Synthesis of Green Recyclable Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanomaterials Coated by Hydrophobic Plant Extracts for Efficient Collection of Oil Spills
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Magnetite Nanomaterials (MNMs)
2.3. Characterization of MNMs
2.4. Efficiency of MAE-MNMs and OBE-MNMs as Oil Spill Collectors
3. Results and Discussion
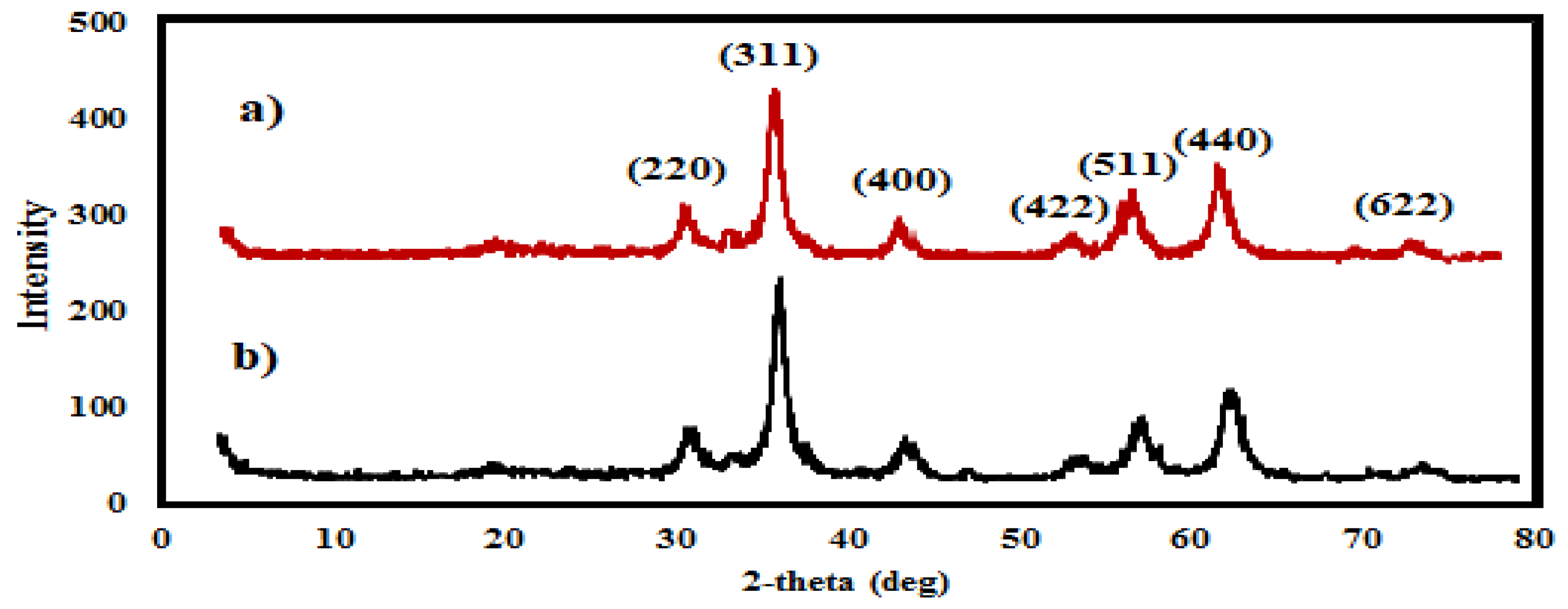
3.1. Characterization of the Prepared MNMs
3.2. Efficiency of MAE-MNMs and OBE-MNMs As Oil Spill Collectors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Etkin, D.S. Estimating cleanup costs for oil spills. In Proceedings of the International Oil Spill Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 7–12 March 1999; pp. 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Fingas, M. Oil Spill Science and Technology; Gulf Professional Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lessard, R.R.; DeMarco, G. The significance of oil spill dispersants. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 2000, 6, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Abdullah, M.M.; ElSaeed, S.M. Application of new amphiphilic ionic liquid based on ethoxylated octadecylammonium tosylate as demulsifier and petroleum crude oil spill dispersant. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abullah, M.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Attah, A.M. Synthesis and application of amphiphilic ionic liquid based on acrylate copolymers as demulsifier and oil spill dispersant. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Abdel-Rauf, M.E.; Maysour, N.E.; Gafer, A.K. Water-based oil spill dispersants based on rosin formaldehyde resins. JDST 2010, 31, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Elsaeed, A.M. Use of rosin-based nonionic surfactants as petroleum crude oil sludge dispersants. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Azim, A.-A.A.; Abdul-Raheim, A.M.; Atta, A.M.; Brostow, W.; Datashvili, T. Swelling and network parameters of crosslinked porous octadecyl acrylate copolymers as oil spill sorbers. e-Polymers 2009, 9, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.S.; Joshi, M.V.; Jayaram, R.V. Treatment of oil spill by sorption technique using fatty acid grafted sawdust. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; El-Ghazawy, R.A.; Farag, R.K.; El-Kafrawy, A.F.; Abdel-Azim, A.A.A. Crosslinked cinnamoyloxyethyl methacrylate and isooctyl acrylate copolymers as oil sorbers. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oribayo, O.; Feng, X.; Rempel, G.L.; Pan, Q. Modification of formaldehyde-melamine-sodium bisulfite copolymer foam and its application as effective sorbents for clean up of oil spills. ChEnS 2017, 160, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, C.; Pricop, L.; Samoila, P.; Rotaru, R.; Harabagiu, V. Surface hydrophobization of polyester fibers with poly (methylhydro-dimethyl) siloxane copolymers: Experimental design for testing of modified nonwoven materials as oil spill sorbents. Polym. Test. 2017, 59, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, C.; Dorneanu, P.P.; Airinei, A.; Olaru, N.; Samoila, P.; Rotaru, A. Design and evaluation of electrospun polysulfone fibers and polysulfone/NiFe2O4 nanostructured composite as sorbents for oil spill cleanup. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 70, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Ezzat, A.O.; Hashem, A.I. Synthesis and application of monodisperse hydrophobic magnetite nanoparticles as an oil spill collector using an ionic liquid. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16524–16530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Al-Hussain, S.A. Functionalization of magnetite nanoparticles as oil spill collector. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6911–6931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Atta, A.M. Novel magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated with sulfonated asphaltene as crude oil spill collectors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 59242–59249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.M.S.; Atta, A.; Allohedan, H.; Alkhathlan, H.; Khan, M.; Ezzat, A. Green synthesis of hydrophobic magnetite nanoparticles coated with plant extract and their application as petroleum oil spill collectors. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.M.S.; Atta, A.; Allohedan, H.; Alkhathlan, H.; Khan, M.; Ezzat, A. Biosynthesized Magnetic Metal Nanoparticles for Oil Spills Remediation. U.S. Patent 990190, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Thakkar, K.N.; Mhatre, S.S.; Parikh, R.Y. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanpuria, P.; Rana, N.K.; Yadav, S.K. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles: Technological concepts and future applications. JNR 2008, 10, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karade, V.; Waifalkar, P.; Dongle, T.; Sahoo, S.C.; Kollu, P.; Patil, P.; Patil, P. Greener synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles using green tea extract and their magnetic properties. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 096102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, Y.P.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Kuwano, N.; Khairudin, N.B.B.A.; Mohamad, S.E.B.; Lee, K.X. Green synthesis of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using seaweed (Kappaphycus alvarezii) extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouz Dizaji, A.; Yilmaz, M.; Piskin, E. Silver or gold deposition onto magnetite nanoparticles by using plant extracts as reducing and stabilizing agents. Artif. Cell Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications—An updated report. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, I.-M.; Park, I.; Seung-Hyun, K.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Rajakumar, G. Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Their characteristic properties and therapeutic applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharde, A.; Rautaray, D.; Bansal, V.; Ahmad, A.; Sarkar, I.; Yusuf, S.M.; Sanyal, M.; Sastry, M. Extracellular biosynthesis of magnetite using fungi. Small 2006, 2, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdeen, M.; Sabry, S.; Ghozlan, H.; El-Gendy, A.A.; Carpenter, E.E. Microbial-physical synthesis of Fe and Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using Aspergillus niger YESM1 and supercritical condition of ethanol. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 9174891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroumand Moghaddam, A.; Namvar, F.; Moniri, M.; Md Tahir, P.; Azizi, S.; Mohamad, R. Nanoparticles biosynthesized by fungi and yeast: A review of their preparation, properties, and medical applications. Molecules 2015, 20, 16540–16565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Shen, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Gu, N. Preparation and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles coated by amino silane. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 212, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Das, A.; Marwal, A.; Verma, R. Bio-reductive synthesis and characterization of plant protein coated magnetite nanoparticles. In Nano Hybrids; Trans Tech Publications: Zürich, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 69–86. [Google Scholar]
- Ta, T.; Vanella, R.; Nash, M. Magnetic separation of elastin-like polypeptide receptors for enrichment of cellular and molecular targets. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7932–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, M.; Waitumbi, J.; Hoffman, A.; Yager, P.; Stayton, P. Multiplexed enrichment and detectionof malarial biomarkers using a stimuli-responsive iron oxide and gold nanoparticle reagent system. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6776–6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.; Judy, J.; Di Carlo, D. Magnetic nanoparticle–mediated massively parallel mechanical modulation of single-cell behavior. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, K.; Tian, W.; Bai, J.; Wang, L.; Gong, X. Application of magnetic adsorbents based on iron oxide nanoparticles for oil spill remediation: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, A.; Aburjai, T.; Hanrahan, J.; Abdel-Halim, H. Medicinal plants used by traditional healers in Jordan, the Tafila region. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ghazali, G.E.; Al-Khalifa, K.S.; Saleem, G.A.; Abdallah, E.M. Traditional medicinal plants indigenous to Al-Rass province, Saudi Arabia. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2680–2683. [Google Scholar]
- Oka, Y.; Shuker, S.; Tkachi, N.; Trabelcy, B.; Gerchman, Y. Nematicidal activity of Ochradenus baccatus against the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne javanica. Plant Pathol. 2014, 63, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collenette, S. Illustrated Guide to the Flowers of Saudi Arabia; Scorpion: Moscow, Russian, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Al-Hussain, S.A. Synthesis of stabilized myrrh-capped hydrocolloidal magnetite nanoparticles. Molecules 2014, 19, 11263–11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- File, P.D. Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards; ASTM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1967; pp. 9–185. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Thundat, T.; Mitra, S.K. Analytical model for zeta potential of asphaltene. Fuel 2013, 108, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grijalva-Monteverde, H.; Arellano-Tánori, O.V.; Valdez, M.A. Zeta potential and Langmuir films of asphaltene polar fractions. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 2416–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zeng, Q.; Goya, G.F.; Torres, T.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Ge, M.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.Z. ZnFe2O4 Nanocrystals: Synthesis and Magnetic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12274–12278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







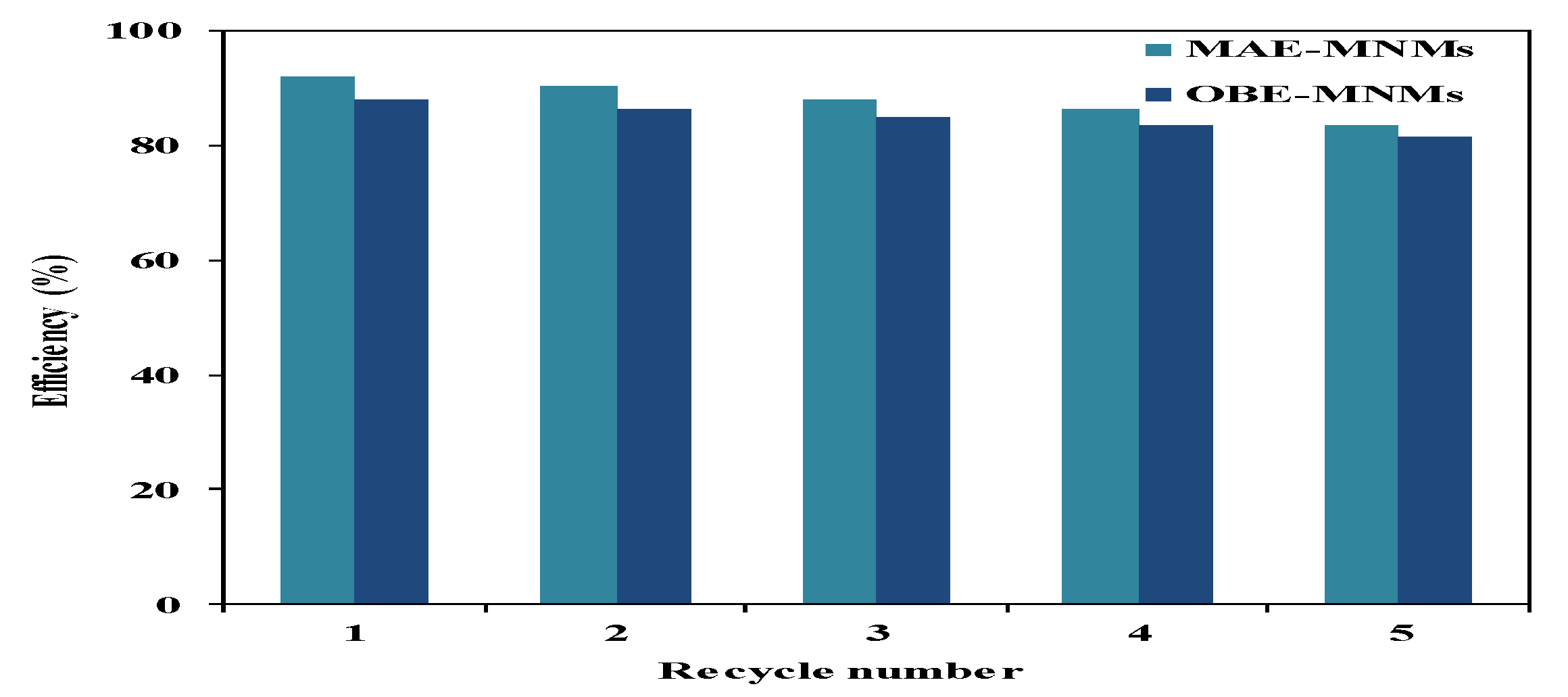

| MNMs | Collection Efficiency (%) Using Different (MNMs: Crude Oil) ) (Wt.:Vol %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 1:10 | 1:25 | 1:50 | |
| MAE-MNM | 95 | 92 | 88 | 80 |
| OBE-MNM | 91 | 88 | 83 | 76 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdullah, M.M.S.; Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Khan, M.; Ezzat, A.O. Synthesis of Green Recyclable Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanomaterials Coated by Hydrophobic Plant Extracts for Efficient Collection of Oil Spills. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101505
Abdullah MMS, Atta AM, Al-Lohedan HA, Alkhathlan HZ, Khan M, Ezzat AO. Synthesis of Green Recyclable Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanomaterials Coated by Hydrophobic Plant Extracts for Efficient Collection of Oil Spills. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(10):1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101505
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdullah, Mahmood M. S., Ayman M. Atta, Hamad A. Al-Lohedan, Hamad Z. Alkhathlan, Merajuddin. Khan, and Abdelrahman O. Ezzat. 2019. "Synthesis of Green Recyclable Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanomaterials Coated by Hydrophobic Plant Extracts for Efficient Collection of Oil Spills" Nanomaterials 9, no. 10: 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101505
APA StyleAbdullah, M. M. S., Atta, A. M., Al-Lohedan, H. A., Alkhathlan, H. Z., Khan, M., & Ezzat, A. O. (2019). Synthesis of Green Recyclable Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanomaterials Coated by Hydrophobic Plant Extracts for Efficient Collection of Oil Spills. Nanomaterials, 9(10), 1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101505






