Adsorption Removal of Multiple Dyes Using Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles from an Escherichia coli Strain Overexpressed Selenite Reductase CsrF
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
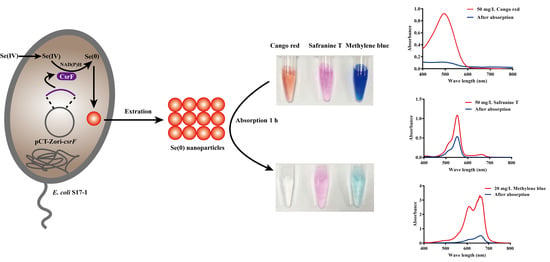
2.2. Bio-SeNPs Production and Extraction
2.3. Characterization of Bio-SeNPs
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Desorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bio-SeNPs Produced by Escherichia coli S17-1-pCT-Zori-csrF
3.2. Characteristics of SeNPs
3.3. Effects of pH on Zeta Potential for Dye Removal
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
3.5. Adsorption Isotherms
3.6. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.7. Desorption and Reusability Study
3.8. Comparison with Other Adsorbents
4. Conclusions and Perspective
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Bio-SeNPs | biogenic Se(0)-nanoparticles |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| TEM | transmission electronic microscopy |
| HAADF | high-angle annular dark field |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| EDS | energy-dispersive X-ray spectrographs |
| FT-IR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
References
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.K.; Dash, R.R.; Bhunia, P. A review on chemical coagulation/flocculation technologies for removal of colour from textile wastewaters. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 93, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, R. Textile dyeing industry an environmental hazard. Nat. Sci. 2012, 4, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razali, M.; Kim, J.F.; Attfield, M.; Budd, P.M.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Szekely, G. Sustainable wastewater treatment and recycling in membrane manufacturing. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 5196–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, F.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, X. The development of sustainable yttrium separation process from rare earth enrichments using bifunctional ionic liquid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 162, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didaskalou, C.; Buyuktiryaki, S.; Kecili, R.; Fonte, C.P.; Szekely, G. Valorisation of agricultural waste with an adsorption/nanofiltration hybrid process: From materials to sustainable process design. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3116–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassin, T.; Reinsch, H.; Van de Voorde, B.; Wuttke, S.; Medina, D.D.; Stock, N.; Bein, T.; Ameloot, R.; De Vos, D. Adsorption and reactive desorption on metal–organic frameworks: A direct strategy for lactic acid recovery. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, R.P.; O’Connor, K.; Seeram, R. Current progress on bio-based polymers and their future trends. Prog. Biomater. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, I.; Hazarika, M.; Tamuly, C. Synthesis, characterization of bio-derived ZnO nanoparticles and its catalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, J.R.; Parker, H.L.; Muñoz García, A.; Hicken, A.; Asemave, K.; Farmer, T.J.; He, H.; Clark, J.H.; Hunt, A.J. Bio-derived materials as a green route for precious & critical metal recovery and re-use. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1951–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Tugarova, A.V.; Kamnev, A.A. Proteins in microbial synthesis of selenium nanoparticles. Talanta 2017, 174, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, G.; Curle, C.; Laishley, E.J. Purification and characterization of an inducible dissimilatory type sulfite reductase from Clostridium pasteurianum. Arch. Microbiol. 1984, 138, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMoll-Decker, H.; Macy, J.M. The periplasmic nitrite reductase of Thauera selenatis may catalyze the reduction of selenite to elemental selenium. Arch. Microbiol. 1993, 160, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Afkar, E.; Lisak, J.; Saltikov, C.; Basu, P.; Oremland, R.S.; Stolz, J.F. The respiratory arsenate reductase from Bacillus selenitireducens strain MLS10. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 226, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.B.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Wu, C.; Li, W.W.; Li, N.; Yang, Z.C.; Tong, Z.H.; Yu, H.Q. Selenite reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 is mediated by fumarate reductase in periplasm. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wu, S.; Li, N.; Wang, D.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G. Novel bacterial selenite reductase CsrF responsible for Se(IV) and Cr(VI) reduction that produces nanoparticles in Alishewanella sp. WH16-1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 342, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Zhang, R.; Dong, C.; Yu, Z.; Ren, J. Novel walnut peptide-selenium hybrids with enhanced anticancer synergism: Facile synthesis and mechanistic investigation of anticancer activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Skalickova, S.; Milosavljevic, V.; Cihalova, K.; Horky, P.; Richtera, L.; Adam, V. Selenium nanoparticles as a nutritional supplement. Nutrition 2017, 33, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacenza, E.; Presentato, A.; Zonaro, E.; Lemire, J.A.; Demeter, M.; Vallini, G.; Turner, R.J.; Lampis, S. Antimicrobial activity of biogenically produced spherical Se-nanomaterials embedded in organic material against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus strains on hydroxyapatite-coated surfaces. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 804–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiyo, F.; Singh, M. Selenium nanoparticles: Potential in cancer gene and drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1075–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.; Jordan, N.; Schild, D.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Weiss, S.; Franzen, C.; Farges, F.; Hübner, R.; Lens, P.N.L. Adsorption of zinc by biogenic elemental selenium nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, F.; Song, C.; Sun, X.; Tan, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solution by biogenic selenium nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 15201–15209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Y. Adsorptive removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions using microgel based on nanocellulose and polyvinylamine. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaghbani, N.; Hafiane, A.; Dhahbi, M. Removal of safranin T from wastewater using micellar enhanced ultrafiltration. Desalination 2008, 222, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestani, B.; Benderdouche, N.; Benstaali, B.; Belhakem, M.; Addou, A. Methylene blue and iodine adsorption onto an activated desert plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8441–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampis, S.; Zonaro, E.; Bertolini, C.; Cecconi, D.; Monti, F.; Micaroni, M.; Turner, R.J.; Butler, C.S.; Vallini, G. Selenite biotransformation and detoxification by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia SeITE02: Novel clues on the route to bacterial biogenesis of selenium nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Mattanovich, D.; Villaverde, A. Systems metabolic engineering, industrial biotechnology and microbial cell factories. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 1475–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Debieux, C.M.; Dridge, E.J.; Mueller, C.M.; Splatt, P.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Knight, I.; Florance, H.; Love, J.; Titball, R.W.; Lewis, R.J.; et al. A bacterial process for selenium nanosphere assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13480–13485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Su, J.; Wang, L.; Yao, R.; Wang, D.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, G.; Rensing, C. Selenite reduction by the obligate aerobic bacterium Comamonas testosteroni S44 isolated from a metal-contaminated soil. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhai, Y.Y.; Gao, Q.; Luo, W.J.; Xia, H.; Zhou, C.G. Highly efficient removal of acid red 18 from aqueous solution by magnetically retrievable chitosan/carbon nanotube: Batch study, isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Shen, S.L.; Wang, S.Q.; Huang, J.; Su, P.; Wang, Q.R.; Zhao, B.X. A dual function magnetic nanomaterial modified with lysine for removal of organic dyes from water solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, W.; Zhang, L.; Kong, Q.; Wang, W. Efficient adsorption of sulfamethazine onto modified activated carbon: A plausible adsorption mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadri, S.; Ganoe, A.; Haik, Y. Removal and recovery of acridine orange from solutions by use of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Is the free energy change of adsorption correctly calculated? J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 1981–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelentsov, V.; Datsko, T. Thermodynamics of fluorine adsorption onto modified trepel. Termotehnica 2013, 1, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, H.; Li, M.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Tian, J.; Liang, H. Study of the interaction of artemisinin with bovine serum albumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2006, 39, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupai, J.; Razali, M.; Buyuktiryaki, S.; Kecili, R.; Szekely, G. Long-term stability and reusability of molecularly imprinted polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Rensing, C.; Zheng, S. Proteins enriched in charged amino acids control the formation and stabilization of selenium nanoparticles in Comamonas testosteroni S44. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Dinh, D.M.; Hsieh, Y.L. Adsorption and desorption of cationic malachite green dye on cellulose nanofibril aerogels. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 173, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. A facile route for preparation of magnetic biomass activated carbon with high performance for removal of dye pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 15599–15608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, D.; Chen, G.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Pal, M.; Zhu, H.; Wu, L.; Lin, J.; Al-Dahyan, D.; Li, W.; et al. Mesoporous silica thin membranes with large vertical mesochannels for nanosize-based separation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1521–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangon, S.; Hunt, A.J.; Attard, T.M.; Mengchang, P.; Ngernyen, Y.; Supanchaiyamat, N. Valorisation of waste rice straw for the production of highly effective carbon based adsorbents for dyes removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, S.; Sivasamy, A.; Sivanesan, S.; Ramamurthi, V.; Swaminathan, G. Removal of safranin basic dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto corncob activated carbon. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 7627–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, F.S.; Elias, M.M.C.; Ferreira, G.M.D.; Adarme, O.F.H.; Savedra, R.M.L.; Siqueira, M.F.; da Silva, L.H.M.; Gil, L.F.; Gurgel, L.V.A. Synthesis and application of a new carboxylated cellulose derivative. Part iii: Removal of auramine-O and safranin-T from mono- and bi-component spiked aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 512, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Dyes | ΔHθ (kJ /mol) | ΔSθ (kJ /mol K) | ΔGθ (kJ/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 303 K | 313 K | 323 K | |||
| Congo red | 1.4546 | 0.0755 | −21.43 | −22.1849 | −22.9398 |
| Safranine T | 6.2332 | 0.0727 | −15.8049 | −16.5318 | −17.2588 |
| Methylene blue | 8.5850 | 0.1153 | −26.3652 | −27.5181 | −28.6710 |
| Adsorbent | Dye | qe (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC-PVAm | Congo red | 1469.7 | [26] |
| Magnetic biomass activated carbon | Congo red | 369.7 | [44] |
| Rice straw based carbon | Congo red | 531.4 | [46] |
| Methylene blue | 527.6 | ||
| Teak wood bark | Methylene blue | 914.6 | [4] |
| Corncob Activated Carbon | Safranin T | 1428.8 | [47] |
| Carboxylated cellulose derivative | Safranin T | 1429.7 | [48] |
| Bio-SeNPs | Congo red | 1577.7 | This work |
| Methylene blue | 1792.2 | ||
| Safranin T | 1911.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, S.; Wang, D.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G. Adsorption Removal of Multiple Dyes Using Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles from an Escherichia coli Strain Overexpressed Selenite Reductase CsrF. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040234
Xia X, Zhou Z, Wu S, Wang D, Zheng S, Wang G. Adsorption Removal of Multiple Dyes Using Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles from an Escherichia coli Strain Overexpressed Selenite Reductase CsrF. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(4):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040234
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Xian, Zijie Zhou, Shijuan Wu, Dan Wang, Shixue Zheng, and Gejiao Wang. 2018. "Adsorption Removal of Multiple Dyes Using Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles from an Escherichia coli Strain Overexpressed Selenite Reductase CsrF" Nanomaterials 8, no. 4: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040234
APA StyleXia, X., Zhou, Z., Wu, S., Wang, D., Zheng, S., & Wang, G. (2018). Adsorption Removal of Multiple Dyes Using Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles from an Escherichia coli Strain Overexpressed Selenite Reductase CsrF. Nanomaterials, 8(4), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040234