Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Composite Nanofibers Containing Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane–Epigallocatechin Gallate Conjugate for Bone Tissue Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the POSS–EGCG Conjugate
2.3. Fabrication of PVDF Composite Nanofibers
2.4. Characterization of the PVDF Composite Nanofibers
2.5. Cell Proliferation
2.6. Superoxide Anion Radical Scavenging Capacity Assay
2.7. ALP Activity and Bone Mineralization Assay
2.8. Quantification of Inflammatory Cytokine
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of the POSS–EGCG Conjugate
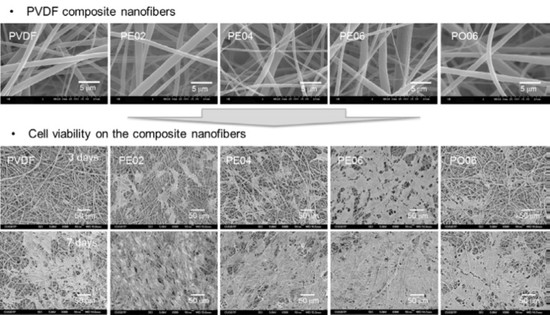
3.2. Fabrication of the PVDF Composite Nanofibers
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of the PVDF Composite Nanofibers
3.4. Cell Proliferation
3.5. ALP Activity and Bone Mineralization
3.6. Quantification of Inflammatory Cytokine
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.; Hwang, H.; Kim, Y.; Jeon, H.; Kim, G. Physical and bioactive properties of multi-layer PCL/silica composite scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 250, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, M.M.; Khorasani, S.N.; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Foroughi, M.R.; Kharaziha, M.; Saadatkish, N.; Ramakrishna, S. Fabrication and characterization of two-layered nanofibrous membrane for guided bone and tissue engineering application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 80, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, C.; Yao, C.; Chung, S.M.; Yao, J.; Lee, I.S.; Kong, X. Silk fibroin membrane used for guided bone tissue regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, R.; Yi, W.; Tao, S.; Wen, Y.; Hongyu, Z. Electrospun PCL/gelatin composite nanofiber structures for effective guided bone regeneration membranes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 324–332. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. Fabrication of novel biomaterials through molecular self-assembly. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Kasuga, T.; Hench, L.L. Preparation of poly(l-lactic acid)-polysiloxane-calcium carbonate hybrid membranes for guided bone regeneration. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, C.; Welland, M.E. Wet-spinning of amyloid protein nanofibers into multifunctional high-performance biofibers. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3453–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, A.; Ito, S.; Iwanaga, N.; Mizuno, T.; Jones, J.R.; Kasuga, T. Poly(γ-glutamic acid)-silica hybrids with fibrous structure: Effect of cation and silica concentration on molecular structure, degradation rate and tensile properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 52491–52499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poologasundarampillai, G.; Wang, D.; Li, S.; Nakamura, J.; Bradley, R.; Lee, P.D.; Stevens, M.M.; McPhail, D.S.; Kasuga, T.; Jones, J.R. Cotton-wool-like bioactive galsses for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3733–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Nakamura, J.; Poologasundarampillai, G.; Kasuga, T.; Jones, J.R.; McPhail, D.S. ToF-SIMS evaluation of calcium-containing silica/γ-PGA hybrid systems for bone regeneration. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 309, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Tominaga, K.; Kidoaki, S. Time-programmed dual release formulation by multilayered drug-loaded nanofiber meshes. J. Control. Release 2010, 143, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moydeen, A.M.; Padusha, M.S.A.; Aboelfetoh, E.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M.H. Fabrication of electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/dextran nanofibers via emulsion process as drug delivery system: Kinetics and in vitro release study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.E.; Skazik, C.; Harwardt, M.; Bartneck, M.; Denecke, B.; Klee, D.; Salber, J.; Zwadlo-Klarwasser, G. Topographical control of human macrophages by a regularly microstructured polyvinylidene fluoride surface. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4056–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Collins, G.; Arinzeh, T.L. Neurite extension of primary neurons on electrospun piezoelectric scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3877–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.C.; Gutiérrez, J.; Barandiarán, J.M. Direct fabrication of a 3D-shape film of polyvinylidende fluoride (PVDF) in the piezoelectric β-phase for sensor and actuator applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.H.; Jaffe, M.; Arinzeh, T.L. Piezoelectric materials for tissue engineering: A review. Acta Biomater. 2015, 24, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, G.G.; Sinibaldi, E.; Ceseracciu, L.; Labardi, M.; Marino, A.; Marras, S.; De Simoni, G.; Mattoli, V.; Ciofani, G. Ultrasound-activated piezoelectric P(VDF-TrFE)/boron nitride nanotube composite films promote differentiation of human SaOS-2 osteoblast-like cells. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Zhou, C. Reversible pH-responsive aggregates based on the self-assembly of functionalized POSS and hyaluronic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.M.; Amna, T.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, H.C.; Hassan, M.S.; Khil, M.S. Novel silicificated PVAc/POSS composite nanofibrous mat via facile electrospinning technique: Potential scaffold for hard tissue engineering. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozga-Wijas, K.; Michalski, A. An efficient synthetic route for a soluble silsesquioxane-daunorubicin conjugate. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 84, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.J.; Bailey, H.H.; Mukhtar, H. Green tea polyphenols for prostate cancer chemoprevention: A translational perspective. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Akhtar, N.; Haqqi, T.M. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate: Inflammation and arthritis. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.N.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): Mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominari, T.; Matsumoto, C.; Watanabe, K.; Hirata, M.; Grundler, F.M.W.; Miyaura, C.; Inada, M. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory bone resorption, and protects against alveolar bone loss in mice. FEBS Open Bio 2015, 5, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroyanagi, G.; Tokuda, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Kainuma, S.; Fujita, K.; Ohguchi, R.; Kawabata, T.; Sakai, G.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Harada, A.; et al. (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate synergistically potentiates prostaglandin E2-stimulated osteoprotegerin synthesis in osteoblast. Prostagladins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 128–129, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.; Deng, J.; Hou, Y.; Xiang, L.; Wu, Y.; Qu, Y.; Man, Y. Application of PEG and EGCG modified collagen-base membrane to promote osteoblasts proliferation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Zha, J.W.; Cui, R.Y.; Fan, B.H.; Yuan, J.K.; Dang, Z.M. Improving dielectric properties of BaTiO3/ferroelectric polymer composites by employing surface hydroxylated BaTiO3 nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendrez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Kool, A.; Bagchi, B.; Hoque, N.A.; Das, S.; Nandy, P. The role of cerium(III)/yttrium(III) nitrate hexahydrate salts on electroactive β phase nucleation and dielectric properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) thin films. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 28487–28496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Shamshirsaz, M.; Latifi, M. Investigation of β phase formation in piezoelectric response of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers: LiCl additive and increasing fibers tension. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.E.; Kim, Y.J. Effects of nanofibrous membranes containing low molecular weight β-glucan on normal and cancer cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 3597–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, I.; Rocha, S.; Pereira, M.C.; Coelho, M.; Rangel, M.; Ivanova, G. NMR structural analysis of epigallocatechin gallate loaded polysaccharide nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, X.Q.; Ren, J.; Zeng, C.M. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) induced intermolecular cross-linking of membrane proteins. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 507, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bors, W.; Michel, C.; Stettmaier, K. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of radical species of proanthocyanidins and gallate esters. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 374, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzonova, I.; Steiner, W.; Znakel, A.; Nyanhongo, G.S.; Guebitz, G.M. Enzymatic synthesis of catechol and hydroxyl-carboxic acid functionalized chitosan microspheres for iron overload therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.S.; Shi, W.X.; Yu, S.L.; Sun, N.; Jin, L.M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Ma, C.; Sun, L.P. Comparative study of anion polyacrylamide (APAM) adsorption-related fouling of a PVDF UF membrane and a modified PVDF UF membrane. Desalination 2012, 286, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, L.; Bon, S.B.; Cardinali, M.; Monticelli, O.; Kenny, J.M. POSS vapor grafting on graphene oxide film. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2012, 537, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Jiang, S.; Song, P.; Song, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, X. Effect of HA-g-PLLA on xanthohumol-loaded PLGA fiber membrane. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.Y.; Cong, P.H.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, T.X.; Huang, S.; Li, T.S. The preparation of PVDF/clay nanocomposites and the investigation of their tribological properties. Wear 2009, 266, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.L.; Yeh, J.K.; Cao, J.J.; Wang, J.S. Green tea and bone metabolism. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouillet, C.; Mazière, J.C.; Mazière, C.; Wattel, A.; Brazier, M.; Kamel, S. Stimulatory effect of naturally occurring flavonols quercetin and kaempferol on alkaline phosphatase activity in MG-63 human osteoblasts through ERK and estrogen receptor pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 67, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vali, B.; Rao, L.G.; El-Sohemy, A. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate increases the formation of mineralized bone nodules by human osteoblast-like cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Sample | Content of POSS–EGCG Conjugate (wt%) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | 0 | 3.5 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 72.6 ± 6.0 |
| PE02 | 2 | 3.6 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 71.3 ± 6.5 |
| PE04 | 4 | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 69.1 ± 7.7 |
| PE06 | 6 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 65.6 ± 7.2 |
| PO06 | 6a | 5.2 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 63.4 ± 8.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, H.-G.; Han, Y.-S.; Jung, K.-H.; Kim, Y.-J. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Composite Nanofibers Containing Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane–Epigallocatechin Gallate Conjugate for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020184
Jeong H-G, Han Y-S, Jung K-H, Kim Y-J. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Composite Nanofibers Containing Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane–Epigallocatechin Gallate Conjugate for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020184
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Hyo-Geun, Yoon-Soo Han, Kyung-Hye Jung, and Young-Jin Kim. 2019. "Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Composite Nanofibers Containing Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane–Epigallocatechin Gallate Conjugate for Bone Tissue Regeneration" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020184
APA StyleJeong, H.-G., Han, Y.-S., Jung, K.-H., & Kim, Y.-J. (2019). Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Composite Nanofibers Containing Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane–Epigallocatechin Gallate Conjugate for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020184