Qualitative and Quantitative Detection of PrPSc Based on the Controlled Release Property of Magnetic Microspheres Using Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of AMNPs
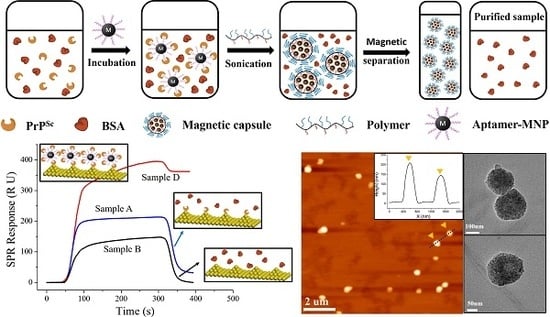
2.3. PrPSc Labeling, Embedding, Enrichment and Release
2.4. Determination of the Induction Heating Time
2.5. In Situ SPR Measurement
2.6. Characterization
2.7. Safety Considerations
2.8. Detection of PrPSc in Real Sample
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of AMNPs and Magnetic Microspheres
3.2. Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Properties
3.3. SPR Sensing for the Detection of Released AMNPs Labeled PrPSc
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biasini, E.; Turnbaugh, J.A.; Unterberger, U.; Harris, D.A. Prion protein at the crossroads of physiology and disease. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.M. Inactivation of Transmissible Degenerative Encephalopathy Agents: A Review. Vet. J. 2000, 159, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, G.S.; Hosszu, L.L.; Power, A.; Hill, A.F.; Kenney, J.; Saibil, H.; Craven, C.J.; Waltho, J.P.; Clarke, A.R.; Collinge, J. Reversible conversion of monomeric human prion protein between native and fibrilogenic conformations. Science 1999, 283, 1935–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.M.; Baldwin, M.; Nguyen, J.; Gasset, M.; Serban, A.; Groth, D.; Mehlhorn, I.; Huang, Z.; Fletterick, R.J.; Cohen, F.E. Conversion of alpha-helices into beta-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10962–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoa, X.D.; Kirk, A.G.; Tabrizian, M. Towards integrated and sensitive surface plasmon resonance biosensors: A review of recent progress. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Situ, C.; Mooney, M.H.; Elliott, C.T.; Buijs, J. Advances in surface plasmon resonance biosensor technology towards high-throughput, food-safety analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmerhorst, E.; Chandler, D.J.; Nussio, M.; Mamotte, C.D. Real-time and Label-free Bio-sensing of Molecular Interactions by Surface Plasmon Resonance: A Laboratory Medicine Perspective. Clin. Biochem. Rev. Aust. Assoc. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 33, 161–173. [Google Scholar]
- Miodek, A.; Poturnayová, A.; Snejdárková, M.; Hianik, T.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. Binding kinetics of human cellular prion detection by DNA aptamers immobilized on a conducting polypyrrole. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 2505–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiayu, W.; Xiong, W.; Jiping, L.; Wensen, L.; Ming, X.; Linna, L.; Jing, X.; Haiying, W.; Hongwei, G. A rapid method for detection of PrP by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacGregor, I.R.; Drummond, O. Species differences in the blood content of the normal cellular isoform of prion protein, PrP(c), measured by time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. Vox Sang. 2001, 81, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.-T.; Seo, H.B.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, S.K.; Song, C.-S.; Gu, M.B. Highly sensitive sandwich-type SPR based detection of whole H5Nx viruses using a pair of aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J. Hollow gold nanoparticle-enhanced SPR based sandwich immunoassay for human cardiac troponin I. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lou, Z.; Park, B.; Kwon, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, B. Surface conformations of an anti-ricin aptamer and its affinity for ricin determined by atomic force microscopy and surface plasmon resonance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 17, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, B.; Guo, C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Xu, B. Molecular-level insights of early-stage prion protein aggregation on mica and gold surface determined by AFM imaging and molecular simulation. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Guo, C.; Lou, Z.; Xu, B. Following the aggregation of human prion protein on Au(111) surface in real-time. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2088–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhie, A.; Kirby, L.; Sayer, N.; Wellesley, R.; Disterer, P.; Sylvester, I.; Gill, A.; Hope, J.; James, W.; Tahiri-Alaoui, A. Characterization of 2′-Fluoro-RNA Aptamers That Bind Preferentially to Disease-associated Conformations of Prion Protein and Inhibit Conversion. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39697–39705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, R.-Y.; Li, J.-H.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Li, H.-Z.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, J.; Wei, D.-G. Preparation and characterization of silica-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles used as precursor of ferrofluids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, M.; Camilo, R.L.; Sampaio, L.C.; Macêdo, M.A.; Nakamura, M.; Toma, H.E. Preparation and characterization of (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 279, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Liu, G.; Deng, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, P.; Xu, Z.; Xu, H.; Chu, P.K. Magnetite-loaded fluorine-containing polymeric micelles for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3013–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horcas, I.; Fernández, R.; Gómez-Rodríguez, J.M.; Colchero, J.; Gómez-Herrero, J.; Baro, A.M. WSXM: A software for scanning probe microscopy and a tool for nanotechnology. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 013705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bürger, A.; Wagner, C.; Viedt, C.; Reis, B.; Hug, F.; Hänsch, G.M. Fibronectin synthesis by human tubular epithelial cells in culture: Effects of PDGF and TGF-β on synthesis and splicing. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Munir, A.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, H.S. Magnetic Nanoparticle Enhanced Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensing and Its Application for the Ultrasensitive Detection of Magnetic Nanoparticle-Enriched Small Molecules. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6782–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homola, J. Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 377, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lou, Z.; Han, H.; Mao, D.; Jiang, Y.; Song, J. Qualitative and Quantitative Detection of PrPSc Based on the Controlled Release Property of Magnetic Microspheres Using Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR). Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020107
Lou Z, Han H, Mao D, Jiang Y, Song J. Qualitative and Quantitative Detection of PrPSc Based on the Controlled Release Property of Magnetic Microspheres Using Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR). Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(2):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020107
Chicago/Turabian StyleLou, Zhichao, He Han, Dun Mao, Yibin Jiang, and Jianyue Song. 2018. "Qualitative and Quantitative Detection of PrPSc Based on the Controlled Release Property of Magnetic Microspheres Using Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)" Nanomaterials 8, no. 2: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020107
APA StyleLou, Z., Han, H., Mao, D., Jiang, Y., & Song, J. (2018). Qualitative and Quantitative Detection of PrPSc Based on the Controlled Release Property of Magnetic Microspheres Using Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR). Nanomaterials, 8(2), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020107