Abstract
Catalytic electrodes were prepared via carbonization of MIL-53(Fe) on the surface of porous carbon felt electrodes (CF) for use in wastewater treatment by the heterogeneous electro-Fenton (EF) process. The best results were obtained when the carbon felt was pretreated with nitric acid, enhancing the affinity of the MIL-53(Fe) for the surface. Following a series of optimization experiments, carbonization conditions of 800 °C for 5 h were used to form Fe-nanoporous carbon (MOFs@CF). The as-prepared electrodes were used as both cathode and heterogeneous catalyst in the EF process for the mineralization of exemplar dye Acid Orange 7 (AO7). Total organic carbon (TOC) removal of 46.1% was obtained within 8 h of electrolysis at around neutral pH (6.5) and the electrode retained over 80% of its original efficiency over five treatment cycles.
1. Introduction
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have been widely investigated for the removal of recalcitrant organic pollutants from wastewater [1,2]. Among them, the electro-Fenton (EF) process is considered as a promising technology for the treatment of contaminated industrial wastewater, a vital issue in both the developing and developed world [3]. Acid Orange 7 (AO7) is a typical example of azo dyes, characterized by the presence of the azo group (-N=N-), which are mainly used in the textile industry [4]. Azo dyes constitute the largest group of synthetic colorants used worldwide, making up around 70% of the mass of all dyestuffs [5]. When exposed into the environment via textile wastewater, they cause a threat to the aquatic medium because of their persistence and toxicity.
The EF process treats contaminated wastewater using classical Fenton’s reaction chemistry in which in situ hydroxyl radicals (OH) are produced via the Fenton’s reaction (Equation (1)) [6,7,8].
H2O2 + Fe2+ → Fe3+ + •OH + OH−
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is formed at the cathode by reduction of the dissolved oxygen (Equation (2)).
O2 + 2H+ + 2e− → H2O2
After that, the organic pollutants (RH) are destroyed by the attack of •OH radicals, according to Equation (3) [9].
•OH + RH → R + H2O
In this process, Fe2+ ions can be regenerated electrochemically by Fe3+ reduction (Equation (4)):
Fe3+ + e− → Fe2+
The application of EF technology to the treatment of AO7 in aqueous solutions was found to mineralize 92% of the dye [10]. The optimal applied current for AO7 decomposition was 300 mA, and the Fe3+ catalyst concentration was 0.1 mM in the solution. A mineralization reaction pathway of AO7 and solution toxicity during the treatment by EF degradation was also studied [10]. The mineralization led to the detoxification of treated AO7 solution at the end of the electrolysis step, proving the environmentally friendly ability of EF technology.
A remaining drawback to the application of EF technology is the requirement for relatively high concentrations of iron (0.1 to 0.2 mM) [11,12] to be added to the wastewater, which essentially results in exchanging one contaminant for another (i.e., replacing organic dyes with iron). In fact, applying a homogeneous EF process often results in the loss of soluble iron catalyst, thus requiring additional post-treatment operations prior to discharge. One approach to limiting the amount of iron released into solution is to use heterogeneous catalysts (instead of soluble iron salts) [13,14,15]. Previous strategies have used clay doped with iron sulfate or pyrite to treat a variety of contaminants. Similarly, heterogeneous catalysts such as iron alginate gel beads, core-shell nanoparticles [16], Fe2O3 modified kaolin, γ-FeOOH, and pyrrhotite were also investigated. These materials retain the iron on their surface or slowly release the iron into solution over time—prolonging the lifetime of the catalyst. Many of these experiments have been performed at strongly acidic pH (2 or 3), and it would be more convenient to perform water treatment at a pH closer to that of natural water. In addition, AOPs based on persulfates [17,18] have been used to treat refinery effluents under alkaline pH [19].
Another emerging iron source is provided by metal organic frameworks (MOFs). These materials have a periodic arrangement of metal nodes and the coordinating ligands can be chosen to affect the accessibility and oxidation level of iron atoms. Recent article catalogue the application of MOFs to the EF reaction [20]. These results show that MOFs have a good retention of performance over multiple (ca. 3–5) EF cycles and offer minimal leaching of iron into solutions. In most cases, the experiments are performed at pH 3–5, with only few studies exploring the pH values expected to be encountered during realistic operation with natural water (6.5–7.5) [20,21,22,23].
Of particular interest to our research group was solving the problem of particle agglomeration and investigating strategies to minimize iron leaching into the solution. We have recently explored methods to alter cheap carbon felt electrodes in order to optimize their performance in the EF process and avoid the introduction of particles to solution—avoiding any occurrence of particle agglomeration [24,25]. Immobilizing the catalyst on the carbon felt surface has little impact on performance, since most of the reaction occurs at the solid-liquid interface [26]. However, in a lab setting, the immobilized electrode does impact the reaction rate due to limited mass transport and long mixing times. Our research group has already explored the carbonization of carbon felt electrodes covered with CoFe Layered Double Hydroxides (LDH) [13]. The material provided good kinetics for the removal of AO7 from solution at pH 6.5, along with the ability to survive multiple cycles and achieve TOC removals of ca. 25% over 8 h. Furthermore, there was no appearance of iron oxide nanoparticles or agglomerates during the treatment. The improved results were attributed to a combination of: (i) large accessible pore volume, (ii) increased H2O2 production due to higher accessible surface area, and iii) surface catalyzed reactions—expanding the effective pH operating window.
In the present study, we explored the performance and stability of a carbon felt electrode modified with carbonized MIL-53(Fe), (MOF@CF). We explored the effect of varying thermal treatment temperature and MIL-53(Fe) loadings on the efficacy of the carbonized MOF@CF electrodes for removing AO7 from aqueous solution. We demonstrated that these materials can effectively mineralize AO7 around neutral pH (6.5) and retain over 80% of original efficiency over five treatment cycles. These results indicate that deriving modified electrodes from carbonized MOFs represents a promising approach, overcoming the disadvantages of homogeneous EF process, and thus contributing to the development of promising economical, efficient, and environmentally friendly technology in the area of biorefractory pollutant treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Carbon felt was obtained from Alfa Aesar (A Johnson Matthey Company, 67300 Schiltigheim, France). The pretreated carbon felt was denoted as raw CF. AO7 (Orange II sodium salt), sodium sulfate (anhydrous, ≥99%), concentrated nitric acid, terephthalic acid (98%), iron (II) sulphate hepta-hydrate (99%), and DMF (99.8%) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (38070 Saint-Quentin-Fallavier, France) and used without any further purification.
2.2. Equipment
The morphologies of the samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Hitachi S-4800, Tokyo, Japan). X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to assess the crystallinity of the prepared materials. In addition, other analysis methods such as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) (ESCALAB 250 Thermal Electron, Waltham, MA, USA) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), were applied to study the Fe-porous carbon. The N2 sorption-desorption isotherms were measured with Micromeritics ASAP 2010 equipment (Norcross, GA, USA, outgassing conditions: 200 °C-12 h).
2.3. Preparation of Carbonized MIL-53(Fe) Electrodes
The commercial CFs were cut with dimensions of 2.0 cm × 1.0 cm × 1.27 cm. They were cleaned either only in ethanol or pretreated first in concentrated nitric acid and then rinsed with deionized water before drying at 60 °C for 24 h. To grow MIL-53(Fe) on the CF surface, a mixture of FeCl3∙6H2O (2.155 g, 7.97 mmol) was dissolved in DMF (150 mL) with terephthalic acid (1.322 g, 7.96 mmol). The mixture was stirred until full dissolution was achieved. Aliquots of the solution (ca. 20–30 mL) were poured into Teflon-lined solvothermal pressure vessels. The pretreated CF was added, and the pressure vessels were sealed and then heated to 150 °C for 18 h. The treated CF was then removed from the pressure vessel and gently washed with methanol until the washing solution became clear. The treated CF was then dried in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h.
The modified carbon felt MIL-53(Fe)@CF was then carbonized in an oven under flowing N2 (200 mL min−1) at selected temperatures of 25 °C, 200 °C, 400 °C, 600 °C, 800 °C, or 1000 °C for a standard duration of 5 h. For a carbonization temperature of 800 °C, other durations have been investigated (15 min, 1 h, 5 h, 10 h), as reported in the discussion. The carbonized electrode materials were designated as pC@CFXXX/Yh where ‘XXX’ is the carbonization temperature and ‘Y’ its duration.
2.4. Mineralization of Azo Dye by Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Process
The mineralization of AO7 dye by a heterogeneous EF process was carried out in a cylindrical glass cell with an effective volume of 200 mL. The cathode (pC@CF800/5h) and anode (Ti/Ni) were placed in parallel with a distance of 3 cm between them. The electrolysis solution was prepared by adding Na2SO4 (50 mM) into the AO7 solution (0.1 mM) and stirring vigorously until complete dilution of the supporting electrolyte. Compressed air (atmospheric air) was bubbled for 15 min at flow rate of 1 dm3 m−1 prior to the experiment in order to oxygenate the solution.
The mineralization of AO7 dye was started by applying the desired electrical current at −40 mA using DC power supply (Lambda Electronique, Melville, Long Island, NY, USA). The current remained constant during the electrolysis and aliquots for testing were withdrawn over the specific period of time. The AO7 mineralization was identified using a TOC-L CSH/CSN Shimadzu (Kyoto, Japan) analyzer to measure the total organic carbon (TOC) removal. Calibration curves for total carbon (TC) and inorganic carbon (IC) analysis were built up by automatic dilution of standard solutions of potassium hydrogenophtalate (TOC) and sodium hydrogen carbonate (IC). The mineralization was performed for 8 h, after which the electrolyte and dye solution was replaced with a freshly prepared solution.
3. Results and Discussion
The synthesis protocol adopted for the preparation of carbon felt electrodes modified by carbonized MOF material (pC@CF800/5h) involved two steps: (i) the growth of MIL-53(Fe) material on the surface of commercial carbon felts, and (ii) calcination (carbonization) of the MOF-modified carbon felts under a controlled atmosphere. The as-prepared electrode material was used in the heterogeneous EF process for the abatement of a model dye pollutant, acid Orange 7 (AO7). Hereafter, the key aspects related to the efficiency and stability of such a reaction system was discussed together with the characteristics of the electrodes. A special focus was placed on demonstrating that these materials can effectively mineralize AO7 around neutral pH (6.5), thus indicating that such electrode modification with carbonized MOFs represents a promising approach in the practical area of wastewater treatment.
3.1. Selection and Preparation of Electrode Materials
MIL-53(Fe) was selected for deposition onto the carbon felt electrode surface because carboxylate ligands provide an O6-coordination environment around the iron centers. Previous studies with MIL-100(Fe) have shown the effectiveness of carboxylate coordination environments for producing catalytic iron oxide sites [27,28,29].
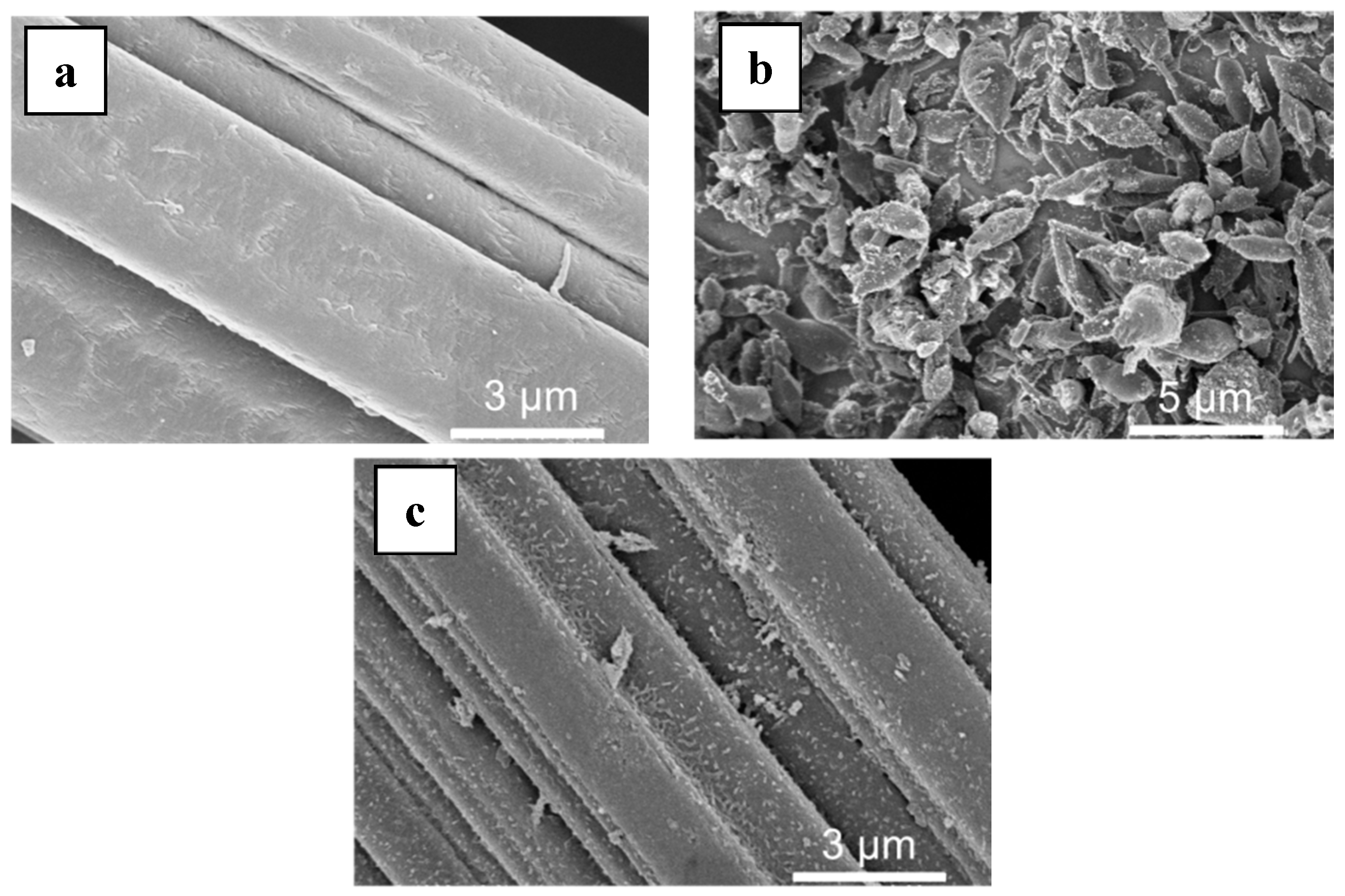
MIL-53(Fe) was grown on the surface of a commercial carbon felt (CF) using a solvothermal synthesis protocol [30,31] in the presence of the carbon felt (Figure 1a) immersed in the reaction mixture. The synthesis led to the formation of MOF-based composite material with MIL-53(Fe) elongated crystals (2–3 µm in size) uniformly covering the carbon fibers (Figure 1b).
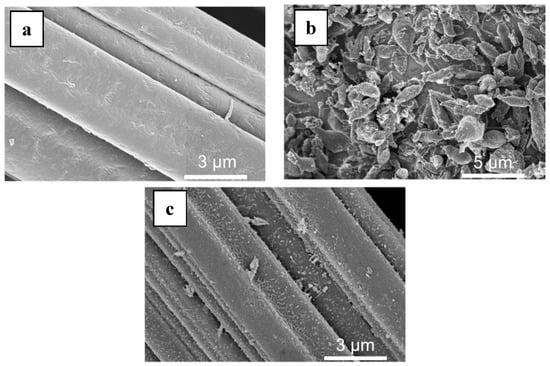
Figure 1.
SEM of (a) raw carbon felt (CF), (b) CF covered with grown MIL-53(Fe) particles, (c) final Fe-MOFs@CF800/5h electrode.
Initial experiments using commercial CF either without any pretreatment, or washed with ethanol, resulted in low loading of MIL-53(Fe) due to weak adhesion of the latter to the surface. To overcome this issue, we determined that pre-treatment with concentrated nitric acid led to improved attachment and increased retention of MIL-53(Fe). The as-treated electrode was washed with methanol until the washing solution was clear, ensuring that no loose material remained and could leach during the EF reaction. Using this method, MIL-53(Fe) loadings of up to 12 wt. % were achieved, producing modified carbon felts (MOF@CF).
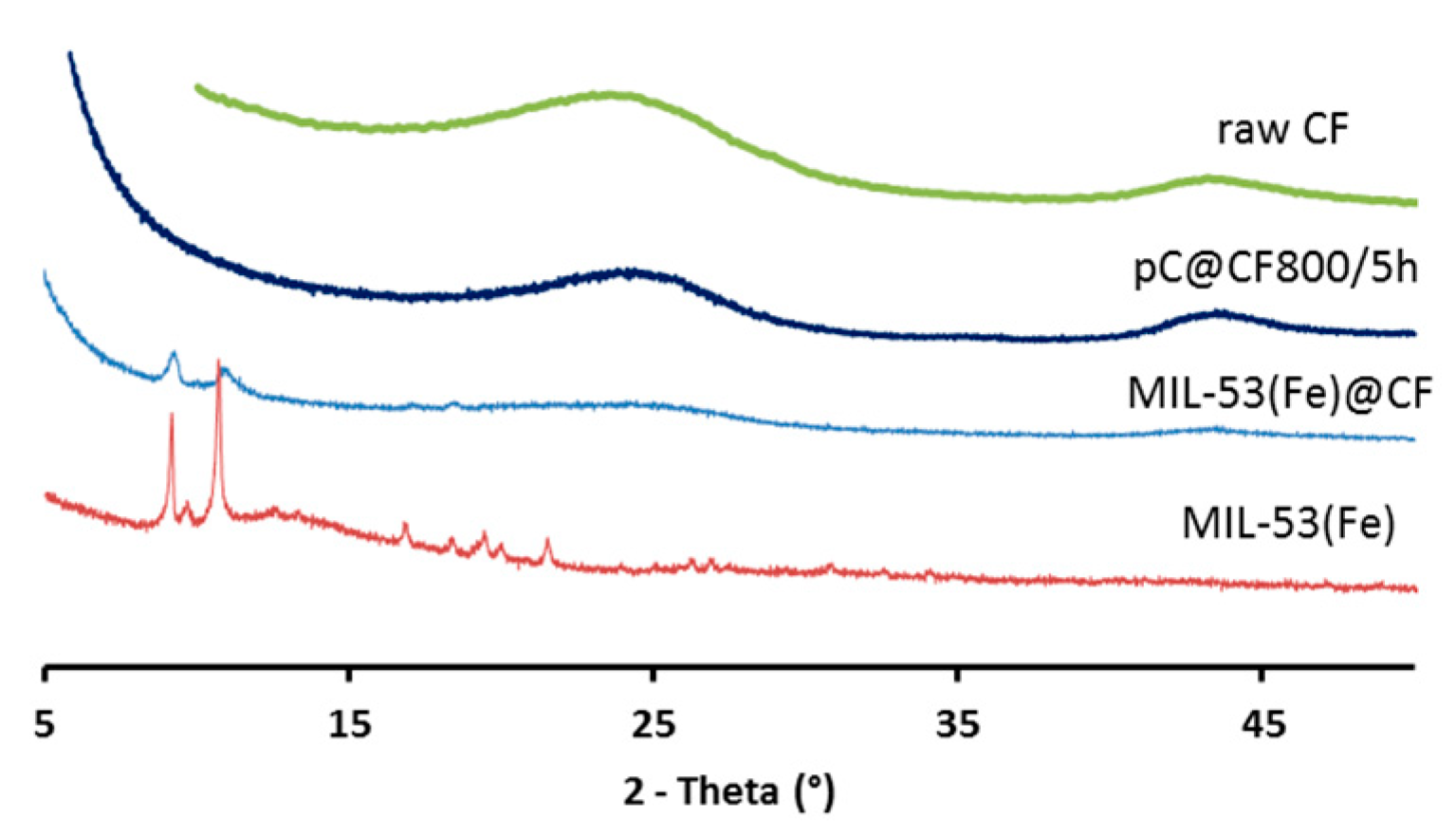
The formation and presence of MOFs was confirmed (Figure 2) by the characteristic XRD peaks (2θ = 9.26°, 11.1°, 16.38°, 17.2°) of MIL-53(Fe). Hence, under the selected reaction conditions, the synthesis resulted in MIL-53(Fe)@CF composite electrode material.
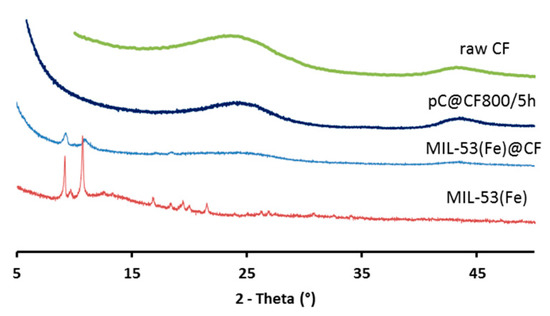
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of raw CF, pC@CF800/5h electrode, virgin MIL-53(Fe)@CF sample and MIL-53(Fe) powder.
3.2. Effect of Carbonization Conditions on Electrode Performance
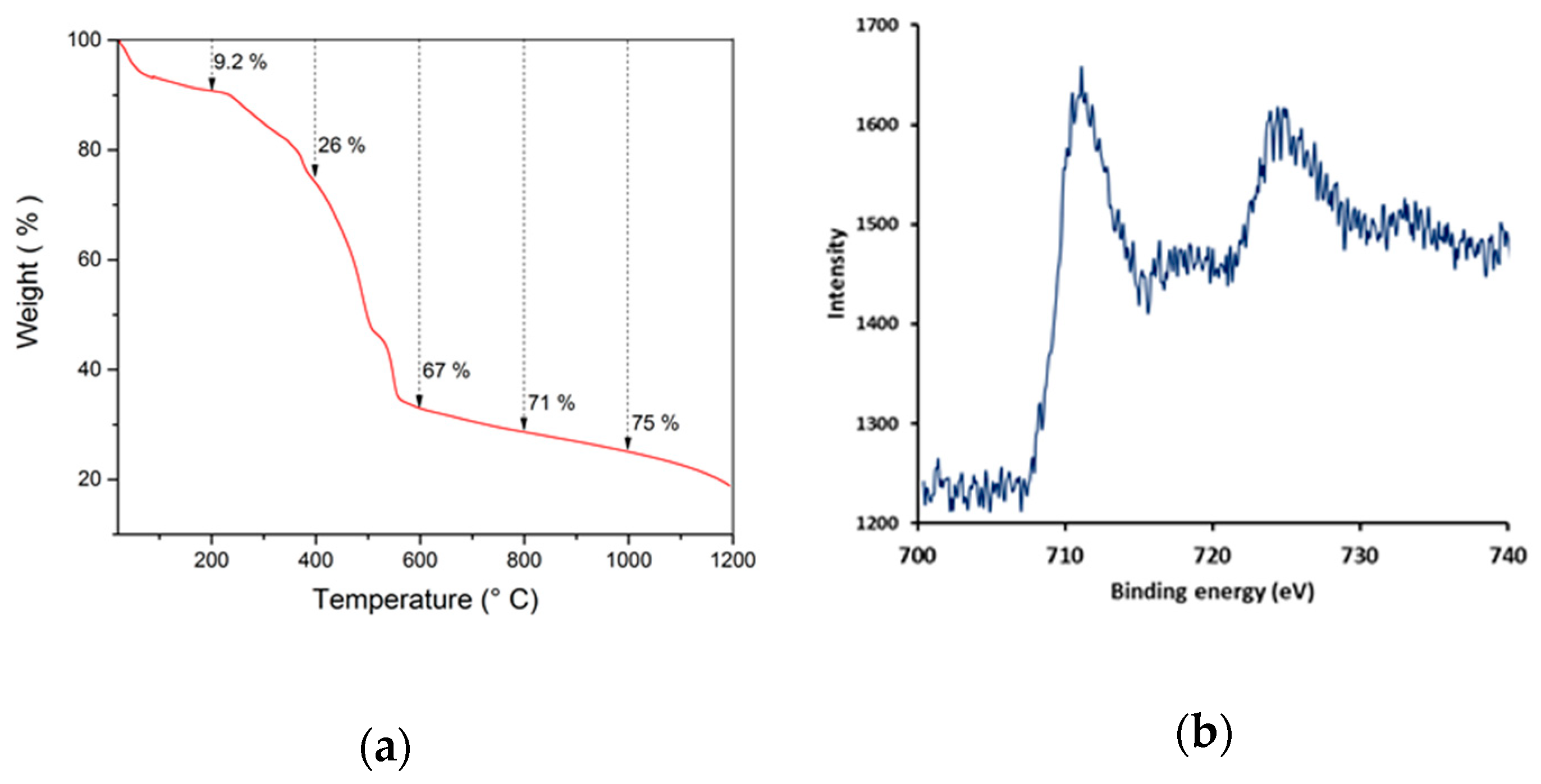
The MIL-53(Fe)@CF samples were carbonized under a nitrogen atmosphere, in order to generate the catalytically active iron-doped porous carbon (pC) thin layers covering the surface of commercial CFs (Figure 1c). To define the optimal thermal treatment, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was used to determine the carbonization behavior of MIL-53(Fe)@CF under nitrogen versus temperature (Figure 3a).
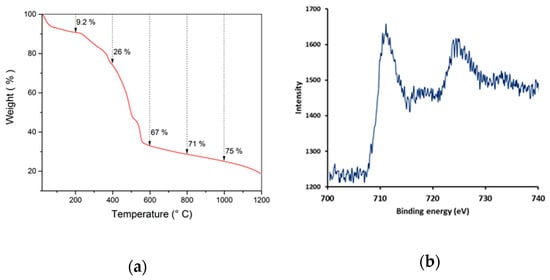
Figure 3.
(a) TGA of MIL-53(Fe) powder under nitrogen with a heating rate of 5 °C/min, (b) XPS spectrum of pC@CF800/5h electrode.
As a result of this investigation, and as already detailed in the experimental section, we prepared a series of pC@CFXXX/5h samples by heating MIL-53(Fe)@CF under N2 at 25 °C, 200 °C, 400 °C, 600 °C, 800 °C, or 1000 °C for 5 h [32,33,34].
The performance of the pC@CFXXX/5h electrodes was evaluated by measuring the removal of total organic carbon from the system over an 8 h period (Table 1). The results indicate that carbonization at temperatures lower than 600 °C actually leads to more dissolved carbon entering the solution. We attribute this result to the dissolution of the remaining MIL-53(Fe) framework that was not fully carbonized under the selected conditions, as already observed in our studies where MFI zeolite was physically deposited onto an electrode surface [24]. However, above 600 °C the framework was successfully carbonized into iron oxide and carbon. We see a ca. 40% reduction in the TOC of the solution—indicative of the electro-Fenton process operating effectively with limited or no dissolution of the residual MIL-53(Fe). This observation suggests that the carbonized form of the MOF is relatively insoluble and/or more strongly adhered to the carbon felt.

Table 1.
Effect of carbonization temperature and duration on the electro-Fenton performance of carbon felt electrodes modified with carbonized MIL-53(Fe).
Having established the optimal carbonization temperature, we performed carbonization at 800 °C for a duration varying between 15 min and 10 h. The results showed that positive TOC removal was obtained with pC@CF800/15 min, and the highest TOC removal (46%) was obtained with the carbon felt carbonized for 5 h. No additional benefit was observed after 10 h carbonization time.
XRD analysis (Figure 2) showed that crystallinity was removed in the pC@CF material (pC@CF800/5h), thus confirming the carbonization of MIL-53(Fe). The XPS analysis of the carbonized sample (Figure 3b) evidenced iron preservation, thus confirming the formation of the heterogenized Fe-based catalyst on the carbon felt surface. The binding energy at 725 eV corresponds to Fe2p1/2, while the peak at 711 eV is assigned to Fe2p2/3, thus confirming the presence of Fe2O3.
The virgin and carbonized CF electrodes were also characterized using N2 physisorption. The carbonized electrode had a surface area about 55 times higher than virgin carbon felt (SBET = 0.1 vs. 5.5 m2/g) forming a porous structure consisting mainly of micropores (pore volume = 0.012 cm2/g).
3.3. Effect of MIL-53(Fe) Concentration on Electrode Performance
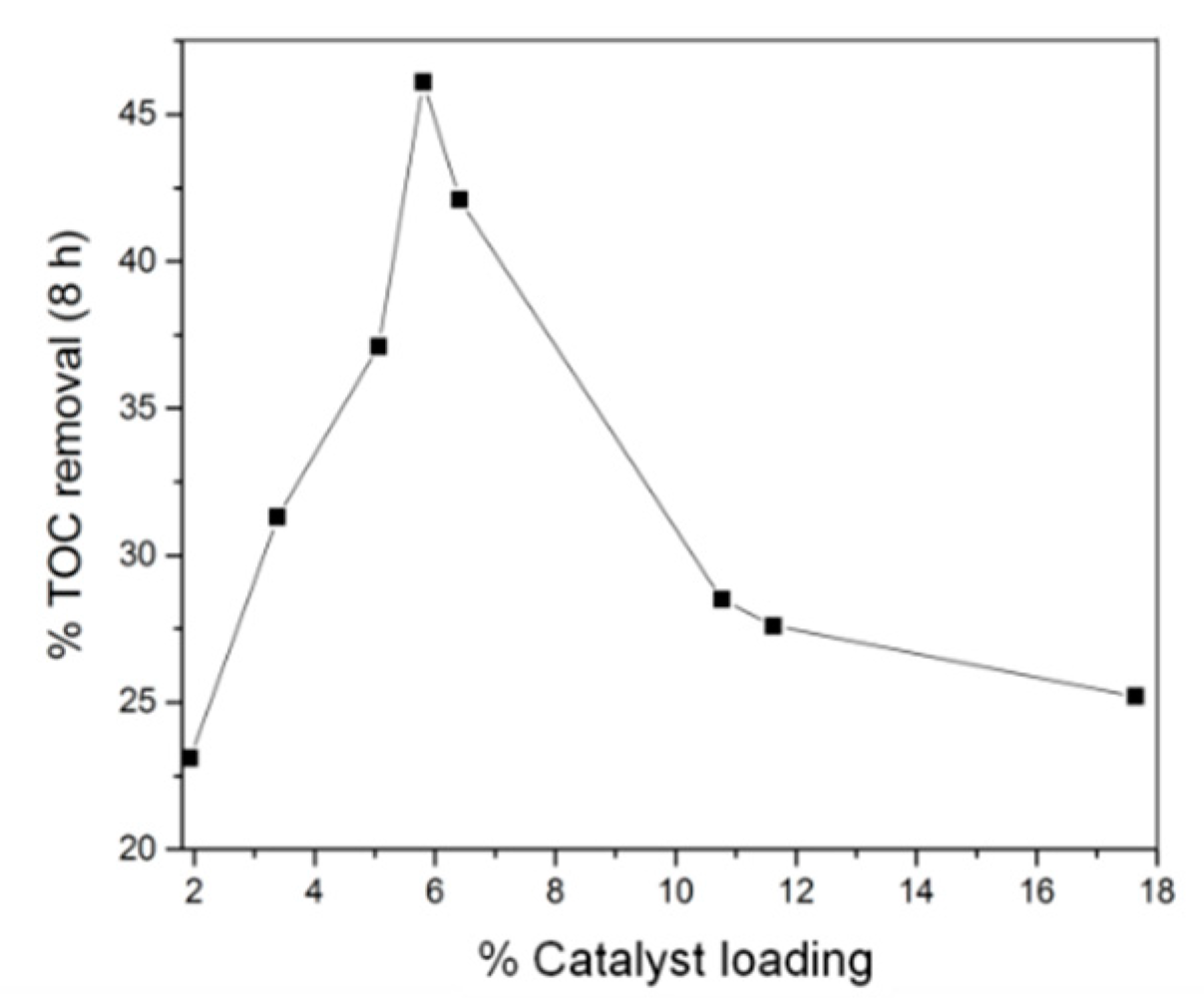
Varying the reaction time of solvothermal synthesis allowed some degree of control over the final density of MIL-53(Fe) on the carbon felt surface. After subsequent carbonization, this translates to a control over the density of iron oxide in the modified carbon felt electrode. Using this strategy, we observed that an increase of the catalyst amount increases electrode performance until a loading of ca. 5.8%, which allows TOC removal of ~46% to be achieved (Figure 4) within 8 h of electrolysis. Increasing the loading past this point caused a reduction in TOC removal. This result can be explained by considering that increasing the concentration of iron sites leads to the competing reaction of electrochemically generated iron(II) with hydroxyl radicals to produce hydroxide ions incapable of further destroying the organic material [35].
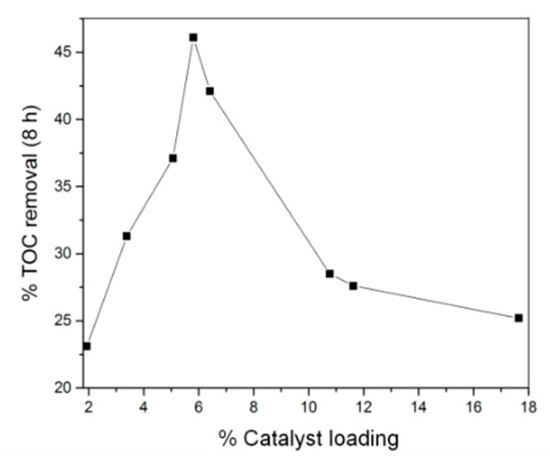
Figure 4.
Percent total organic carbon (TOC) removal of 200 mL Acid Orange 7 (AO7) (0.1 mM) after 8 h treatment by heterogeneous EF process as a function of catalyst loading deposited on carbonized CF@MIL-53(Fe) cathode.
3.4. Stability of the Carbonized MIL-53(Fe) Electrode
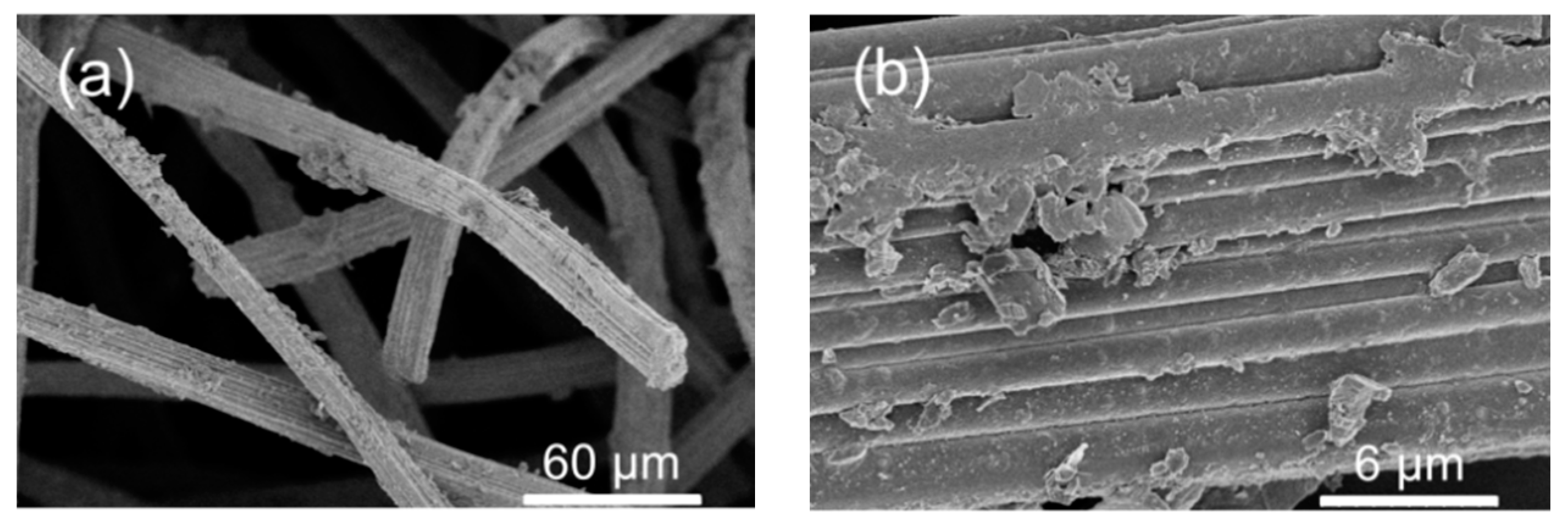
The stability of the carbonized MIL-53(Fe) electrode (pC@CF800/5h) was investigated by measuring the leaching of iron into solution and the retention of performance in TOC removal. The conditions were reasonably harsh, with each experiment involving exposure to a vigorously stirred solution at pH 6.5 for 8 h. In such conditions, the electrodes produced from MIL-53(Fe) grown directly onto the electrode surface retained TOC removal of up to 29% after 10 cycles (Table 2). Moreover, the TOC removal was almost double that of electrode materials prepared from physically deposited MFI zeolite (27% after 8 h, 1 cycle) as published recently by our research group [24]. The partial decline of the catalytic activity could be explained by a washing of the iron catalyst out of the electrode during its repetitive use in several EF cycles (Table 3) and/or electrode fouling (Figure 5) limiting the access to the catalytic sites. Hence, from an industrial point of view the stability of the electrode is still relatively too low for possible larger scale applications.

Table 2.
Amount of Fe leaching in solution and percent TOC removal after 8 h heterogeneous electro-Fenton (EF) treatment using pC@CF800/5h cathode.

Table 3.
Elemental composition of raw CF, pC@CF800/5h electrode after 1 cycle and pC@CF800/5h electrode after 10 cycles heterogeneous EF process.
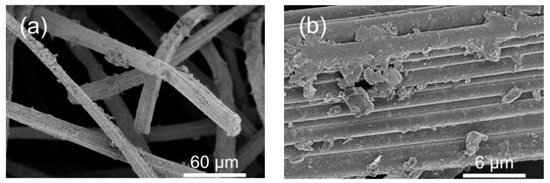
Figure 5.
(a,b) SEM observations of pC@CF800/5h cathode after ten cycles heterogeneous EF process.
Finally, the specific energy consumption per unit TOC mass (ECTOC) was also evaluated according to Equation (5) [36]:
where V is the average cell voltage (V), I is the applied current (A), t is the electrolysis time (h), and Vs is the solution volume (L).
At ~46% TOC removal, the ECTOC was 0.605 kWh g−1, hence comparable value to that already observed for another heterogeneous EF process using an Fe-alginate beads catalyst (0.87 kWh·g−1 ECTOC at 60% TOC removal) [37].
To conclude on the efficiency of the developed heterogeneous EF system, comparisons with other data available in the literature with similar Fe-based catalytic sources such as Fe@Fe2O3, pyrite, CoFe/FeIIFeIII-LDH etc. are summarized in Table 4. It must be underlined that compared to other studies in the area of EF processes applying high electric current density or other types of anode (e.g., boron-doped diamond (BDD) anode), the present work offers attractive results of ~46% TOC removal (AO7, 0.1 mM) at low current density of 3.8 mA cm−2 and nearly neutral pH (6.5); thus, proving the system to be very promising for the removal of organic pollutants from the natural water environment. Further improvements of the system (e.g., higher catalyst loading, application of other MOF materials, different deposition protocols, carbonization treatments etc.) leading to more stable and active heterogenized catalysts will be the subject of our future communication. It will focus on improving the system’s performance and reducing the energy consumption for total degradation of water pollutants.

Table 4.
Summary of catats for heterogeneous EF process using CF cathode.
4. Conclusions
We have presented the growth of a metal organic framework (MIL-53(Fe)) on the surface of a carbon felt electrode, followed by its carbonization in order to produce a recyclable catalytic electrode for the electro-Fenton reaction. We have systematically investigated preparation conditions, establishing that catalyst loadings, thermolysis temperature, and thermolysis time play an important role in the efficiency of the final material. Electrodes prepared under the optimal conditions of 5.8% catalyst loading with carbonization at 800 °C for 5 h achieved TOC removal of ca. 45% under the experimental conditions with the model electrolyte. Our focus is now on both exploring the wide range of MOFs available for improving the efficiency of the catalytic site and investigating system performance under realistic operating conditions.
Author Contributions
T.X.H.L., M.G.C., M.D. and M.B. conceived and designed the experiments; M.G.C. performed the materials synthesis; T.X.H.L. carried out the material characterization and catalytic experiments; T.X.H.L., M.G.C. and M.D. analyzed the data and interpreted the results; A.J. and M.C. contributed to discussions; T.X.H.L., M.G.C. and M.D. drafted the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by ANR, project ECOTS/CELECTRON.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Boczkaj, G.; Fernandes, A. Wastewater treatment by means of Advanced Oxidation Processes at basic pH conditions: A review. Chem. Eng. 2017, 320, 608–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagol, M.; Przyjazny, A.; Boczkaj, G. Wastewater treatment by means of advanced oxidation processes based on cavitation—A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 599–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Quan, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H. Enhanced electro-Fenton performance by fluorine-doped porous carbon for removal of organic pollutants in wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.H.; Van Nguyen, T.; Yacouba, Z.A.; Zoungrana, L.; Avril, F.; Petit, E.; Mendret, J.; Bonniol, V.; Bechelany, M.; Lacour, S.; et al. Toxicity Removal Assessments Related to Degradation Pathways of Azo Dyes: Toward an Optimization of Electro-Fenton Treatment. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.P.; Sousa, S.; Rodrigues, J.; Antunes, H.; Porter, J.J.; Gonçalves, I.; Ferreira-Dias, S. Adsorption of Acid Orange 7 Dye in Aqueous Solutions by Spent Brewery Grains. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 40, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.H.; Bechelany, M.; Cretin, M. Carbon Felt Based-Electrodes for Energy and Environmental Applications: A Review. Carbon 2017, 122, 564–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.H.; Esmilaire, R.; Drobek, M.; Bechelany, M.; Vallicari, C.; Nguyen, D.L.; Julbe, A.; Tingry, S.; Cretin, M. Design of a Novel Fuel Cell-Fenton System: A Smart Approach to Zero Energy Depollution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 17686–17693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.H.; Charmette, C.; Bechelany, M.; Cretin, M. Facile Preparation of Porous Carbon Cathode to Eliminate Paracetamol in Aqueous Medium Using Electro-Fenton System. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 188, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.H.; Van Nguyen, T.; Amadou Yacouba, Z.; Zoungrana, L.; Avril, F.; Nguyen, D.L.; Petit, E.; Mendret, J.; Bonniol, V.; Bechelany, M.; et al. Correlation between Degradation Pathway and Toxicity of Acetaminophen and Its By-Products by Using the Electro-Fenton Process in Aqueous Media. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özcan, A.; Oturan, M.A.; Oturan, N.; Şahin, Y. Removal of Acid Orange 7 from Water by Electrochemically Generated Fenton’s Reagent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, S.; Bellakhal, N.; Oturan, N.; Oturan, M.A.; Dachraoui, M. Degradation of Acid Orange 7 by Electrochemically Generated •OH Radicals in Acidic Aqueous Medium Using a Boron-Doped Diamond or Platinum Anode: A Mechanistic Study. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, M.; Oturan, M.A. Degradation of Alizarin Red by Electro-Fenton Process Using a Graphite-Felt Cathode. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 7084–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Huong Le, T.X.; Bechelany, M.; Esposito, G.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Oturan, M.A.; Cretin, M. A Hierarchical CoFe-Layered Double Hydroxide Modified Carbon-Felt Cathode for Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Process. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3655–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Huong Le, T.X.; Bechelany, M.; Oturan, N.; Papirio, S.; Esposito, G.; van Hullebusch, E.; Cretin, M.; Oturan, M.A. Electrochemical Mineralization of Sulfamethoxazole over Wide PH Range Using FeIIFeIIILDH Modified Carbon Felt Cathode: Degradation Pathway, Toxicity and Reusability of the Modified Cathode. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, S.; Quan, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, H. Superpermeable nanoporous carbon-based catalytic membranes for electro-Fenton driven high-efficiency water treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 23502–23512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; Yang, S.; Cai, Y. Continuous generation of hydroxyl radicals for highly efficient elimination of chlorophenols and phenols catalyzed by heterogeneous Fenton-like catalysts yolk/shell Pd@Fe3O4@metal organic frameworks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 346, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.S.; Khan, J.A.; Sayed, M.; Khan, Z.U.H.; Rizwan, A.D.; Muhammad, N.; Boczkaj, G.; Murtaza, B.; Imran, M.; Khan, H.M.; et al. Solar light driven degradation of norfloxacin using as-synthesized Bi3+ and Fe2+ co-doped ZnO with the addition of HSO5−: Toxicities and degradation pathways investigation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Makos, P.; Boczkaj, G. Treatment of bitumen post oxidative effluents by sulfate radicals based advanced oxidation processes (S-AOPs) under alkaline pH conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Makos, P.; Khan, J.A.; Boczkaj, G. Pilot scale degradation study of 16 selected volatile organic compounds by hydroxyl and sulfate radical based advanced oxidation processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Lai, C.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Zhang, C.; Qin, L.; Hu, L.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, W. Metal-organic frameworks for highly efficient heterogeneous Fenton-like catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 368, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.H.; Esmilaire, R.; Drobek, M.; Bechelany, M.; Vallicari, C.; Cerneaux, S.; Julbe, A.; Cretin, M. Nitrogen-Doped Graphitized Carbon Electrodes for Biorefractory Pollutant Removal. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 15188–15197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.J.; Cho, D.-W.; Yu, I.K.M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Yip, A.C.K. Photo-Fenton abatement of aqueous organics using metal-organic frameworks: An advancement from benchmark zeolite. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, G. Catalytic activity of MOF(2Fe/Co)/carbon aerogel for improving H2O2 and OH generation in solar photo–electro–Fenton process. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.H.; Drobek, M.; Bechelany, M.; Motuzas, J.; Julbe, A.; Cretin, M. Application of Fe-MFI Zeolite Catalyst in Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Process for Water Pollutants Abatement. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 278, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.H.; Alemán, B.; Vilatela, J.J.; Bechelany, M.; Cretin, M. Enhanced Electro-Fenton Mineralization of Acid Orange 7 Using a Carbon Nanotube Fiber-Based Cathode. Front. Mater. 2018, 5, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, B.; Deng, Y.; Chen, H.; Luo, S.; Sun, C.; Yang, P.; Yang, S. Adsorption and Heterogeneous Fenton Degradation of 17α-Methyltestosterone on Nano Fe3O4/MWCNTs in Aqueous Solution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 107, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y. Magnetic porous Fe3O4/carbon octahedra derived from iron-based metal-organic framework as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-F.; Qiu, L.-G.; Ke, F.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Yuan, Y.-P.; Xu, G.-S.; Jiang, X. A novel magnetic recyclable photocatalyst based on a core–shell metal–organic framework Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) for the decolorization of methylene blue dye. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 14329–14334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J. Fe-based metal organic framework/graphene oxide composite as an efficient catalyst for Fenton-like degradation of methyl orange. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 50829–50837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.-J.; Yuan, Y.-P.; Sun, J.-X.; Peng, F.-M.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, L.-G.; Xie, A.-J.; Shen, Y.-H.; Zhu, J.-F. New photocatalysts based on MIL-53 metal–organic frameworks for the decolorization of methylene blue dye. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ai, L.; Jiang, J. Solvothermal synthesis of MIL–53(Fe) hybrid magnetic composites for photoelectrochemical water oxidation and organic pollutant photodegradation under visible light. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 3074–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ao, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, H.; Rykov, A.I.; Wang, J. Topotactic Transformation of Metal–Organic Frameworks to Graphene-Encapsulated Transition-Metal Nitrides as Efficient Fenton-like Catalysts. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 11532–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Rykov, A.I.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Graphene encapsulated FexCoy nanocages derived from metal–organic frameworks as efficient activators for peroxymonosulfate. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 7486–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, S.; Quan, H.; Hua, L.; Luo, X.; Guo, L. Heterogeneous Fenton-like catalysis of Fe-MOF derived magnetic carbon nanocomposites for degradation of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 49024–49030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajootan, E.; Arami, M.; Rahimdokht, M. Discoloration of wastewater in a continuous electro-Fenton process using modified graphite electrode with multi-walled carbon nanotubes/surfactant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 130, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.J.; Hernández-Ramírez, A.; Peralta-Hernández, J.M.; Arias, C.; Brillas, E. Application of solar photoelectro-Fenton technology to azo dyes mineralization: Effect of current density, Fe2+ and dye concentrations. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, S.B.; Fourcade, F.; Assadi, A.; Soutrel, I.; Amrane, B.; Monser, L. Effective heterogeneous electro-Fenton process for the degradation of a malodorous compound, indole, using iron loaded alginate beads as a reusable catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 182, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, H.; Zhou, S.; Zeng, Y. Bio-Electro-Fenton System for Enhanced Estrogens Degradation. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 138, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, S.; Oturan, M.A.; Labiadh, L.; Guersalli, A.; Abdelhedi, R.; Oturan, N.; Brillas, E. Degradation of Tyrosol by a Novel Electro-Fenton Process Using Pyrite as Heterogeneous Source of Iron Catalyst. Water Res. 2015, 74, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, A.; Atılır Özcan, A.; Demirci, Y.; Şener, E. Preparation of Fe2O3 modified Kaolin and Application in Heterogeneous Electro-Catalytic Oxidation of Enoxacin. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 200, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plakas, K.V.; Sklari, S.D.; Yiankakis, D.A.; Sideropoulos, G.T.; Zaspalis, V.T.; Karabelas, A.J. Removal of Organic Micropollutants from Drinking Water by a Novel Electro-Fenton Filter: Pilot-Scale Studies. Water Res. 2016, 91, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labiadh, L.; Oturan, M.A.; Panizza, M.; Ben Hamadi, N.; Ammar, S. Complete Removal of AHPS Synthetic Dye from Water Using New Electro-Fenton Oxidation Catalyzed by Natural Pyrite as Heterogeneous Catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Zhou, S.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y. A Novel Bioelectro-Fenton System for Coupling Anodic COD Removal with Cathodic Dye Degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birjandi, N.; Younesi, H.; Ghoreyshi, A.A.; Rahimnejad, M. Electricity Generation through Degradation of Organic Matters in Medicinal Herbs Wastewater Using Bio-Electro-Fenton System. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barhoumi, N.; Olvera-Vargas, H.; Oturan, N.; Huguenot, D.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S.; Brillas, E.; Oturan, M.A. Kinetics of Oxidative Degradation/Mineralization Pathways of the Antibiotic Tetracycline by the Novel Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Process with Solid Catalyst Chalcopyrite. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 209, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).