Dewetted Gold Nanostructures onto Exfoliated Graphene Paper as High Efficient Glucose Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrode Fabrication
2.3. Instrumental Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
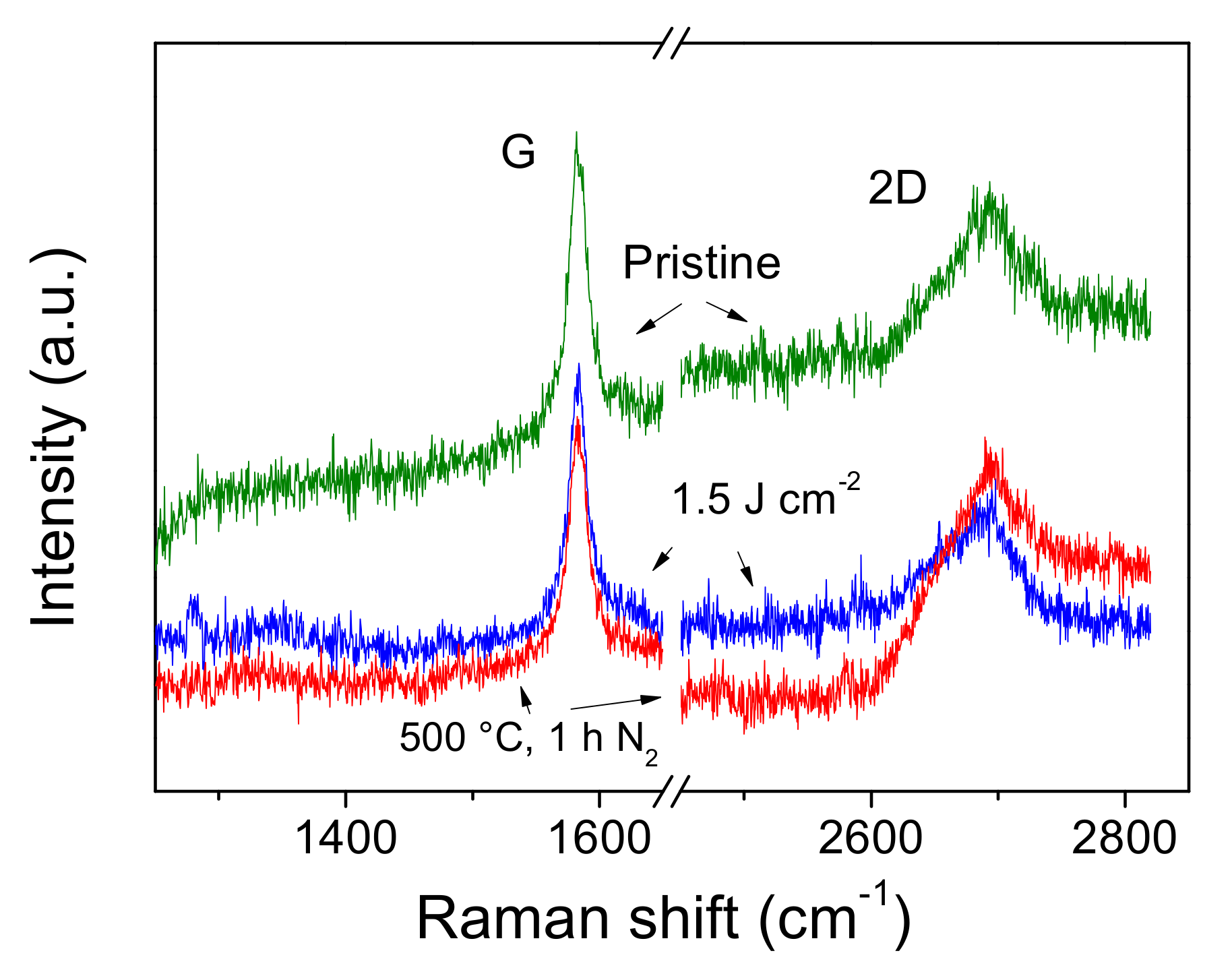
3.1. Morphological and Structural Characterization of Laser Irradiated Graphene Paper
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of Graphene Paper Modified by Laser Irradiation
3.3. GP-AuNPs Morphology Characterization
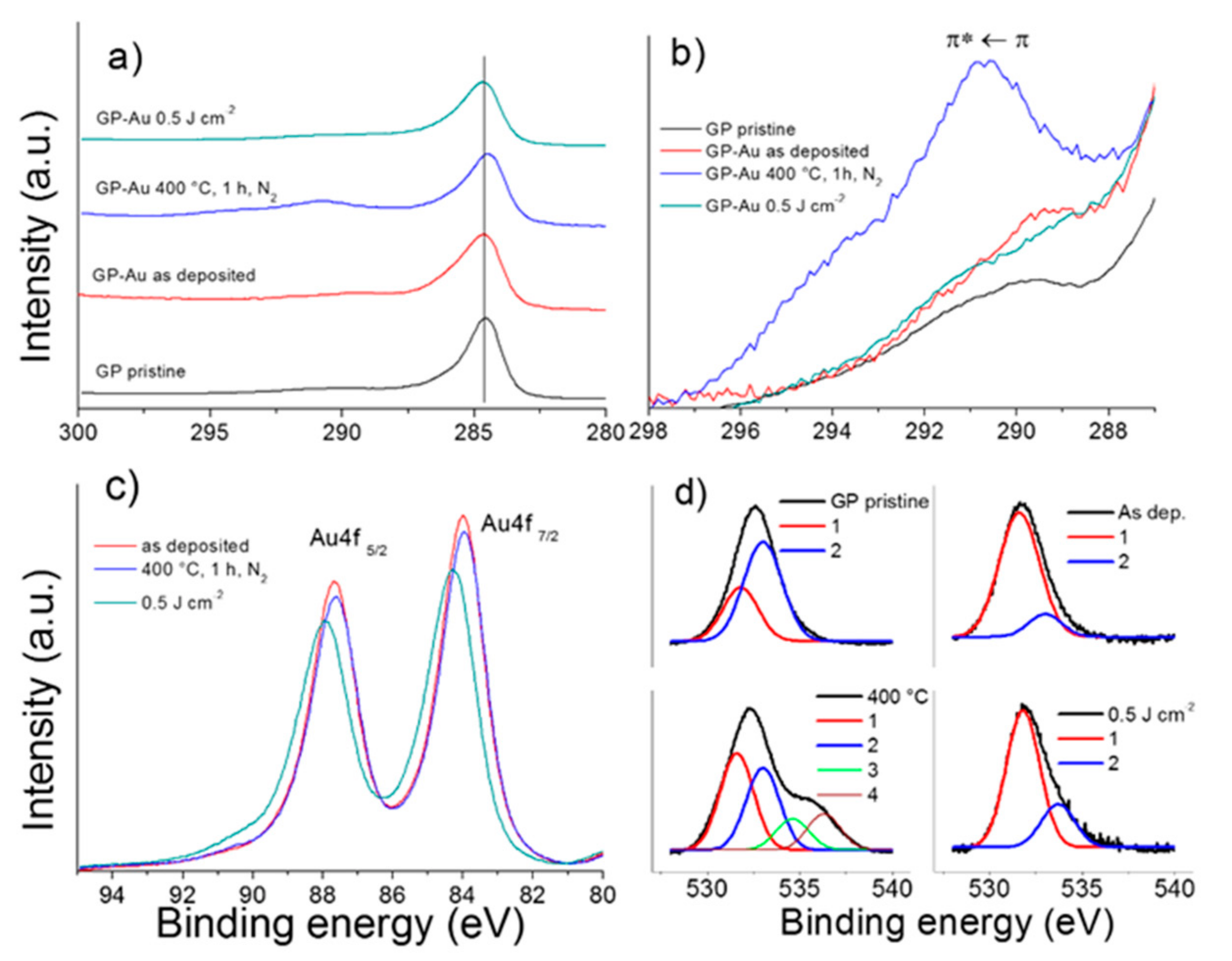
3.4. XPS Characterization of GP-Au Nanostructures
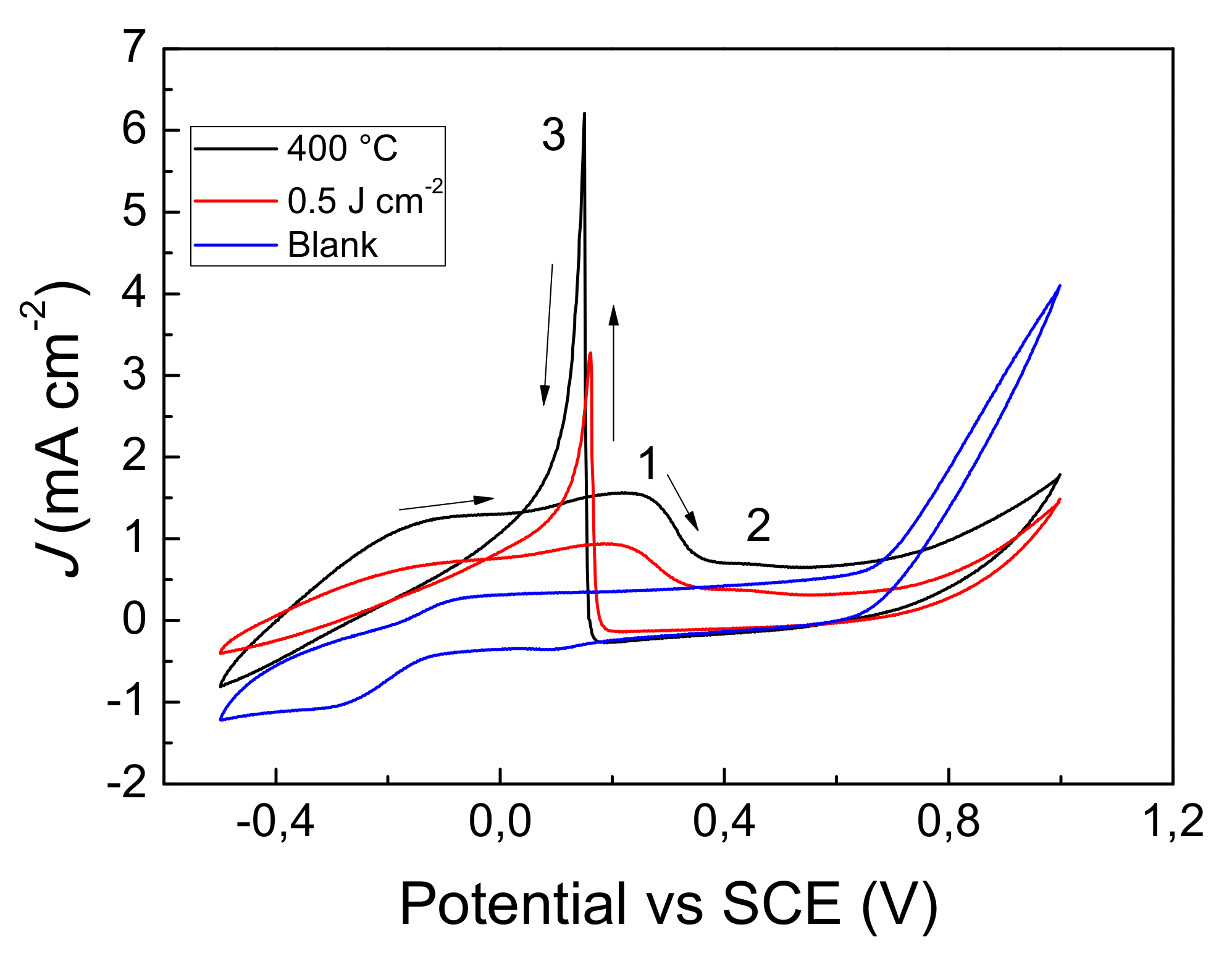
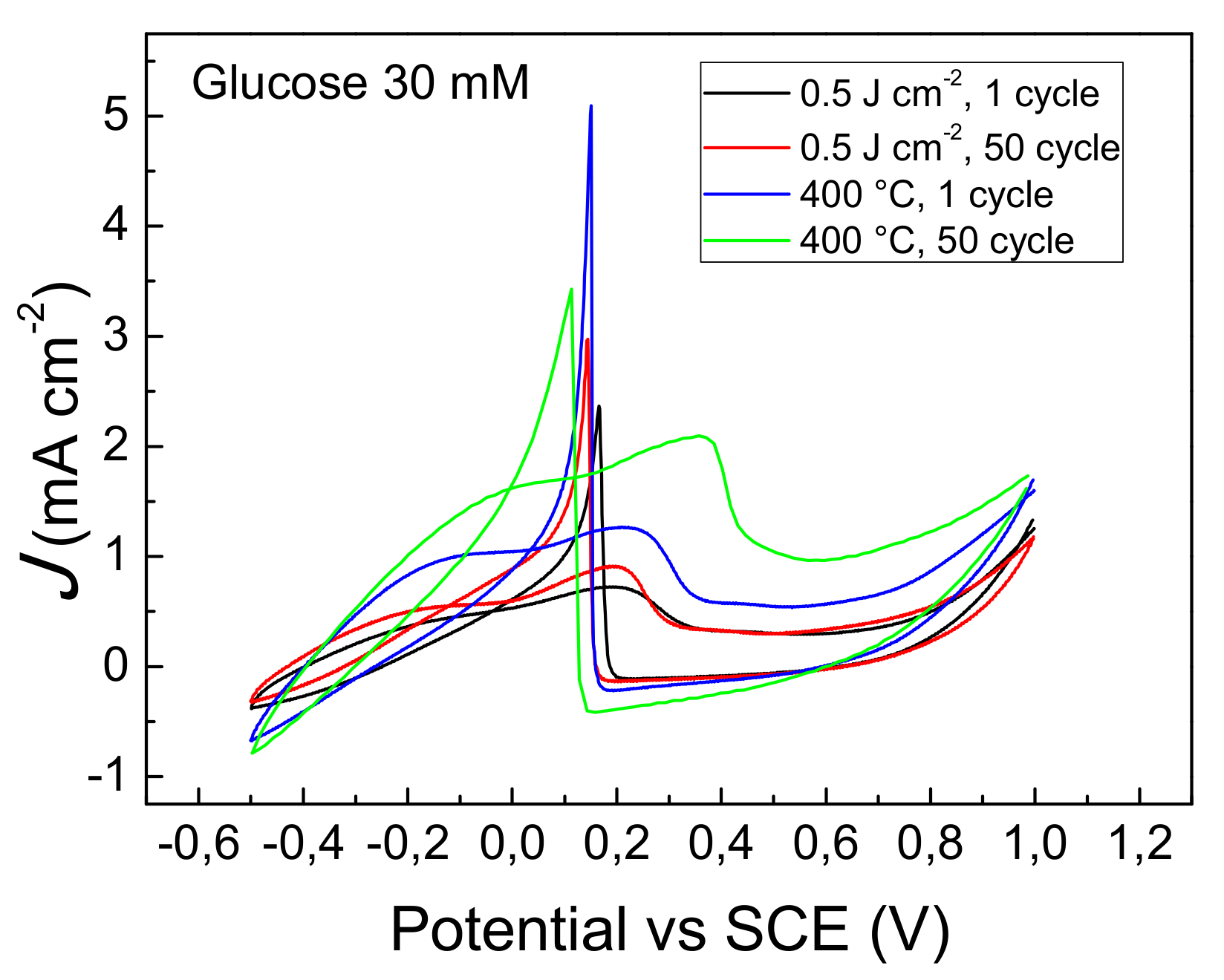
3.5. Glucose Sensing
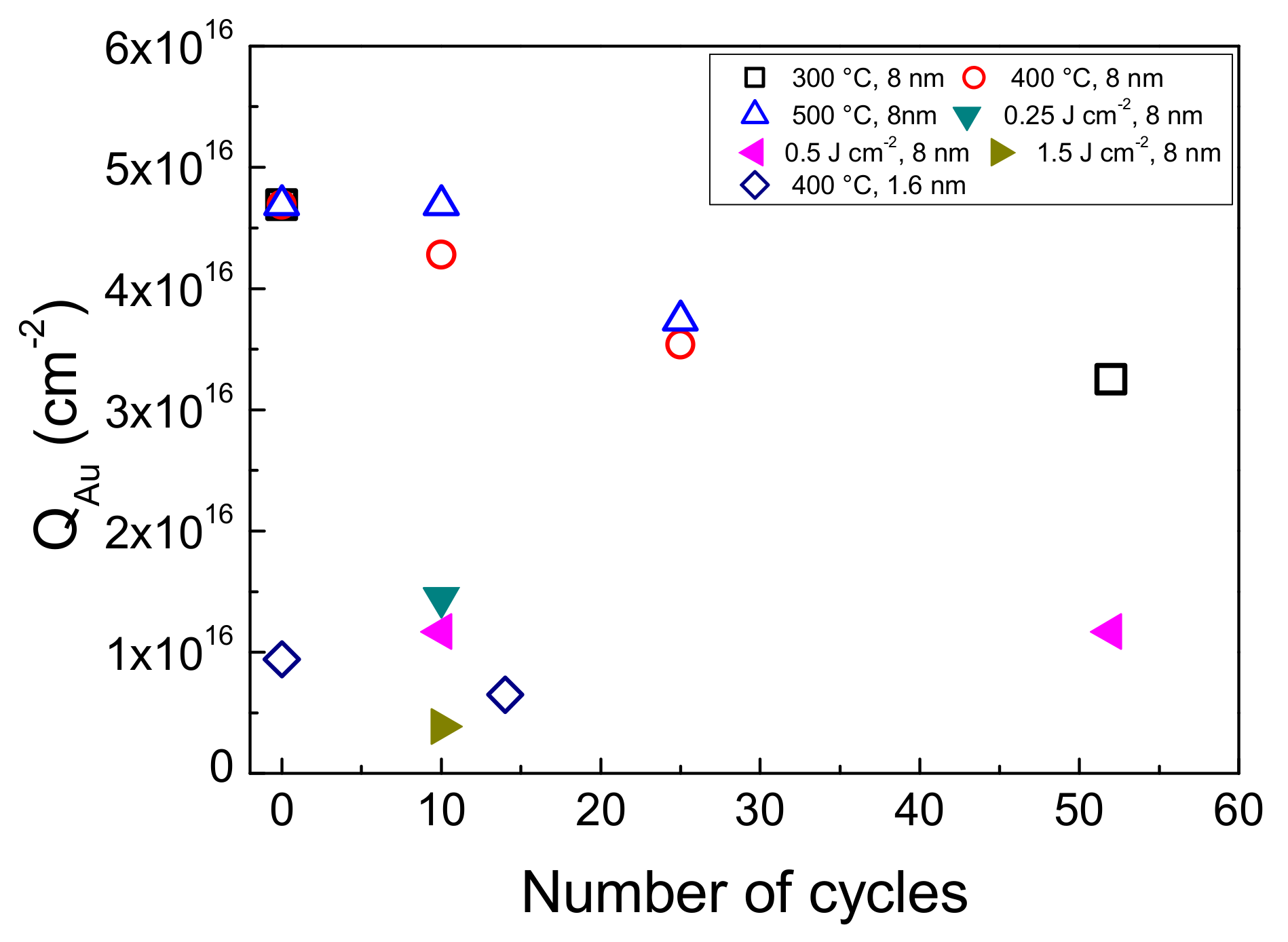
3.6. Electrode Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sciuto, E.L.; Bongiorno, C.; Scandurra, A.; Petralia, S.; Cosentino, T.; Conoci, S.; Sinatra, F.; Libertino, S. Functionalization of bulk SiO2 surface with biomolecules for sensing applications: Structural and functional characterizations. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bülbül, G.; Hayat, A.; Andreescu, S. Portable nanoparticle-based sensors for food safety assessment. Sensors 2015, 15, 30736–30758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Sánchez, M.; Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Tribidasari, T.W.; Ivandini, A.; Honda, Y.; Pino, F.; Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A.; Einaga, Y.; Merkoc, A. Microfluidic platform for environmental contaminants sensing and degradation based on boron-doped diamond electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Cardenas, J.A.; Garcia-Maroto, F.; Alvarez-Bermejo, J.A.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. DNA sequencing sensors: An overview. Sensors 2017, 17, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melmed, S.; Polonsky, K.S.; Larsen, P.R.; Kronenberg, H.M. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, 13th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 978-0-323-29738-7. [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzeisen-Redeker, G.; Staib, A.; Strasser, M.; Müller, U.; Schoemaker, M. Overview of a novel sensor for continuous glucose monitoring. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NKWOOD Research. Available online: www.inkwoodresearch.com (accessed on 18 January 2019).
- Global Blood Glucose Sensor Market Research Report 2018. Marketresearchpro. Available online: https://marketresearchpro.net (accessed on 18 January 2019).
- Aitkenhead, M.J.; Gaskin, G.J.; Lafouge, N.; Hawes, C. Phylis: A low-cost portable visible range spectrometer for soil and plants. Sensors 2017, 17, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, S.; Sreekanth, K.V.; Shang, J.; Yu, T.; Chen, C.; Yin, F.; Baillargeat, D.; Coquet, P.; Ho, H.; Kabashin, A.V.; et al. Graphene–gold metasurface architectures for ultrasensitive plasmonic biosensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6163–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinhold, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Klar, P.J. Modifying graphene’s lattice dynamics by hotelectron injection from single gold nanoparticles. Commun. Phys. 2019, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Sanchez, D.; Villabona-Leal, G.; Saucedo-Orozco, I.; Bracamonte, V.; Perez, E.; Bittencourt, C.; Quintana, M. Stable graphene oxide–gold nanoparticle platforms for biosensing applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.; Work, T.M.; Bushway, A.A.; Bushway, R.J. HPLC determination of fructose, glucose, and sucrose in potatoes. J. Food Sci. 1981, 46, 300–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, D.; Takeoka, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Kataoka, K. Simple and precise preparation of a porous gel for a colorimetric glucose sensor by a templating technique. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 115, 4329–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Nalwa, H.S. (Eds.) Handbook of Electrochemical Nanotechnology; American Scientific Publishers: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2009; ISBN 1-58883-039-X. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.Y.; Liang, F.F.; Tian, H.F.; Hu, J.B. Nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on ITO electrode modified with gold nanoparticles by ion implantation. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 120, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Park, S.J.; Yun, K.S.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, S.H. Enzymeless glucose sensor integrated with chronically implantable nerve cuff electrode for in-situ inflammation monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, S.; Sciuto, E.L.; Messina, M.A.; Scandurra, A.; Mirabella, S.; Priolo, F.; Conoci, S. Miniaturized and multi-purpose electrochemical sensing device based on thin Ni oxides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 263, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekarchizadeh, H.; Kadivar, M.; Ensafi, A.A. Rapid nonenzymatic monitoring of glucose and fructose using a CuO/multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposite-modified glassy carbon electrode. Chin. J. Catal. 2013, 34, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yanga, W.; Chena, L.; Jia, J. Three-dimensional copper foam supported cuo nanowire arrays: An efficient non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 235, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Lemire, C.; Shaikhutdinov, S.K.; Freund, H.J. Surface chemistry of catalysis by gold. Gold Bull. 2004, 37, 72–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juríka, T.; Podešvab, P.; Farka, Z.; Kovár, D.; Skládal, P.; Foret, F. Nanostructured gold deposited in gelatin template applied for electrochemical assay of glucose in serum. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 188, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Wang, P.; Zhou, C.; Xia, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, Z. An ultrasensitive non-enzymatic amperometric glucose sensor basedon a Cu-coated nanoporous gold film involving co-mediating. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.; Koper, M.T.M. Electrocatalysis on gold. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 13583–13594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Toit, H.; Di Lorenzo, M. Electrodeposited highly porous gold microelectrodes for the direct electrocatalytic oxidation of aqueous glucose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hebie, S.; Cornu, L.; Napporn, T.W.; Rousseau, J.; Kokoh, B.K. Insight on the surface structure effect of free gold nanorods on glucose electrooxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 9872–9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Cao, X.W.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, R. Electrochemical oxidation and determination of glucose in alkaline media based on Au (111)-like nanoparticle array on indium tin oxide electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 138, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Shukla, S.K.; Taher, A.; Siwal, S.; Mallick, K. Organic-inorganic hybrid supramolecular assembly: An efficient platform for nonenzymatic glucose sensor. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2852–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Dempsey, E.; Laffir, F. Carbon nanochips and nanotubes decorated PtAuPd-based nanocomposites for glucose sensing: Role of support material and efficient Pt utilisation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 205, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Jiang, S.S.; Zhang, H.Y.; Jiang, J.Q.; Liu, X.Y. A novel non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on Cu nanoparticle modified graphene sheets electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 709, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.H.; Mai, Z.B.; Zou, X.Y.; Cai, P.X.; Mo, J.Y. A novel sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2007, 18, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jin, L.; Xu, W. New approach to fabricate nanoporous gold film. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2007, 18, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawan, S.; Wannapob, R.; Kanatharana, P.; Limbut, W.; Numnuam, A.; Samanman, S.; Thavarungkul, P. One-step porous gold fabricated electrode for electrochemical impedance spectroscopy immunosensor detection. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 111, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Meng, M.W.; Long, T.F.; Wang, H.Q.; Jiang, Z.L. The preparation of nanoporous gold electrodes by electrochemical alloying/dealloying process at room temperature and its properties. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 2296–2298. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.R.; Mitchell, D.T. Template-synthesized nanomaterials in electrochemistry. Electroanal. Chem. 1999, 21, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- McCreery, R.L. Advanced carbon electrode materials for molecular electrochemistry. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2646–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scandurra, A.; Ruffino, F.; Sanzaro, S.; Grimaldi, M.G. Laser and thermal dewetting of gold layer onto graphene paper for non-enzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose and fructose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 127113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, L.; Compagnini, G.; Puglisi, O.; Scandurra, A.; Cataliotti, R.S. Vibrational and photoelectron investigation of amorphous fluorinated carbon films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 17437–17441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziambaras, E.; Kleis, J.; Schröder, E.; Hyldgaard, P. Potassium intercalation in graphite: A van der Waals density-functional study. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 155425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.; Zhai, Y.; Dong, S. Electrochemical sensing and biosensing platform based on chemically reduced graphene oxide. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5603–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, J.E.B. Kinetics of rapid electrode reactions. Part 2.—Rate constants and activation energies of electrode reactions. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1952, 48, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.N. Electrochemistry at Solid Electrodes; Marcel-Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, R.S. Theory and application of cyclic voltammetry for measurement of electrode reaction kinetics. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadara, R.O.; Jenkinson, N.; Banks, C.E. Characterisation of commercially available electrochemical sensing platforms. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cosandey, F.; Persaud, R.; Madey, T.E. Initial, growth and morphology of thin Au films on TiO2 (110). Surf. Sci. 1999, 439, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffino, F.; Torrisi, V.; Grillo, R.; Cacciato, G.; Zimbone, M.; Piccitto, G.; Grimaldi, M.G. Nanoporous Au structures by dealloying Au/Ag thermal- or laser-dewetted bilayers on surfaces. Superlattices Microstruct. 2017, 103, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. (Ed.) Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, D.; Seah, M.P. (Eds.) Practical Surface Analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1990; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Leiro, J.A.; Heinonen, M.H.; Laiho, T.; Batirev, I.G. C ore-level XPS spectra of fullerene, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite, and glassy carbon. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2003, 128, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, V.; Hahn, H.T. Synergistic, effect of fullerene-capped gold nanoparticles on graphene electrochemical supercapacitors. Adv. Nanopart. 2013, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, A.M.; Hunt, A.J.; Budarin, V.L.; Parker, H.L.; Shuttleworth, P.S.; Ellis, G.J.; Clark, J.H. Starch-derived carbonaceous mesoporous materials (Starbon®) for the selective adsorption and recovery of critical metals. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2146–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klyushin, A.Y.; Rocha, T.C.R.; Hävecker, M.; Knop-Gericke, A.; Schlögl, R. A near ambient pressure XPS study of Au oxidation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 7881–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buk, V.; Pemble, M.E. A highly sensitive glucose biosensor based on a micro disk array electrode design modified with carbon quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 298, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branagan, D.; Breslin, C.B. Electrochemical detection of glucose at physiological pH using gold nanoparticles deposited on carbon nanotubes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buk, V.; Pemble, M.E.; Twomey, K. Fabrication and evaluation of a carbon quantum dot/gold nanoparticle nanohybrid material integrated onto planar micro gold electrodes for potential bioelectrochemical sensing applications. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 293, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiyi, L.; Juanjuan, Z.; Zhouping, W.; Zaijuna, L.; Junkang, L.; Zhiguo, G.; Guangli, W. Novel graphene-gold nanohybrid with excellent electrocatalytic performance for the electrochemical detection of glucose. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2015, 208, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


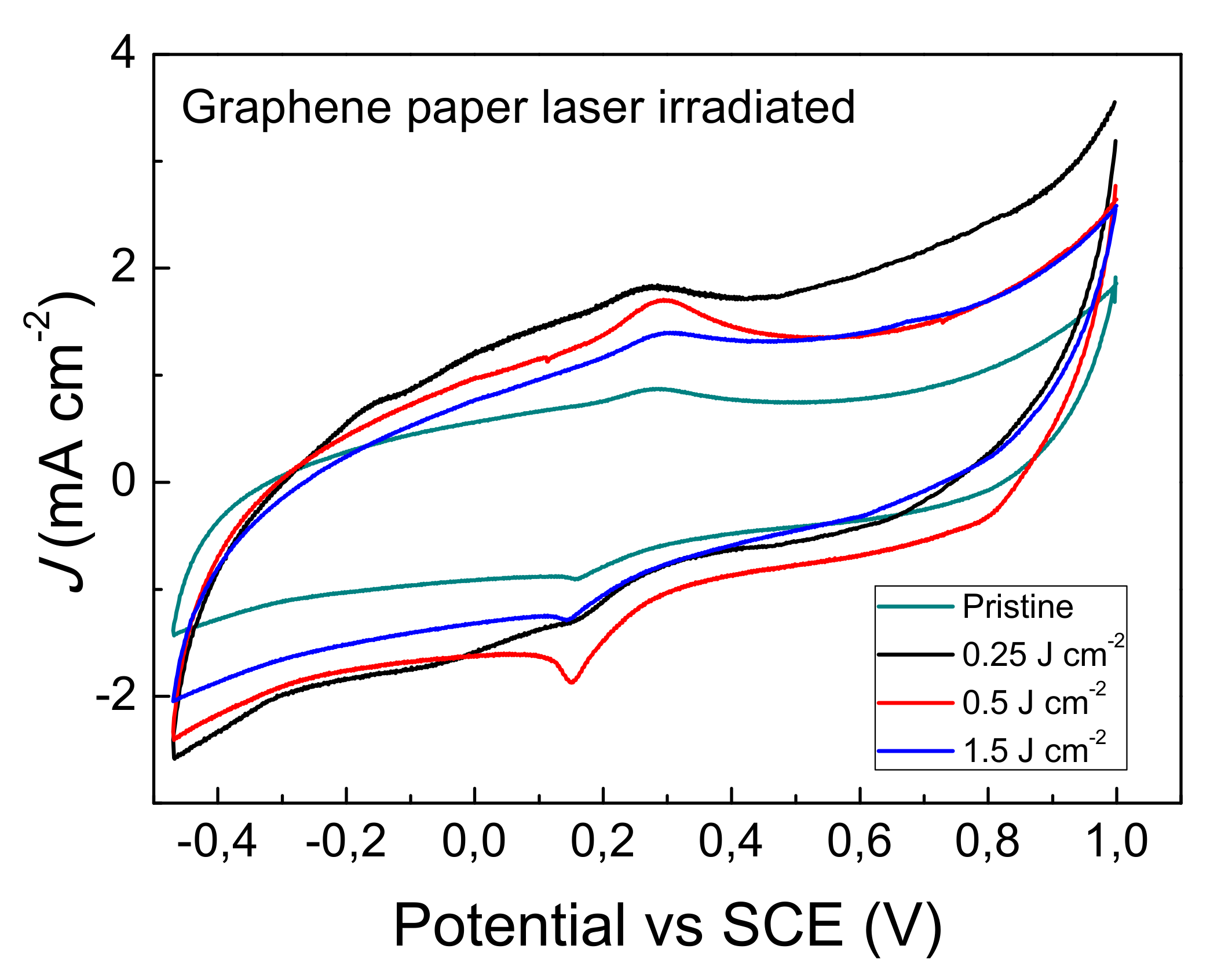



| Sample | Working Area(1) AR-S (cm2) | Areal = AR-S/AGeom | ΔEp = Ea − Ec (mV) | k0 (×10−3) (cm s−1) | C (mF cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine | 0.764 | 1.70 | 84.4 | 4 | 35.3 |
| 0.25 Jcm−2 | 0.477 | 1.91 | 101 | 2 | 69.1 |
| 0.5 Jcm−2 | 0.954 | 3.82 | 128.8 | 1.2 | 60.7 |
| 1.5 Jcm−2 | 0.582 | 2.32 | 134 | 1.1 | 53.3 |
| Sample | Au | C | O |
|---|---|---|---|
| As deposited | 12.3 | 77.4 | 10.3 |
| 400 °C, 1 h, N2 | 5.3 | 67.3 | 27.4 |
| 0.5 Jcm−2 | 3.9 | 86.5 | 9.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scandurra, A.; Ruffino, F.; Censabella, M.; Terrasi, A.; Grimaldi, M.G. Dewetted Gold Nanostructures onto Exfoliated Graphene Paper as High Efficient Glucose Sensor. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121794
Scandurra A, Ruffino F, Censabella M, Terrasi A, Grimaldi MG. Dewetted Gold Nanostructures onto Exfoliated Graphene Paper as High Efficient Glucose Sensor. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(12):1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121794
Chicago/Turabian StyleScandurra, Antonino, Francesco Ruffino, Maria Censabella, Antonio Terrasi, and Maria Grazia Grimaldi. 2019. "Dewetted Gold Nanostructures onto Exfoliated Graphene Paper as High Efficient Glucose Sensor" Nanomaterials 9, no. 12: 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121794
APA StyleScandurra, A., Ruffino, F., Censabella, M., Terrasi, A., & Grimaldi, M. G. (2019). Dewetted Gold Nanostructures onto Exfoliated Graphene Paper as High Efficient Glucose Sensor. Nanomaterials, 9(12), 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121794









