Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Curcumin into Human Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Nanoparticles
2.2.1. Preparation of Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.2.2. Preparation of Magnetic Alginate Nanoparticles
2.2.3. Preparation of Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Layer-by-Layer Nanoparticles
2.3. Curcumin Loaded Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Layer-by-Layer Nanoparticles
2.4. Release of CUR from CMACPs
2.5. Particle Characterisation
2.5.1. Nanoparticle Tracking and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.5.3. Atomic Force Microscopy Analysis
2.5.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis
2.6. Cellular Uptake Assays
2.7. Magnetically Targeted Delivery Assay
2.8. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterisation of Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Layer-by-Layer Nanoparticles and Curcumin Loaded Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles
3.1.1. Zeta Potential, Size and FTIR Spectra
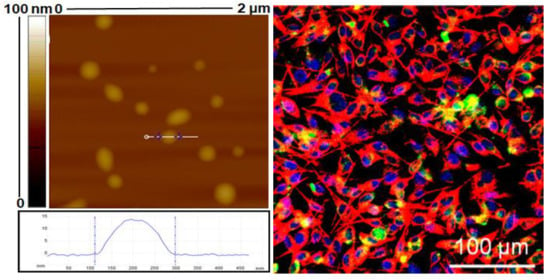
3.1.2. Morphology Characterisation
3.2. Loading and Release of Curcumin
3.3. Cellular Uptake Assays
3.3.1. CUR Uptake Assay by Flow Cytometry
3.3.2. Magnetically Targeted Delivery Assay
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Yallapu, M.M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C. Curcumin nanomedicine: A road to cancer therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1994–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Hidaka, K.; Shinohara, A.; Maekawa, T.; Takeda, Y.; Yamaguchi, H. Chemical studies on antioxidant mechanism of curcuminoid: Analysis of radical reaction products from curcumin and Linoleate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruby, A.; Kuttan, G.; Babu, K.D.; Rajasekharan, K.; Kuttan, R. Anti-tumour and antioxidant activity of natural curcuminoids. Cancer Lett. 1995, 94, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, T.; Gulcin, I. Antioxidant and radical scavenging properties of curcumin. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2008, 174, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouet, I.; Ohshima, H. Curcumin, an anti-tumor promoter and anti-inflammatory agent, inhibits induction of nitric oxide synthase in activated macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 206, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamori, T.; Lubet, R.; Steele, V.E.; Kelloff, G.J.; Kaskey, R.B.; Rao, C.V.; Reddy, B.S. Chemopreventive effect of curcumin, a naturally occurring anti-inflammatory agent, during the promotion/progression stages of colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Harikumar, K.B. Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 40–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sidhu, G.S.; Singh, A.K.; Thaloor, D.; Banaudha, K.K.; Patnaik, G.K.; Srimal, R.C.; Maheshwari, R.K. Enhancement of wound healing by curcumin in animals. Wound Repair Regen. 1998, 6, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchatcharam, M.; Miriyala, S.; Gayathri, V.S.; Suguna, L. Curcumin improves wound healing by modulating collagen and decreasing reactive oxygen species. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 290, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negi, P.; Jayaprakasha, G.; Jagan Mohan Rao, L.; Sakariah, K. Antibacterial activity of turmeric oil: A byproduct from curcumin manufacture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4297–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, S.H.; Joung, D.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Kang, O.H.; Kim, S.B.; Seo, Y.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, D.S.; Shin, D.W.; Kweon, K.T.; et al. Synergistic antibacterial effect of curcumin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaee, R.; Momtazi, A.A.; Monemi, A.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin: A potentially powerful tool to reverse cisplatin-induced toxicity. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 117, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilken, R.; Veena, M.S.; Wang, M.B.; Srivatsan, E.S. Curcumin: A review of anti-cancer properties and therapeutic activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Kumar, A.; Bharti, A.C. Anticancer potential of curcumin: Preclinical and clinical studies. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 363–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Hill, D.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. Curcumin, a dietary component, has anticancer, chemosensitization, and radiosensitization effects by down-regulating the MDM2 oncogene through the PI3K/mTOR/ETS2 pathway. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapal, A.; Tiku, P.K. Complexation of curcumin with soy protein isolate and its implications on solubility and stability of curcumin. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Deng, Z.; Lou, W.; Xu, H.; Bai, Q.; Ma, J. Preparation and characterization of cationic curcumin nanoparticles for improvement of cellular uptake. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A.; Bora, U.; Kasoju, N.; Goswami, P. Synthesis of novel biodegradable and self-assembling methoxy poly (ethylene glycol)–palmitate nanocarrier for curcumin delivery to cancer cells. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoba, G.; Joy, D.; Joseph, T.; Majeed, M.; Rajendran, R.; Srinivas, P. Influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in animals and human volunteers. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Lou, H.; Zhao, L.; Fan, P. Validated LC/MS/MS assay for curcumin and tetrahydrocurcumin in rat plasma and application to pharmacokinetic study of phospholipid complex of curcumin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiyaboonchai, W.; Tungpradit, W.; Plianbangchang, P. Formulation and characterization of curcuminoids loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 337, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Braiteh, F.S.; Kurzrock, R. Liposome-encapsulated curcumin: In vitro and in vivo effects on proliferation, apoptosis, signaling, and angiogenesis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 104, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajj Ali, H.; Michaux, F.; Ntsama, B.; Sandrine, I.; Durand, P.; Jasniewski, J.; Linder, M. Shea butter solid nanoparticles for curcumin encapsulation: Influence of nanoparticles size on drug loading. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ma, X.; Lei, Y.; Luo, Y. Solid lipid nanoparticles coated with cross-linked polymeric double layer for oral delivery of curcumin. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, Q.; Xu, X.; Li, N. Development and evaluation of a novel phytosome-loaded chitosan microsphere system for curcumin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 448, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.-B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, A.-Z.; Li, J.-S.; Hu, J.-Y.; Li, G.; Li, Z. Solubility enhancement of curcumin via supercritical CO2 based silk fibroin carrier. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 103, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Muthana, M.; Mukherjee, J.; Falconer, R.J.; Biggs, C.A.; Zhao, X. Magnetic-silk core-shell nanoparticles as potential carriers for targeted delivery of curcumin into human breast cancer cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Maya, S.; Deepa, N.; Chennazhi, K.; Nair, S.; Tamura, H.; Jayakumar, R. Efficient water soluble O-carboxymethyl chitosan nanocarrier for the delivery of curcumin to cancer cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán, M.G.; Coburn, J.M.; Lozano-Pérez, A.A.; Cenis, J.L.; Víllora, G.; Kaplan, D.L. Production of curcumin-loaded silk fibroin nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuah, L.H.; Billa, N.; Roberts, C.J.; Burley, J.C.; Manickam, S. Curcumin-containing chitosan nanoparticles as a potential mucoadhesive delivery system to the colon. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, R.; Gupta, P.; Dziubla, T.; Hilt, J.Z. Single step synthesis, characterization and applications of curcumin functionalized iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 67, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agnihotri, S.A.; Mallikarjuna, N.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Recent advances on chitosan-based micro-and nanoparticles in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, S.H.; Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Alginate gel particles–A review of production techniques and physical properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampino, A.; Borgogna, M.; Blasi, P.; Bellich, B.; Cesàro, A. Chitosan nanoparticles: Preparation, size evolution and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 455, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Dünnhaupt, S. Chitosan-based drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhunchu, S.; Rojsitthisak, P. Biopolymeric alginate-chitosan nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy. Die Pharmazie-An Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 69, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Deepagan, V.; Rani, V.D.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.; Jayakumar, R. Preparation, characterization, in vitro drug release and biological studies of curcumin loaded dextran sulphate–chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Ghasemi-Kasman, M.; Ghasemi, S.; Tabari, M.G.; Pourbagher, R.; Kazemi, S.; Alinejad-Mir, A. Induction of apoptosis in hela cancer cells by an ultrasonic-mediated synthesis of curcumin-loaded chitosan–alginate–sTPP nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 8545–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maghsoudi, A.; Yazdian, F.; Shahmoradi, S.; Ghaderi, L.; Hemati, M.; Amoabediny, G. Curcumin-loaded polysaccharide nanoparticles: Optimization and anticariogenic activity against Streptococcus mutans. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.F.; Bueno, P.V.; Almeida, E.A.; Rodrigues, F.H.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Characterization of N-trimethyl chitosan/alginate complexes and curcumin release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 57, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruebo, M.; Fernández-Pacheco, R.; Ibarra, M.R.; Santamaría, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2007, 2, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannone, A.; Magin, R.; Walczak, T.; Federico, M.; Swartz, H.; Tomasi, A.; Vannini, V. Blood clearance of dextran magnetite particles determined by a noninvasive in vivo ESR method. Magn. Reson. Med. 1991, 22, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancarella, S.; Greco, V.; Baldassarre, F.; Vergara, D.; Maffia, M.; Leporatti, S. Polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticles for curcumin delivery to cancer cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2015, 15, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlov, A.M.; Gabriel, S.A.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Gould, D.J. Improved and targeted delivery of bioactive molecules to cells with magnetic layer-by-layer assembled microcapsules. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9686–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Romero, G.; Rojas, E.; Ma, L.; Moya, S.; Gao, C. Layer by layer chitosan/alginate coatings on poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles for antifouling protection and Folic acid binding to achieve selective cell targeting. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, F.; Sun, L.; He, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, F.; Ge, L.; Webster, T.J.; Zheng, C. Doxorubicin-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles coated with chitosan/alginate by layer by layer technology for antitumor applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidar, Z.S.; Hamdy, R.C.; Tabrizian, M. Protein release kinetics for core–shell hybrid nanoparticles based on the layer-by-layer assembly of alginate and chitosan on liposomes. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Moya, S.; Ma, L.; Gao, C.; Shen, J. Polyelectrolyte coated PLGA nanoparticles: Templation and release behavior. Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.L.; Johnston, A.P.; Caruso, F. Layer-by-layer-assembled capsules and films for therapeutic delivery. Small 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Zhu, W. Preparation of superparamagnetic Fe3O4@ alginate/chitosan nanospheres for Candida rugosa lipase immobilization and utilization of layer-by-layer assembly to enhance the stability of immobilized lipase. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5169–5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, S.H.; Bhandari, B.; Webb, R.; Bansal, N. Visualizing the interaction between sodium caseinate and calcium alginate microgel particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dos Santos Silva, M.; Cocenza, D.S.; Grillo, R.; de Melo, N.F.S.; Tonello, P.S.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Cassimiro, D.L.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Paraquat-loaded alginate/chitosan nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and soil sorption studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, L.; Kokini, J. An optimal window for the fabrication of Edible Polyelectrolyte Complex Nanotubes (EPCNs) from bovine serum albumin (BSA) and sodium alginate. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, I.; Paoletti, S. Material properties of alginates. In Alginates: Biology and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, S.; Dey, R.; Islam, M.; Patel, R.; Jha, U.; Patnaik, T.; Airoldi, C. Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution using aluminum-impregnated chitosan biopolymer. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 2096–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Fani, A.; Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Soliva-Fortuny, R.; Martín-Belloso, O. Layer-by-layer assembly of food-grade alginate/chitosan nanolaminates: Formation and physicochemical characterization. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.C.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Bourbon, A.I.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Vicente, A.A. Hollow chitosan/alginate nanocapsules for bioactive compound delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasan, K.M. Role of Lipid Excipients in Modifying Oral and Parenteral Drug Delivery: Basic Principles and Biological Examples; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, F. Enhanced swelling and methylene blue adsorption of polyacrylamide-based superabsorbents using alginate modified montmorillonite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevadiya, B.D.; Joshi, G.V.; Patel, H.A.; Ingole, P.G.; Mody, H.M.; Bajaj, H.C. Montmorillonite-alginate nanocomposites as a drug delivery system: Intercalation and in vitro release of vitamin B1 and vitamin B6. J. Biomater. Appl. 2010, 25, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, C.; Finch, D.S.; Ralph, B.; Gilding, K. Determination of the cation content of alginate thin films by FTIR spectroscopy. Polymer 1997, 38, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daemi, H.; Barikani, M. Synthesis and characterization of calcium alginate nanoparticles, sodium homopolymannuronate salt and its calcium nanoparticles. Sci. Iran. 2012, 19, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Feng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ren, J.; Xu, Q.; Fan, L. Chemical structure and remarkably enhanced mechanical properties of chitosan-graft-poly (acrylic acid)/polyacrylamide double-network hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Mahalingam, S.; Edirisinghe, M.; Chen, B. Highly stretchable and highly resilient polymer–clay nanocomposite hydrogels with low hysteresis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 22223–22234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, G.; Keen, I.; Drew, B.; Chandler-Temple, A.; Rintoul, L.; Fredericks, P.; Grøndahl, L. Interactions between alginate and chitosan biopolymers characterized using FTIR and XPS. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2533–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, F.-H.; Gan, Y. AFM tip-sample convolution effects for cylinder protrusions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, N.; Aditya, S.; Yang, H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, S.O.; Ko, S. Co-delivery of hydrophobic curcumin and hydrophilic catechin by a water-in-oil-in-water double emulsion. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altunbas, A.; Lee, S.J.; Rajasekaran, S.A.; Schneider, J.P.; Pochan, D.J. Encapsulation of curcumin in self-assembling peptide hydrogels as injectable drug delivery vehicles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5906–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Lim, G.P.; Begum, A.N.; Ubeda, O.J.; Simmons, M.R.; Ambegaokar, S.S.; Chen, P.P.; Kayed, R.; Glabe, C.G.; Frautschy, S.A. Curcumin inhibits formation of amyloid β oligomers and fibrils, binds plaques, and reduces amyloid in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 5892–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manju, S.; Sreenivasan, K. Conjugation of curcumin onto hyaluronic acid enhances its aqueous solubility and stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Yu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Lou, H.; Zhai, G. Enhancement of oral absorption of curcumin by self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 371, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, C.E.; Fedewa, S.A.; Goding Sauer, A.; Kramer, J.L.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Breast cancer statistics, 2015: Convergence of incidence rates between black and white women. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, C.; Acharya, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Dilnawaz, F.; Sahoo, S.K. Curcumin-encapsulated MePEG/PCL diblock copolymeric micelles: A novel controlled delivery vehicle for cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, M.S.; Chauhan, N.; Yallapu, M.M.; Gara, R.K.; Maher, D.M.; Kumari, S.; Sikander, M.; Khan, S.; Zafar, N.; Jaggi, M. Curcumin nanoformulation for cervical cancer treatment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan Yallapu, M.; Ray Dobberpuhl, M.; Michele Maher, D.; Jaggi, M.; Chand Chauhan, S. Design of curcumin loaded cellulose nanoparticles for prostate cancer. Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, R.; Abraham, P.M.; Poddar, P. Temperature-dependent spectroscopic evidences of curcumin in aqueous medium: A mechanistic study of its solubility and stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 14533–14540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangalathillam, S.; Rejinold, N.S.; Nair, A.; Lakshmanan, V.-K.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Curcumin loaded chitin nanogels for skin cancer treatment via the transdermal route. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejinold, N.S.; Sreerekha, P.; Chennazhi, K.; Nair, S.; Jayakumar, R. Biocompatible, biodegradable and thermo-sensitive chitosan-g-poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) nanocarrier for curcumin drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunwar, A.; Barik, A.; Mishra, B.; Rathinasamy, K.; Pandey, R.; Priyadarsini, K. Quantitative cellular uptake, localization and cytotoxicity of curcumin in normal and tumor cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2008, 1780, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, N.L.; Estrela-Lopis, I.; Böttner, J.; Lopes, C.A.; Guido, B.C.; de Sousa, A.R.; Báo, S.N. Exploring cellular uptake of iron oxide nanoparticles associated with rhodium citrate in breast cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5511–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettler, K.; Veltman, K.; van de Meent, D.; van Wezel, A.; Hendriks, A.J. Cellular uptake of nanoparticles as determined by particle properties, experimental conditions, and cell type. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, N.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M. Methotrexate-modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles and their intracellular uptake into human cancer cells. Langmuir 2005, 21, 8858–8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syng-ai, C.; Kumari, A.L.; Khar, A. Effect of curcumin on normal and tumor cells: Role of glutathione and bcl-2. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shishodia, S.; Amin, H.M.; Lai, R.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) inhibits constitutive NF-κB activation, induces G1/S arrest, suppresses proliferation, and induces apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, W.; Su, X.; Gregory, D.A.; Li, W.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, X. Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Curcumin into Human Breast Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110907
Song W, Su X, Gregory DA, Li W, Cai Z, Zhao X. Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Curcumin into Human Breast Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(11):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110907
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Wenxing, Xing Su, David Alexander Gregory, Wei Li, Zhiqiang Cai, and Xiubo Zhao. 2018. "Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Curcumin into Human Breast Cancer Cells" Nanomaterials 8, no. 11: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110907
APA StyleSong, W., Su, X., Gregory, D. A., Li, W., Cai, Z., & Zhao, X. (2018). Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Curcumin into Human Breast Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials, 8(11), 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110907