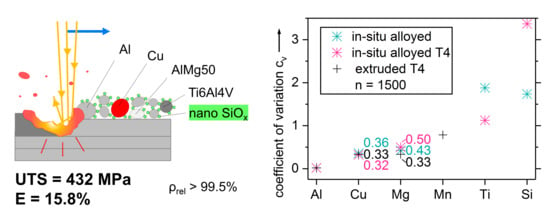
Laser Alloying Advantages by Dry Coating Metallic Powder Mixtures with SiOx Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Incoming Inspection of Metal Powders
3.2. Experimental Establishment of the Initial Situation in LBM of Al-Cu Powder Mixtures Without SiOx
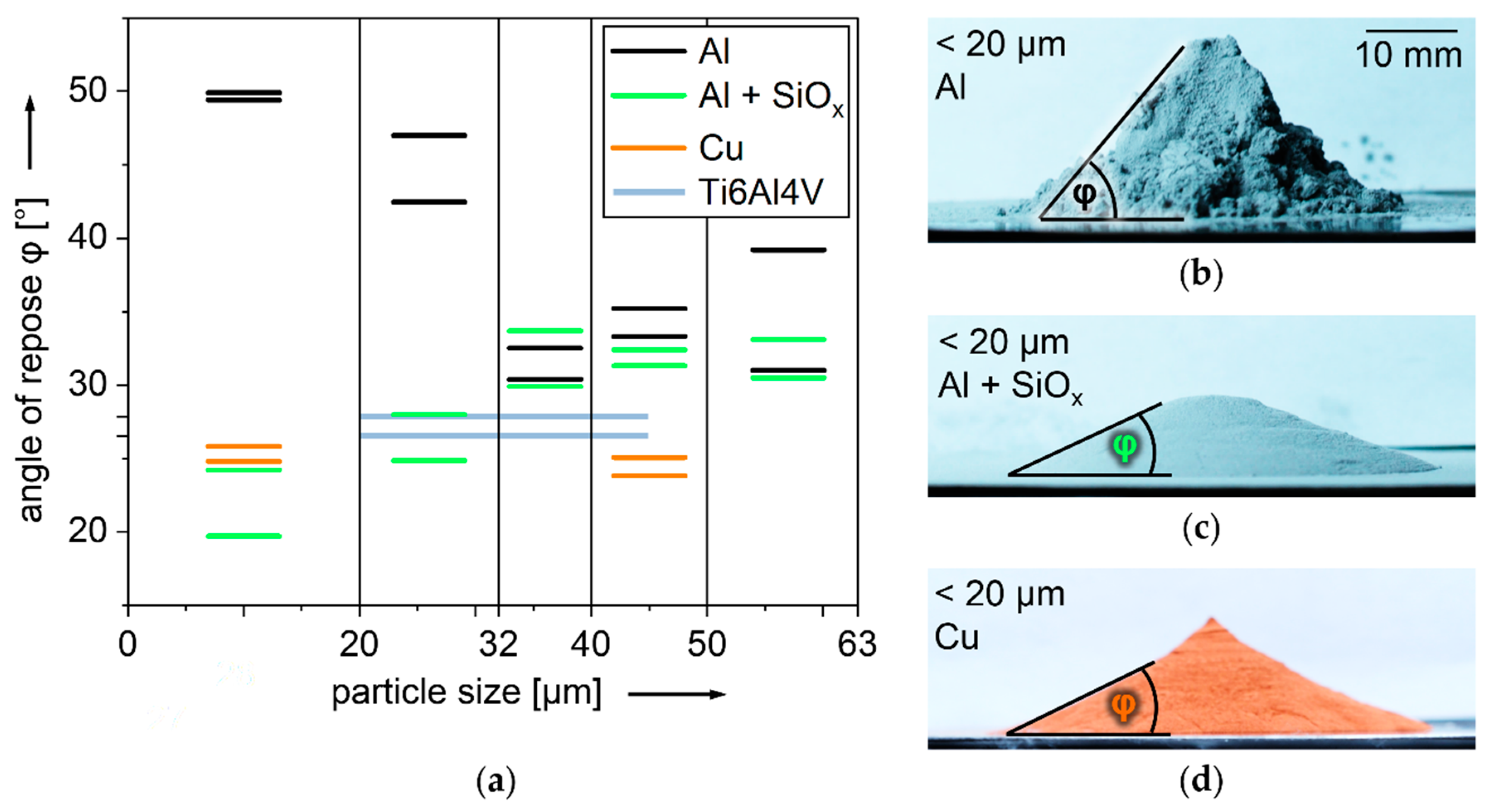
3.3. Angle of Repose φ of Different Powders and Particle Size Fractions with and without Dry Coated SiOx
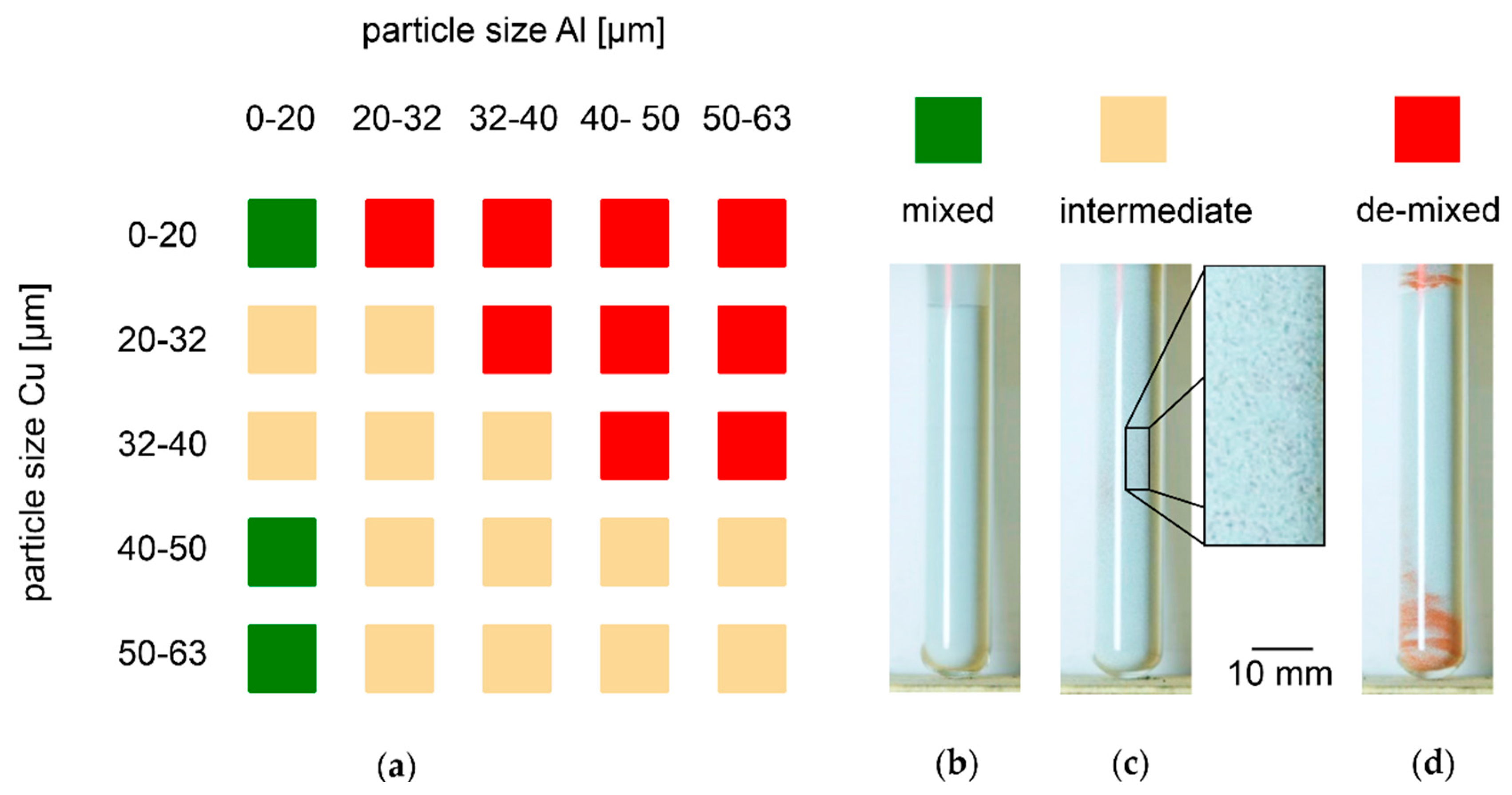
3.4. Segregation Behavior of Free-flowing Powder Mixtures with SiOx and Varied PSD in Vibrated Test Tubes
3.5. Light Microscopic Analysis of Mixture Homogeneity in Thin Powder Layers
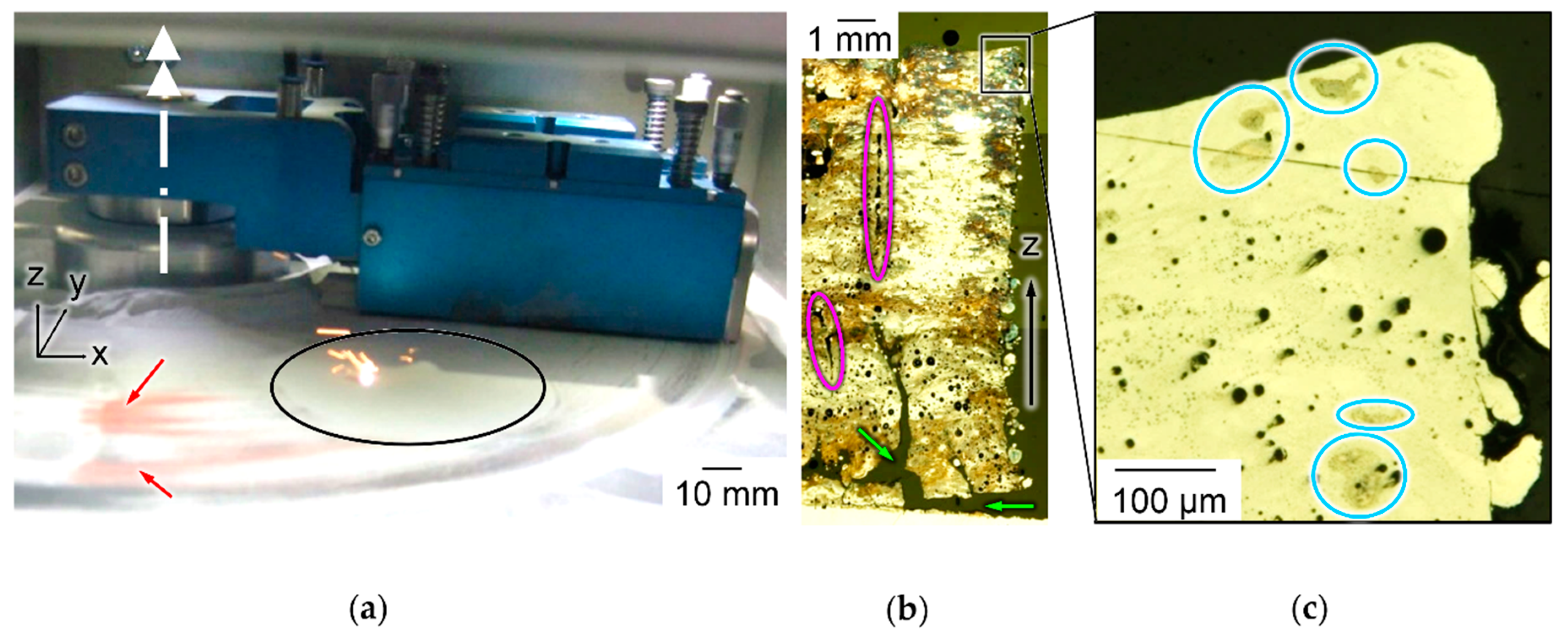
3.6. Micrographic Definition of LBM Process Maps
- (1)
- Al and Cu < 20 µm: 1.42 g/cm³
- (2)
- Al < 20 µm and Cu 32–40 µm: 1.45 g/cm³
- (3)
- Al 20–32 µm and Cu < 20 µm: 1.47 g/cm³
- (1)
- Al and Cu < 20 µm: 65.9 HV0.1 ± 6.2
- (2)
- Al < 20 µm and Cu 32–40 µm: 68.4 HV0.1 ± 7.5
- (3)
- Al 20–32 µm and Cu < 20 µm: 66.5 HV0.1 ± 5.6
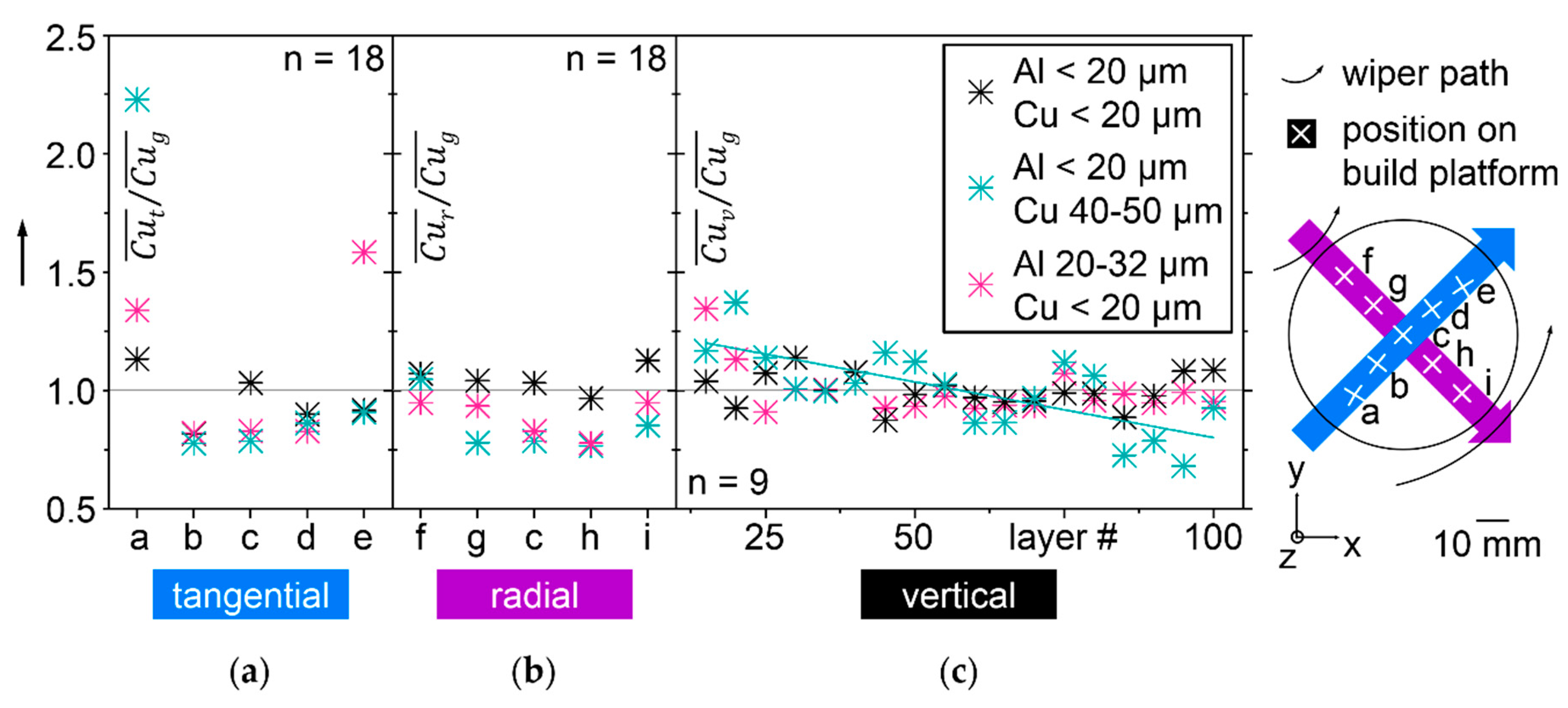
3.7. Chemical Homogeneity Analysis of LBM Samples via EDX and BSE
3.8. Tensile Tests
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
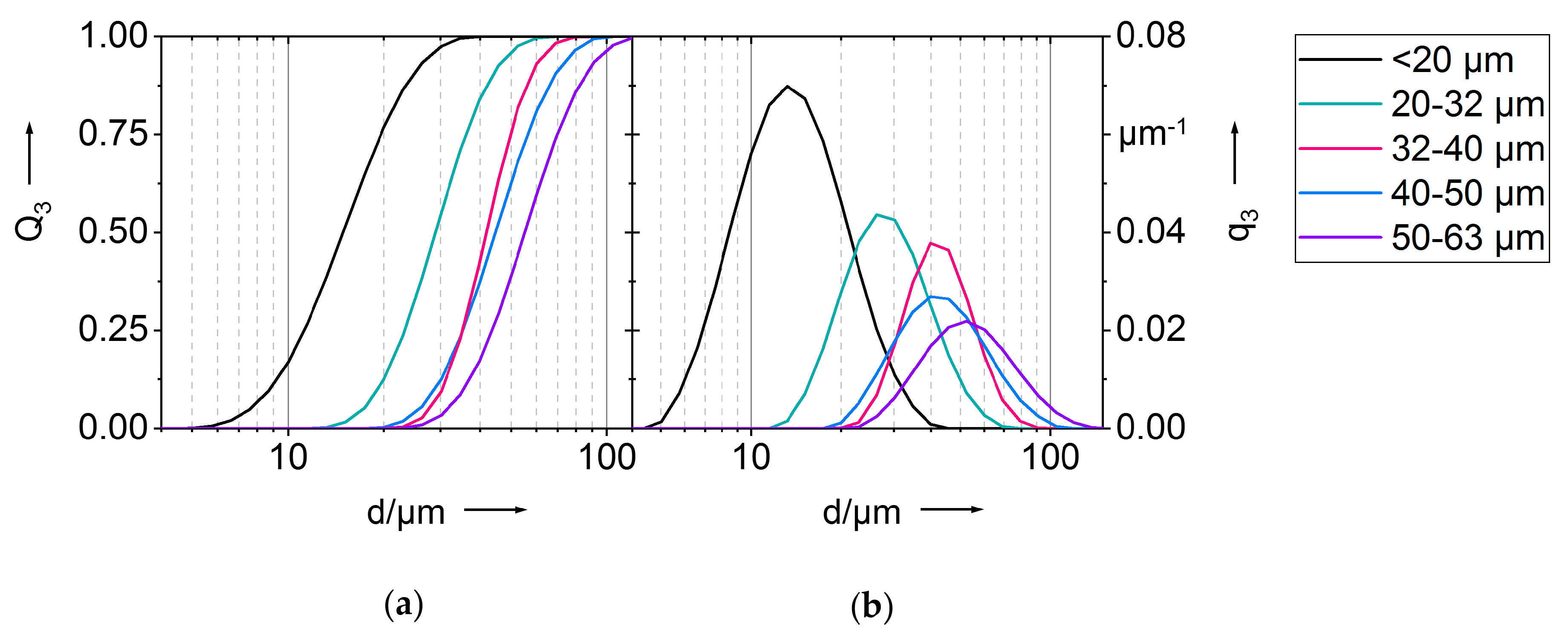
| <20 | 20–32 | 32–40 | 40–50 | 50–63 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d10,3 | 8.78 | 19.2 | 30.5 | 28.9 | 35.7 |
| d50,3 | 14.9 | 30.0 | 41.9 | 44.7 | 55.3 |
| d90,3 | 24.4 | 43.5 | 57.5 | 68.4 | 85.0 |
References
- Schmidt, M.; Merklein, M.; Bourell, D.; Dimitrov, D.; Hausotte, T.; Wegener, K.; Overmeyer, L.; Vollertsen, F.; Levy, G.N. Laser-based additive manufacturing in industry and academia. CIRP Ann. 2017, 66, 561–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlers, T.T.; Caffrey, T.; Campbell, R.I. Wohlers Report 2016. 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing State of the Industry: Annual Worldwide Progress Report, 21st ed.; Wohlers Associates, Inc.: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gausemeier, J.; Schmidt, M.; Leyens, C.; Anderl, R.; Winzer, P.; Schmid, H.-J.; Seliger, G.; Straube, F.; Kohlhuber, M.; Kage, M.; et al. Additive Manufacturing. 2017. Available online: https://www.acatech.de/Publikation/additive-manufacturing/ (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- ISO. Additive Manufacturing—General Principles—Part 2: Overview of Process Categories and Feedstock (ISO 17296-2:2015), 2nd ed.; Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/61626.html (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Fachausschuss 105 Additive Manufacturing. In Additive Fertigungsverfahren Grundlagen, Begriffe, Verfahrensbeschreibungen Additive Manufacturing Processes, Rapid Manufacturing Basics, Definitions, Processes; Beuth Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Available online: https://www.beuth.de/de/technische-regel/vdi-3405/222780081?websource=vdin (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Karg, M.; Ahuja, B.; Schmidt, M. Strategy towards tailored high-performance metal materials for additive manufacturing. In Proceedings of the International Symposium “Additive Manufacturing”, Dresden, Germany, 26 February 2015; p. 69. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/318787770_Strategy_towards_tailored_high-performance_metal_materials_for_additive_manufacturing (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Louvis, E.; Fox, P.; Sutcliffe, C.J. Selective Laser Melting of aluminium components. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2011, 211, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkhair, N.T.; Everitt, N.M.; Ashcroft, I.; Tuck, C. Reducing porosity in AlSi10Mg parts processed by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2014, 1–4, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, M.C.H.; Hentschel, O.; Ahuja, B.; Junker, D.; Hassler, U.; Schäperkötter, C.S.; Haimerl, A.; Arnet, H.; Merklein, M.; Schmidt, M. Comparison of process characteristics and resulting microstructures of maraging steel 1.2709 in Additive Manufacturing via Laser Metal Deposition and Laser Beam Melting in Powder Bed. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Additive Technologies—iCAT 2016, Nürnberg, Germany, 29–30 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bischof, C.; Scheitler, C.; Kneisel, L.; Schmidt, M. Influence of Preheating Temperature and Carbon Content on Crack Formation during Laser Beam Melting of AISI H11 Tool Steel. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Additive Technologies—iCAT 2016, Nürnberg, Germany, 29–30 November 2016; pp. 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Karg, M.; Ahuja, B.; Schaub, A.; Schmidt, J.; Sachs, M.; Mahr, A.; Wiesenmayer, S.; Wigner, L.; Wirth, K.-E.; Peukert, W.; et al. Effect of process conditions on mechanical behavior of aluminium wrought alloy EN AW-2618A additively manufactured by Laser Beam Melting in powder bed. In Proceedings of the 8th International WLT Conference on Lasers in Manufacturing, Lasers in Manufacturing 2015, München, Germany, 22–25 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nyrhilä, O.; Syrjälä, S. Manufacturing of Dimensionally Precise Pieces by Sintering. Available online: https://www.google.com.tw/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&ved=2ahUKEwjQjYe7pJTeAhWEAYgKHRWTC0wQFjABegQICBAC&url=http%3A%2F%2Fpatentimages.storage.googleapis.com%2Fpdfs%2Faefdf08d9c460ff89d72%2FEP0420962B1.pdf&usg=AOvVaw3ndSc87RBQ8S09tQGzsR71 (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Nyrhilä, O. Method for Fabricating Dimensionally Accurate Pieces by Laser Sintering. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US5732323/zh (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Coremans, A.L.P. Laserstrahlsintern von Metallpulver. Prozeßmodellierung, Systemtechnik, Eigenschaften laserstrahlgesinterter Metallkörper; Bericht aus dem Lehrstuhl für Fertigungstechnologie; Meisenbach: Bamberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Schueren, B.; Kruth, J.P. Powder deposition in selective metal powder sintering. Rapid Prototyp. J. 1995, 1, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruth, J.-P.; van der Schueren, B.; Bonse, J.E.; Morren, B. Basic Powder Metallurgical Aspects in Selective Metal Powder Sintering. CIRP Ann. 1996, 45, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J.T.; Stucky, M.J. Laser Additive Manufacturing processing of a Mixture of Iron and Nickel powders. In Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium. Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 10 August 2016; pp. 426–437. Available online: Sffsymposium.engr.utexas.edu/sites/default/files/2016/030-Strauss.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Roberts, C.E.; Bourell, D.; Watt, T.; Cohen, J. A Novel Processing Approach for Additive Manufacturing of Commercial Aluminum Alloys. Phys. Procedia 2016, 83, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, P.; Mumtaz, K.; Todd, I.; Hopkinson, N. AlSi12 in situ alloy formation and residual stress reduction using anchorless selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 7, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Coddet, P.; Dembinski, L.; Liao, H.; Coddet, C. Microstructure and strength analysis of eutectic Al-Si alloy in situ manufactured using selective laser melting from elemental powder mixture. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 691, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaak, C.; Kleszczynski, S.; Tillmann, W.; Witt, G. Investigation of LBM-processed bimodal powder mixtures of the nickel base alloy HX and WC–Co. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 1, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Joguet, D.; Robin, G.; Peltier, L.; Laheurte, P. In situ elaboration of a binary Ti-26Nb alloy by selective laser melting of elemental titanium and niobium mixed powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 62, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakhmalev, P.; Yadroitsev, I.; Yadroitsava, I.; Smidt, O. Functionalization of Biomedical Ti6Al4V via In Situ Alloying by Cu during Laser Powder Bed Fusion Manufacturing. Materials 2017, 10, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrancken, B.; Thijs, L.; Kruth, J.-P.; van Humbeeck, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a novel β titanium metallic composite by selective laser melting. Acta Mater. 2014, 68, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Deng, L.; Prashanth, K.G.; Pauly, S.; Eckert, J.; Scudino, S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Cu alloys fabricated by selective laser melting of powder mixtures. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 735, 2263–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, M.; Ahuja, B.; Schmidt, M. In situ-Legierungsbildung beim Laserstrahlschmelzen von Metallen aus Mischungen elementar reiner Pulver. In Proceedings of the Industriekolloquium des Sonderforschungsbereichs 814—Additive Fertigung, Nürnberg, Germany, 10 December 2015; pp. 57–70. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328407544_In-situ-Legierungsbildung_beim_Laserstrahlschmelzen_von_Metallen_aus_Mischungen_elementar_reiner_Pulver (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Wang, P.; Gammer, C.; Brenne, F.; Niendorf, T.; Eckert, J.; Scudino, S. A heat treatable TiB 2 /Al-3.5Cu-1.5Mg-1Si composite fabricated by selective laser melting: Microstructure, heat treatment and mechanical properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 147, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinekötter, R.; Reh, L. Continuous Mixing of Fine Particles. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 1995, 12, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Y. In situ TiC particle reinforced Ti–Al matrix composites: Powder preparation by mechanical alloying and Selective Laser Melting behavior. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 9230–9240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, H.; Prashanth, K.G.; Zhang, L.-C.; Calin, M.; Okulov, I.V.; Scudino, S.; Yang, C.; Eckert, J. Effect of Powder Particle Shape on the Properties of In Situ Ti–TiB Composite Materials Produced by Selective Laser Melting. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrt, J.T.; Kleszczynski, S.; Notthoff, C.; Lau, M.; Gökce, B.; Barcikowski, S. Laser powder bed fusion of nano-WC-modified and nano-TiO2-modified metal powders. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Additive Technologies iCAT 2016, Nürnberg, Germany, 29–30 November 2016; pp. 26–38. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316316942_Laser_powder_bed_fusion_of_nano-WC-modified_and_nano-TiO2-modified_metal_powders (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Streubel, R.; Wilms, M.B.; Doñate-Buendía, C.; Weisheit, A.; Barcikowski, S.; Schleifenbaum, J.H.; Gökce, B. Depositing laser-generated nanoparticles on powders for additive manufacturing of oxide dispersed strengthened alloy parts via laser metal deposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 40310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, M.; Laumer, T.; Schmidt, M. Additive Manufacturing of Gradient and Multimaterial Components. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Competitive Manufacturing, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 30 January–1 February 2013; Available online: http://conferences.sun.ac.za/index.php/doie/coma13/paper/view/370/303 (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Laumer, T.; Karg, M.; Schmidt, M. Laser Beam Melting of Multi-Material Components. Phys. Procedia 2012, 39, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, C.; Nitsch, G.; Scheitler, C.; Dressler, A.; Schmidt, M. Laser beam melting of water atomized iron base alloy FE 4800 with in situ alloying of carbon nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual international Conference of the Rapid Product Development Association of South Africa, Johannesburg, South Africa, 28–29 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Karg, M.C.H.; Ahuja, B.; Schmidt, J.; Winzer, B.; Wirth, K.-E.; Peukert, W.; Schmidt, M. Laser Beam Melting in Powder Bed of Non-Spherical Aluminium Microparticles Dry Coated with Metal Nanoparticles. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/318723564_Laser_Beam_Melting_in_Powder_Bed_of_nonspherical_aluminium_microparticles_dry_coated_with_metal_nanoparticles (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Sommer, K. Mechanismen des Pulvermischens. Chem. Ing. Tech. 1977, 49, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.C. The segregation of particulate materials. A review. Powder Technol. 1976, 15, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, S.R.; Forsyth, A.J.; Rhodes, M.J.; Osborne, C.F. Effect of interparticle force on mixing and segregation of dry granular materials. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 2004, 70, 31301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosato, A.; Strandburg, K.J.; Prinz, F.; Swendsen, R.H. Why the Brazil nuts are on top: Size segregation of particulate matter by shaking. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möbius, M.E.; Lauderdale, B.E.; Nagel, S.R.; Jaeger, H.M. Size separation of granular particles. Nature 2001, 414, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, M. Entmischungserscheinungen in Kugelschüttungen. Chem. Ing. Tech. 1969, 41, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, D. Pulver und Schüttgüter. Fließeigenschaften und Handhabung, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Available online: https://www.springer.com/de/book/9783642538841 (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Schmidt, M.; Pohle, D.; Rechtenwald, T. Selective Laser Sintering of PEEK. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2007, 56, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümel, C.; Sachs, M.; Laumer, T.; Winzer, B.; Schmidt, J.; Schmidt, M.; Peukert, W.; Wirth, K.-E. Increasing flowability and bulk density of PE-HD powders by a dry particle coating process and impact on LBM processes. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, M.C.H.; Munk, A.; Ahuja, B.; Backer, M.V.; Schmitt, J.P.; Stengel, C.; Kuryntsev, S.V.; Schmidt, M. Expanding particle size distribution and morphology of aluminium-silicon powders for Laser Beam Melting by dry coating with silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2019, 264, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpf, H. Die Wissenschaft des Agglomerierens. Chemie Ing. Technol. 1974, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutný, D.; Paloušek, D.; Koukal, O.; Zikmund, T.; Pantelejev, L. Processing of High Strength Al-Cu alloy Using 400W Selective Laser Melting—Initial Study. In Proceedings of the Lasers in Manufacturing Conference, Munich, Germany, 22–25 June 2015; Available online: https://www.wlt.de/lim/Proceedings/Stick/PDF/Contribution347_final.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Koukal, O.; Koutny, D.; Palousek, D.; Vrana, R.; Zikmund, T.; Pantelejev, L. Research about the Influence of Process Parameters of Selective Laser Melting on Material EN AW 2618. In Proceedings of the EURO PM 2015, Reims, France, 4–7 September 2014; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283121784_Research_about_the_influence_of_process_parameters_of_Selective_Laser_Melting_on_material_EN_AW_2618?_sg=aQdvqoMm2vLb_tn8ZyzYWD_h3DpFG0I9Lj6sdstGxpl6njhKAbTQrvfZO7QmC1zy8FM8agS1xdOdpYHsKcQ9WzewO8do30d25De5BS14.9CANfcAvi_eQHj3su9VMAzwACq-faQelqv5jAtXOyDjYxsZJBvdBiwwip21NFhCcp1xaaqYh5D9BuIoLszNPzQ (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Zatočilová, A.; Zikmund, T.; Kaiser, J.; Paloušek, D.; Koutný, D. Measurement of the Porosity of Additive-Manufactured Al-Cu Alloy Using X-Ray Computed Tomography. SSP 2016, 258, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Nie, X.; Qi, T.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, X. Fabrication and heat treatment of high strength Al-Cu-Mg alloy processed using selective laser melting. In Proceedings of the SPIE LASE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Qi, T.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, X. Selective laser melting of high strength Al–Cu–Mg alloys: Processing, microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 656, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nie, X.; Zhu, H.; Zeng, X.; Yang, C. Study on High Strength Al-Cu-Mg Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Chin. J. Laser 2016, 43, 503007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantělejev, L.; Koutný, D.; Paloušek, D.; Kaiser, J. Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of 2618 Al-Alloy Processed by SLM Remelting Strategy. MSF 2017, 891, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Nie, X.; Yin, J.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, X. Effect of Zirconium addition on crack, microstructure and mechanical behavior of selective laser melted Al-Cu-Mg alloy. Scr. Mater. 2017, 134, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutny, D.; Palousek, D.; Pantelejev, L.; Hoeller, C.; Pichler, R.; Tesicky, L.; Kaiser, J. Influence of Scanning Strategies on Processing of Aluminum Alloy EN AW 2618 Using Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2018, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Hu, Z.; Ke, L.; Zeng, X. Analysis of processing parameters and characteristics of selective laser melted high strength Al-Cu-Mg alloys: From single tracks to cubic samples. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2018, 256, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Hu, Z.; Ke, L.; Zeng, X. Effect of Zr content on formability, microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Zr modified Al-4.24Cu-1.97Mg-0.56Mn alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 764, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Nie, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, X. On the role of atmospheric oxygen into mechanical properties and fracture behavior of selective laser melted AlCu5MnCdVA. Mater. Des. 2018, 150, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gammer, C.; Brenne, F.; Prashanth, K.G.; Mendes, R.G.; Rümmeli, M.H.; Gemming, T.; Eckert, J.; Scudino, S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a heat-treatable Al-3.5Cu-1.5Mg-1Si alloy produced by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, B.; Karg, M.; Nagulin, K.Y.; Schmidt, M. Fabrication and Characterization of High Strength Al-Cu Alloys Processed Using Laser Beam Melting in Metal Powder Bed. Phys. Procedia 2014, 56, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karg, M.C.H.; Ahuja, B.; Kuryntsev, S.; Schmidt, M. Processability of high strength Aluminium-Copper alloys AW-2022 and 2024 by Laser Beam Melting in Powder Bed. In Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 4–6 August 2014; pp. 420–436. Available online: http://sffsymposium.engr.utexas.edu/sites/default/files/2014-036-Karg.pdf. (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Blümel, C. Charakterisierung der Trockenen Beschichtung zur Herstellung von maßgeschneiderten Kompositpartikeln. 2015. Available online: https://www.tib.eu/de/suchen/id/TIBKAT%3A827329997/Charakterisierung-der-Trockenen-Beschichtung-zur/ (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- DIN-ISO. Surface Active Agents; Powders and Granules; Measurement of the Angle of Repose. 1983. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/10196.html (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Buchbinder, D.F.S. Selective Laser Melting von Aluminiumgusslegierungen. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kempen, K. Expanding the Materials Palette for Selective Laser Melting of Metals. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN. Aluminium and Aluminium Alloys—Chemical Composition and form of Products. Available online: https://infostore.saiglobal.com/preview/is/en/2013/i.s.en573-3-2013.pdf?sku=1689920 (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Aluminum Association. International Alloy Designations and Chemical Teal Sheets—Composition Limits for Wrought Aluminum and Wrought Aluminum Alloys. 2015. Available online: https://www.aluminum.org/sites/default/files/Teal%20Sheets.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Eschbach, L. Entwicklung von Sprühkompaktierten AlCuMgAg-Legierungen mit Hoher Warmfestigkeit und Zähigkeit. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gegner, J. Komplexe Diffusionsprozesse in Metallen. Experimentelle Analyse und Mathematische Simulation der Randentkohlung und Gasaufkohlung, inneren Oxidation und Sauerstoffsegregation an Metall-Oxid-Phasengrenzen; mit 10 Tabellen; Habilitation Thesis of Siegen University, Expert: Renningen, Germany, 2006; ISBN 978-3-8169-2546-0. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN ISO. Metallic Powders—Determination of Apparent Density—Part 2: Scott Volumeter Method. 1981. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/9559.html (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Karg, M.; Ahuja, B.; Wiesenmayer, S.; Kuryntsev, S.; Schmidt, M. Effects of Process Conditions on the Mechanical Behavior of Aluminium Wrought Alloy EN AW-2219 (AlCu6Mn) Additively Manufactured by Laser Beam Melting in Powder Bed. Micromachines 2017, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiners, W. Direktes Selektives Laser Sintern Einkomponentiger Metallischer Werkstoffe. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V. Testing of Metallic Materials—Tensile Test Pieces. 2009. Available online: https://www.beuth.de/en/standard/din-50125/262241217 (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- DIN EN ISO. Metallic Materials-Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. 2009. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/61856.html (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Technical Committee 105 Additive Manufacturing. VDI Guideline: VDI 3405 Part 2 Additive Manufacturing Processes, Beam Melting of Metallic Parts-Qualification, Quality Assurance and Post Processing, Berlin. 2012. Available online: https://www.beuth.de/de/technische-regel/vdi-3405-blatt-2/186062672?websource=vdin (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- DIN EN ISO. Metallic Materials—Vickers Hardness Test—Part 1: Test Method. 2018. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/64065.html (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- DIN EN ISO. Micrographic Determination of the Apparent Grain Size (ISO/FDIS 643:2015). Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/61697.html (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Flumerfelt, J.F. Aluminium Powder Metallurgy Processing. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten, C.; Buchbinder, D.; Pirch, N.; Meiners, W.; Wissenbach, K.; Poprawe, R. Formation and reduction of hydrogen porosity during selective laser melting of AlSi10Mg. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2015, 221, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyda, V.; Kaufmann, N.; Emmelmann, C. Investigation of Aging Processes of Ti-6Al-4 V Powder Material in Laser Melting. Phys. Procedia 2012, 39, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, T.P. Herstellung von Knochenimplantaten aus Titanwerkstoffen Durch Laserformen. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, B.; Schaub, A.; Karg, M.; Lechner, M.; Merklein, M.; Schmidt, M. Developing LBM Process Parameters for Ti-6Al-4V Thin Wall Structures and Determining the Corresponding Mechanical Characteristics. Phys. Procedia 2014, 56, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierings, A.B.; Voegtlin, M.; Bauer, T.; Wegener, K. Powder flowability characterisation methodology for powder-bed-based metal additive manufacturing. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 1, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutter-Günther, M.; Horn, M.; Seidel, C.; Reinhart, G. Influence of Particle Size Distribution on Powder Flowability and Part Properties in Laser Beam Melting: Einfluss der Korngrößenverteilung auf Fließfähigkeit und Bauteilqualität beim Laserstrahlschmelzen. In Rapid. Tech—International Trade Show & Conference for Additive Manufacturing, Proceedings of the 14th Rapid. Tech Conference, Erfurt, Germany, 20–22 June 2017; Kynast, M., Eichmann, M., Witt, G., Eds.; Hanser, Carl: München, Germany, 2017; pp. 297–311. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317432212_Einfluss_der_Korngrossenverteilung_auf_Fliessfahigkeit_und_Bauteilqualitat_beim_Laserstrahlschmelzen_Proceedings_of_the_14th_RapidTech_Conference_Erfurt_Germany_20_-_22_June_2017 (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- German, R.M. Particle Packing Characteristics; Metal Powder Industries Federation: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, S.D.S.; Araújo, N.A.M.; Andrade, J.S.; Herrmann, H.J. How dense can one pack spheres of arbitrary size distribution? EPL 2012, 97, 18004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, A.M.; Küng, V.E.; Pobel, C.; Markl, M.; Körner, C. Predictive Simulation of Process Windows for Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing: Influence of the Powder Bulk Density. Materials 2017, 10, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körner, C.; Attar, E.; Heinl, P. Mesoscopic simulation of selective beam melting processes. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2011, 211, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierings, A.B.; Levy, G. Comparison of density of stainless steel 316L parts produced with selective laser melting using different powder grades. In Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 3–9 August 2009; pp. 342–353. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, G. Die Metallurgie des Schweissens. Eisenwerkstoffe—Nichteisenmetallische Werkstoffe, 4th ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Newbury, D.E. Mistakes encountered during automatic peak identification of minor and trace constituents in electron-excited energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis. Scanning 2009, 31, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niendorf, T.; Leuders, S.; Riemer, A.; Richard, H.A.; Tröster, T.; Schwarze, D. Highly Anisotropic Steel Processed by Selective Laser Melting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2013, 44, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobrecht, J.; Rumpler, E. Werkstofftechnik—Metalle, 2nd ed.; Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag: Munich, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Karg, M.; Rasch, M.; Cvecek, K.; Schmidt, M. Verfahren zur schichtweisen Fertigung eines Bauteils, Pulvermischung für die additive Fertigung und Bauteil aus einer Legierung oder einem Metallmatrix- Verbundwerkstoff. DE 10 2017 210 603.4.
- DIN ISO. Representation of Results of Particle Size Analysis—Part 1: Graphical Representation, 1st ed. 1998. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/25860.html (accessed on 15 September 2018).













| ρA/ρB | 1.13 | 1.15 | 1.15 | ≈1 | 1.90 | 2.01 | 2.32 | 3.30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | [18] | [19,20] | [21] | [22] | [23] | [24] | [25,26] | |
| A-B | Ni-Fe | Al-Si | Al-Si | HX-WC | Ti-Nb | Ti6Al4V-Cu | Ti6Al4V-Mo | Al-Cu |
| A/B [wt%] | 36/63 | 99.4/0.6 | 88/12 | 95/5 | 58.2/38.6 | 98.6/1.4 | 90/10 | 95.5/4.5 |
| 90/10 | 60/40 |
| Al | Cu | Mg | Ti | V | Fe | Si | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 99.7 | 0.13 | 0.03 | |||||
| Cu | 99.98 | 0.02 | ||||||
| AlMg50 | 48.4 | 51.3 | 0.13 | 0.23 | ||||
| Ti6Al4V | 5.34 | 0.17 | 90.7 | 3.61 | 0.24 |
| Al | Cu | Mg | Mn | Ti | V | Fe | Si | Zn | Impurities | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Powder mixture | 93.72 | 4.00 | 1.57 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.26 | |
| LBM sample | 93.79 | 4.66 | 1.02 | 0.33 | 0.2 | |||||
| Extruded sample | 93.6 | 4.36 | 1.25 | 0.78 | ||||||
| EN AW-2024 [67] | bal. | 3.8–4.9 | 1.2–1.8 | 0.3–0.9 | <0.15 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.25 | <0.15 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karg, M.C.H.; Rasch, M.; Schmidt, K.; Spitzer, S.A.E.; Karsten, T.F.; Schlaug, D.; Biaciu, C.-R.; Gorunov, A.I.; Schmidt, M. Laser Alloying Advantages by Dry Coating Metallic Powder Mixtures with SiOx Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100862
Karg MCH, Rasch M, Schmidt K, Spitzer SAE, Karsten TF, Schlaug D, Biaciu C-R, Gorunov AI, Schmidt M. Laser Alloying Advantages by Dry Coating Metallic Powder Mixtures with SiOx Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(10):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100862
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarg, Michael C. H., Michael Rasch, Konstantin Schmidt, Sophia A. E. Spitzer, Till F. Karsten, Daniel Schlaug, Cosmin-Rudolf Biaciu, Andrey I. Gorunov, and Michael Schmidt. 2018. "Laser Alloying Advantages by Dry Coating Metallic Powder Mixtures with SiOx Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 8, no. 10: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100862
APA StyleKarg, M. C. H., Rasch, M., Schmidt, K., Spitzer, S. A. E., Karsten, T. F., Schlaug, D., Biaciu, C.-R., Gorunov, A. I., & Schmidt, M. (2018). Laser Alloying Advantages by Dry Coating Metallic Powder Mixtures with SiOx Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 8(10), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100862