miele, E.; De Angelis, F.; Di Fabrizio, E.; Proietti Zaccaria, R.; Capiglia, C. Review on recent progress of nanostructured anode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 257, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, E.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Hou, J.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Cao, A.; Fang, Y. Carbon nanotube network embroidered graphene films for monolithic all-carbon electronics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, H.; Jian, M.; Li, Y.; Xia, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Ma, M.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Extremely Black Vertically Aligned Carbon Nanotube Arrays for Solar Steam Generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28596–28603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyyappan, M.; Delzeit, L.; Cassell, A.; Hash, D. Carbon nanotube growth by PECVD: A review. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2003, 12, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welna, D.T.; Qu, L.; Taylor, B.E.; Dai, L.; Durstock, M.F. Vertically aligned carbon nanotube electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susantyoko, R.A.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Q.; Fitzgerald, E.; Zhang, Q. Sputtered nickel oxide on vertically-aligned multiwall carbon nanotube arrays for lithium-ion batteries. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 68, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Susantyoko, R.A.; Zhang, Q. A hierarchical 3D carbon nanostructure for high areal capacity and flexible lithium ion batteries. Carbon N. Y. 2016, 98, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Amade, R.; Moreno, H.; Bertran, E. RF-PECVD growth and nitrogen plasma functionalization of CNTs on copper foil for electrochemical applications. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2014, 49, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Yuen, M.M.F. Growth of Vertically Aligned Carbon Nanotube Arrays on Al Substrates through Controlled Diffusion of Catalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 15636–15642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froeis, T.; Lenninger, M.; Bechtold, T.; Grabher, G.; Hofer, J.; Riedmann, M. Electrode for a Galvanic Cell. U.S. Patent 14/423,577, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiló-Aguayo, N.; Amann, P.; Pena Espiñeira, P.; Petrasch, J.; Bechtold, T.; Espiñeira, P.P.; Petrasch, J.; Bechtold, T. X-ray micro tomography of three-dimensional embroidered current collectors for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 306, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, R.; von Sacken, U.; Dahn, J.R. Studies of lithium intercalation into carbons using nonaqueous electrochemical cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 2009–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susantyoko, R.A.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Pey, K.L.; Fitzgerald, E.; Zhang, Q. Germanium coated vertically-aligned multiwall carbon nanotubes as lithium-ion battery anodes. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 77, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Lv, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xia, Q. Electrochemical properties of iron oxides/carbon nanotubes as anode material for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 274, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Mi, R.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L. Lithium storage performance of carbon nanotubes with different nitrogen contents as anodes in lithium ions batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 105, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakkumar, S.R.; Nerkar, J.Y.; Pandolfo, A.G. Rate capability of graphite materials as negative electrodes in lithium-ion capacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3330–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Amade, R.; Jover, E.; Bertran, E. Functionalization of carbon nanotubes by water plasma. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 385604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguiló-Aguayo, N.; Amade, R.; Hussain, S.; Bertran, E.; Bechtold, T. New Three-Dimensional Porous Electrode Concept: Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes Directly Grown on Embroidered Copper Structures. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120438
Aguiló-Aguayo N, Amade R, Hussain S, Bertran E, Bechtold T. New Three-Dimensional Porous Electrode Concept: Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes Directly Grown on Embroidered Copper Structures. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(12):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120438
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguiló-Aguayo, Noemí, Roger Amade, Shahzad Hussain, Enric Bertran, and Thomas Bechtold. 2017. "New Three-Dimensional Porous Electrode Concept: Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes Directly Grown on Embroidered Copper Structures" Nanomaterials 7, no. 12: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120438
APA StyleAguiló-Aguayo, N., Amade, R., Hussain, S., Bertran, E., & Bechtold, T. (2017). New Three-Dimensional Porous Electrode Concept: Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes Directly Grown on Embroidered Copper Structures. Nanomaterials, 7(12), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120438