Biomedical Applications of Graphene-Based Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
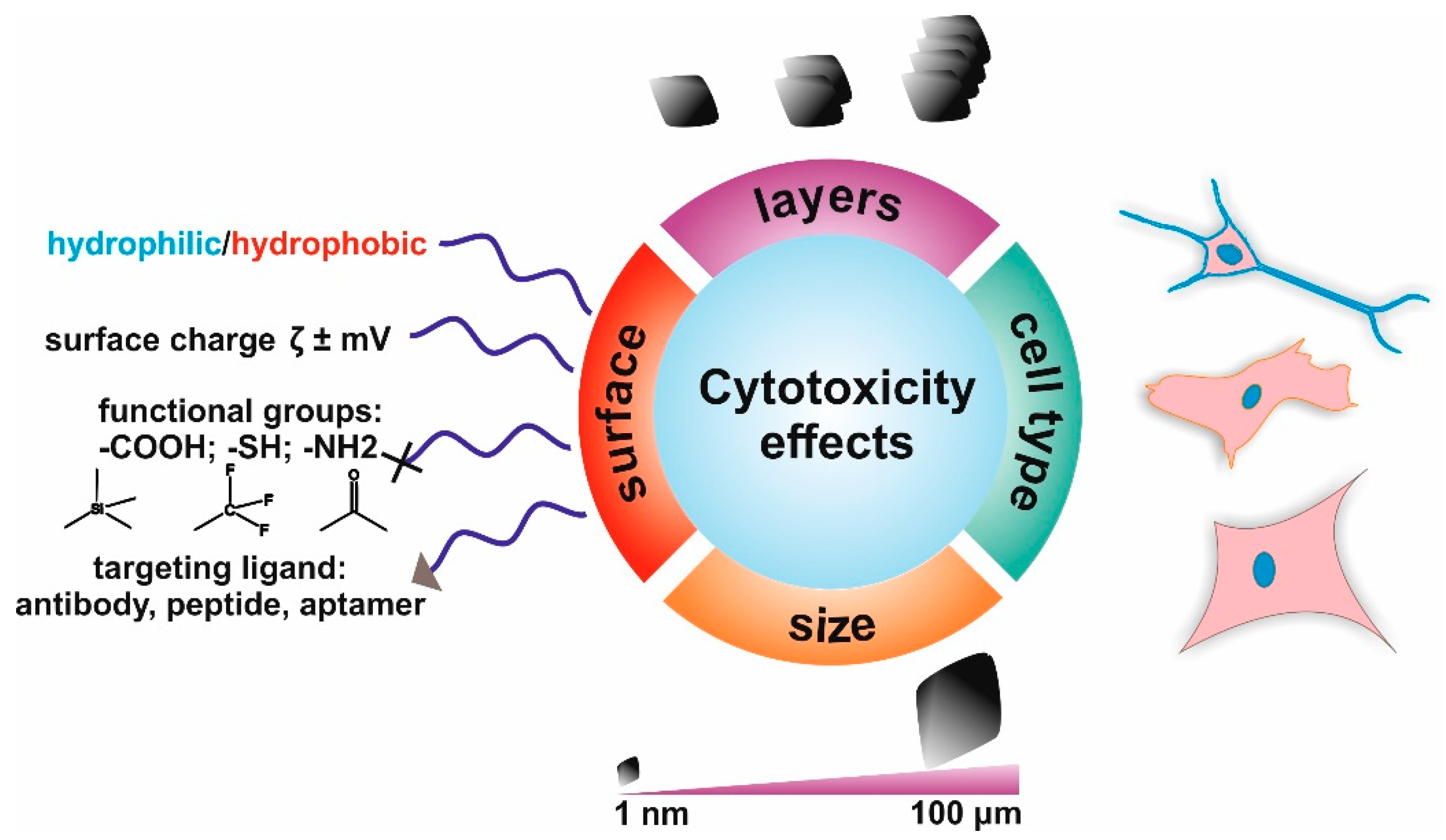
2. The Toxicity of Graphene-Based Materials
3. Graphene-Based Materials in Anticancer Drug Delivery Systems
4. Graphene and Graphene Oxide in Tissue Engineering
4.1. Two-Dimensional (2D) Substrates
4.2. Beyond 2D
5. Graphene-Based Materials in Bio-Imaging
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, A.; Hasan, A.; Al Kindi, H.; Gaharwar, A.K.; Rao, V.T.S.; Nikkhah, M.; Shin, S.R.; Krafft, D.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Shum-Tim, D.; et al. Injectable Graphene Oxide/Hydrogel-Based Angiogenic Gene Delivery System for Vasculogenesis and Cardiac Repair. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 8050–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chen, A.; Qin, M.; Huang, R.; Zhang, G.; Xue, B.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W. Hierarchical construction of a mechanically stable peptide-graphene oxide hybrid hydrogel for drug delivery and pulsatile triggered release in vivo. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Huczko, A.; Oraon, R.; Adhikari, A.D.; Nayak, G.C. Magical Allotropes of Carbon: Prospects and Applications. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 41, 257–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Dearden, A.; Crean, J.; Han, L.; Liu, S.; Wen, X.; De, S. New materials graphyne, graphdiyne, graphone, and graphane: Review of properties, synthesis, and application in nanotechnology. Nanotechnology 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.K.; Tour, J.M. Graphene: Powder, flakes, ribbons, and sheets. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO/TS 80004-13:2017, Nanotechnologies—Vocabulary—Part 13: Graphene and Related Two-Dimensional (2D) Materials ISO/TS; International Organization for Standardization, Switzerland: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, I.A.; Bozhenko, K.V.; Boldyrev, A.I. Is graphene aromatic? Nano Res. 2012, 5, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of Graphitic Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rourke, J.P.; Pandey, P.A.; Moore, J.J.; Bates, M.; Kinloch, I.A.; Young, R.J.; Wilson, N.R. The Real Graphene Oxide Revealed: Stripping the Oxidative Debris from the Graphene-like Sheets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3173–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, B.R.; Knight, T.; Gies, V.; Jakubek, Z.J.; Zou, S. Manipulation and Quantification of Graphene Oxide Flake Size: Photoluminescence and Cytotoxicity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28911–28921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Merino, M.J.; Guardia, L.; Paredes, J.I.; Villar-Rodil, S.; Solis-Fernandez, P.; Martinez-Alonso, A.; Tascon, J.M.D. Vitamin C Is an Ideal Substitute for Hydrazine in the Reduction of Graphene Oxide Suspensions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 6426–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, S.V.; Novoselov, K.S.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Schedin, F.; Elias, D.C.; Jaszczak, J.A.; Geim, A.K. Giant intrinsic carrier mobilities in graphene and its bilayer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balandin, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C.N. Superior thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.R.; Blake, P.; Grigorenko, A.N.; Novoselov, K.S.; Booth, T.J.; Stauber, T.; Peres, N.M.R.; Geim, A.K. Fine structure constant defines visual transparency of graphene. Science 2008, 320, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.R.; Wu, H.A.; Jayaram, P.N.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Geim, A.K. Unimpeded Permeation of Water Through Helium-Leak-Tight Graphene-Based Membranes. Science 2012, 335, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.H.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, E.-Y.; Kim, S.O. Peptide/Graphene Hybrid Assembly into Core/Shell Nanowires. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2060–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Weaver, C.L.; Tan, S.; Cui, X.T. Pure graphene oxide doped conducting polymer nanocomposite for bio-interfacing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goenka, S.; Sant, V.; Sant, S. Graphene-based nanomaterials for drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2014, 173, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wychowaniec, J.K.; Iliut, M.; Zhou, M.; Moffat, J.; Elsawy, M.A.; Pinheiro, W.A.; Hoyland, J.A.; Miller, A.F.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Saiani, A. Designing Peptide/Graphene Hybrid Hydrogels through Fine-Tuning of Molecular Interactions. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2731–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, Q.; Gong, P.; Ma, L.; Yang, S. A Novel Wound Dressing Based on Ag/Graphene Polymer Hydrogel: Effectively Kill Bacteria and Accelerate Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3933–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial Activity of Graphite, Graphite Oxide, Graphene Oxide, and Reduced Graphene Oxide: Membrane and Oxidative Stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N.; Qu, X. Detection of a Prognostic Indicator in Early-Stage Cancer Using Functionalized Graphene-Based Peptide Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, P.; Bhirde, A.; Jin, A.; Ma, Y.; Niu, G.; Neamati, N.; Chen, X. A nanoscale graphene oxide-peptide biosensor for real-time specific biomarker detection on the cell surface. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9768–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuchowska, A.; Chudy, M.; Dybko, A.; Brzozka, Z. Graphene as a new material in anticancer therapy-in vitro studies. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, S.; Song, Q.; Huang, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Dai, J.; Tang, M.; Cheng, G. Three-dimensional graphene foam as a biocompatible and conductive scaffold for neural stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimene, D.; Alge, D.L.; Gaharwar, A.K. Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications: Emerging Trends and Future Prospects. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7261–7284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbacova, M.; Broz, A.; Kong, J.; Kalbac, M. Graphene substrates promote adherence of human osteoblasts and mesenchymal stromal cells. Carbon 2010, 48, 4323–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verre, A.F.; Faroni, A.; Maria Iliut, M.; Silva, C.; Muryn, C.; Reid, A.J.; Vijayaraghavan, A. Improving the glial differentiation of human Schwann-like adipose-derived stem cells with graphene oxide substrates. Interface Focus 2018, 8, 20180002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakus, A.E.; Secor, E.B.; Rutz, A.L.; Jordan, S.W.; Hersam, M.C.; Shah, R.N. Three-Dimensional Printing of High-Content Graphene Scaffolds for Electronic and Biomedical Applications. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4636–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.H.; Bhang, S.H.; Kim, T.; Yu, T.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, B.S. Dual Roles of Graphene Oxide in Chondrogenic Differentiation of Adult Stem Cells: Cell-Adhesion Substrate and Growth Factor-Delivery Carrier. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6455–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, W.G.; Jin, M.; Park, S.; Yoon, H.H.; Jeong, G.J.; Bhang, S.H.; Park, H.; Char, K.; Kim, B.S. Delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and substance P using graphene oxide for bone regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed.; Gold Book; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Xu, Z.; Gao, C. Multifunctional, Ultra-Flyweight, Synergistically Assembled Carbon Aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2554–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Records, G.W. Guinness World Records 2015; Guinness World Records Limited: London, UK, 2015; p. 203. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, D.L. Porous, 3-D Forms of Graphene Developed at MIT Can Be 10 Times as Strong as Steel but Much Lighter. Available online: https://news.mit.edu/2017/3-d-graphene-strongest-lightest-materials-0106 (accessed on 1 September 2018).
- Zheng, X.; Lee, H.; Weisgraber, T.H.; Shusteff, M.; DeOtte, J.; Duoss, E.B.; Kuntz, J.D.; Biener, M.M.; Ge, Q.; Jackson, J.A.; et al. Ultralight, ultrastiff mechanical metamaterials. Science 2014, 344, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Tai, N.-H. Carbon materials as oil sorbents: A review on the synthesis and performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1550–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimman, R.; Prabhakaran, K. Preparation of carbon foams by thermo-foaming of activated carbon powder dispersions in an aqueous sucrose resin. Carbon 2012, 50, 5583–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gash, A.; Reese, D. Aerogels: The Materials Science of Empty Space. Available online: https://step.llnl.gov/programs/science-on-saturday/lecture/425 (accessed on 1 September 2018).
- Lee, H.; Rho, J.; Messersmith, P.B. Facile Conjugation of Biomolecules onto Surfaces via Mussel Adhesive Protein Inspired Coatings. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asha, S.; Ananth, A.N.; Jose, S.P.; Rajan, M.A.J. Reduced graphene oxide aerogel networks with soft interfacial template for applications in bone tissue regeneration. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogharabi, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Faramarzi, M.A. Safety concerns to application of graphene compounds in pharmacy and medicine. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Liu, Z. Graphene in biomedicine: Opportunities and challenges. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russier, J.; Treossi, E.; Scarsi, A.; Perrozzi, F.; Dumortier, H.; Ottaviano, L.; Meneghetti, M.; Palermo, V.; Bianco, A. Evidencing the mask effect of graphene oxide: A comparative study on primary human and murine phagocytic cells. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11234–11247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sydlik, S.A.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Webber, M.J.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. In vivo compatibility of graphene oxide with differing oxidation states. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3866–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.; Joung, D.; Dowding, J.M.; Reid, D.; Anderson, J.; Zhai, L.; Khondaker, S.I.; Self, W.T.; et al. Oxygenated Functional Group Density on Graphene Oxide: Its Effect on Cell Toxicity. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2013, 30, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.T.; Chang, H.X.; Chen, S.; Lai, C.; Khademhosseini, A.; Wu, H.K. Regulating Cellular Behavior on Few-Layer Reduced Graphene Oxide Films with Well-Controlled Reduction States. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marzi, L.; Ottaviano, L.; Perrozzi, F.; Nardone, M.; Santucci, S.; De Lapuente, J.; Borras, M.; Treossi, E.; Palermo, V.; Poma, A. Flake size-dependent cyto and genotoxic evaluation of graphene oxide on in vitro A549, CaCo2 and vero cell lines. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2014, 28, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ou, L.; Song, B.; Liang, H.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Deng, B.; Sun, T.; Shao, L. Toxicity of graphene-family nanoparticles: A general review of the origins and mechanisms. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Mei, N. Assessment of the toxic potential of graphene family nanomaterials. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marta, D.A.; Adalberto, C.; Stefania, L.; Silvia, G. Toxicity Assessment of Carbon Nanomaterials in Zebrafish during Development. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.; Li, B.; Tian, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; et al. Strongly green-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6858–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Macosko, C.W.; Haynes, C.L. Cytotoxicity of Graphene Oxide and Graphene in Human Erythrocytes and Skin Fibroblasts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2607–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelin, M.; Fusco, L.; León, V.; Martín, C.; Criado, A.; Sosa, S.; Vázquez, E.; Tubaro, A.; Prato, M. Differential cytotoxic effects of graphene and graphene oxide on skin keratinocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasocka, I.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L.; Skibniewski, M.; Skibniewska, E.; Strupinski, W.; Pasternak, I.; Kmieć, H.; Kowalczyk, P. Biocompatibility of pristine graphene monolayer: Scaffold for fibroblasts. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 48, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, O.J.; Son, Y.M.; Hwang, B.U.; Sohn, I.Y.; Lee, N.E. Cellular Oxidative Stress Response to Graphene Oxide Films Functionalized by NH3 Plasma. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 8549–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Take, S.; Tani, R.; Maru, J.; Obara, S.; Endoh, S. Assessment of cytotoxicity and mutagenicity of exfoliated graphene. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 52, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Eppakayala, V.; Kim, J.H. Green synthesis of graphene and its cytotoxic effects in human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.P.; Gliga, A.R.; Lazzaretto, B.; Brandner, B.; Fielden, M.; Vogt, C.; Newman, L.; Rodrigues, A.F.; Shao, W.; Fournier, P.M.; et al. Graphene oxide is degraded by neutrophils and the degradation products are non-genotoxic. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurapati, R.; Mukherjee, S.P.; Martín, C.; Bepete, G.; Vázquez, E.; Pénicaud, A.; Fadeel, B.; Bianco, A. Degradation of Single-Layer and Few-Layer Graphene by Neutrophil Myeloperoxidase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11722–11727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Ruan, J.; Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Wo, Y.; Guo, S.; Cui, D. Biocompatibility of Graphene Oxide. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan, A.; Panchakarla, L.S.; Sadanandan, A.R.; Ashokan, A.; Chandran, P.; Girish, C.M.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.V.; Rao, C.N.; Koyakutty, M. Hemocompatibility and macrophage response of pristine and functionalized graphene. Small 2012, 8, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-T.; Cao, L.; Luo, P.G.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Meziani, M.J.; Liu, Y.; Qi, G.; Sun, Y.-P. Carbon Dots for Optical Imaging in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11308–11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Yan, L.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Xu, H.; Yin, Z.Q. Evaluation of the toxicity of graphene oxide exposure to the eye. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, N.; Ni, D.; Yue, H.; Wei, W.; Ma, G. Surface-Engineered Graphene Navigate Divergent Biological Outcomes toward Macrophages. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5239–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W.; Shim, G.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Choe, Y.S.; Oh, Y.K. Safety and tumor tissue accumulation of pegylated graphene oxide nanosheets for co-delivery of anticancer drug and photosensitizer. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3402–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, V.C.; Jachak, A.; Hurt, R.H.; Kane, A.B. Biological Interactions of Graphene-Family Nanomaterials: An Interdisciplinary Review. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Feng, L.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, K.; Liu, T.; Yang, G.; Liu, Z. Surface Coating-Dependent Cytotoxicity and Degradation of Graphene Derivatives: Towards the Design of Non-Toxic, Degradable Nano-Graphene. Small 2014, 10, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurapati, R.; Bonachera, F.; Russier, J.; Sureshbabu, A.R.; Menard-Moyon, C.; Kostarelos, K.; Bianco, A. Covalent chemical functionalization enhances the biodegradation of graphene oxide. 2D Mater. 2018, 5, 015020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, Y.; McIntyre, J.; Prina-Mello, A. Graphene toxicity as a double-edged sword of risks and exploitable opportunities: A critical analysis of the most recent trends and developments. 2D Mater. 2017, 4, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitounis, D.; Ali-Boucetta, H.; Hong, B.H.; Min, D.H.; Kostarelos, K. Prospects and Challenges of Graphene in Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Brian, D. Inkjet printing ultra-large graphene oxide flakes. 2D Mater. 2017, 4, 021021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriy, A.D.; Sasha, S.; Eric, J.Z.; Richard, D.P.; Geoffrey, H.B.D.; Guennadi, E.; Sonbinh, T.N.; Rodney, S.R. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide paper. Nature 2007, 448, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, W.; Li, P.; Liao, S.; Qiu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhu, C.; Liu, L. Powder, Paper and Foam of Few-Layer Graphene Prepared in High Yield by Electrochemical Intercalation Exfoliation of Expanded Graphite. Small 2014, 10, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. Structural Diversity of Bulky Graphene Materials. Small 2014, 10, 2200–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostarelos, K.; Novoselov, K.S. Exploring the Interface of Graphene and Biology. Science 2014, 344, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parviz, D.; Strano, M. Endotoxin-Free Preparation of Graphene Oxide and Graphene-Based Materials for Biological Applications. Curr. Protoc. Chem. Biol. 2018, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Kang, S.-G.; Tian, X.; Garate, J.A.; Zhao, L.; Ge, C.; Zhou, R. Protein corona mitigates the cytotoxicity of graphene oxide by reducing its physical interaction with cell membrane. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15214–15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Li, N.; Pu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, T.; Tao, J. Advanced review of graphene-based nanomaterials in drug delivery systems: Synthesis, modification, toxicity and application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Robinson, J.T.; Sun, X.; Dai, H. PEGylated nanographene oxide for delivery of water-insoluble cancer drugs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10876–10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Giovannucci, E.L. Cancer risk: Many factors contribute. Science 2015, 347, 728–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barahuie, F.; Saifullah, B.; Dorniani, D.; Fakurazi, S.; Karthivashan, G.; Hussein, M.Z.; Elfghi, F.M. Graphene oxide as a nanocarrier for controlled release and targeted delivery of an anticancer active agent, chlorogenic acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Z.; Ge, H.; Liu, L.; Zhu, C.; Min, L.; Liu, M.; Fan, L.; Li, D. Carboxymethyl cellulose modified graphene oxide as pH-sensitive drug delivery system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Meng, F.; Li, X. Functionalized Graphene Oxide as a nanocarrier of new Copper (II) complexes for targeted therapy on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, C.C.; Slavko, K.; Marina, K.; Massimo, U.; Silvia, M. Luminescent supramolecular hydrogels from a tripeptide and nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, D.; Tan, H.; Pan, C.; Chen, X. Injectable Graphene Oxide/Graphene Composite Supramolecular Hydrogel for Delivery of Anti-Cancer Drugs. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2014, 51, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, W.; Teng, L.; Jin, M.; Lu, B.; Ren, L.; Wang, Y. Graphene Oxide Hybrid Supramolecular Hydrogels with Self-Healable, Bioadhesive and Stimuli-Responsive Properties and Drug Delivery Application. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavinkumar, T.; Varunkumar, K.; Ravikumar, V.; Manivannan, S. Anticancer activity of graphene oxide- reduced graphene oxide- silver nanoparticle composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Gurunathan, S.; Kim, J.H. Graphene oxide-silver nanocomposite enhances cytotoxic and apoptotic potential of salinomycin in human ovarian cancer stem cells (OvCSCs): A novel approach for cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.J.; Kim, T.H.; Zhang, Z.; Azizi, E.; Pham, T.M.; Paoletti, C.; Lin, J.; Ramnath, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Hayes, D.F.; et al. Sensitive capture of circulating tumour cells by functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, S.S.; Papaefthymiou, G.C.; Yi, D.K. Functionalization of Graphene Oxide and its Biomedical Applications. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2015, 40, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, N.R.; Nafiujjaman, M.; Lee, J.S.; Lim, H.N.; Lee, Y.K.; Kwon, I.K. Graphene quantum dot- based theranostic agents for active targeting of breast cancer. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 11420–11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, A.J.; Sen, S.; Sweeney, H.L.; Discher, D.E. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 2006, 126, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Li, T.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Gao, C.; Zhang, S.; Xie, E. Graphene-based composite materials beneficial to wound healing. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2978–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Y.; Pang, D.W.P.; Hwang, S.M.; Tuan, H.Y.; Hu, Y.C. A graphene-based platform for induced pluripotent stem cells culture and differentiation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.C.; Lim, C.H.Y.X.; Shi, H.; Tang, L.A.L.; Wang, Y.; Lim, C.T.; Loh, K.P. Origin of Enhanced Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation on Graphene and Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7334–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, W.C.; Manga, K.K.; Ang, P.K.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.P.; Lim, C.T.; Loh, K.P. Fluorinated Graphene for Promoting Neuro-Induction of Stem Cells. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4285–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, B.; Banerjee, A. Short peptide based hydrogels: Incorporation of graphene into the hydrogel. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9259–9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and Graphene Oxide: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, K.; Li, N.; Shi, Z.; Ge, Z.; Jin, Z. Fabrication, Mechanical Properties, and Biocompatibility of Graphene-Reinforced Chitosan Composites. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2345–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depan, D.; Girase, B.; Shah, J.S.; Misra, R.D.K. Structure-process-property relationship of the polar graphene oxide-mediated cellular response and stimulated growth of osteoblasts on hybrid chitosan network structure nanocomposite scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3432–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. High strength graphene oxide/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 10399–10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.H.; Park, C.B. Myoblast differentiation on graphene oxide. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Choi, K.S.; Kim, Y.; Lim, K.T.; Seonwoo, H.; Park, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Choung, P.H.; Cho, C.S.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. Bioactive effects of graphene oxide cell culture substratum on structure and function of human adipose-derived stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101, 3520–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, L.A.; Dalby, M.J. Nanotopography—Potential relevance in the stem cell niche. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 1574–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, T.R.; Andersen, H.; Makam, V.S.; Khaw, C.; Bae, S.; Xu, X.F.; Ee, P.L.R.; Ahn, J.H.; Hong, B.H.; Pastorin, G.; et al. Graphene for Controlled and Accelerated Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4670–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Q.; Pang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.R.; Zhang, R.; Lu, B.Z.; Wang, J.Y. Effects of surface charges of graphene oxide on neuronal outgrowth and branching. Analyst 2014, 139, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.R.; Aghaei-Ghareh-Bolagh, B.; Dang, T.T.; Topkaya, S.N.; Gao, X.; Yang, S.Y.; Jung, S.M.; Oh, J.H.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Tang, X.; et al. Cell-laden Microengineered and Mechanically Tunable Hybrid Hydrogels of Gelatin and Graphene Oxide. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6385–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Mattiassi, S.; Loeblein, M.; Chin, E.; Ma, D.; Coquet, P.; Viasnoff, V.; Teo, E.H.T.; Goh, E.L.; Yim, E.K.F. Human rett-derived neuronal progenitor cells in 3D graphene scaffold as an in vitro platform to study the effect of electrical stimulation on neuronal differentiation. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 13, 034111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Shirazian, S.A.; Rahighi, R. Rolled graphene oxide foams as three- dimensional scaffolds for growth of neural fibers using electrical stimulation of stem cells. Carbon 2016, 97, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Qiu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, H. Graphene microfiber as a scaffold for regulation of neural stem cells differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasnim, N.; Thakur, V.; Chattopadhyay, M.; Joddar, B. The Efficacy of Graphene Foams for Culturing Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Differentiation into Dopaminergic Neurons. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 3410168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesan, S.; Melchionna, M.; Prato, M. Wire up on Carbon Nanostructures! How to Play a Winning Game. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9441–9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-C.; Zhang, Y.S.; Akpek, A.; Shin, S.R.; Khademhosseini, A. 4D bioprinting: The next-generation technology for biofabrication enabled by stimuli-responsive materials. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, D.; Vranic, S.; Withers, F.; Sanchez-Romaguera, V.; Macucci, M.; Yang, H.F.; Sorrentino, R.; Parvez, K.; Son, S.K.; Iannaccone, G.; et al. Water-based and biocompatible 2D crystal inks for all-inkjet-printed heterostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziyad, S.H. Bio-Inspired/-Functional Colloidal Core-Shell Polymeric-Based NanoSystems: Technology Promise in Tissue Engineering, Bioimaging and NanoMedicine. Polymers 2010, 2, 323–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragazzi, M.; Piana, S.; Longo, C.; Castagnetti, F.; Foroni, M.; Ferrari, G.; Gardini, G.; Pellacani, G. Fluorescence confocal microscopy for pathologists. Modern Pathology 2013, 27, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zong, C.; Shen, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, B.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Z. Mechanism of cellular uptake of graphene oxide studied by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Small 2012, 8, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Li, F.; Thrall, M.J.; Yang, Y.; Xing, J.; Hammoudi, A.A.; Zhao, H.; Massoud, Y.; Cagle, P.T.; Fan, Y.; et al. On-the-spot lung cancer differential diagnosis by label-free, molecular vibrational imaging and knowledge-based classification. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 096004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, C.L.; Xie, X.S. Coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering microscopy: Chemical imaging for biology and medicine. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2008, 1, 883–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, T.B.; Cheng, J.X. In vivo coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering imaging of sciatic nerve tissue. J. Microsc. 2007, 225, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, R.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yu, S.; Kong, J. MRI-visualized, dual-targeting, combined tumor therapy using magnetic graphene-based mesoporous silica. Small 2014, 10, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Yang, K.; Hong, H.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Nayak, T.R.; Zhang, Y.; Theuer, C.P.; Barnhart, T.E.; Liu, Z.; Cai, W. Tumor vasculature targeting and imaging in living mice with reduced graphene oxide. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3002–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.-C.; Kang, S.-M.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, S.Y.; Vilian, A.T.E.; Lee, I.; Han, Y.-K.; Park, J.H.; Cho, W.-S.; Roh, C.; et al. Nano-graphene oxide composite for in vivo imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feleppa, E.J.; Mamou, J.; Porter, C.R.; Machi, J. Quantitative Ultrasound in Cancer Imaging. Semin. Oncol. 2011, 38, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubovic, R.; Ramjist, J.; Gupta, S.; Guha, D.; Sahgal, A.; Foster, F.S.; Yang, V.X.D. High-Frequency Micro-Ultrasound Imaging and Optical Topographic Imaging for Spinal Surgery: Initial Experiences. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2379–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Yeager, D.; Emelianov, S.Y. Chapter 9—Photoacoustic Imaging for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy Guidance. In Cancer Theranostics; Chen, X., Wong, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 139–158. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, K.I.; Subramanian, S.; Murugesan, R.; Mitchell, J.B.; Krishna, M.C. Spatially resolved biologic information from in vivo EPRI, OMRI, and MRI. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1125–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, M.C.; Devasahayam, N.; Cook, J.A.; Subramanian, S.; Kuppusamy, P.; Mitchell, J.B. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance for Small Animal Imaging Applications. ILAR J. 2001, 42, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jares-Erijman, E.A.; Jovin, T.M. FRET imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Matsumoto, K.I.; Mitchell, J.B.; Krishna, M.C. Radio frequency continuous-wave and time-domain EPR imaging and Overhauser-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of small animals: Instrumental developments and comparison of relative merits for functional imaging. NMR Biomed. 2004, 17, 263–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratasz, A.; Pandian, R.P.; Deng, Y.; Petryakov, S.; Grecula, J.C.; Gupta, N.; Kuppusamy, P. In vivo imaging of changes in tumor oxygenation during growth and after treatment. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 57, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Shankar, R.A.; Zweier, J.L. In vivo measurement of arterial and venous oxygenation in the rat using 3D spectral-spatial electron paramagnetic resonance imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 1998, 43, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, M.C.; Subramanian, S.; Kuppusamy, P.; Mitchell, J.B. Magnetic resonance imaging for in vivo assessment of tissue oxygen concentration. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2001, 11, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodetsky, A.A.; Kirilyuk, I.A.; Khramtsov, V.V.; Komarov, D.A. Functional electron paramagnetic resonance imaging of ischemic rat heart: Monitoring of tissue oxygenation and pH. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyodo, F.; Soule, B.P.; Matsumoto, K.-I.; Matusmoto, S.; Cook, J.A.; Hyodo, E.; Sowers, A.L.; Krishna, M.C.; Mitchell, J.B. Assessment of Tissue Redox Status Using Metabolic Responsive Contrast Agents and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boś-Liedke, A.; Walawender, M.; Woźniak, A.; Flak, D.; Gapiński, J.; Jurga, S.; Kucińska, M.; Plewiński, A.; Murias, M.; Elewa, M.; et al. EPR Oximetry Sensor—Developing a TAM Derivative for In Vivo Studies. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 76, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrówczyński, R.; Coy, L.E.; Scheibe, B.; Czechowski, T.; Augustyniak-Jabłokow, M.; Jurga, S.; Tadyszak, K. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy of Polydopamine Radicals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 10341–10347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.B.; Khan, N.; Zaki, B.; Hartford, A.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Swartz, H.M. Clinical Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Oximetry using India Ink. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 662, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumbusch, A.; Holtom, G.R.; Xie, X.S. Three-Dimensional Vibrational Imaging by Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 4142–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.L.; Potma, E.O.; Puoris’haag, M.; Côté, D.; Lin, C.P.; Xie, X.S. Chemical imaging of tissue in vivo with video-rate coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16807–16812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Graphene quantum dots: Emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Huang, P. Chapter 9—Graphene-Based Nanomaterials in Bioimaging. In Biomedical Applications of Functionalized Nanomaterials; Sarmento, B., das Neves, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 247–287. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, W.; Song, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhu, C.; Du, D.; Wang, S.; Asiri, A.M.; Lin, Y. Recent advances in emerging 2D nanomaterials for biosensing and bioimaging applications. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.M.; Kang, J.H.; Hong, B.H. Graphene-based nanomaterials for versatile imaging studies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4835–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, A.; Deshpande, S.; Shinde, D.B.; Pillai, V.K.; Singh, N. Mitigating the Cytotoxicity of Graphene Quantum Dots and Enhancing Their Applications in Bioimaging and Drug Delivery. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Sun, X.; Lee, S.-T.; Liu, Z. Graphene in Mice: Ultrahigh In vivo Tumor Uptake and Efficient Photothermal Therapy. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3318–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Feng, L.; Liu, Z. Photothermally Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy Delivered by Nano-Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7000–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Hung, W.T.; Chen, I.W.; Chen, S.Y. Quantum-dot-tagged reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for bright fluorescence bioimaging and photothermal therapy monitored in situ. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Namgung, R.; Singha, K.; Oh, I.-K.; Kim, W.J. Graphene Oxide–Polyethylenimine Nanoconstruct as a Gene Delivery Vector and Bioimaging Tool. Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si Duck, O.; Jungkil, K.; Dae Hun, L.; Ju Hwan, K.; Chan Wook, J.; Sung, K.; Suk-Ho, C. Structural and optical characteristics of graphene quantum dots size-controlled and well-aligned on a large scale by polystyrene-nanosphere lithography. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 025308. [Google Scholar]
- Samantara, A.K.; Acharya, C.; Satpathy, D.; Panda, C.R.; Bhaskara, P.K.; Sasmal, A. Chapter 13—Functionalized graphene: An unique platform for biomedical application. In Fullerens, Graphenes and Nanotubes; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 545–584. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Song, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Graphene oxide covalently grafted upconversion nanoparticles for combined NIR mediated imaging and photothermal/photodynamic cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7715–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Wu, L.; Qu, X. New Horizons for Diagnostics and Therapeutic Applications of Graphene and Graphene Oxide. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollavelli, G.; Ling, Y.-C. Multi-functional graphene as an in vitro and in vivo imaging probe. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2532–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Hu, L.; Ma, X.; Ye, S.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Multimodal Imaging Guided Photothermal Therapy using Functionalized Graphene Nanosheets Anchored with Magnetic Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1868–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Tao, H.; Yang, K.; Feng, L.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z. A functionalized graphene oxide-iron oxide nanocomposite for magnetically targeted drug delivery, photothermal therapy, and magnetic resonance imaging. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Aburto, R.; Narayanan, T.N.; Nagaoka, Y.; Hasumura, T.; Mitcham, T.M.; Fukuda, T.; Cox, P.J.; Bouchard, R.R.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S.; et al. Fluorinated Graphene Oxide; a New Multimodal Material for Biological Applications. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5632–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, P. Graphene-based nanomaterials for bioimaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tadyszak, K.; Wychowaniec, J.K.; Litowczenko, J. Biomedical Applications of Graphene-Based Structures. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110944
Tadyszak K, Wychowaniec JK, Litowczenko J. Biomedical Applications of Graphene-Based Structures. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(11):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110944
Chicago/Turabian StyleTadyszak, Krzysztof, Jacek K. Wychowaniec, and Jagoda Litowczenko. 2018. "Biomedical Applications of Graphene-Based Structures" Nanomaterials 8, no. 11: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110944
APA StyleTadyszak, K., Wychowaniec, J. K., & Litowczenko, J. (2018). Biomedical Applications of Graphene-Based Structures. Nanomaterials, 8(11), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110944





