NiS2@MoS2 Nanospheres Anchored on Reduced Graphene Oxide: A Novel Ternary Heterostructure with Enhanced Electromagnetic Absorption Property
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of NiS2 Nanospheres
2.3. Synthesis of NiS2@MoS2/rGO Composites
2.4. Characterization and Measurement
2.5. EM Absorption Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
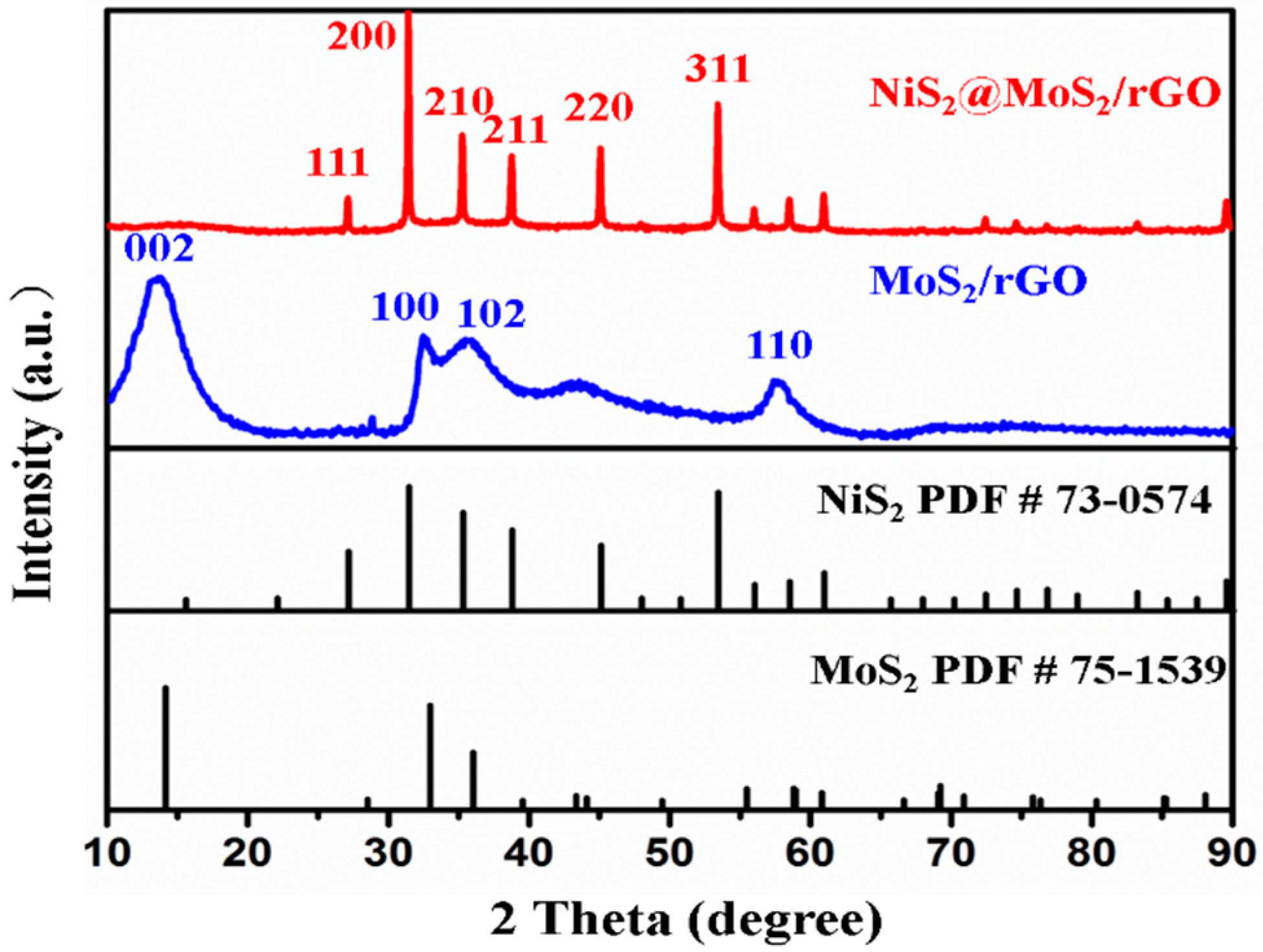
3.1. Characterization of Samples
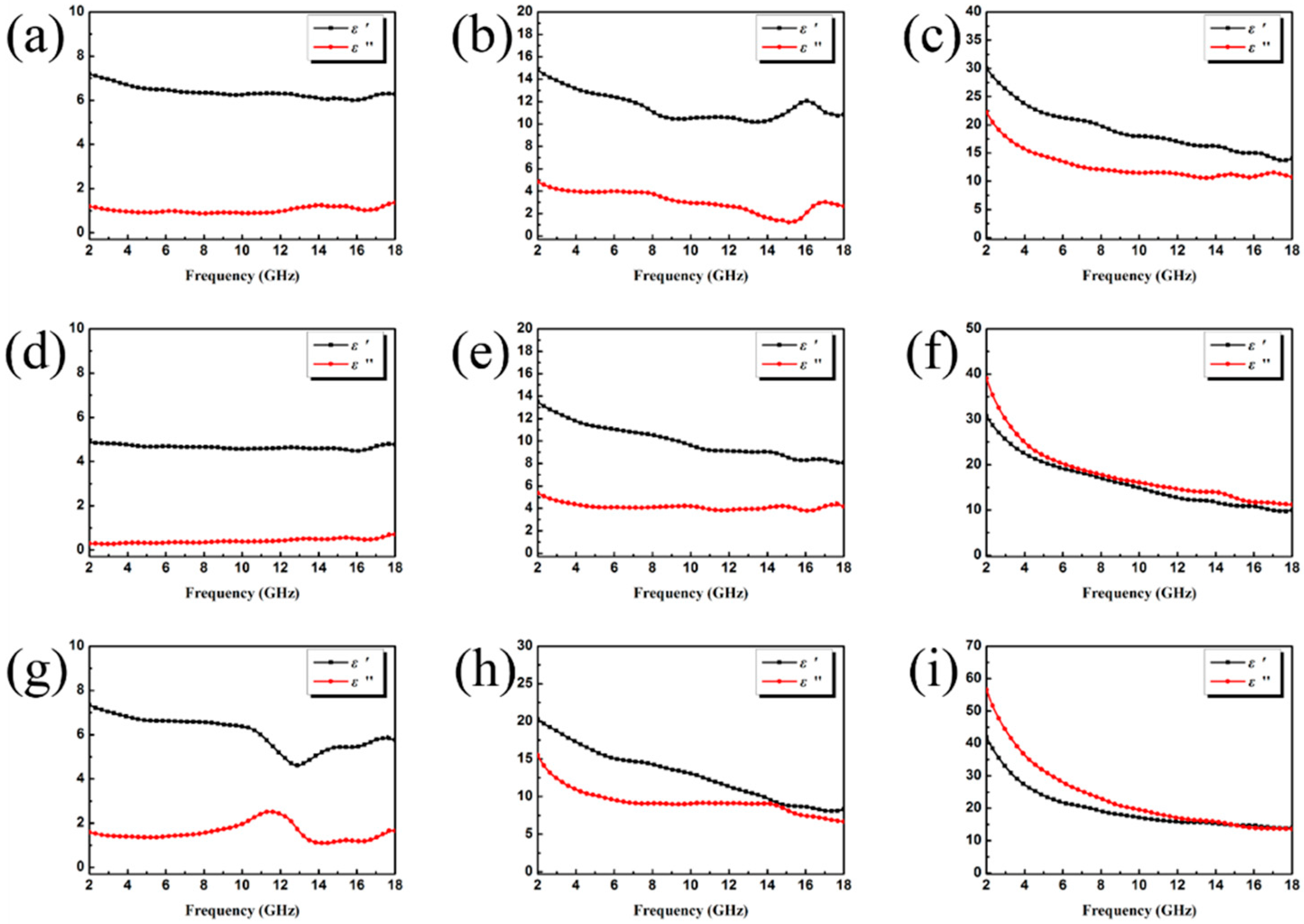
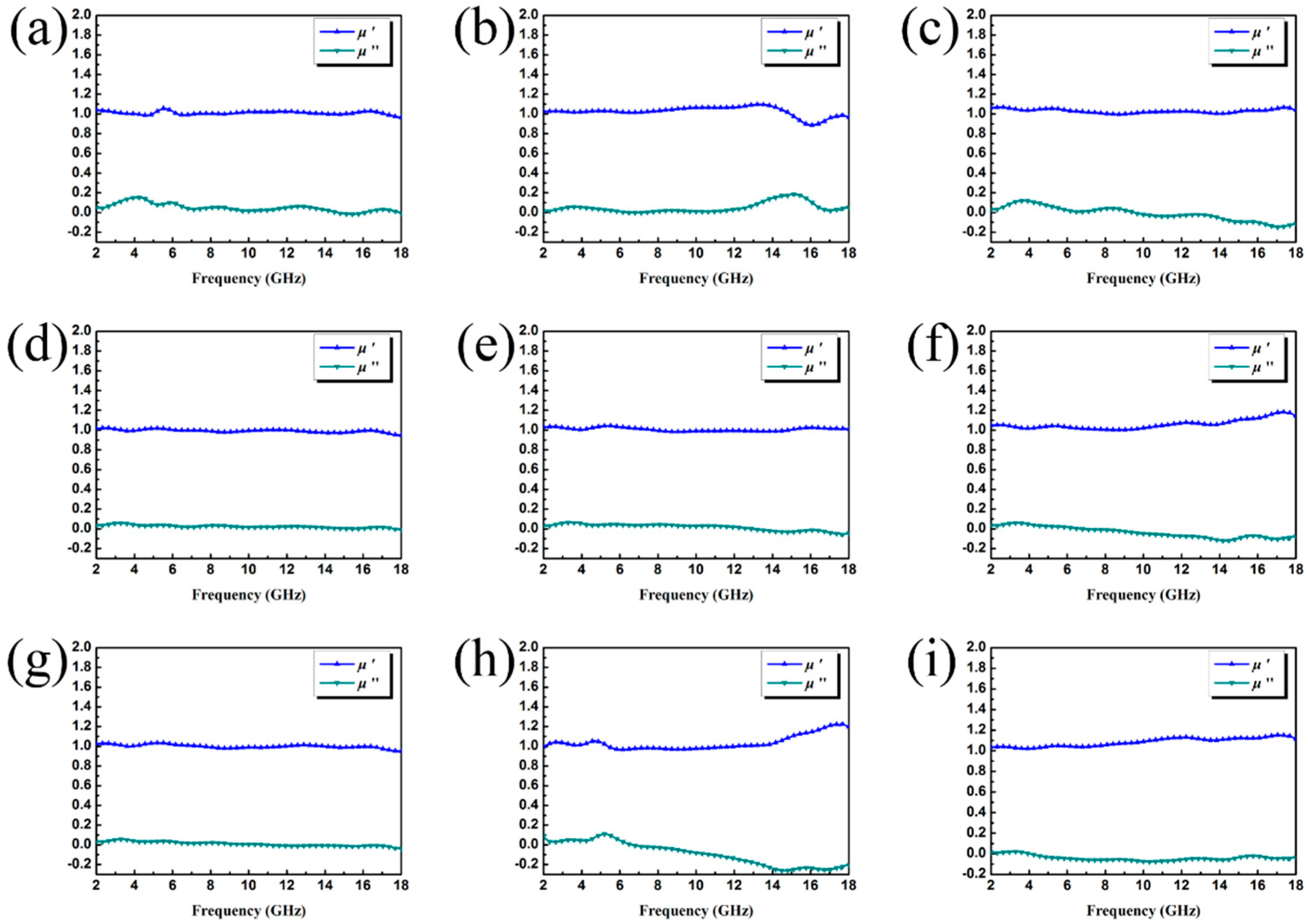
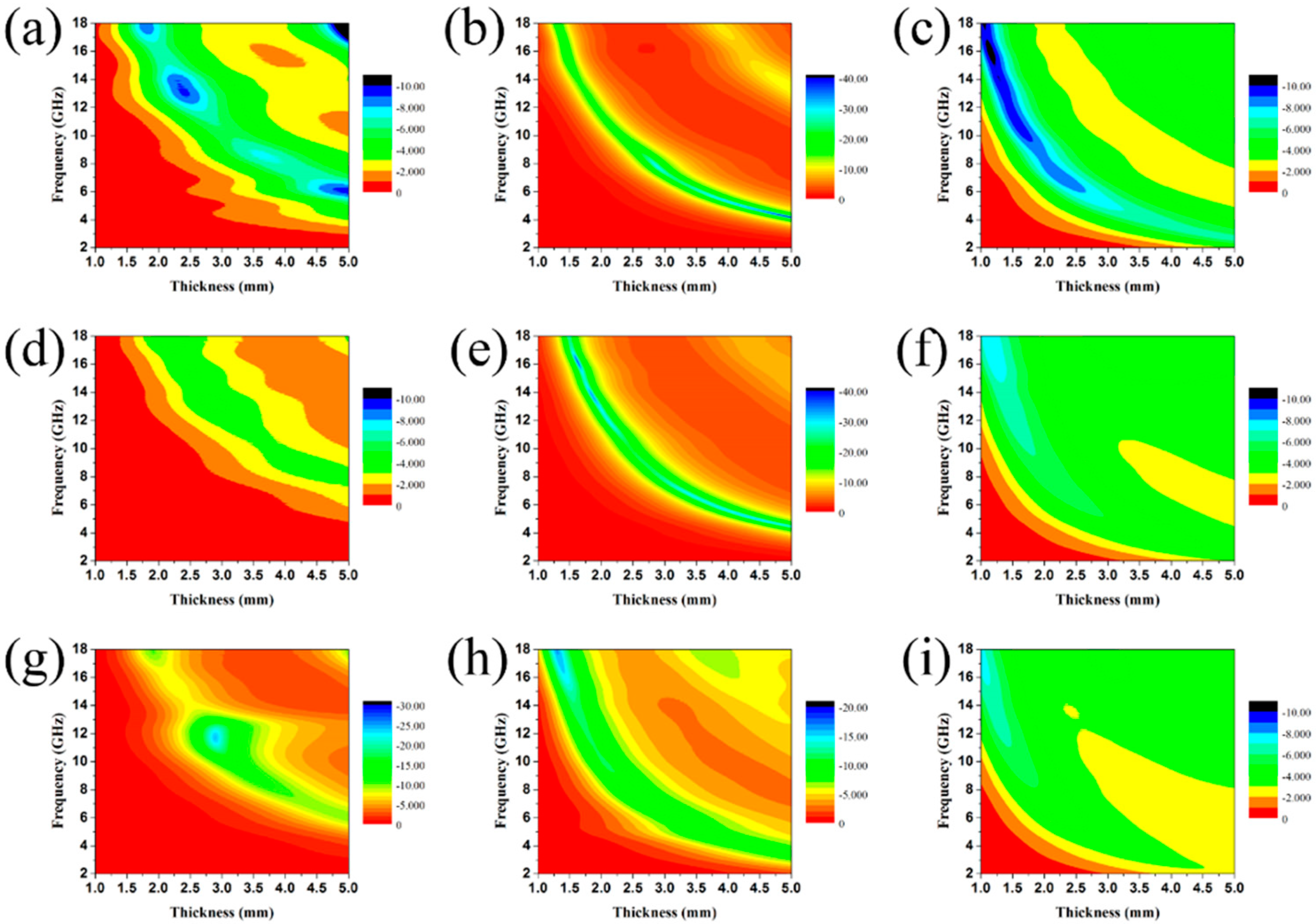
3.2. Electromagnetic Absorption Property
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, X.; Lv, X.; Sui, M.; Weng, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Decorating mof-derived nanoporous co/c in chain-like polypyrrole (ppy) aerogel: A lightweight material with excellent electromagnetic absorption. Materials 2018, 11, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, M.; Lü, X.; Xie, A.; Xu, W.; Rong, X.; Wu, G. The synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) polydopamine-functioned carbonyl iron powder@polypyrrole (cip@ppy) aerogel composites for excellent microwave absorption. Synth. Met. 2015, 210, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Weng, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, X.; Gu, G. Synthesis of Fe3O4/polypyrrole/polyaniline nanocomposites by in-situ method and their electromagnetic absorbing properties. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Sun, M.; Zhang, K.; Wu, F.; Xie, A.; Wang, M. Three-dimensional (3D) α-Fe2O3/polypyrrole (ppy) nanocomposite for effective electromagnetic absorption. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 065021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Sun, M.; Zhang, K.; Dai, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, D.; Xie, A.; Wu, F. Using γ-Fe2O3 to tune the electromagnetic properties of three-dimensional (3D) polypyrrole (ppy) and its broadband electromagnetic absorber. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68128–68133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yang, Q.; Liao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Fu, Y. A novel 3D silver nanowires@polypyrrole sponge loaded with water giving excellent microwave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yuan, X.; Li, L.; Song, Q.; Lv, X.; Gu, G.; Sui, M. Hollow cube-like cus derived from Cu2O crystals for the highly efficient elimination of electromagnetic pollution. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 6735–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Zhang, C.; Oyler, N.A.; Chen, X. Hydrogenated TiO2 nanocrystals: A novel microwave absorbing material. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6905–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Li, D.; Jiang, L.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Y.; An, J.; Ren, W.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; et al. Interface transformation for enhanced microwave-absorption properties of core double-shell nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 694, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, A.; Saeed, A.; Iqbal, S.; Shoaib, M.; Ahmad, I.; ur Rahman, M.S.; Bashir, M.I.; Yaseen, M.; Hussain, W. Morphological and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 nanoferrite: A promising microwave absorbing material. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 7346–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, D. Microwave absorbing property of a hybrid absorbent with carbonyl irons coating on the graphite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Ruan, X.; Yan, J.; Yun, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y. Enhanced radar and infrared compatible stealth properties in hierarchical SnO2@ZnO nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 3443–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sui, M.; Cui, G.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Lv, X.; Wu, F.; Gu, G. Fe3O4 nanoparticles decorated on a cus platelet-based sphere: A popcorn chicken-like heterostructure as an ideal material against electromagnetic pollution. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17489–17496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, A.; Sun, M.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, W.; Wu, F.; He, M. In situ growth of MoS2 nanosheets on reduced graphene oxide (rgo) surfaces: Interfacial enhancement of absorbing performance against electromagnetic pollution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2016, 18, 24931–24936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, A.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Tian, X. Novel rGO/α-Fe2O3 composite hydrogel: Synthesis, characterization and high performance of electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yin, X.; Han, M.; Li, X.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide foam modified with ZnO nanowires for enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 2017, 116, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Mou, Z.; Lu, G.; Chen, N.; Dong, Z.; Hu, M.; Qu, L. 3D graphene-Fe3O4 nanocomposites with high-performance microwave absorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2013, 15, 13038–13043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Murugadoss, V.; Kong, J.; He, Z.; Mai, X.; Shao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, C.; Angaiah, S.; et al. Overview of carbon nanostructures and nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave shielding. Carbon 2018, 140, 696–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M. Synthesis of graphene/thorns-like polyaniline/alpha-Fe2O3@SiO2 nanocomposites for lightweight and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; He, J.; Li, G.; Tang, J.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Xue, H. Laminated magnetic graphene with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ma, L.; Tian, N.; Gan, M.; Xu, F.; Zeng, J.; Tu, Y. Synthesis and electromagnetic properties of pani/pvp/cip core–shell composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2014, 186, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.F.R.; Costa, T.P.; Bini, R.A.; Faria, F.S.E.D.V.; Azevedo, R.B.; Jafelicci, M.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Martínez, M.A.R.; Mantilla, J.C.; Marques, R.F.C.; et al. Surface functionalization of magnetite nanoparticle: A new approach using condensation of alkoxysilanes. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2017, 521, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cao, Q.; Bi, H.; Liang, C.; Yuan, K.; She, W.; Yang, Y.; Che, R. CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Che, R.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z. Hierarchical Fe3O4@TiO2 yolk-shell microspheres with enhanced microwave-absorption properties. Chemistry 2013, 19, 6746–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Shao, G.; Fan, B.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, R. Investigation of the electromagnetic absorption properties of Ni@TiO2 and Ni@SiO2 composite microspheres with core-shell structure. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2015, 17, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Shao, G.; Fan, B.; Zhao, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, R. Facile preparation and enhanced microwave absorption properties of core-shell composite spheres composited of Ni cores and TiO2 shells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2015, 17, 8802–8810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.H.; Asadnia, A. Synthesis, characterization, and microwave-absorbing properties of polypyrrole/MnFe2O4 nanocomposite. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 198973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Yin, X.; Ren, S.; Duan, W.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L. Core/shell structured C/ZnO nanoparticles composites for effective electromagnetic wave absorption. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 6467–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Xi, K.; Cao, Q.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Du, Y. Excellent microwave absorption property of graphene-coated Fe nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, B.; Liang, X.; Xu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Ji, G.; Du, Y. A permittivity regulating strategy to achieve high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers with compatibility of impedance matching and energy conservation. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Song, S.; Zhang, H. Hydrothermal synthetic strategies of inorganic semiconducting nanostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5714–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Bao, Q.; Tang, L.A.L.; Zhong, Y.; Loh, K.P. Hydrothermal dehydration for the “green” reduction of exfoliated graphene oxide to graphene and demonstration of tunable optical limiting properties. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 2950–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, E. Electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution using the MS2@MoS2/rGO (M = Fe or Ni) hybrid catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11795–11798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-J.; Wang, S.-W.; Wang, G.-S.; Li, Z.; Guo, A.-P.; Zhu, J.-Q.; Liu, D.-P.; Yin, P.-G. Facile synthesis of NiS2@MoS2 core–shell nanospheres for effective enhancement in microwave absorption. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 22454–22460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, P.; Tong, T.; Fan, K.; Yu, J. In situ fabrication of Ni–Mo bimetal sulfide hybrid as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution over a wide ph range. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6179–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Qu, F.; Liu, Z.; Du, G.; Asiri, A.M.; Yao, Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, X. A self-supported NiMoS4 nanoarray as an efficient 3D cathode for the alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16585–16589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Lan, D.; Lin, K.; Qin, M.; Kou, K.; Wu, G.; Wu, H. Progress in low-frequency microwave absorbing materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 17122–17136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Samples | rGO (mg) | NiS2 (mg) | (NH4)6Mo7O24·2H2O (mg) | CH4N2S (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample A | 50 | 50 | 39 | 105 |
| Sample B | 50 | 100 | 39 | 105 |
| Sample C | 50 | 100 | 78 | 210 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Lv, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Sui, M.; Liu, H.; Sun, X. NiS2@MoS2 Nanospheres Anchored on Reduced Graphene Oxide: A Novel Ternary Heterostructure with Enhanced Electromagnetic Absorption Property. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020292
Zhang Z, Lv X, Chen Y, Zhang P, Sui M, Liu H, Sun X. NiS2@MoS2 Nanospheres Anchored on Reduced Graphene Oxide: A Novel Ternary Heterostructure with Enhanced Electromagnetic Absorption Property. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020292
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhi, Xuliang Lv, Yiwang Chen, Pin Zhang, Mingxu Sui, Hui Liu, and Xiaodong Sun. 2019. "NiS2@MoS2 Nanospheres Anchored on Reduced Graphene Oxide: A Novel Ternary Heterostructure with Enhanced Electromagnetic Absorption Property" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020292
APA StyleZhang, Z., Lv, X., Chen, Y., Zhang, P., Sui, M., Liu, H., & Sun, X. (2019). NiS2@MoS2 Nanospheres Anchored on Reduced Graphene Oxide: A Novel Ternary Heterostructure with Enhanced Electromagnetic Absorption Property. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020292





