A Novel Fluorescence and SPE Adsorption Nanomaterials of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Quantum Dot-Grafted Covalent Organic Frameworks for the High Selectivity and Sensitivity Detection of Ferulic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Preparation of MIPs Based on QD-Grafted COFs
2.4. Fluorescence Analysis of MIPs Based on QD-Grafted COFs
2.5. Procedures for SPE Enrichment Coupled with HPLC
3. Results
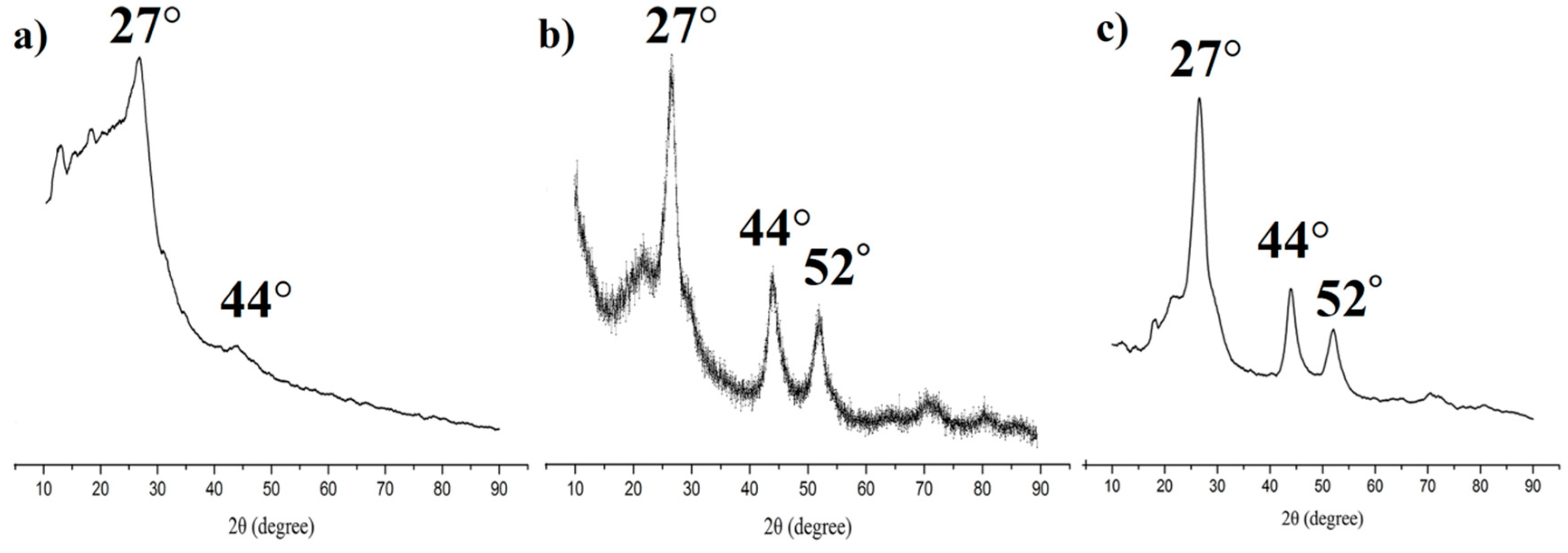
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the MIPs Based on QD-Grafted COFs
3.2. Fluorescent Properties of MIPs Based on QD-Grafted COFs
3.3. Adsorption Properties
3.3.1. Adsorption Time of MIPs Based on QD-Grafted COFs for FA Molecules
3.3.2. Selectivity of the MIPs Based on QD-Grafted COFs
3.4. The Standard Curve and the Detection Limit of MIPs Based on QD-Grafted COFs
3.5. FA Detection in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, X. An essay on synthetic chemistry of colloidal nanocrystals. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 425–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ji, X.; Lü, C.; Yang, B.; Gao, M. From water-soluble CdTe nanocrystals to fluorescent nanocrystal–polymer transparent composites using polymerizable surfactants. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Niu, Y.; Cao, H.; Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, X. Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature 2014, 515, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susha, A.S.; Javier, A.M.; Parak, W.J.; Rogach, A.L. Luminescent CdTe nanocrystals as ion probes and pH sensors in aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 281, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Shi, H.; Huang, J.; Huo, X. Fluorescent nanoparticles for chemical and biological sensing. Sci. China Chem. 2011, 54, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; He, X.-W.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Composite of CdTe quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer as a sensing material for cytochrome c. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2553–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Huy, B.; Seo, M.-H.; Zhang, X.; Lee, Y.-I. Selective optosensing of clenbuterol and melamine using molecularly imprinted polymer-capped CdTe quantum dots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Geng, W.; Wang, Y. A dual-function molecularly imprinted optopolymer based on quantum dots-grafted covalent-organic frameworks for the sensitive detection of tyramine in fermented meat products. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ni, T.; Mu, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, B. Sensitive detection of pyrraline with a molecularly imprinted sensor based on metal-organic frameworks and quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-P.; Li, Y.-K.; Chen, T.-M. A highly sensitive system for urea detection by using CdSe/ZnS core-shell quantum dots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1835–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Han, C. Sonochemical synthesis of cyclodextrin-coated quantum dots for optical detection of pollutant phenols in water. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6053–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, K.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. A novel quantum dots-labeled on the surface of molecularly imprinted polymer for turn-off optosensing of dicyandiamide in dairy products. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côté, A.P.; Benin, A.I.; Ockwig, N.W.; Keeffe, M.; Matzger, A.J.; Yaghi, O.M. Porous, crystalline, covalent organic frameworks. Science 2005, 310, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, H.; Mu, Y.; Liu, X. A robust and luminescent covalent organic framework as a highly sensitive and selective sensor for the detection of Cu2+ ions. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 6613–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, P.J.; Gándara, F.; Yaghi, O.M. Chemistry of covalent organic frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 3053–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.-Y.; Wang, W. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs): From design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 548–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandambeth, S.; Biswal, B.P.; Chaudhari, H.D.; Rout, K.C.; Kunjattu, H.S.; Mitra, S.; Karak, S.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Kharul, U.K.; et al. Selective molecular sieving in self-standing porous covalent-organic-framework membranes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Xu, F.; Sun, B.; Fu, R.; He, H.; Matyjaszewski, K. Design and preparation of porous polymers. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3959–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Bonde, S.J.; Kamra, T.; Bülow, L.; Leo, J.C.; Linke, D.; Ye, L. Bacterial imprinting at pickering emulsion interfaces. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10687–10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Ma, T.; Lu, X.; Li, J. Ultrasensitive detection of clenbuterol by a covalent imprinted polymer as a biomimetic antibody. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Lan, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Wei, L.; Gao, Z.; Li, J. Determination of clenbuterol in pork and potable water samples by molecularly imprinted polymer through the use of covalent imprinting method. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, M.; Sudheer, A.R.; Menon, V.P. Ferulic acid: Therapeutic potential through its antioxidant property. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2007, 40, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaniak, A.; Szelag, M.; Molski, M. Theoretical investigation of stereochemistry and solvent influence on antioxidant activity of ferulic acid. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2013, 1012, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.; Flores, J.; Cruz, A.S.; Leyva-Gómez, G.; Krötzsch, E. Controlled release of ferulic acid from a hybrid hydrotalcite and its application as an antioxidant for human fibroblasts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 181, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.Y.; Champagne, E.T. Ferulic acid enhances IgE binding to peanut allergens in Western blots. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1639–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarbossa, A.; Monti, S.; Lenci, F.; Bramanti, E.; Bizzarri, R.; Barone, V. The effects of ferulic acid on β-amyloid fibrillar structures investigated through experimental and computational techniques. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 2924–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, T.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, B. Grafting of quantum dots on covalent organic frameworks via a reverse microemulsion for highly selective and sensitive protein optosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 269, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fang, G.; Wang, S. Molecularly imprinted optosensing material based on hydrophobic CdSe quantum dots via a reverse microemulsion for specific recognition of ractopamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| The samples | Fluorescence method | SPE-HPLC/MS method | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (mg kg−1) | RSD (%) | Content (mg kg−1) | RSD (%) | |
| Highland barley bran | 3.10 ± 0.12 | 3.87% | 3.11 ± 0.09 | 2.89% |
| Wheat bran | 1.64 ± 0.04 | 2.44% | 1.63 ± 0.03 | 1.84% |
| Corn silk | 2.33 ± 0.06 | 2.58% | 2.33 ± 0.04 | 1.72% |
| Vinasse | 1.67 ± 0.08 | 4.79% | 1.66 ± 0.03 | 1.81% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. A Novel Fluorescence and SPE Adsorption Nanomaterials of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Quantum Dot-Grafted Covalent Organic Frameworks for the High Selectivity and Sensitivity Detection of Ferulic Acid. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020305
Wang Y, Wang Y, Liu H. A Novel Fluorescence and SPE Adsorption Nanomaterials of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Quantum Dot-Grafted Covalent Organic Frameworks for the High Selectivity and Sensitivity Detection of Ferulic Acid. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020305
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu, Yuzhen Wang, and Huilin Liu. 2019. "A Novel Fluorescence and SPE Adsorption Nanomaterials of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Quantum Dot-Grafted Covalent Organic Frameworks for the High Selectivity and Sensitivity Detection of Ferulic Acid" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020305
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, Y., & Liu, H. (2019). A Novel Fluorescence and SPE Adsorption Nanomaterials of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Quantum Dot-Grafted Covalent Organic Frameworks for the High Selectivity and Sensitivity Detection of Ferulic Acid. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020305





