New Polymers for Needleless Electrospinning from Low-Toxic Solvents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
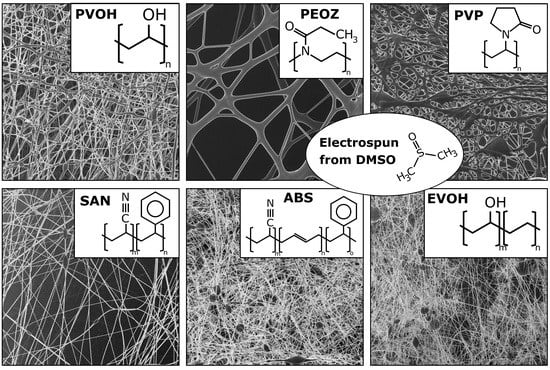
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: A Fascinating Method for the Preparation of Ultrathin Fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmelsmann, N.; Homburg, S.V.; Ehrmann, A. Needleless Electrospinning of Pure and Blended Chitosan. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 225, 012098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.X.; Qi, K.; Wang, L.D.; Zhou, Y.M.; Liu, R.T.; Cui, S.Z. Combined Application of Multinozzle Air-jet Electrospinning and Airflow Twisting for the Efficient Preparation of Continuous-Twisted Nanofiber Yarn. Fiber Polym. 2015, 16, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.N.; Song, M.Y.; Li, D.W.; Yang, Z.P.; Cao, J.H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wei, Q.F. Preparation of Self-Clustering Highly Oriented Nanofibers by Needleless Electrospinning Methods. Fiber Polym. 2016, 17, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsey, S.; Absar, S.; Choi, H. Comparative study of polymer dissolution techniques for electrospinning. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 10, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, T.; Brikmann, J.; Meissner, H.; Ehrmann, A. Influence of Solution and Spinning Parameters on Nanofiber Mat Creation of Poly(ethylene oxide) by Needleless Electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Medzg. 2017, 23, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.L.; Nie, L.; Jiang, M.J.; Bie, F.S.; Shao, L.J.; Qi, C.Z.; Zhang, X.M.; Liu, X.J. Palladium immobilized on in-situ cross-linked chitosan superfine fibers for catalytic application in an aqueous medium. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 11023–11030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri, M.; Karimi-Nazari, E.; Hosseini, H.; Emamgholi, A. New Chitosan/Poly(ethylene oxide)/Thyme Nanofiber Prepared by Electrospinning Method for Antimicrobial Wound Dressing. J. Nanostruct. 2016, 6, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, T.; Wehlage, D.; Böhm, T.; Remche, A.; Ehrmann, A. Needleless Electrospinning of PAN Nanofibre Mats. Tekstilec 2017, 60, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Rodriguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T.; Finsterbusch, K.; Ehrmann, A. Investigation of Needleless Electrospun PAN Nanofiber Mats. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1952, 020085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.D.; Han, C.; Bo, X.J.; Liu, J.; Guo, L.P. Prussian blue analogues derived iron-cobalt alloy embedded in nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofibers for efficient oxygen reduction reaction in both alkaline and acidic solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 533, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xiao, N.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, H.Q.; Ji, Y.Q.; Qiu, J.S. Electrospun nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers with tuned microstructure and enhanced lithium storage properties. Carbon 2018, 139, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimethyl Sulfoxide. Toxnet—Toxicology Data Network. Available online: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/a?dbs+hsdb:@term+@DOCNO+80 (accessed on 26 December 2018).
- Sabantina, L.; Rodríguez-Cano, M.A.; Klöcker, M.; García-Mateos, F.J.; Ternero-Hidalgo, J.J.; Mamun, A.; Beermann, F.; Schwakenberg, M.; Voigt, A.-L.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; et al. Fixing PAN Nanofiber Mats during Stabilization for Carbonization and Creating Novel Metal/Carbon Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Wehlage, D.; Klöcker, M.; Mamun, A.; Grothe, T.; García-Mateos, F.J.; Rodríguez-Marasol, J.; Cordero, T.; Finsterbusch, K.; Ehrmann, A. Stabilization of Electrospun PAN/Gelatin Nanofiber Mats for Carbonization. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 6131085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Klöcker, M.; Wortmann, M.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T.; Moritzer, E.; Finsterbusch, K.; Ehrmann, A. Stabilization of PAN nanofiber mats obtained by needleless electrospinning using DMSO as solvent. J. Ind. Text. 2019. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Großerhode, C.; Wehlage, D.; Grothe, T.; Grimmelsmann, N.; Fuchs, S.; Hartmann, J.; Mazur, P.; Reschke, V.; Siemens, H.; Rattenholl, A.; et al. Investigation of microalgae growth on electrospun nanofiber mats. AIMS Bioeng. 2017, 4, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döpke, C.; Grothe, T.; Kosmalska, D.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Magnetic nanofiber mats for data storage and transfer. Nanomaterials 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Polk, S.; Sori, N.; Thayer, N.; Kemper, N.; Maghdouri-White, Y.; Bulysheva, A.A.; Francis, M.P. Pneumatospinning of collagen microfibers from benign solvents. Biofabrication 2018, 10, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, X.; Wang, H.J.; Lin, T.; Zhu, Z.T. Effects of hydrogen bonding on starch granule dissolution, spinnability of starch solution, and properties of electrospun starch fibers. Polymer 2018, 153, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betatache, A.; Braiek, M.; Chateaux, J.F.; Lagarde, F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Molecular imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) nanofibers electrospun on gold electrodes for impedimetric creatinine sensing. In Materials and Applications for Sensors and Transducers II; Key Engineering Materials; Hristoforou, E., Vlachos, D.S., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications: Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 543, pp. 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Betatache, A.; Chateaux, J.F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Conception and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymer nanofibers of poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) and their use as membrane in electrochemical sensor for creatinine detection. J. New Technol. Mater. 2018, 8, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.J.; Chi, M.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Chen, J.T. Fabrication, morphology control, and electroless metal deposition of electrospun ABS fibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognitzki, M.; Frese, T.; Steinhart, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H.; Schaper, A.; Hellwig, M. Preparation of fibers with nanoscaled morphologies: Electrospinning of polymer blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2001, 41, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Aigner, A.; Czubayko, F.; Kissel, T.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers by electrospinning as a protein delivery system and the retardation of enzyme release by additional polymer coatings. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buruaga, L.; Gonzalez, A.; Iruin, J.J. Electrospinning of poly (2-ethyl-2-oxazoline). J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 3186–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudkova, V.; Krumme, A.; Märtson, T.; Rikko, M.; Tarassova, E.; Viirsalu, M. The impact of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride on electrospinning process of SAN polymer solutions and electrospun fiber morphology. J. Electrostat. 2014, 72, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, J.; Fei, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, W. Preparation and characterization of electrospinning PLA/curcumin composite membranes. Fibers Polym. 2010, 11, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.J.; Nangrejo, M.; Edirisinghe, M. A novel method of selecting solvents for polymer electrospinning. Polymer 2010, 51, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.; Wendt, R. Estimation of the Surface Free Energy of Polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meichsner, G.; Mezger, T.; Schröder, J. Benetzung von Festkörpern. In Lackeigenschaften Messen und Steuern; Ulrich, Z., Ed.; Vincentz Network: Hannover, Germany, 2003; p. 106. ISBN 3-87870-739-8. [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt, C. Solvatochromic dyes as solvent polarity indicators. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2319–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, M.G.; Layman, J.M.; Cashion, M.P.; Long, T.E. Phospholipid nonwoven electrospun membranes. Science 2006, 311, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, M.G.; Wilkes, G.L.; Colby, R.H.; Long, T.E. Correlations of solution rheology with electrospun fiber formation of linear and branched polyesters. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D.H. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.X.; Ma, Z.W.; Xie, Y.Z.; Su, Y.R.; Zhao, H.T.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, J.Y.; Li, J.; Xie, E.Q. Photoluminescence of rare earth3+ doped uniaxially aligned HfO2 nanotubes prepared by sputtering with electrospun polyvinylpyrolidone nanofibers as templates. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 024309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.G.; Shen, X.X.; Branford-White, C.; White, K.; Zhu, L.M.; Bligh, S.A. Oral fast-dissolving drug delivery membranes prepared from electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone ultrafine fibers. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 055104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Abbreviation | Polymer | Supplier | MW (g/mol) | Concentration (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVOH | poly(vinyl alcohol) | Nippon Gohsei | 20,000 | 30 |
| PEOZ | poly(2ethyl2oxazolene) | Kremer Pigmente | 200,000 | 40 |
| PVP | poly(vinylpyrrolidone) | Sigma Aldrich | 360,000 | 20 |
| SAN | poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile) | Sigma Aldrich | 165,000 | 22 |
| EVOH | poly(vinyl alcohol-co-ethylene) | Sigma Aldrich | n/a 1 | 20 |
| ABS | acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | INEOS | n/a | 25 |
| PVOH | PEOZ | PVP |
 |  |  |
| SAN | ABS | EVOH |
 |  |  |
| Polymers | Total Surface Free Energy (mN/m) | Polar (mN/m) | Disperse (mN/m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M 1 | SD 2 | |||
| PVOH * | 37 [32] | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| PEOZ | 41.86 | 0.80 | 15.21 | 26.65 |
| PVP | 44.72 | 0.81 | 16.25 | 28.47 |
| SAN | 42.82 | 0.76 | 4.07 | 38.75 |
| EVOH | 38.57 | 0.90 | 9.65 | 28.92 |
| ABS | 41.51 | 0.65 | 7.06 | 34.45 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wortmann, M.; Frese, N.; Sabantina, L.; Petkau, R.; Kinzel, F.; Gölzhäuser, A.; Moritzer, E.; Hüsgen, B.; Ehrmann, A. New Polymers for Needleless Electrospinning from Low-Toxic Solvents. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010052
Wortmann M, Frese N, Sabantina L, Petkau R, Kinzel F, Gölzhäuser A, Moritzer E, Hüsgen B, Ehrmann A. New Polymers for Needleless Electrospinning from Low-Toxic Solvents. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleWortmann, Martin, Natalie Frese, Lilia Sabantina, Richard Petkau, Franziska Kinzel, Armin Gölzhäuser, Elmar Moritzer, Bruno Hüsgen, and Andrea Ehrmann. 2019. "New Polymers for Needleless Electrospinning from Low-Toxic Solvents" Nanomaterials 9, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010052
APA StyleWortmann, M., Frese, N., Sabantina, L., Petkau, R., Kinzel, F., Gölzhäuser, A., Moritzer, E., Hüsgen, B., & Ehrmann, A. (2019). New Polymers for Needleless Electrospinning from Low-Toxic Solvents. Nanomaterials, 9(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010052