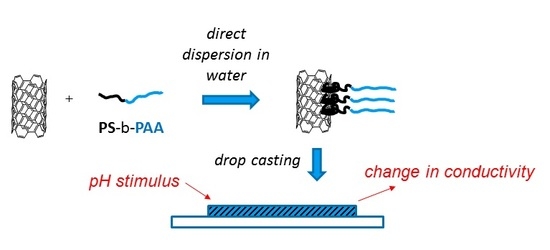
Design of a pH-Responsive Conductive Nanocomposite Based on MWCNTs Stabilized in Water by Amphiphilic Block Copolymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Polymers Preparation
2.2.1. Preparation of PS-Br Macroinitiator
2.2.2. Preparation of PS-b-PAA Polymer
2.3. Nanocomposite Preparation and Setup Preparation for the Resistive and pH-Responsive Behaviour
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polymers Synthesis
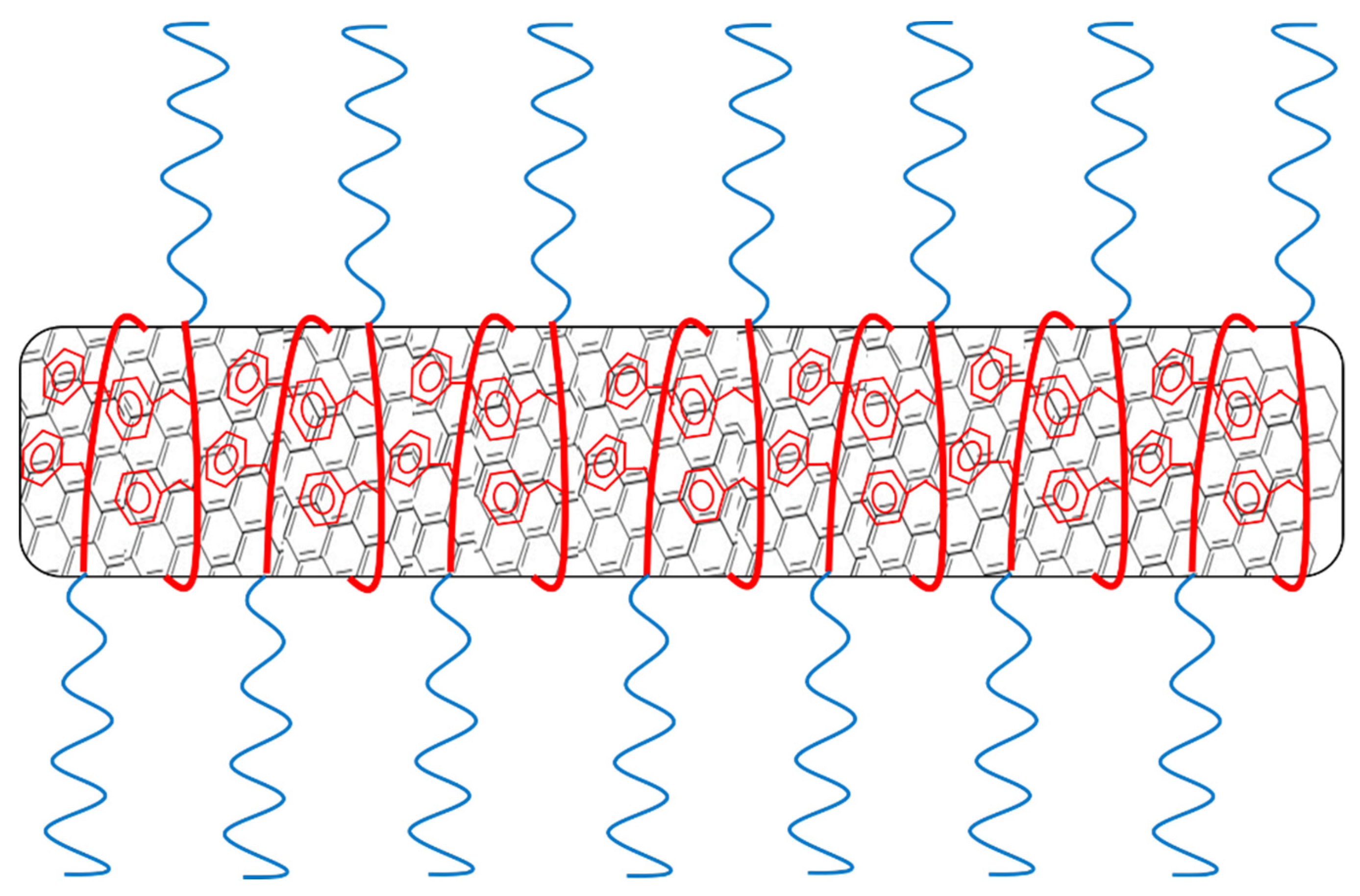
3.2. Polymer/MWCNT Dispersions in Water: Effect of Polymer Structure on Stability
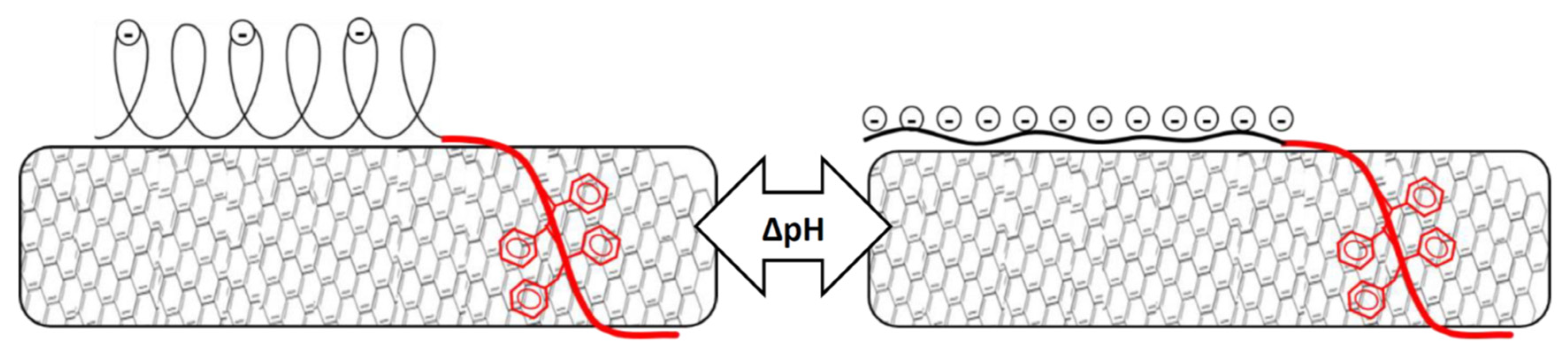
3.3. Effect of pH on Stability of Polymer/MWCNT Dispersions
3.4. Characterization via Zeta-Potential Measurements and SEM Microscopy
3.5. Resistivity of MWCNTs/Polymer Composites
3.6. Investigation of pH Responsive Behavior of the Composite
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Volder, M.F.L.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. CNTs: Present and Future Commercial Applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.Q.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P.M. Reliability and current carrying capacity of carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 1172–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Locascio, M.; Zapol, P.; Li, S.; Mielke, S.L.; Schatz, G.C.; Espinosa, H.D. Measurements of near-ultimate strength for multiwalled carbon nanotubes and irradiation-induced crosslinking improvements. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop, E.; Mann, D.; Wang, Q.; Goodson, K.; Dai, H. Thermal conductance of an individual single-wall carbon nanotube above room temperature. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliore, N.; Polgar, L.; Araya-Hermosilla, R.; Picchioni, F.; Raffa, P.; Pucci, A. Effect of the polyketone aromatic pendent groups on the electrical conductivity of the derived MWCNTs-based nanocomposites. Polymers (Basel) 2018, 10, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sacco, F.; Pucci, A.; Raffa, P.; Di Sacco, F.; Pucci, A.; Raffa, P. Versatile multi-functional block copolymers made by atom transfer radical polymerization and post-synthetic modification: Switching from volatile organic compound sensors to polymeric surfactants for water rheology control via hydrolysis. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergué, N.; Ernould, B.; Minoia, A.; De Winter, J.; Gerbaux, P.; Lazzaroni, R.; Gohy, J.-F.; Dubois, P.; Coulembier, O. Diblock copolymers consisting of a redox polymer block based on a stable radical linked to an electrically conducting polymer block as cathode materials for organic radical batteries. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Hermosilla, R.; Pucci, A.; Raffa, P.; Santosa, D.; Pescarmona, P.P.; Gengler, R.Y.N.; Rudolf, P.; Moreno-Villoslada, I.; Picchioni, F. Electrically-responsive reversible Polyketone/MWCNT network through Diels-Alder chemistry. Polymers (Basel) 2018, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantha-Iyengar, G.; Shanmugasundaram, K.; Nallal, M.; Lee, K.P.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Lakshmi, D.; Sai-Anand, G. Functionalized conjugated polymers for sensing and molecular imprinting applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 88, 1–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tans, S.J.; Verschueren, A.R.M.; Dekker, C. Room-temperature transistor based on a single carbon nanotube. Nature 1998, 393, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Chang, D.W.; Baek, J.B.; Lu, W. Carbon nanomaterials for advanced energy conversion and storage. Small 2012, 8, 1130–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Du, X.; Logan, J.M.; Sippel, J.; Nikolou, M.; Kamaras, K.; Reynolds, J.R.; Tanner, D.B.; Hebard, A.F.; et al. Transparent, conductive carbon nanotube films. Science 2004, 305, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Watanabe, T.; Honma, I.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H. Effect of solution pH and ionic strength on the stability of poly(acrylic acid)-encapsulated multiwalled carbon nanotubes aqueous dispersion and its application for NADH sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, R.M.F.; Abreu, B.; Claro, B.; Buzaglo, M.; Regev, O.; Furó, I.; Marques, E.F. Dispersing carbon nanotubes with ionic surfactants under controlled conditions: Comparisons and insight. Langmuir 2015, 31, 10955–10965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, B.E. Dispersion of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs) in Aqueous Solution and Reversion of SWCNT Aggregates. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Terentjev, E.M. Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes: Mixing, Sonication, Stabilization, and Composite Properties. Polymers (Basel) 2012, 4, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Taton, T.A. Micelle-encapsulated carbon nanotubes: A route to nanotube composites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 5650–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.L.; Huang, A.Y.; Peng, H.; Chiang, I.W.; Khabashesku, V.N.; Margrave, J.L. Sidewall amino-functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes through fluorination and subsequent reactions with terminal diamines. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Gao, C.; Yan, D. Constructing amphiphilic polymer brushes on the convex surfaces of multi-walled carbon nanotubes by in situ atom transfer radical polymerization. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Gao, C.; Yan, D. Controlled functionalization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by in situ atom transfer radical polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 412–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, I.-Y.; Chang, D.W.; Kumar, N.A.; Baek, J.-B. Functionalization of carbon nanotubes. In Carbon Nanotubes—Polymer Nanocomposites; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, W.H.; Wang, Q.; Collins, F. Dispersion of carbon nanotubes with SDS surfactants: A study from a binding energy perspective. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonard, J.M.; Stora, T.; Salvetat, J.P.; Maier, F.; Stöckli, T.; Duschl, C.; Forró, L.; De Heer, W.A.; Châtelain, A. Purification and size-selection of carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 1997, 9, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karajanagi, S.S.; Yang, H.; Asuri, P.; Sellitto, E.; Dordick, J.S.; Kane, R.S. Protein-assisted solubilization of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Langmuir 2006, 22, 1392–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Liu, N.; Gao, S.; Mamat, X.; Su, Y.; Wagberg, T.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Hu, G. A facile electrochemical sensor based on PyTS-CNTs for simultaneous determination of cadmium and lead ions. Sensors (Switzerland) 2018, 18, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujigaya, T.; Nakashima, N. Non-covalent polymer wrapping of carbon nanotubes and the role of wrapped polymers as functional dispersants. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 024802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, Y.; Fujigaya, T.; Niidome, Y.; Nakashima, N. Single-walled carbon nanotubes/DNA hybrids in water are highly stable. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 455, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y. Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes with Stimuli—Responsive Molecules and Polymers; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Katchalsky, A.; Eisenberg, H. Molecular weight of polyacrylic and polymethacrylic acid. J. Polym. Sci. 1951, 6, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunlan, J.C.; Liu, L.; Kim, Y.S. Tunable single-walled carbon nanotube microstructure in the liquid and solid states using poly(acrylic acid). Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etika, K.C.; Cox, M.A.; Grunlan, J.C. Tailored dispersion of carbon nanotubes in water with pH-responsive polymers. Polymer 2010, 51, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunlan, J.C.; Liu, L.; Regev, O. Weak polyelectrolyte control of carbon nanotube dispersion in water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 317, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Aubin, K.; Poulin, P.; Saadaoui, H.; Maugey, M.; Zakri, C. Dispersion and film-forming properties of poly(acrylic acid)-stabilized carbon nanotubes. Langmuir 2009, 25, 13206–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffa, P.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Broekhuis, A.A.; Picchioni, F. The effect of hydrophilic and hydrophobic block length on the rheology of amphiphilic diblock Polystyrene-b-Poly(sodium methacrylate) copolymers prepared by ATRP. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 428, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffa, P.; Brandenburg, P.; Wever, D.A.Z.; Broekhuis, A.A.; Picchioni, F. Polystyrene-poly(sodium methacrylate) amphiphilic block copolymers by ATRP: Effect of structure, pH, and ionic strength on rheology of aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 7106–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, P. Polystyrene-based amphiphilic block copolymers: Synthesis, properties and applications. In Polystyrene: Synthesis, Characteristics and Applications; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 31–52. ISBN 9781633213715 | 9781633213562. [Google Scholar]
- Meijerink, M.; van Mastrigt, F.; Franken, L.E.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Picchioni, F.; Raffa, P. Triblock copolymers of styrene and sodium methacrylate as smart materials: Synthesis and rheological characterization. Pure Appl. Chem. 2017, 89, 1641–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, T.; Swanson, L.; Geoghegan, M.; Rimmer, S. The pH-responsive behaviour of poly(acrylic acid) in aqueous solution is dependent on molar mass. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2542–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.A.; Matyjaszewski, K. Atom transfer radical polymerization of tert-butyl acrylate and preparation of block copolymers. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 4039–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarevsky, N.V.; Pintauer, T.; Matyjaszewski, K. Deactivation efficiency and degree of control over polymerization in ATRP in protic solvents. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 9768–9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripin, D.H.; Evans, D.A. Evans pKa Table. Available online: http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/reich/pkatable/index.htm (accessed on 8 July 2019).
- Calisi, N.; Giuliani, A.; Alderighi, M.; Schnorr, J.M.; Swager, T.M.; Di Francesco, F.; Pucci, A. Factors affecting the dispersion of MWCNTs in electrically conducting SEBS nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naotoshi, N. Chemistry of the Carbon Nanotubes. Kobunshi 2005, 54, 572–575. [Google Scholar]
- Vaisman, L.; Wagner, H.D.; Marom, G. The role of surfactants in dispersion of carbon nanotubes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 128–130, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, H.; Kamburova, K.; Maeda, H.; Radeva, T. Investigation of pH dependence of poly(acrylic acid) conformation by means of electric birefringence. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 354, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintis, D.G.; Mavrantzas, V.G. Effect of pH and Molecular Length on the Structure and Dynamics of Short Poly(acrylic acid) in Dilute Solution: Detailed Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 4204–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laguecir, A.; Ulrich, S.; Labille, J.; Fatin-Rouge, N.; Stoll, S.; Buffle, J. Size and pH effect on electrical and conformational behavior of poly(acrylic acid): Simulation and experiment. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balberg, I.; Azulay, D.; Toker, D.; Millo, O. Percolation and tunneling in composite materials. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2004, 18, 2091–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D.; Aharony, A. Introduction to Percolation Theory; Taylor & Francis: Milton Park, Didcot, UK, 1994; ISBN 9780748402533. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar, P.F.; Chan, K.J.; Stephens, S.T.; Cola, B.A. Enhanced Electrical Conductivity of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids Mixed with Carbon Nanotubes: A Spectroscopic Study. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, H481–H486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, J.; Jarosz, P.R.; Schauerman, C.M.; Moses, B.T.; Landi, B.J.; Cress, C.D.; Raffaelle, R.P. High conductivity carbon nanotube wires from radial densification and ionic doping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 182106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Suzuki, A. Theory of temperature dependence of the conductivity in carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 013711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Hermosilla, R.; Pucci, A.; Araya-Hermosilla, E.; Pescarmona, P.P.; Raffa, P.; Polgar, L.M.; Moreno-Villoslada, I.; Flores, M.; Fortunato, G.; Broekhuis, A.A.; et al. An easy synthetic way to exfoliate and stabilize MWCNTs in a thermoplastic pyrrole-containing matrix assisted by hydrogen bonds. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85829–85837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, F.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, J. The switch-type humidity sensing properties of polyacrylic acid and its copolymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 2005–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Polymer | Concentration (mmol/mL) | Total Surface Coverage PAA (m2/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| PAA454 | 1.41·10–5 | 917 |
| PS26PAA81 | 5.38·10–5 | 649 |
| PS26PAA226 | 2.42·10–5 | 795 |
| PS26PAA580 | 1.03·10–5 | 864 |
| Sample | pH | Zeta Potential |
|---|---|---|
| PS26PAA580 | 5 | −15 mV |
| PS26PAA580 with MWCNTs | 5 | −7 mV |
| PS26PAA580 | 9.5 | −66 mV |
| PS26PAA580 with MWCNTs | 9.5 | −58 mV |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
den Hoed, F.; Pucci, A.; Picchioni, F.; Raffa, P. Design of a pH-Responsive Conductive Nanocomposite Based on MWCNTs Stabilized in Water by Amphiphilic Block Copolymers. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101410
den Hoed F, Pucci A, Picchioni F, Raffa P. Design of a pH-Responsive Conductive Nanocomposite Based on MWCNTs Stabilized in Water by Amphiphilic Block Copolymers. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(10):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101410
Chicago/Turabian Styleden Hoed, Frank, Andrea Pucci, Francesco Picchioni, and Patrizio Raffa. 2019. "Design of a pH-Responsive Conductive Nanocomposite Based on MWCNTs Stabilized in Water by Amphiphilic Block Copolymers" Nanomaterials 9, no. 10: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101410
APA Styleden Hoed, F., Pucci, A., Picchioni, F., & Raffa, P. (2019). Design of a pH-Responsive Conductive Nanocomposite Based on MWCNTs Stabilized in Water by Amphiphilic Block Copolymers. Nanomaterials, 9(10), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101410