Gelled Electrolyte Containing Phosphonium Ionic Liquids for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Characterization Methods
2.2. Preparation of Gelled Electrolyte
2.3. Preparation of the Cathode (LiFePO4) and Assembly of the Cell
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. Transport Properties in Phosphonium Electrolyte
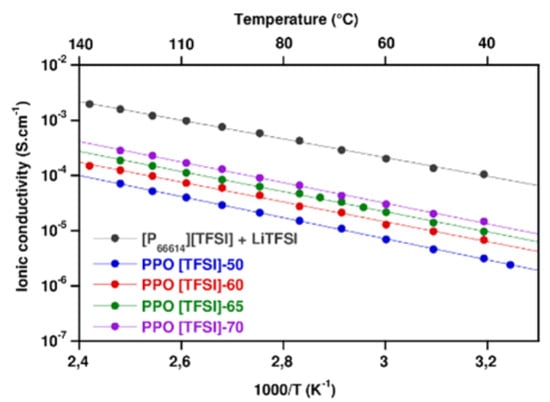
3.1.1. Ionic Conductivity
3.1.2. Diffusion Coefficient
3.1.3. Lithium Solubility
3.2. IL Confinement within the Epoxy Network
3.2.1. Effect of IL Content on the Exudation
3.2.2. Effect of IL on Reaction Progress
3.3. Influence of the Electrolyte on the Final Properties of Epoxy Based-Networks
3.3.1. On the Thermal Stability of Networks
3.3.2. On the Viscoelastic Properties
3.4. Effect of Electrolyte on the Transport and Electrochemical Properties
3.4.1. Transport Properties
3.4.2. Electrochemical Stability
3.4.3. Cycling Performance of Li|LiFePO4 Cell
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larcher, D.; Tarascon, J.M. Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, P.G.; Freunberger, S.A.; Hardwick, L.J.; Tarascon, J.M. Li–O2 and Li–S batteries with high energy storage. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhi, A.K.; Nanjundaswamy, K.S.; Goodenough, J.B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohzuku, T.; Ueda, A.; Yamamoto, N. Zero-Strain Insertion Material of Li [Li1/3Ti5/3] O4 for Rechargeable Lithium Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 1431–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Ohno, H.; Scrosati, B. Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passerini, S.; Montanino, M.; Appetecchi, G.B. Lithium Polymer Batteries Based on Ionic Liquids. In Polymer for Energy Storage and Conversion; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, S.; Quartarone, E.; Mustarelli, P.; Magistris, A.; Fagnoni, M.; Protti, S.; Gerbaldi, C.; Spinella, A. Lithium ion conducting PVdF-HFP composite gel electrolytes based on N-methoxyethyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl)-imide ionic liquid. J. Power Source 2010, 195, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids. Green solvents for the future. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokuda, H.; Ishii, K.; Susan, M.A.; Tsuzuki, S.; Hayamizu, K.; Watanabe, M. Physicochemical properties and structures of room-temperature ionic liquids. 3. Variation of cationic structures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2833–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier-Bourbigou, H.; Magna, L. Ionic liquids: Perspectives for organic and catalytic reactions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 182, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, G.H. Electrochemical reduction mechanisms and stabilities of some cation types used in ionic liquids and other organic salts. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 83, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.T.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Alessandrini, F.; Passerini, S. Solvent-free, PYR1ATFSI ionic liquid-based ternary polymer electrolyte systems: I. Electrochemical characterization. J. Power Source 2007, 171, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.T.; Jeong, S.S.; Xue, M.Z.; Balducci, A.; Winter, M.; Passerini, S.; Alessandrini, F.; Appetecchi, G.B. Development of ionic liquid-based lithium battery prototypes. J. Power Source 2012, 199, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Cui, W.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; An, M. Characterization and properties of ternary P (VdF-HFP)-LiTFSI-EMITFSI ionic liquid polymer electrolytes. Solid State Sci. 2012, 14, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appetecchi, G.B.; Kim, G.T.; Montanino, M.; Carewska, M.; Marcilla, R.; Mecerreyes, D.; De Meatza, I. Ternary polymer electrolytes containing pyrrolidinium-based polymeric ionic liquids for lithium batteries. J. Power Source 2010, 195, 3668–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbaldi, C.; Nair, J.R.; Ahmad, S.; Meligrana, G.; Bongiovanni, R.; Bodoardo, S.; Penazzi, N. UV-cured polymer electrolytes encompassing hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquid for lithium batteries. J. Power Source 2010, 195, 1706–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepniak, I. Compatibility of poly (bisAEA4)-LiTFSI–MPPipTFSI ionic liquid gel polymer electrolyte with Li4Ti5O12 lithium ion battery anode. J. Power Source 2014, 247, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepniak, I.; Andrzejewska, E.; Dembna, A.; Galinski, M. Characterization and application of N-methyl-N-propylpiperidinium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide ionic liquid–based gel polymer electrolyte prepared in situ by photopolymerization method in lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 121, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirshova, N.; Bismarck, A.; Carreyette, S.; Fontana, Q.P.; Greenhalgh, E.S.; Jacobsson, P.; Johansson, P.; Marczewski, M.J.; Kalinka, G.; Kucernak, A.R.; et al. Structural supercapacitor electrolytes based on bicontinuous ionic liquid–epoxy resin systems. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 15300–15309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotta, D.; Bernard, J.; Sauvant-Moynot, V. Application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to the study of ionic transport in polymer-based electrolytes. Prog. Organ. Coat. 2010, 69, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frackowiak, E.; Lota, G.; Pernak, J. Room-temperature phosphonium ionic liquids for supercapacitor application. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 164104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunashima, K.; Yonekawa, F.; Sugiya, M. Lithium secondary batteries using a lithium nickelate-based cathode and phosphonium ionic liquid electrolytes. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2009, 12, A54–A57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armel, V.; Velayutham, D.; Sun, J.; Howlett, P.C.; Forsyth, M.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Pringle, J.M. Ionic liquids and organic ionic plastic crystals utilizing small phosphonium cations. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7640–7650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Howlett, P.C.; Pringle, J.M.; Janikowski, J.; Armand, M.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. An organic ionic plastic crystal electrolyte for rate capability and stability of ambient temperature lithium batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3352–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.A.; Livi, S.; Netto, D.B.; Soares, B.G.; Duchet, J.; Gérard, J.F. New epoxy systems based on ionic liquid. Polymer 2013, 54, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livi, S.; Silva, A.A.; Thimont, Y.; Nguyen, T.K.; Soares, B.G.; Gérard, J.F.; Duchet-Rumeau, J. Nanostructured thermosets from ionic liquid building block–epoxy prepolymer mixtures. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 28099–28106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclère, M.; Livi, S.; Maréchal, M.; Picard, L.; Duchet-Rumeau, J. The properties of new epoxy networks swollen with ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56193–56204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.E. Use of the stimulated echo in NMR diffusion studies. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 52, 2523–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Gonzalo, C.; Howlett, P.C.; Hodgson, J.L.; Madsen, L.A.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Insights into the reversible oxygen reduction reaction in a series of phosphonium-based ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 25062–25070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharaskar, S.A.; Wasewar, K.L.; Varma, M.N.; Shende, D.Z.; Tadi, K.K.; Yoo, C.K. Synthesis, characterization, and application of novel trihexyl tetradecyl phosphonium bis (2, 4, 4-trimethylpentyl) phosphinate for extractive desulfurization of liquid fuel. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 123, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, M.; Mendon, S.K.; Rawlins, J.W. Disecondary amine synthesis and its reaction kinetics with epoxy prepolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotta, D. Liquides Ioniques Gélifiées Pour les Batteries Lithium-Ion. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Picardie Jules Verne, Amiens, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cossy, J.; Bellosta, V.; Hamoir, C.; Desmurs, J.R. Regioselective ring opening of epoxides by nucleophiles mediated by lithium bistrifluoromethanesulfonimide. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 7083–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušek, K.; Dušková-Smrčková, M. Polymer Networks. In Macromolecular Engineering; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; p. 1687. [Google Scholar]
- Gennes, P.G. Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]










| Name | Structure | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| PPO |  | Sigma Aldrich; 320 g/eq |
| Jeffamine®D2000 |  | Supplied by Huntsmann; 514 g/eq |
| [P66614][TMP] |  | Supplied by Cytec; Molar mass = 773.27 g·mol−1 m.p. =−72 °C Td max = 350 °C |
| [P66614][TFSI] |  | Supplied by Cytec; Molar mass = 764.0 g·mol−1 m.p. = −72.4 °C Td = 450 °C |
| LiTFSI |  | Supplied by Sigma Aldrich; Molar mass = 287.0 g·mol−1 |
| LiTMP |  | Supplied by Solvionic Molar mass = 780.27 g·mol−1 |
| Sample | Ea (J·mol−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| [P66614][TFSI] + LiTFSI | 470 | 0.999 |
| [P66614][TMP] + LiTMP | 530 | 0.998 |
| T (°C) | [P66614][TFSI] + LiTFSI | T (°C) | [P66614][TMP] + LiTMP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D [H] | 28.5 | 9.25 × 10−8 | 54 | 2.3 × 10−8 |
| 86 | 1.1 × 10−7 | |||
| D [Li] | 21 | 9.35 × 10−9 | 54 | No signal |
| 86 | No signal |
| Sample | Composition (wt %) | Exudation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | IL | LiTFSI | ||
| PPO [TFSI]-50 | 50 | 41.0 | 9.0 | No |
| PPO [TFSI]-60 | 40 | 49.2 | 10.8 | No |
| PPO [TFSI]-65 | 35 | 53.3 | 11.7 | No |
| PPO [TFSI]-70 | 30 | 57.4 | 12.6 | No |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Peak Assignment |
|---|---|
| 7099 | O–H overtone |
| 6600–6480 | Primary and Secondary amine combination band Overtones of N–H stretching |
| 6072 | Terminal epoxy first overtone of C–H stretching |
| 5880–5500 | C–H overtone (CH2, CH3) |
| 5249 | −OH due to moisture (O–H asymmetric stretching and bending) |
| 4935 | Primary amine combination band N–H stretching and bending |
| 4530 | Epoxy combination band (C–H stretching and epoxy ring breathing) |
| System | PPO-Jeffamine | PPO-Jeffamine + ([P66614][TFSI] + LiTFSI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step of Curing | First Step | Second Step | First Step | Second Step |
| kE (h−1/2) | 0.272 | 0.988 | 0.268 | 7.989 |
| (R2) | (0.994) | (0.996) | (0.989) | (0.993) |
| kPA (h−1/2) | 0.534 | 0.534 | 0.532 | 30.266 |
| (R2) | (0.999) | (0.999) | (0.999) | (0.999) |
| kSA (h−1/2) | 0.190 | 0.243 | 0.186 | 3.039 |
| (R2) | (0.988) | (0.996) | (0.990) | (0.990) |
| Electrolyte Content | Tα (°C) | Rubbery State E′ (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| (wt %) | ||
| 0 | −49.2 | 0.33 |
| 50 | −48.8 | 0.25 |
| 60 | −46.9 | 0.20 |
| 70 | −43.0 | 0.06 |
| Sample | Ea (J·mol−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| [P66614][TFSI] + LiTFSI | 440 | 0.999 |
| PPO [TFSI]-50 | 500 | 0.999 |
| PPO [TFSI]-60 | 470 | 0.997 |
| PPO [TFSI]-65 | 475 | 0.999 |
| PPO [TFSI]-70 | 490 | 0.999 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leclère, M.; Bernard, L.; Livi, S.; Bardet, M.; Guillermo, A.; Picard, L.; Duchet-Rumeau, J. Gelled Electrolyte Containing Phosphonium Ionic Liquids for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060435
Leclère M, Bernard L, Livi S, Bardet M, Guillermo A, Picard L, Duchet-Rumeau J. Gelled Electrolyte Containing Phosphonium Ionic Liquids for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(6):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060435
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeclère, Mélody, Laurent Bernard, Sébastien Livi, Michel Bardet, Armel Guillermo, Lionel Picard, and Jannick Duchet-Rumeau. 2018. "Gelled Electrolyte Containing Phosphonium Ionic Liquids for Lithium-Ion Batteries" Nanomaterials 8, no. 6: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060435
APA StyleLeclère, M., Bernard, L., Livi, S., Bardet, M., Guillermo, A., Picard, L., & Duchet-Rumeau, J. (2018). Gelled Electrolyte Containing Phosphonium Ionic Liquids for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials, 8(6), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060435